D2D (Device to Device) communication joint mode selection and proportional fairness scheduling optimization method
A proportional fair scheduling and optimization method technology, applied in multiplexing communication, electrical components, orthogonal multiplexing systems, etc., can solve problems such as ignoring user fairness, D2D communication mode selection, or single optimization of resource scheduling
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
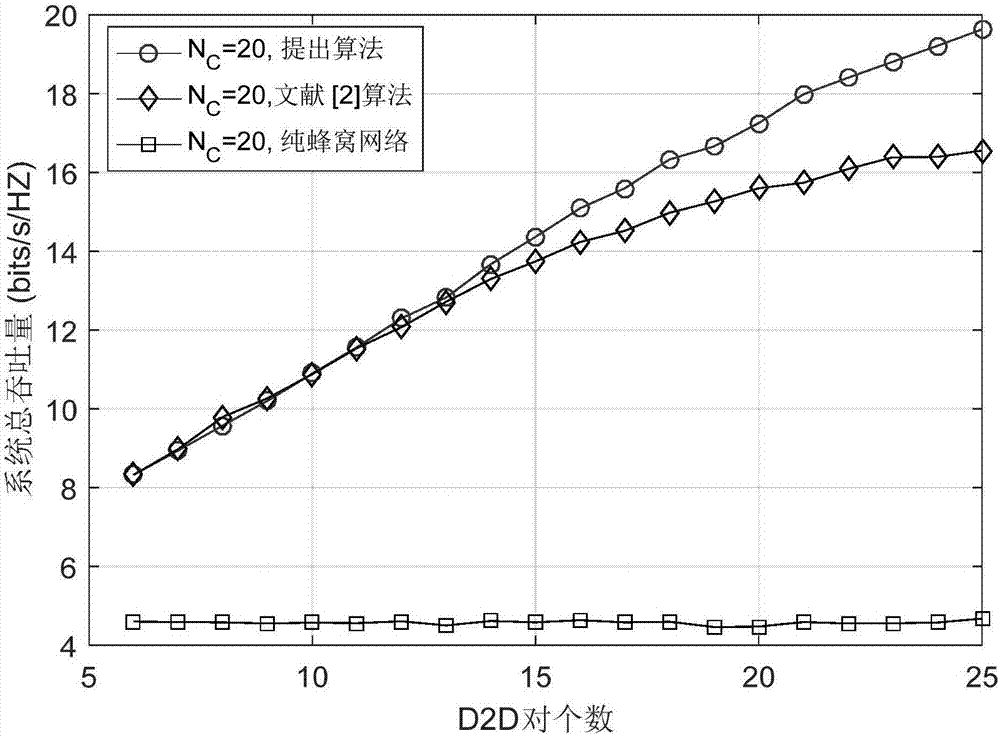
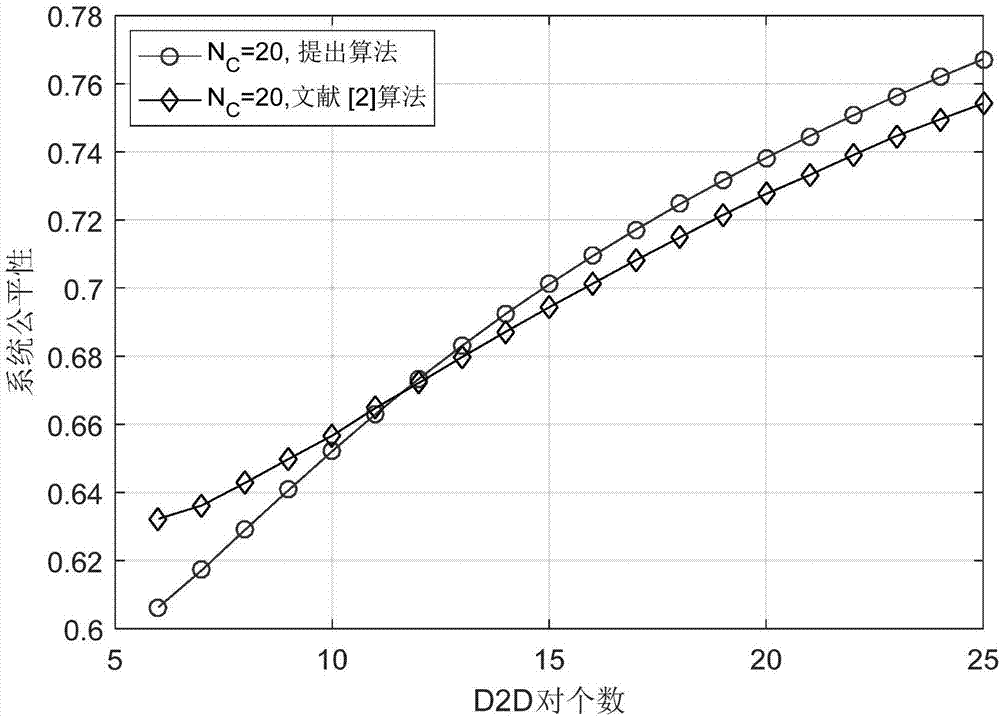
[0071] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 2 Describe this embodiment, a D2D communication joint mode selection and proportional fair scheduling optimization method in this embodiment, which is characterized in that the method is specifically carried out according to the following steps:
[0072] Step 1: Algorithm starts;
[0073] Step 2: Initialize the average transmission rate of all users in the first time slot:
[0074] Randomly generate a set of average transmission rates of cellular users D2D user average transmission rate set
[0075] in, is the average transmission rate of cellular user 1 in the first time slot, is the average transmission rate of cellular user 2 in the first time slot, for cellular user N C The average transmission rate in the first time slot; is the average transmission rate of D2D user 1 in the first time slot, is the average transmission rate of cellular user 2 in the first time slot, For D2D user N D The average trans...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0128] Specific embodiment two: the difference between this embodiment and specific embodiment one is: the tth time slot is calculated in the step four, cellular user i C Channel Gain with Base Station Channel gain between D2D pairs cellular user i C with D2D pair i D Interference channel gain between receivers and D2D for i D Channel gain to base station interfering link The specific process is:
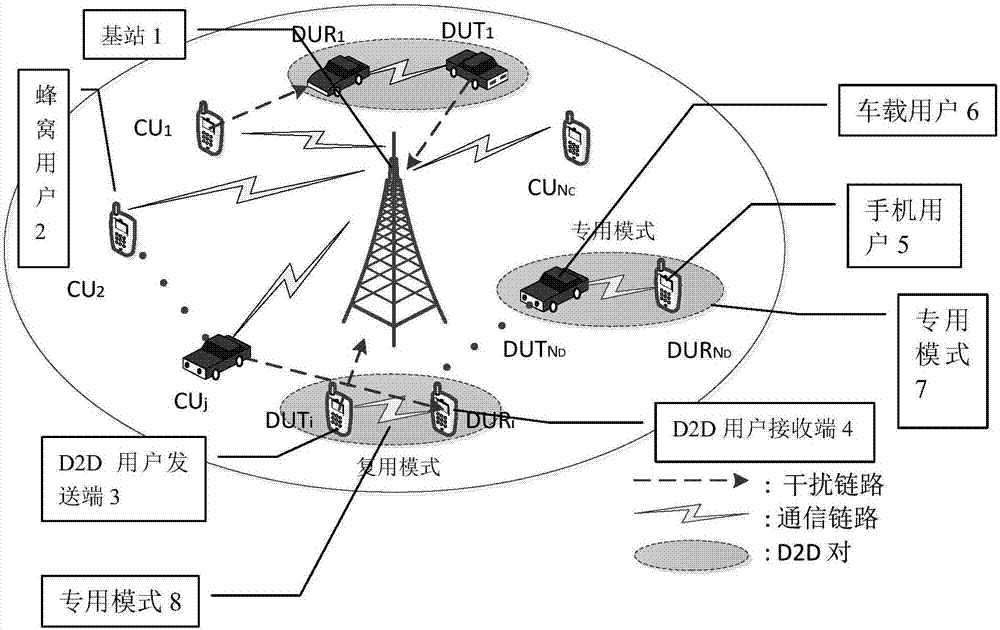
[0129] The network system model in which D2D communication multiplexes cellular user uplink resources in the hybrid network of D2D and cellular network in step 4 includes a base station 1, N C cellular users 2 and N D D2D senders 3 and N D A D2D receiving terminal 4, the terminal user can be a traditional mobile phone user 5 or a vehicle user 6, and the D2D terminal can choose a dedicated mode communication 7, or a multiplex mode communication 8 (such as figure 1 );
[0130] In the mixed network model of D2D and cellular network, all cellular user CUs and D2D sending ...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0143] Embodiment 3: The difference between this embodiment and Embodiment 1 or 2 is that in Step 6, according to Step 5, the joint mode selection of the mixed network model of D2D and the cellular network and the proportional fairness control problem are mathematically modeled, Get the mathematical model; the specific process is:
[0144] The mathematical model is obtained by taking the maximum sum of the proportional fairness functions of all users in the tth time slot as the objective function:
[0145]
[0146]
[0147]
[0148]
[0149]
[0150]
[0151]
[0152]
[0153]
[0154] where x * is the optimal solution of the corresponding mode selection and channel allocation matrix x when formula (17) reaches the maximum value, p * is the optimal solution of the power matrix corresponding to p when formula (17) reaches the maximum value; N C is the number of cellular users, and the value is a positive integer; N D is the number of D2D pairs, and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com