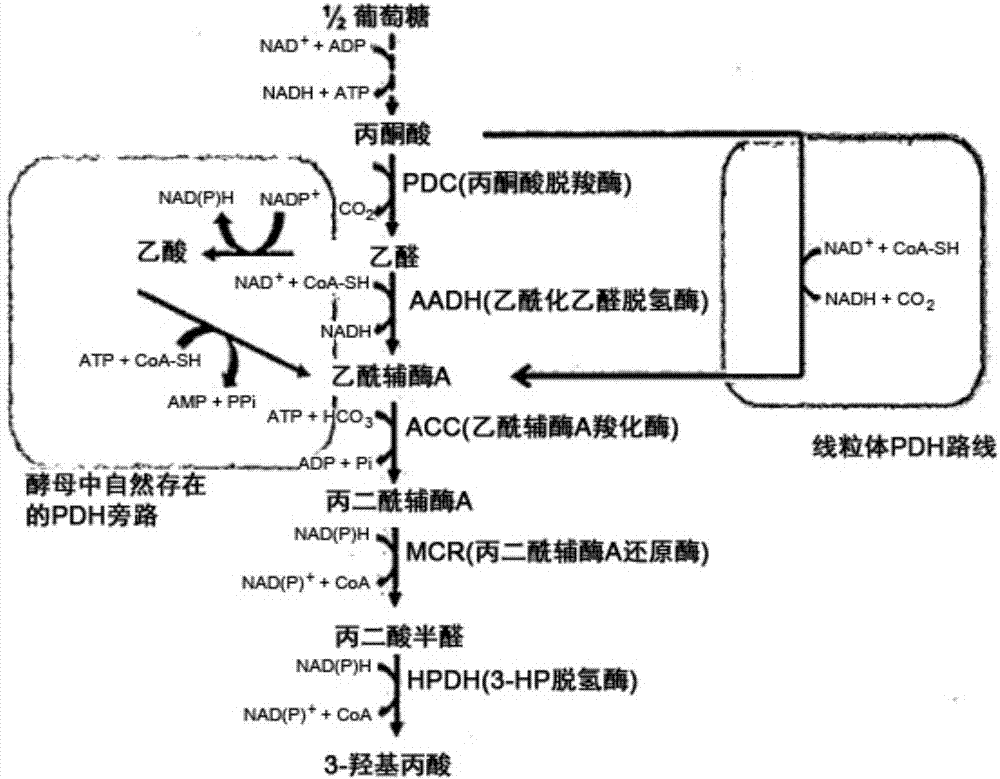
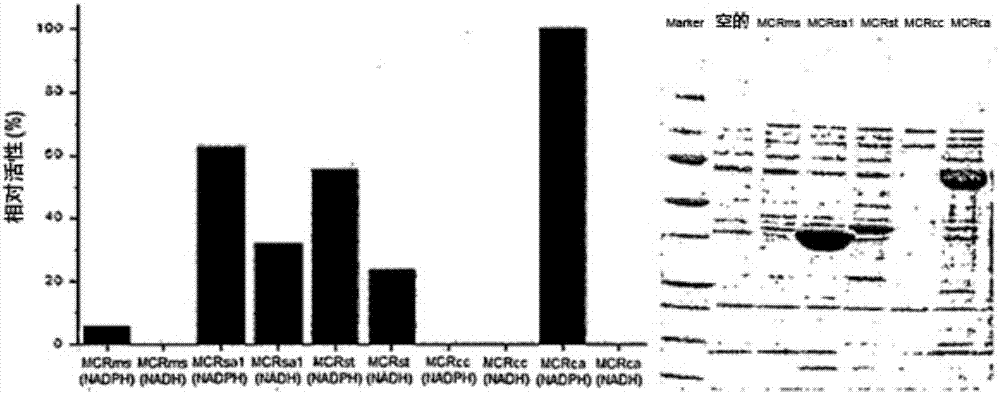
Recombinant yeast producing 3-hydroxypropionic acid and method for producing 3-hydroxypropionic acid using the same
A technology for recombining yeast and yeast, applied in microorganism-based methods, biochemical equipment and methods, recombinant DNA technology, etc., can solve problems such as low 3-HP productivity and complex 3-HP metabolic pathways
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0104] Example 1 Selection of host yeast strains based on tolerance to 3-HP
[0105] An essential feature of 3-HP-producing organisms is a good tolerance to high concentrations of 3-HP, which enables product accumulation during fermentation with minimal loss of strain performance. A large, diverse set of 718 wild-type yeast strains was screened to identify those strains that can tolerate high concentrations of 3-HP at low pH and can grow and metabolize glucose under these conditions ( Table 12).
[0106] The entire panel of strains was initially screened for acid tolerance using a number of agar plate and liquid medium microtiter plate based growth assays. Subsets of strains were then evaluated for their ability to tolerate large amounts of 3-HP at low pH in shake flask cultures. None of these screening methods in isolation is a perfect indicator of 3-HP tolerance in industrial settings, but the combination of many methods provides a comprehensive and robust means of identif...
Embodiment 2
[0138] Example 2 Bioinformatics Genome Mining to Obtain Pathway Enzyme Candidates
[0139] Homology-based database searches were performed to identify candidate enzymes for specific functions. In each case, the database is searched with multiple query sequences. In addition, members of related protein families were retrieved from Uniprot / SwissProt based on InterPro domain annotations. Homology-based searches were performed against the Uniprot (SwissProt and TrEMBL) and GenBank protein databases (nr, pat, and env_nr) using blastp, and against the GenBank nucleotide databases (tsa_nt, env_nt, and pat) using tblastn. Sequences with E values less than 1e-30 were extracted; however, in some cases additional analyzes were performed for sequences with E values less than 1e-80. Using the query sequence as a guide in translation, the nucleotide hits were translated into protein sequences using GeneWise. The task of translating long ACC sequences was too difficult for GeneWise, t...
Embodiment 3
[0160] The measurement of embodiment 3 enzyme activity
[0161] ACC Spectrophotometric Enzyme Assay
[0162] The spectrophotometric ACC assay is a coupled assay in which the product produced by the ACC reaction is further consumed in a reaction requiring the cofactor NAD(P)H, the oxidation of the cofactor NAD(P)H can be monitored spectrophotometrically.
[0163] Kroeger et al. (2011, Anal. Biochem. 411:100-105) describe a conjugation assay in which malonyl-CoA produced by ACC1 is passed through purified malonyl-CoA reductase (MCR) in the presence of NADPH as coenzyme. In the reaction of the factor, it is further converted into malonate semialdehyde. ACC activity is measured by following NADPH oxidation.
[0164] Diacovich et al. (2002, J. Biol. Chem. 277:31228-31236) combined ADP conversion (the hydrolysis product of ATP used as a cofactor in the ACC reaction) with the pyruvate kinase reaction requiring ADP, which The reaction is further coupled to the formation of pyruvate...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com