Extraction method for comprehensive utilization of schisandrae chinensis
An extraction method, the technology of Schisandra chinensis, applied in the field of comprehensive utilization of Schisandra chinensis extraction, can solve the problems of unsatisfactory antibacterial effect and waste of supercritical extracts
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0064] Take 100Kg of dried fruit of Schisandra chinensis, add 10 times the amount (v / w) and 8 times the amount (v / w) of water respectively, soak it twice at 60°C for 2 hours each time, combine the soaking liquid, and pass it through the inorganic ceramic Membrane filtration, the filtrate is filtered with a nanofiltration membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 2000 Daltons, the filtrate is concentrated under reduced pressure, added 2Kg of medicinal starch, mixed, and spray-dried to obtain 19Kg of brown dry powder containing Schisandra organic acid, wherein the total The content of organic acid is 43.15%.
[0065] Add 2 times the volume of water to the remaining liquid, filter it with a nanofiltration membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 2000 Daltons, discard the filtrate, and spray dry the remaining liquid to obtain 5.9Kg of the polysaccharide part of Schisandra chinensis, which is a light brown powder. The content of total polysaccharide is 57.91%.
[0066] Dry th...
Embodiment 2
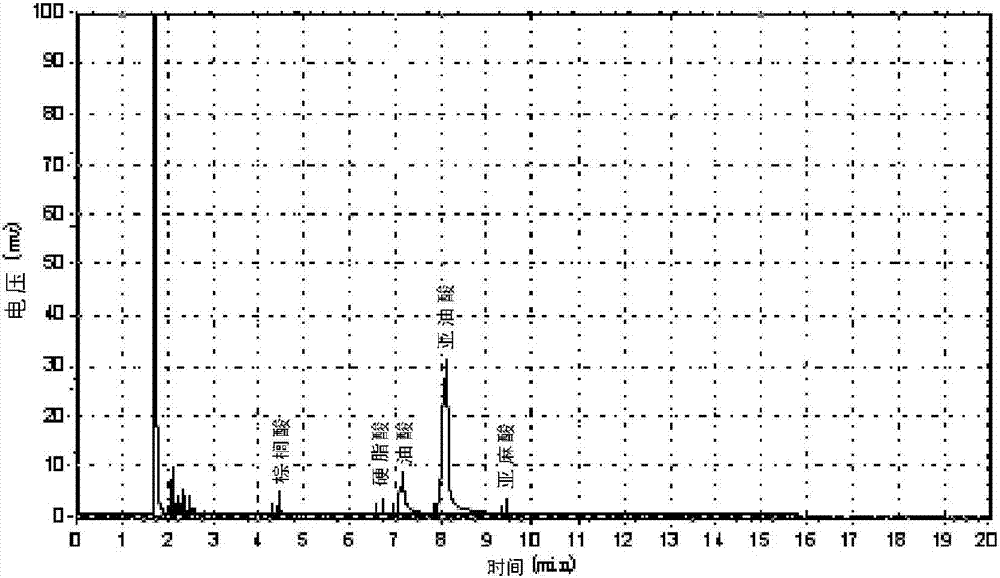
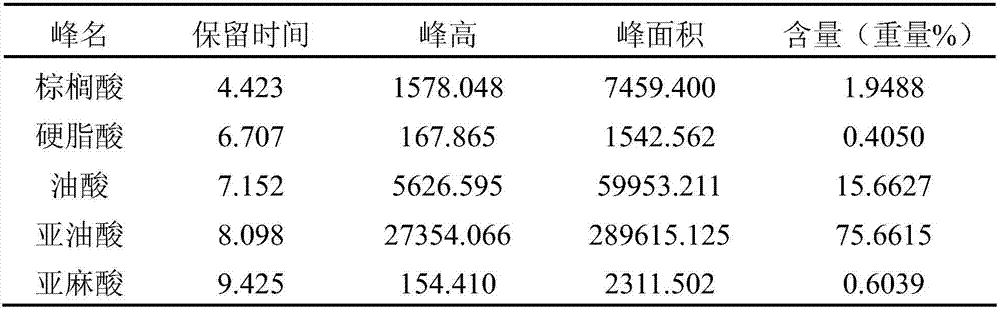
[0069] Put about 13.0Kg of Schisandra oil and distilled water obtained in Example 1 into a flat-bottomed flask at an oil:water ratio of 2:1.3 to 2:1.5, slowly heat up to 80 to 85°C under stirring, and slowly drop in 40% NaOH solution, so that the final pH value of the reaction solution reaches 12, stir and keep warm for 5 to 6 hours, then transfer it into a separatory funnel, let it stand to separate layers, and remove the lower layer of glycerin. Transfer the treated reaction solution into a flat-bottomed flask again, slowly raise the temperature to 90-95°C, slowly drop in 28% sulfuric acid solution to make the final pH of the reaction solution 2, keep it warm for 4-5 hours, and then transfer it into a separatory funnel. Wash with distilled water at 60-70°C until neutral, and after standing to separate layers, remove the lower water layer to obtain 12.1Kg of crude fatty acid.
[0070]Add 6.1Kg of urea into a certain amount of anhydrous methanol, heat to reflux, and dissolve a...
Embodiment 3
[0072] Take 100Kg of dried fruit of Schisandra chinensis, add 10 times the amount (v / w) and 8 times the amount (v / w) of water to soak twice at 60°C for 2 hours each time. Membrane filtration, the filtrate is filtered with a nanofiltration membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 2000 Daltons, the filtrate is concentrated under reduced pressure, 2Kg of medicinal starch is added to mix, and spray-dried to obtain 19.1Kg of brown dry powder containing Schisandra organic acid, wherein The content of total organic acids is 44.76%.
[0073] Add 2 times the volume of water to the remaining liquid, filter it with a nanofiltration membrane with a molecular weight cut-off of 2000 Daltons, discard the filtrate, and spray dry the remaining liquid to obtain 5.3Kg Schisandra polysaccharide, which is a light brown powder. The content of polysaccharide is 52.23%.
[0074] The soaked Schisandra chinensis (that is, Schisandra slag) was dried, crushed into coarse powder, and then subcritical ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com