Phosphate cement based patching material and preparation method thereof
A technology for repairing materials and magnesium phosphate cement, applied in the field of phosphate cement-based repairing materials and their preparation, can solve the problems of short setting time and difficult adjustment, delay the hydration process, solve the limited effect of setting retardation, and improve water resistance. sexual effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
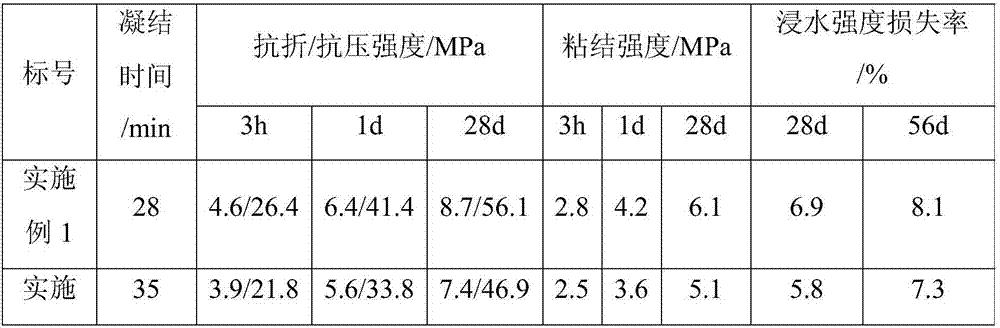
[0026] A phosphate cement-based repair material, which consists of the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of magnesium phosphate cement, 20 parts of fly ash, 120 parts of aggregates, 0.5 parts of water glass, and polypropylene fibers (average length 12mm) 0.5 part, 20 parts water. Among them, magnesium phosphate cement is composed of 60% magnesium oxide, 37% potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 3% composite retarder by mass percentage (composite retarder is composed of 40% borax, 40% dodecahydrate disodium hydrogen phosphate and 20% anhydrous calcium chloride, all three are analytically pure) mixed.
[0027] The phosphate cement-based repair material is prepared through the following steps: weighing magnesium oxide, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, and a composite retarder in the above proportions and mixing them evenly to obtain magnesium phosphate cement, then adding mineral admixtures according to the proportions, collecting After mixing evenly, add water glass, ...
Embodiment 2
[0030]A phosphate cement-based repair material, which consists of the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of magnesium phosphate cement, 25 parts of fly ash, 125 parts of aggregates, 0.8 parts of water glass, and polypropylene fibers (average length 12mm) 1 part, 25 parts water. Among them, magnesium phosphate cement is composed of 66% magnesium oxide, 30% potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 4% composite retarder by mass percentage (composite retarder is composed of 40% borax, 40% dodecahydrate disodium hydrogen phosphate and 20% anhydrous calcium chloride, all three are analytically pure) mixed.
[0031] The phosphate cement-based repair material is prepared by the following steps: weighing magnesium oxide, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, and a composite retarder in the above proportions and mixing them evenly to obtain magnesium phosphate cement, and then adding minerals according to the proportion to mix After mixing evenly, add water glass, fiber and water and ...
Embodiment 3
[0033] A phosphate cement-based repair material, which is composed of the following components in parts by weight: 100 parts of magnesium phosphate cement, 40 parts of fly ash, 140 parts of aggregate, 1 part of water glass, polyvinyl alcohol fiber (average length 12mm) ) 0.5 parts, 28 parts of water. Among them, magnesium phosphate cement is composed of 56% magnesium oxide, 40% potassium dihydrogen phosphate, 4% composite retarder by mass percentage (composite retarder is composed of 40% borax, 40% dodecahydrate disodium hydrogen phosphate and 20% anhydrous calcium chloride, all three are analytically pure) mixed.
[0034] The phosphate cement-based repair material is prepared by the following steps: weighing magnesium oxide, potassium dihydrogen phosphate, and a composite retarder in the above proportions and mixing them evenly to obtain magnesium phosphate cement, and then adding minerals according to the proportion to mix After mixing evenly, add water glass, fiber and wat...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com