Method for manufacturing plant specimens
A production method and plant specimen technology, applied in the field of plant specimen production, can solve problems such as difficulty in three-dimensional display, rough production of plant specimens, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
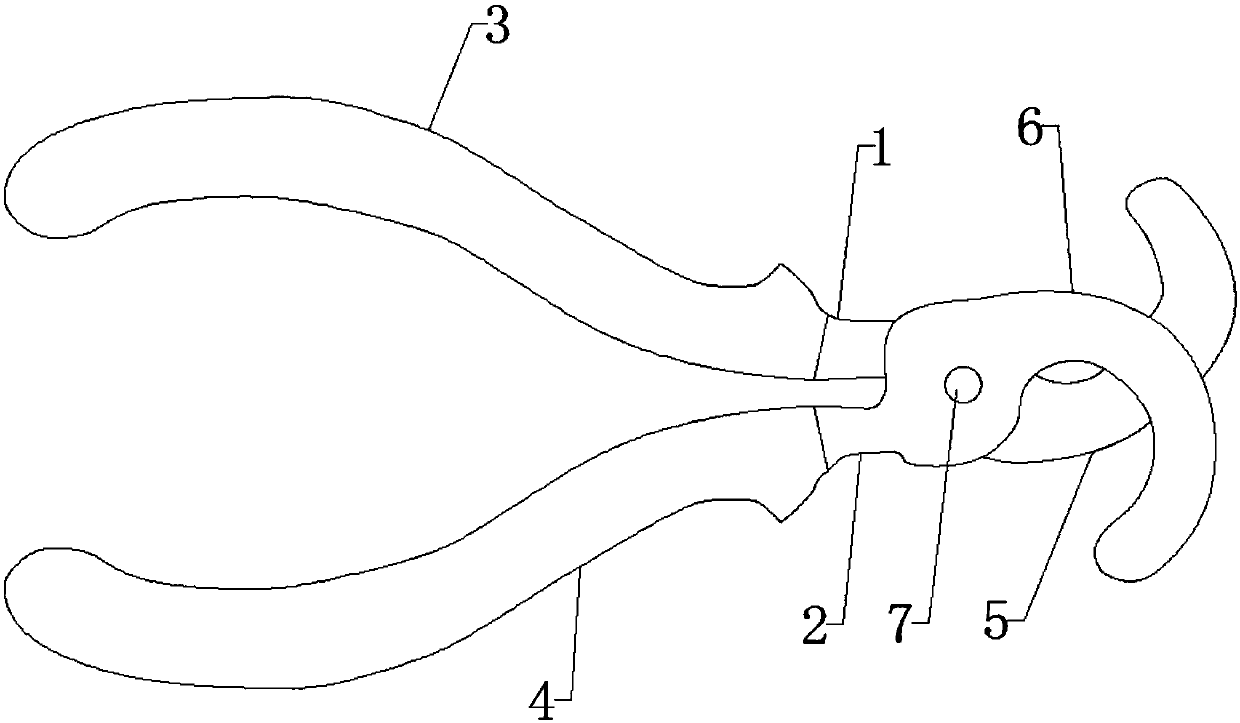
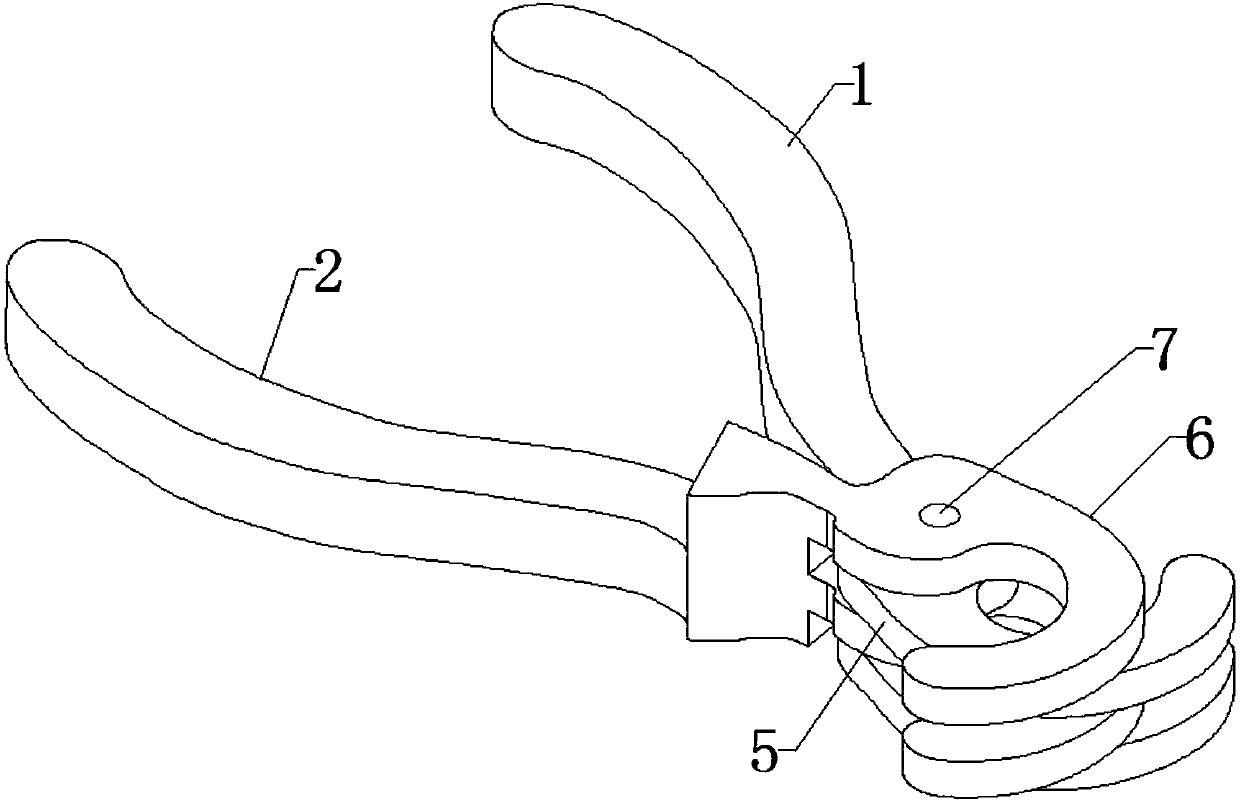
[0047] see Figure 1-2 , a plant specimen cross fixed forceps, comprising a first forceps handle 1 and a second forceps handle 2, the front end of the first forceps handle 1 is fixedly connected with an arc-shaped first jaw arm 5, and the front end of the second forceps handle 2 An arc-shaped second jaw arm 6 is fixedly connected, the rear ends of the first jaw arm 5 and the second jaw arm 6 are hinged by a rotating shaft 7, and the first jaw arm 5 and the second jaw arm 6 are alternately arranged; The first jaw arm cover 8 is equipped with a detachable first jaw arm cover 8, and the second jaw arm cover 9 is equipped with a detachable second jaw arm cover 9.
[0048] Both the first jaw arm cover 8 and the second jaw arm cover 9 are Teflon sleeves to prevent the α-cyanoacrylate compound from polymerizing, and the resulting polymer condenses on the jaws of the fixed forceps.
[0049] The first pliers handle 1 is fixedly set with a first pliers handle cover 3, and the second pl...
Embodiment 2
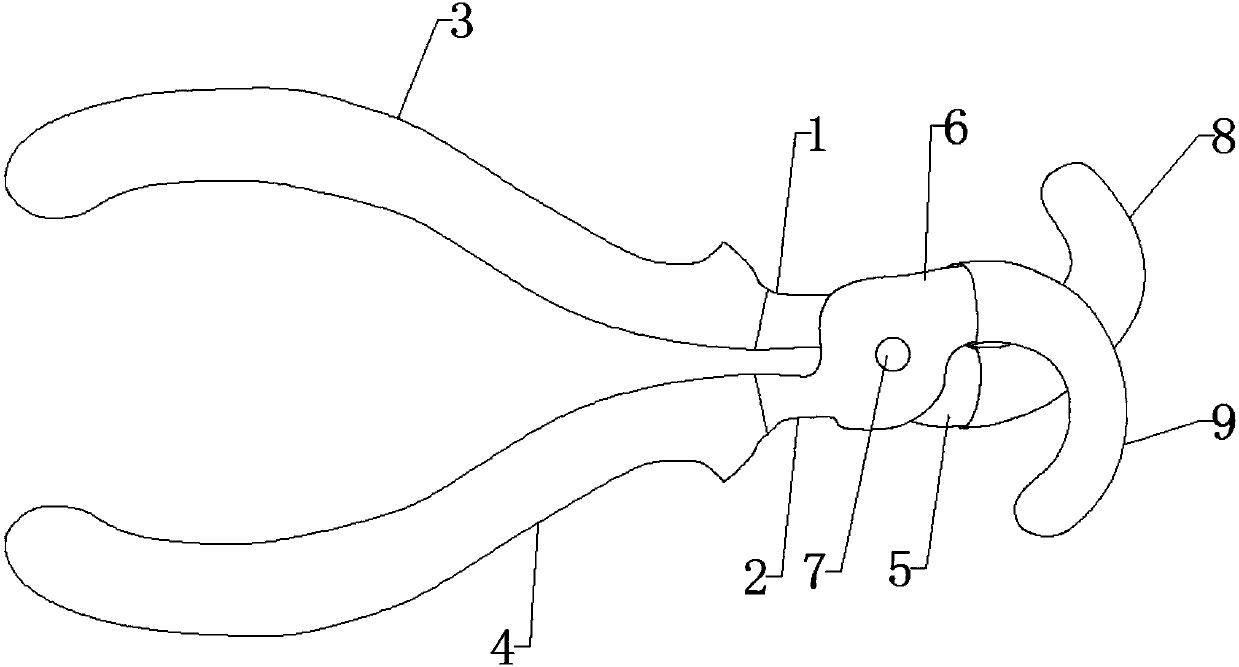
[0052] see image 3 , Embodiment 2 is basically the same as Embodiment 1, and the similarities will not be repeated. The difference is that there are two first jaw arms 5, two second jaw arms 6, and two first jaw arms. 5 is fixed on the front end of the same first jaw handle 1, and the two second jaw arms 6 are fixed on the front end of the same second jaw handle 2, and the two first jaw arms 5 and the two second jaw arms 6 Hinged together by the same rotating shaft 7, two first jaw arms 5 and two second jaw arms 6 are alternately arranged.
[0053] The four-jaw arm cross-type fixed forceps can be applied to plant stem specimens with thicker stems and longer lengths to be manipulated. The utility model has a simple structure and is easy to use.
Embodiment 3 3
[0054] Embodiment 3 The making of three-ball syringa branch stem specimen
[0055] Plant material: some branches of Platanus tribulus (about 0.5cm-1cm in diameter, unlimited in length, the branches should be as dry as possible).
[0056] Utensils: Hammer, covered vessel of appropriate size, herbarium cross-set forceps.
[0057] Reagent: absolute ethanol, banana water (composition: butyl ester: ethyl ester: acetone: cyclohexanone: No. 120 gasoline weight ratio 25:12:3:5:55), 95% ethanol solution (volume fraction) , α ethyl cyanoacrylate.
[0058] experiment procedure:
[0059] (1) place the three-ball syringa branches in 95% ethanol solution (volume fraction), soak until the 95% ethanol solution changes color (discoloration to slightly yellow), take it out (because the thickness of the branches is different, the soaking time also varies difference, generally 12-24h);
[0060] (2) beat the sycamore stem of step (1) repeatedly with a hammer until the phloem and xylem of the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com