Patents
Literature
436 results about "D channel" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
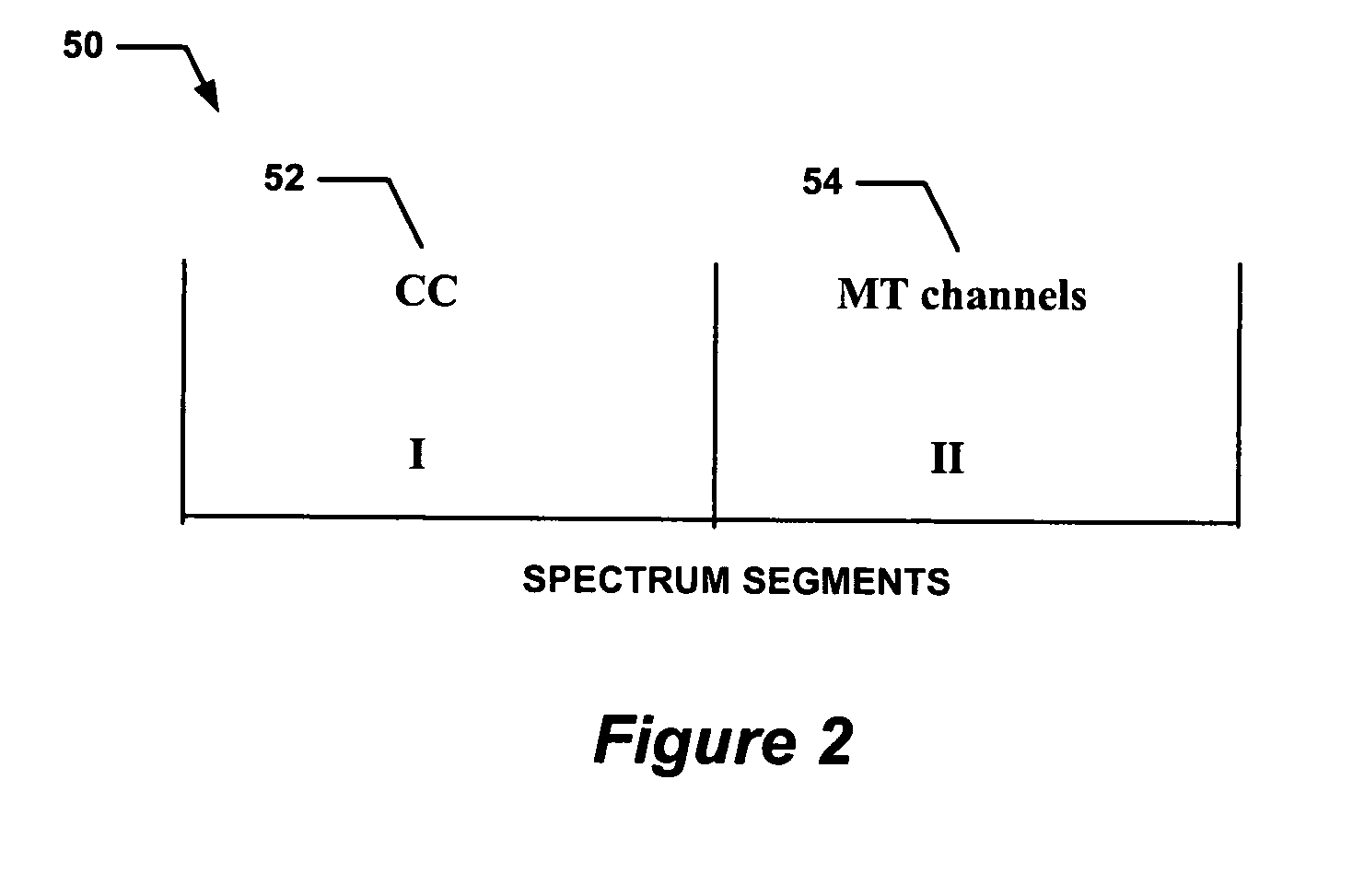
D channel (delta channel) is a telecommunications term which refers to the ISDN channel in which the control and signalling information is carried. The bit rate of the D channel of a basic rate interface is 16 kbit/s, whereas it amounts to 64 kbit/s on a primary rate interface.
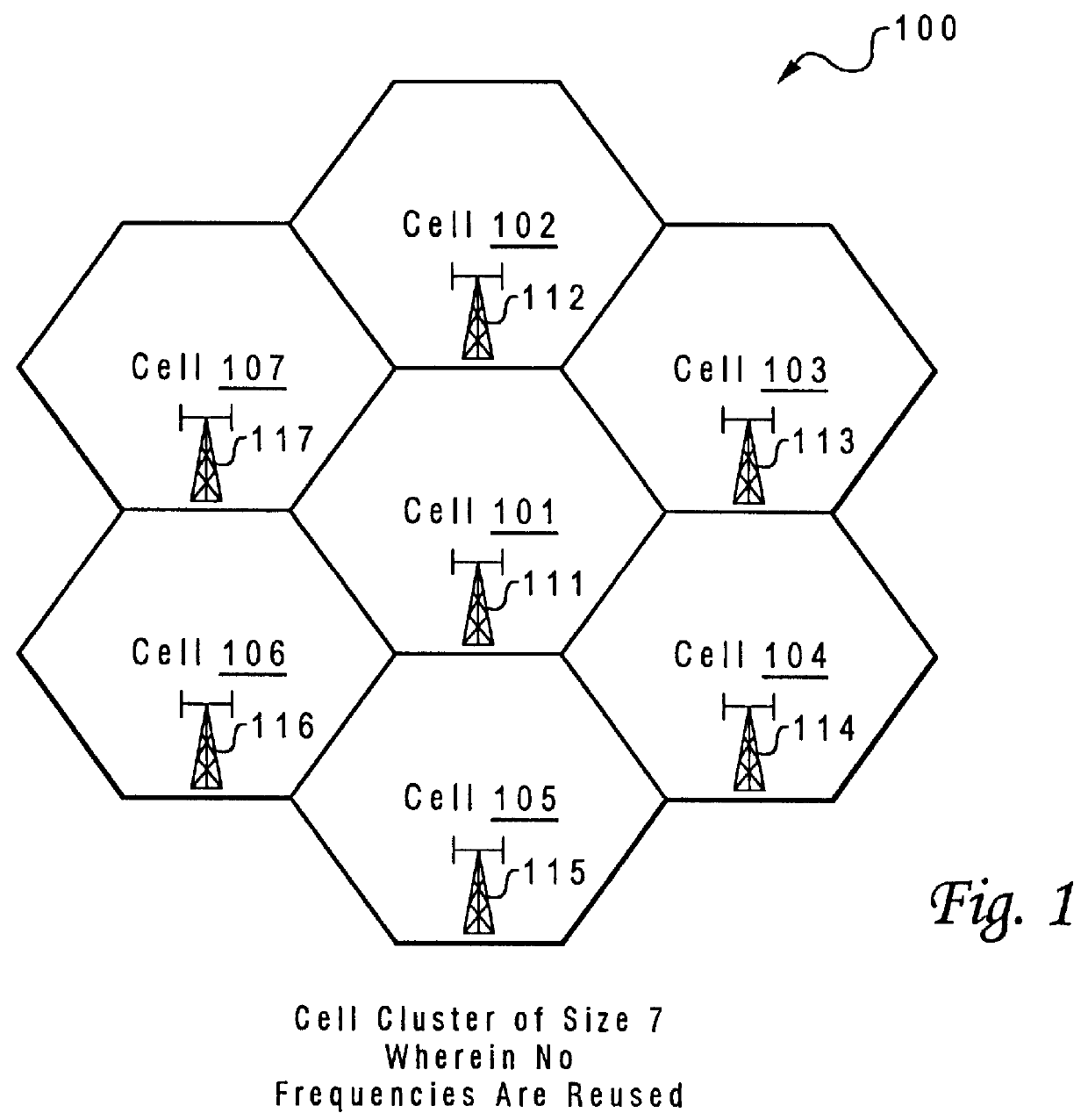
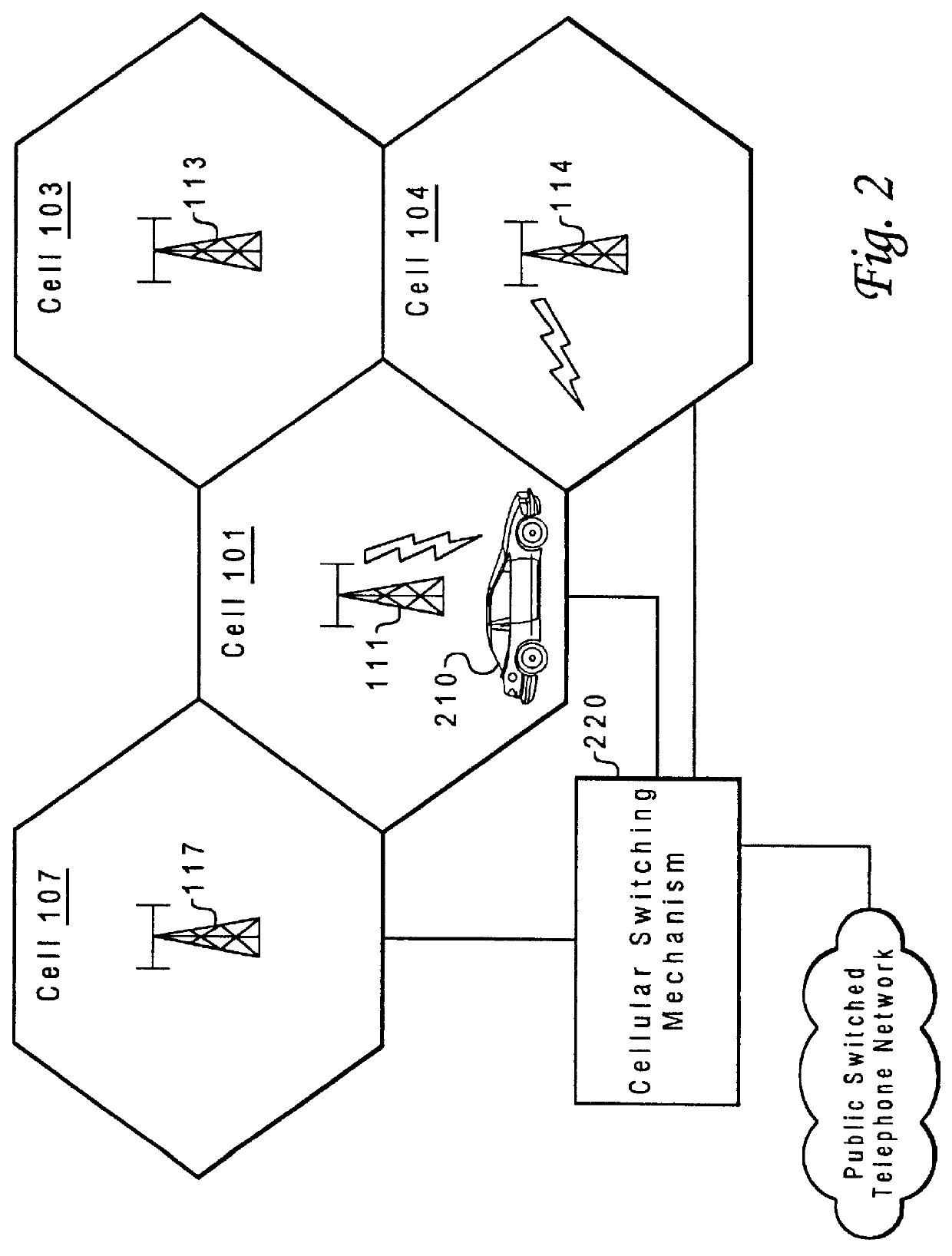
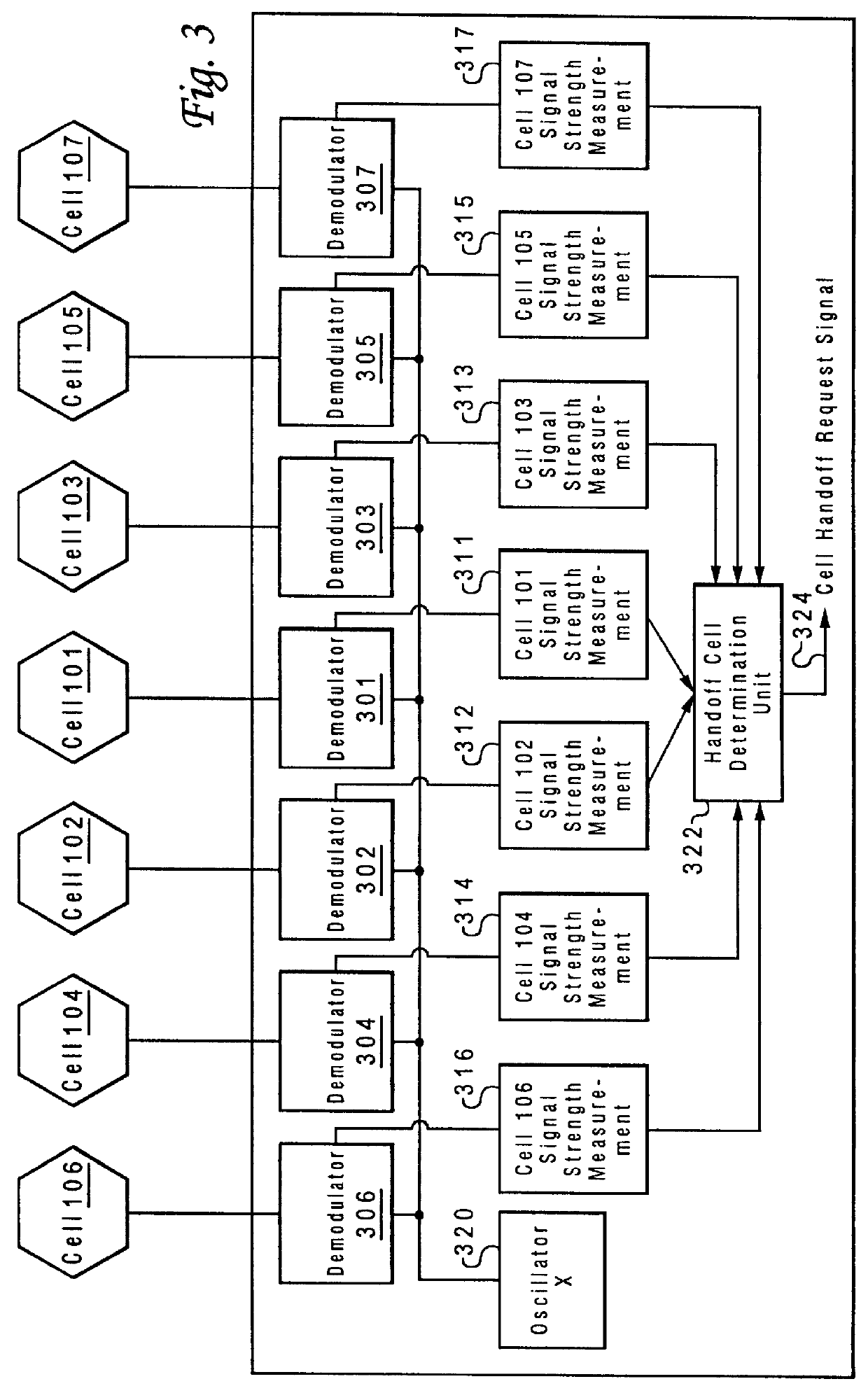
Method and system for assuring near uniform capacity and quality of channels in cells of wireless communications systems having cellular architectures
InactiveUS6011970AMaximized cellular concept of frequency reuseReduce power outputRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsTransmission monitoringCellular architectureSignal-to-noise ratio (imaging)
A method and system for use with wireless communication systems having a cellular architecture with at least a first and a second cell. The method and system provided ensure near uniform capacity and quality of channels within the second cell via the following steps. The noise signal power in unused data channels within the second cell is monitored. When a request for channel access is received, a determination is made whether the request for channel access is either a request for handoff from the first cell into the second cell, or not. In the event that the request is not a request for handoff, a determination is made whether idle channels exist to satisfy the request for channel access. In the event of a determination either that the request for channel access is a request for handoff, or both that the request is not a request for handoff and that idle channels exist to satisfy the request, a measured received signal power of a mobile unit subscriber unit making the request is determined. One of the unused channels in the second cell is then preferentially assigned to the mobile subscriber unit where such preference in assigning is to assign a channel, provided that a signal to noise ratio calculated upon the monitored received signal power and the monitored noise signal power of the preferentially assigned noisy channel meets or exceeds a required signal to noise ratio.
Owner:NORTEL NETWORKS LTD
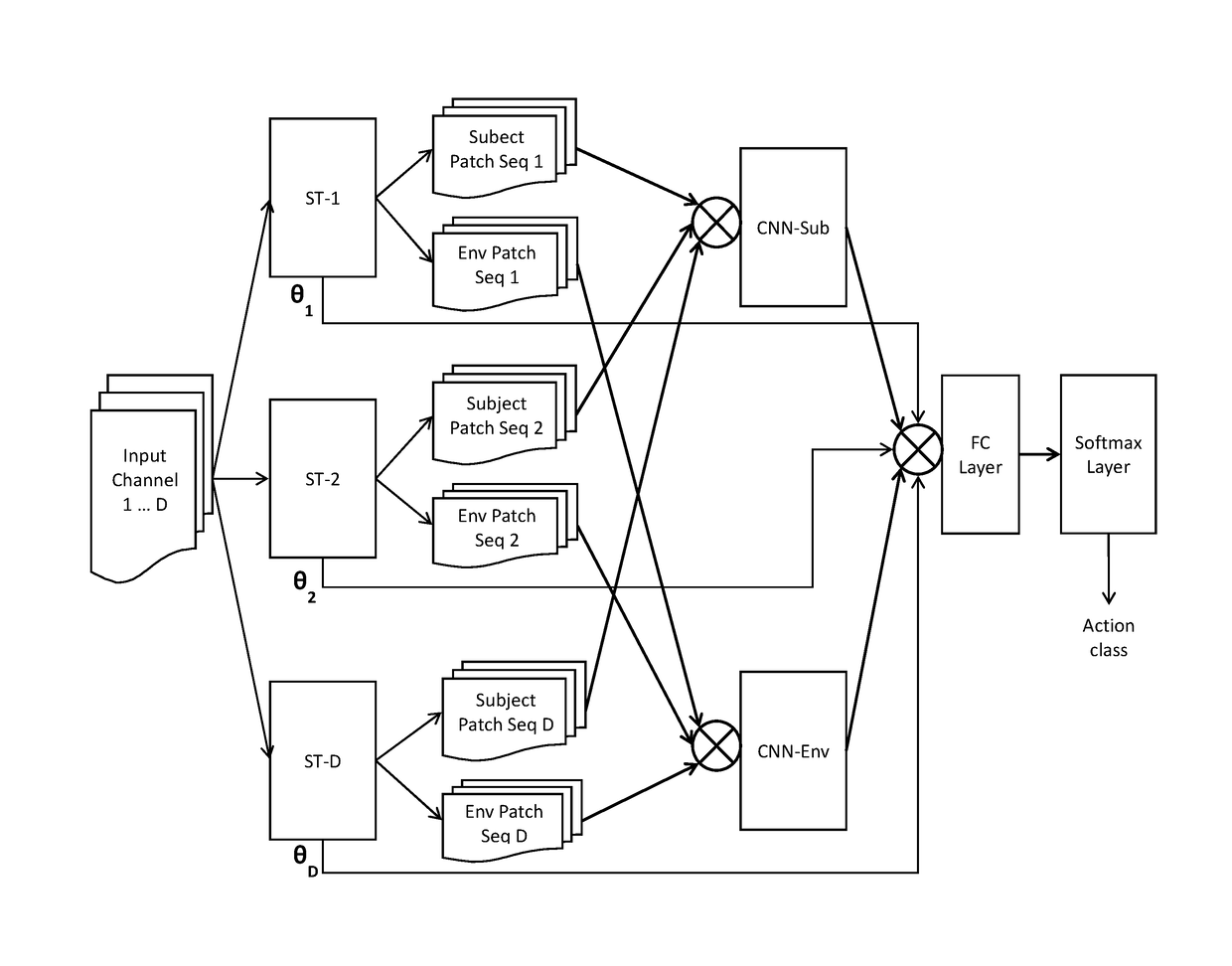
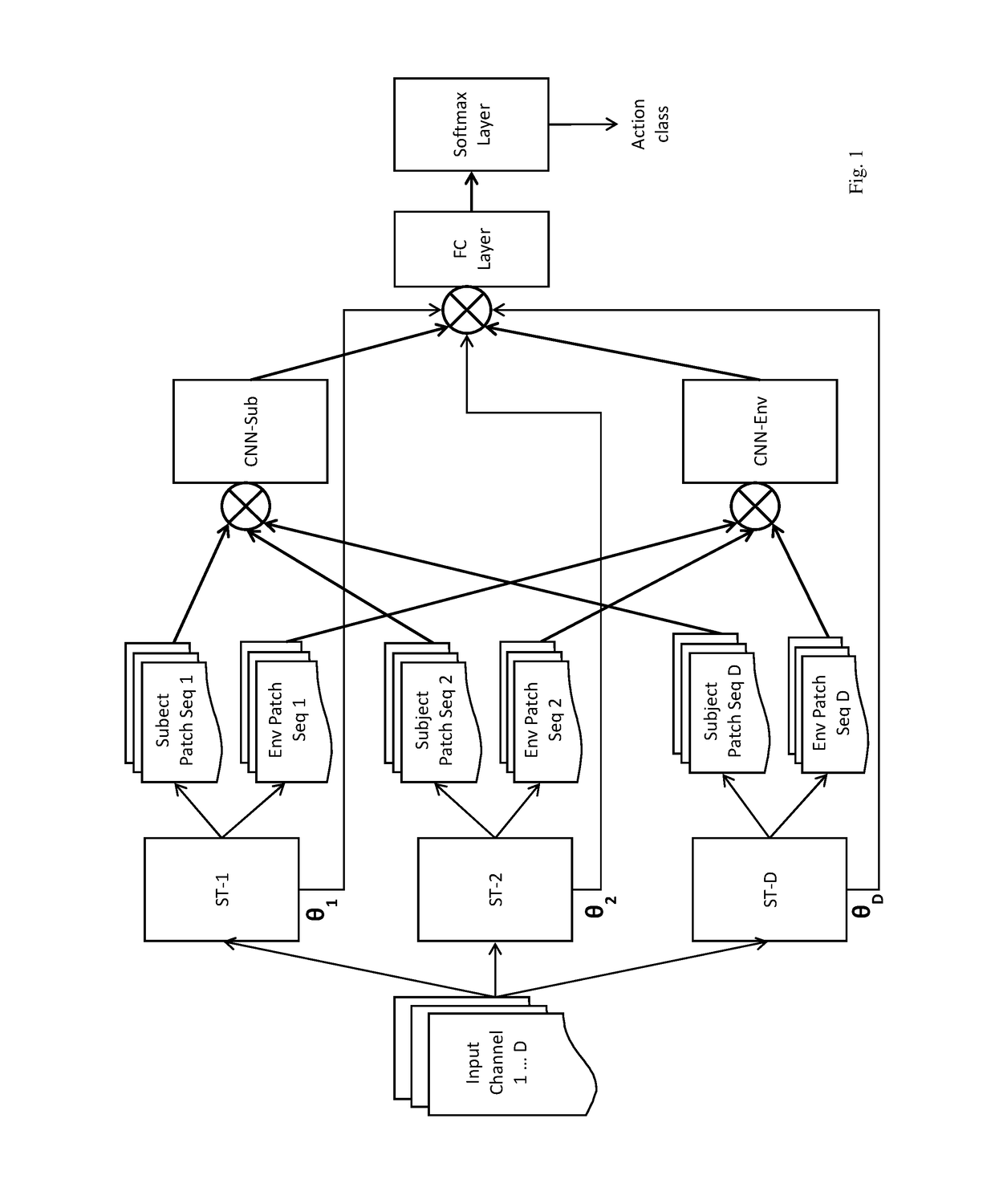
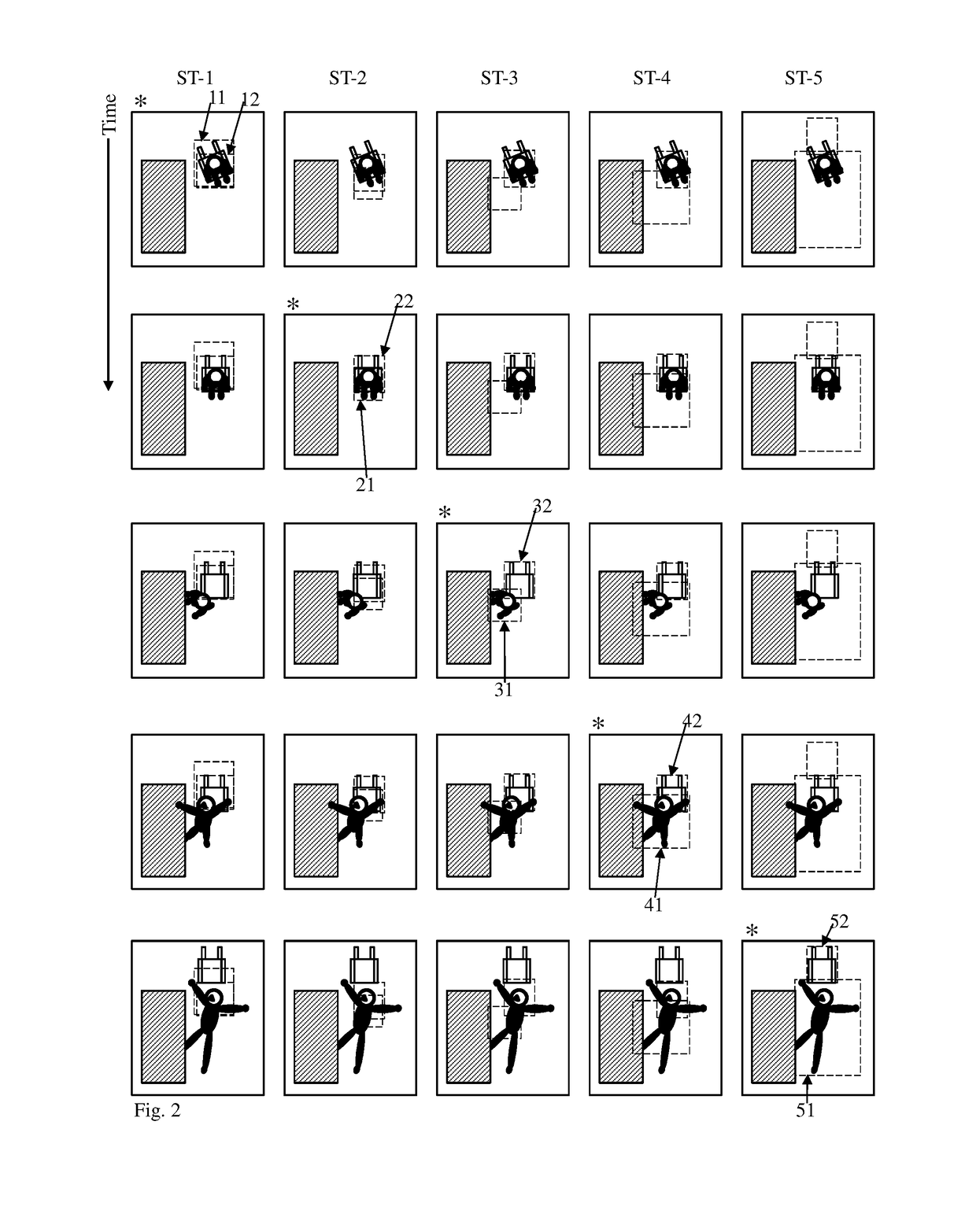
Self-attention deep neural network for action recognition in surveillance videos
An artificial neural network for analyzing input data, the input data being a 3D tensor having D channels, such as D frames of a video snippet, to recognize an action therein, including: D spatial transformer modules, each generating first and second spatial transformations and corresponding first and second attention windows using only one of the D channels, and transforming first and second regions of each of the D channels corresponding to the first and second attention windows to generate first and second patch sequences; first and second CNNs, respectively processing a concatenation of the D first patch sequences and a concatenation of the D second patch sequences; and a classification network receiving a concatenation of the outputs of the first and second CNNs and the D sets of transformation parameters of the first transformation outputted by the D spatial transformer modules, to generate a predicted action class.
Owner:KONICA MINOLTA LAB U S A INC
High-speed transparent access to multiple services
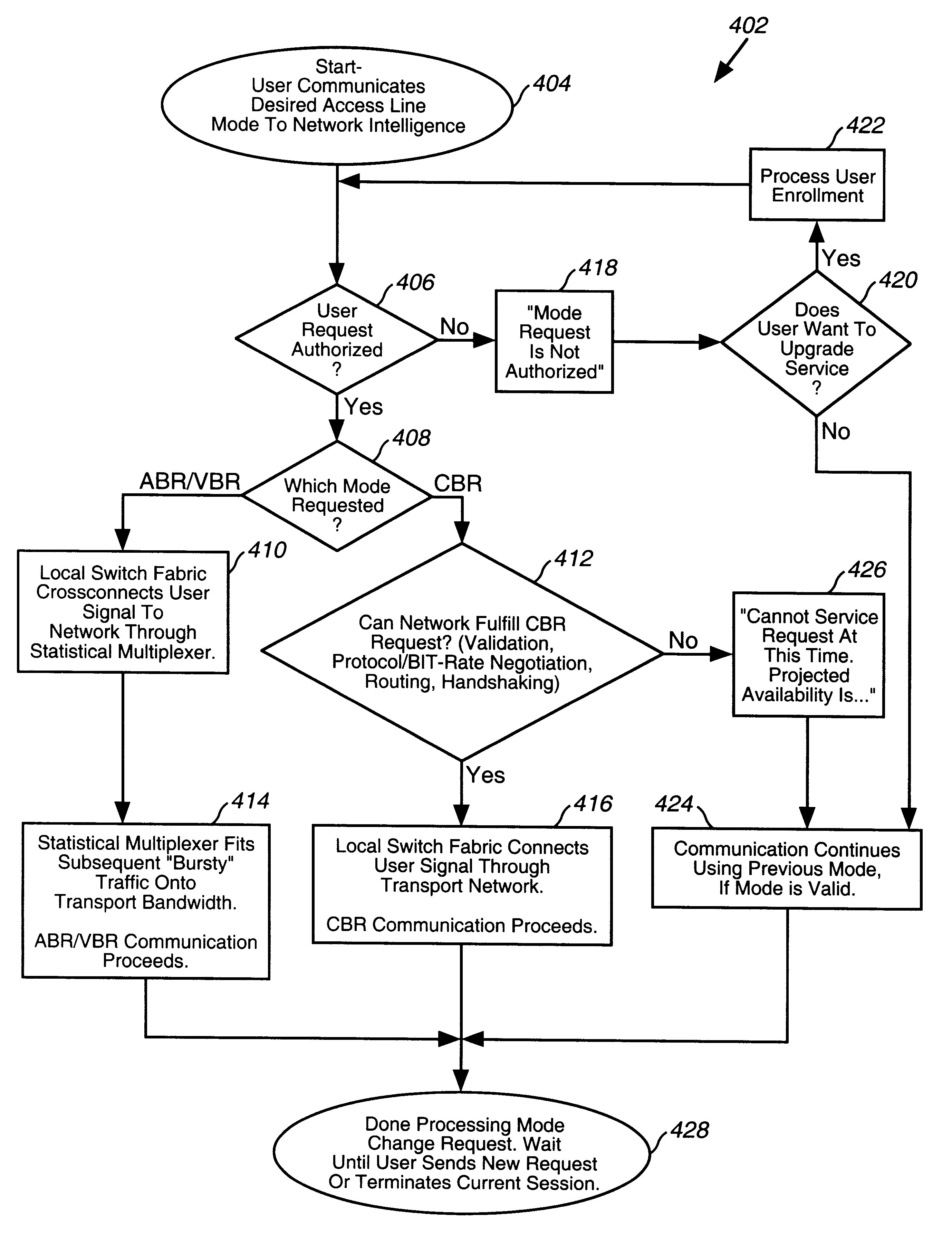
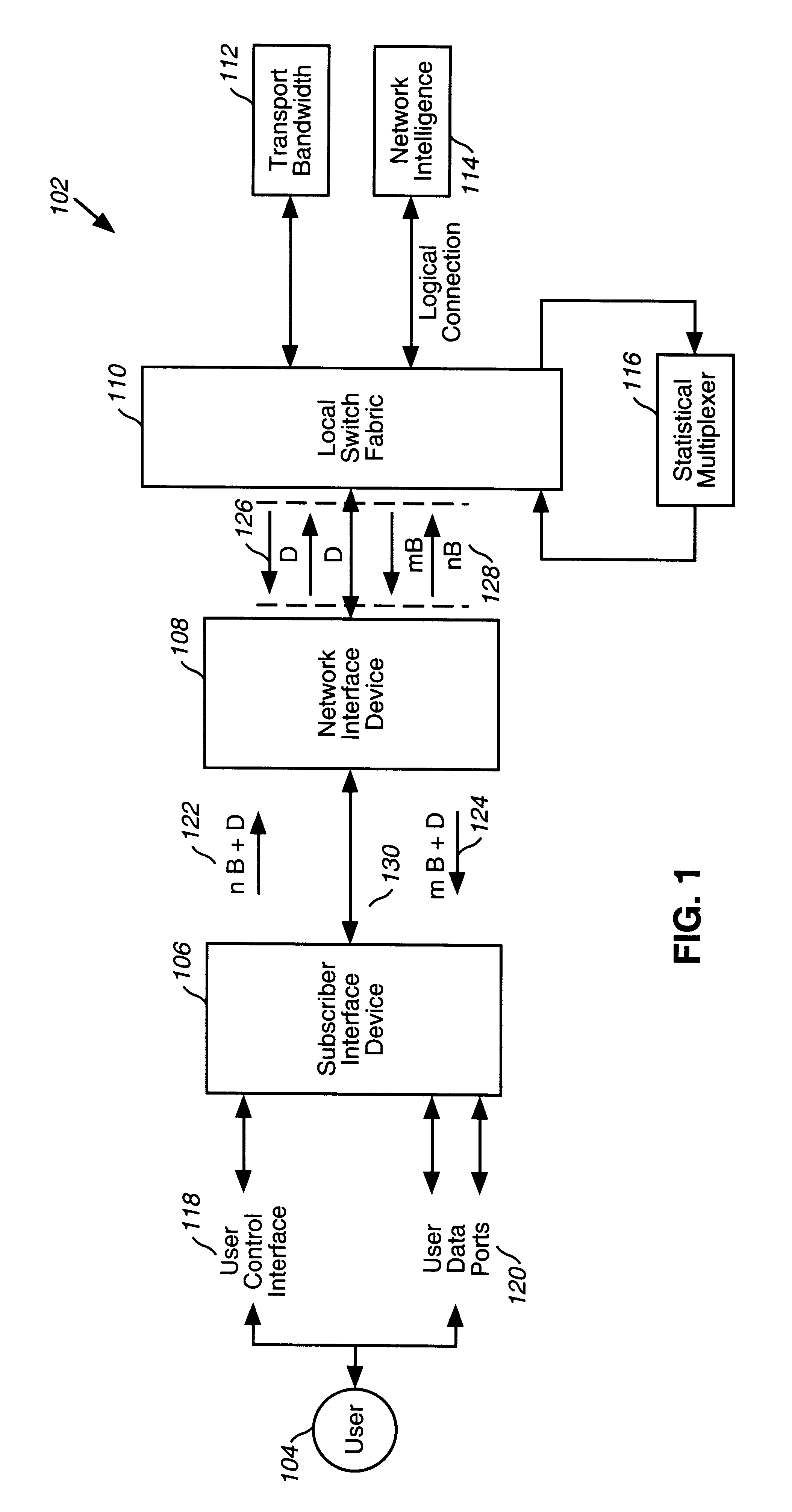
A system, method and computer program product are described, by which a user, through a control interface in a subscriber interface device, requests from network intelligence both transport network bandwidth and type of service line mode as part of call setup. An improved system by which requests to change access line mode and bandwidth are communicated over transmission facilities via D channels through local switch fabric to local or remote network intelligence is detailed. Connections over the transmission facilities, established between user B channels and B channels of transport bandwidth or between user B channels and the Stat Mux function, are described. An improved system is summarized, in which connections directly to transport bandwidth support point-to-point n B+D upstream and m B+D downstream service, and connections via stat mux allow connectionless traffic to share a portion of the transport bandwidth on an as needed basis. The ability to request and change access to available bit rate (ABR), variable bit rate (VBR) and constant bit rate (CBR) services, in a connection-oriented (CONS) or connectionless (CLNS) network, are described.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
Frequency hopping spread spectrum communications system
InactiveUS6888876B1Modulated-carrier systemsDiversity/multi-antenna systemsMicrocontrollerTransceiver
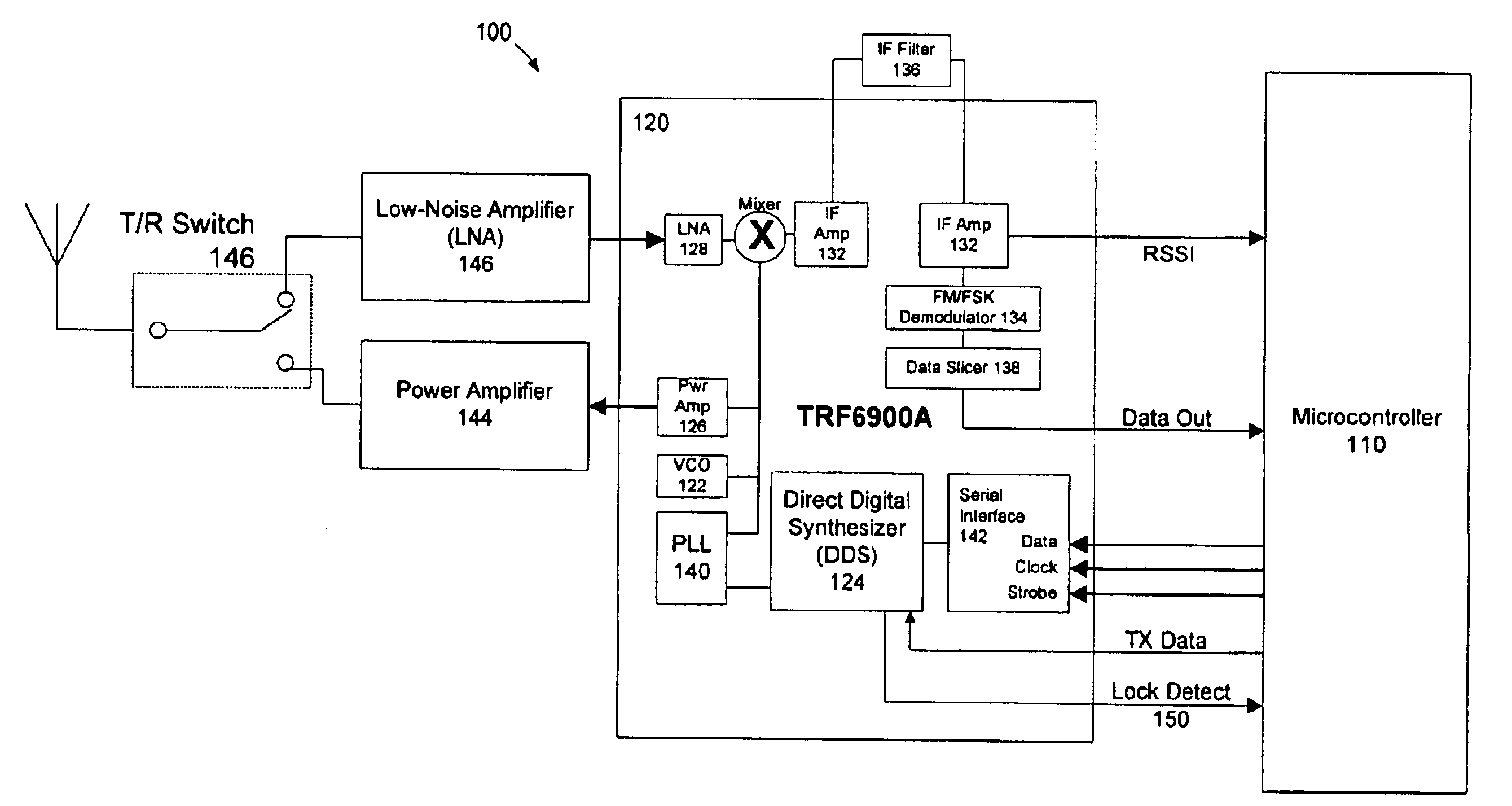
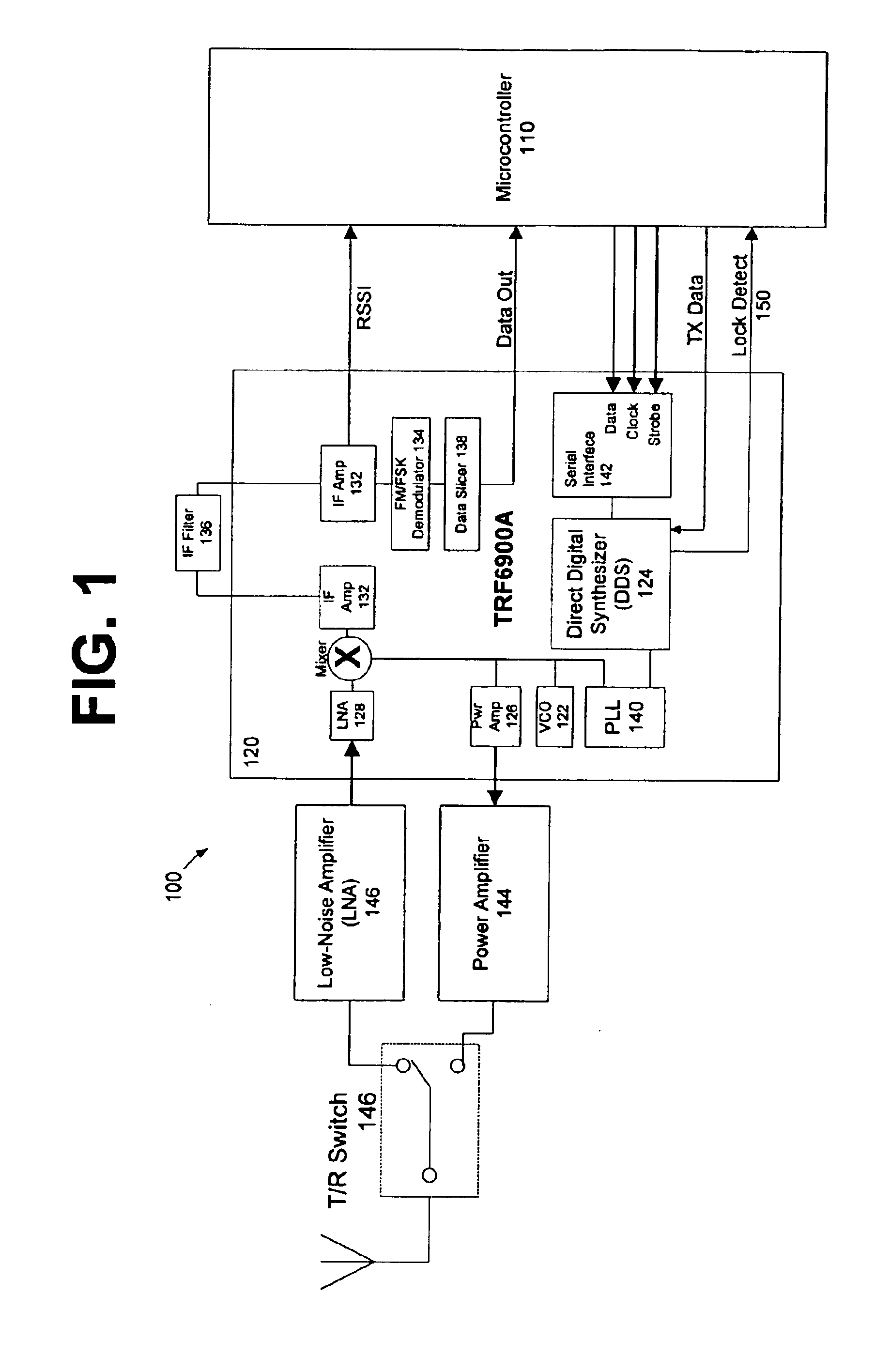
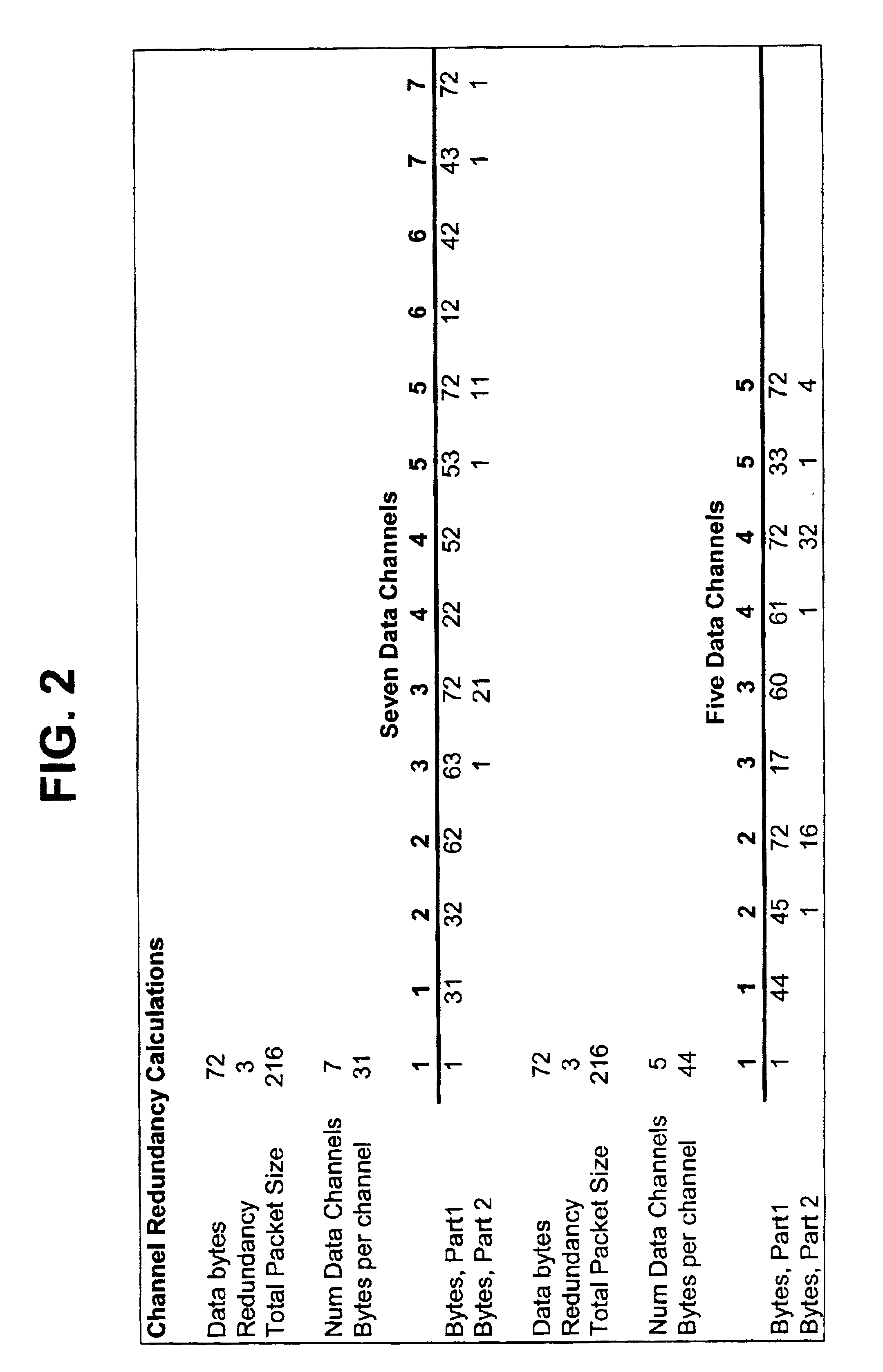
The present invention is directed to a frequency hopping spread spectrum transceiver. The transceiver includes a microcontroller; a transmitter having a voltage controlled oscillator, a direct digital synthesizer, and a power amplifier; and a receiver having an amplifier, a mixer, an IF amplifier, a demodulator, and a data slicer. When transmitting, the transmitter communicates a preamble over a predetermined number of preamble channels, and thereafter communicate groups of data bytes that each comprise a subset of the data message over a predetermined sequence of data channels. When receiving, the receiver investigates the predetermined number of preamble channels to search for the preamble, each of the predetermined number of preamble channels being associated with a predetermined number of data channels in each sequence of data channels. A number of bytes that comprises each group of data bytes is determined in accordance with a number of channels in the sequence of data channels and the predetermined number of times each byte of the data message is to be transmitted.
Owner:ELSTER ELECTRICTY LLC
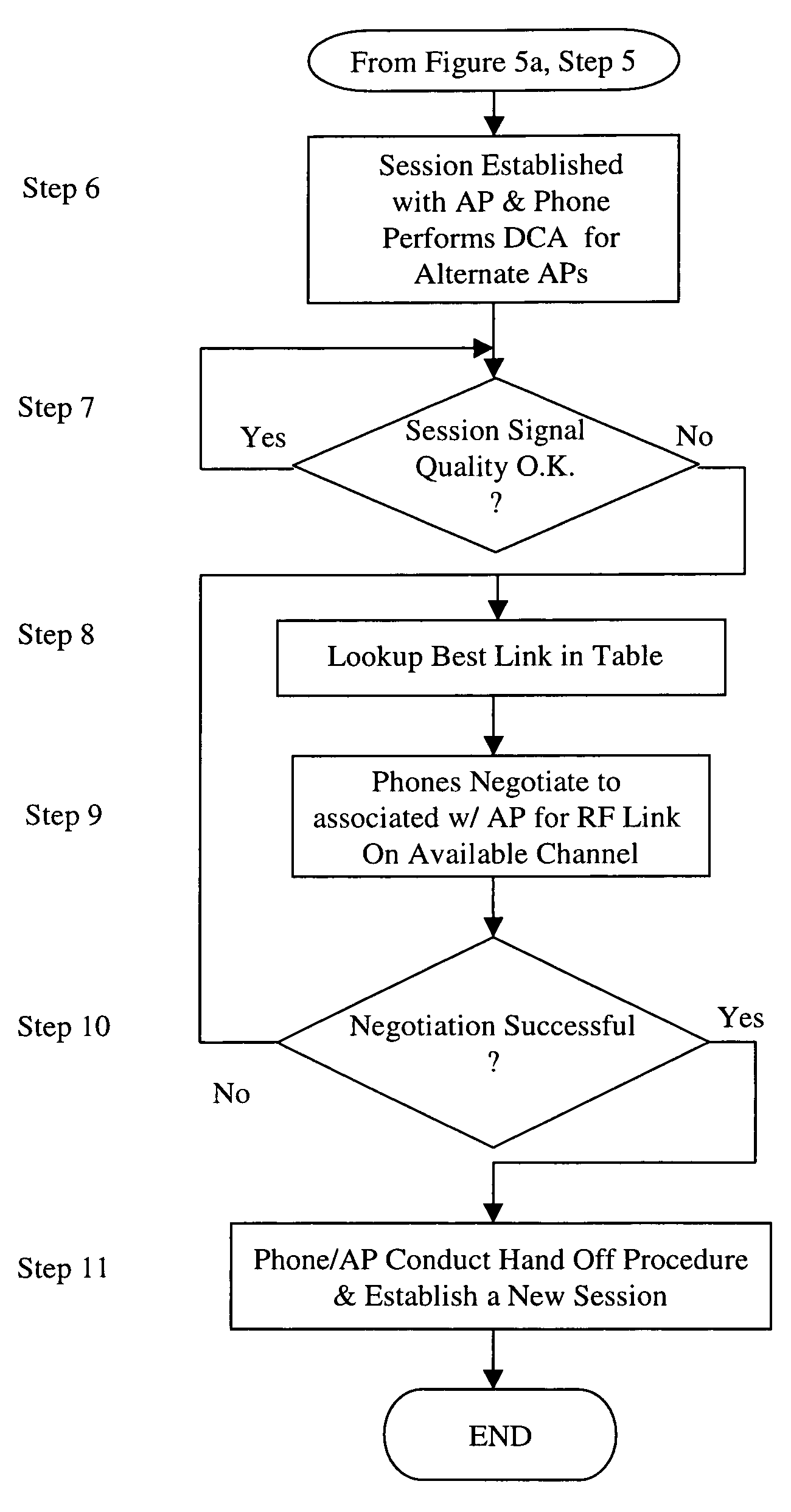
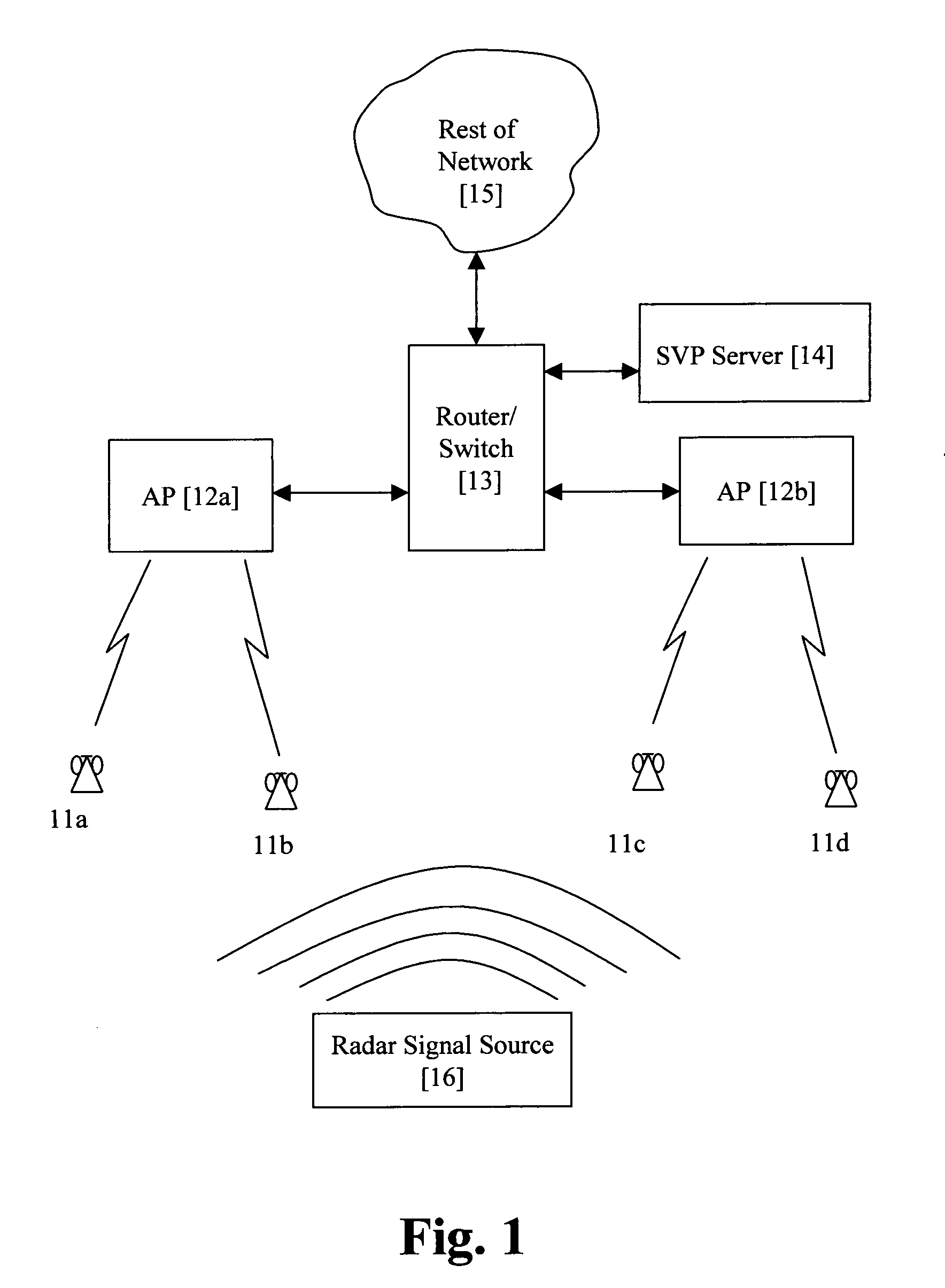
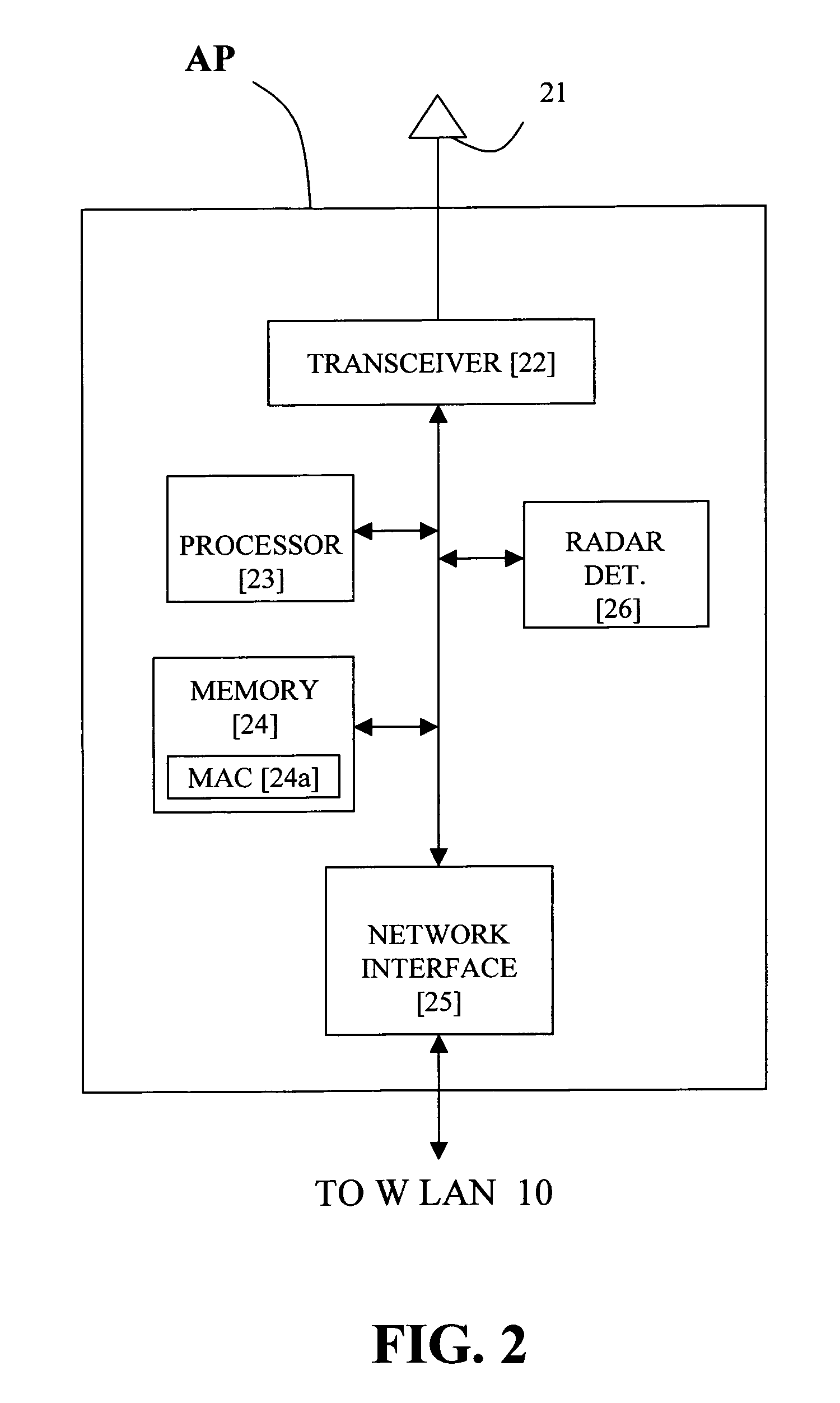
Method for determining DFS channel availability in a wireless LAN
InactiveUS20080056200A1Radio/inductive link selection arrangementsRadio transmissionWireless lanRadio frequency
A LAN has a wireless portion which includes access points and wireless communications devices and a wired portion which includes such things as routers, servers, and a PBX. The LAN operates in a radio frequency band where certain channels (DFS channels) are shared with a signal that is of higher priority than the communications signals transmitted and received by the access point and the wireless communications devices. If a higher priority signal is sensed on a particular channel of the wireless medium by a master device, it is necessary for all of the slave devices communicating on this channel to stop transmitting on that channel within a short period of time. The wireless communications devices are mobile and can be easily transported around in space or roam during a communications session. While roaming during a communications session, it is likely that the communications device will move out of range of an access point with which it is currently associated and possibly cause the session to end prematurely, and so it is important that a handoff procedure operates so that a communications session is continuous as the communications device roams from access point to access point. By setting and maintaining a timer dedicated to each available DFS channel, it is possible to ensure that the communications sessions is not interrupted during the roaming process in an environment were certain channels are shared with a higher priority signal.
Owner:SPECTRALINK
Optofluidic microscope device with photosensor array
ActiveUS20110181884A1Improve abilitiesPrevent rotationScattering properties measurementsTransmissivity measurementsElectric fieldMicroscope
Embodiments of the present invention relate to techniques for improving optofluidic microscope (OFM) devices. One technique which may be used eliminates the aperture layer covering the light detector layer. Other techniques retain the aperture layer, reversing the relative position of the light source and light detector such that light passes through the aperture layer before passing through the fluid channel to the light detector. Another technique adds an optical tweezer for controlling the movement of objects moving through the fluid channel. Another technique adds an optical fiber bundle to relay light from light transmissive regions to a remote light detector. Another technique adds two electrodes at ends of the fluid channel to generate an electrical field capable of moving objects through the fluid channel while suppressing rotation. These techniques can be employed separately or in combination to improve the capabilities of OFM devices.
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Protocol for wireless multi-channel access control
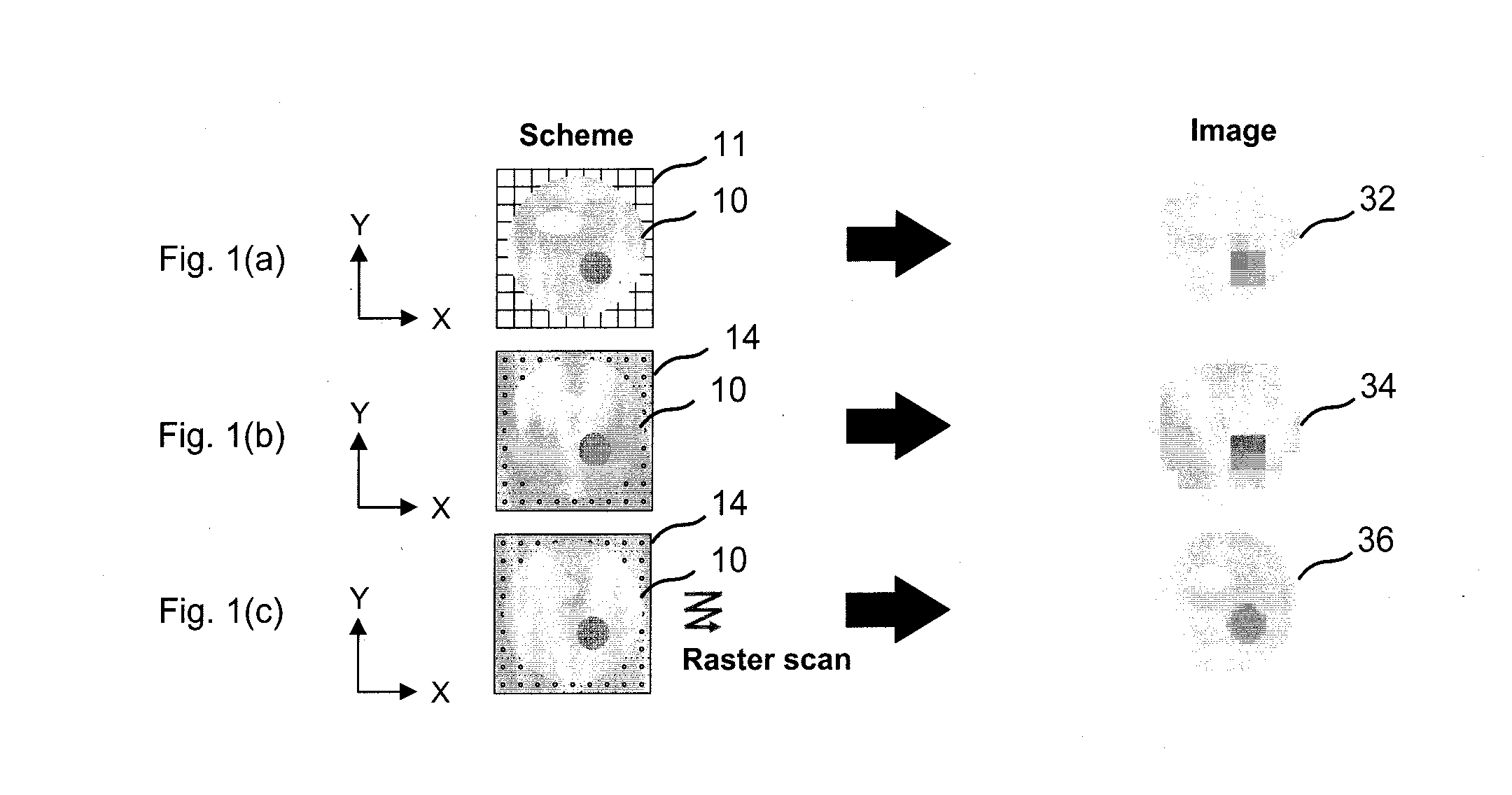
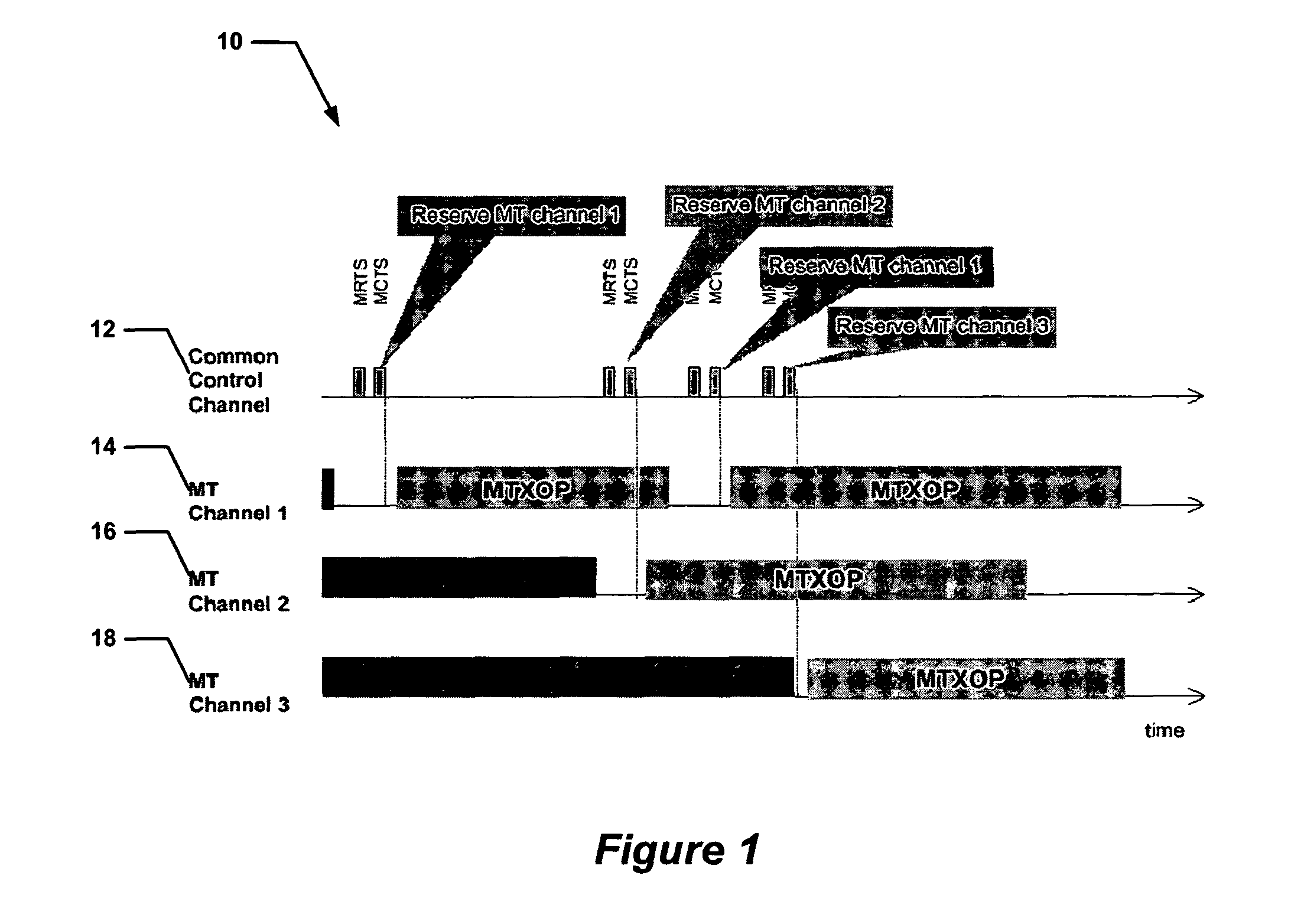
A method and apparatus for providing channel access coordination in a BSS or a wireless mesh is presented. A control channel is assigned to a control radio. At least one data channel is assigned to at least one data radio. Control signals are transmitted and received on the control channel, and data is transmitted and received on the at least one data channel. Acknowledgements for the data are received on the control channel. A node having a plurality of radios can transmit and receive traffic on different data channels simultaneously.
Owner:AVAYA INC
Transmission apparatus and reception apparatus
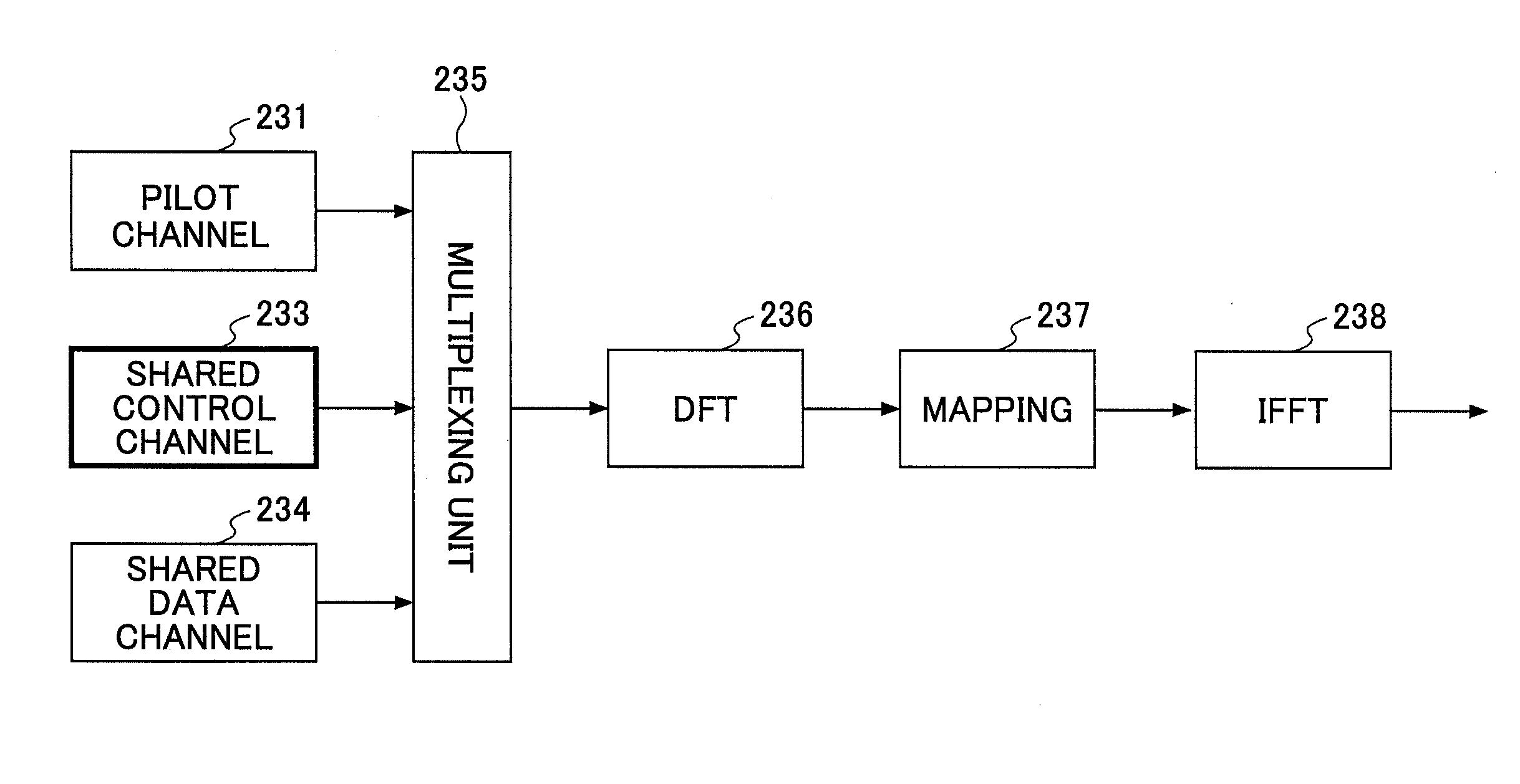
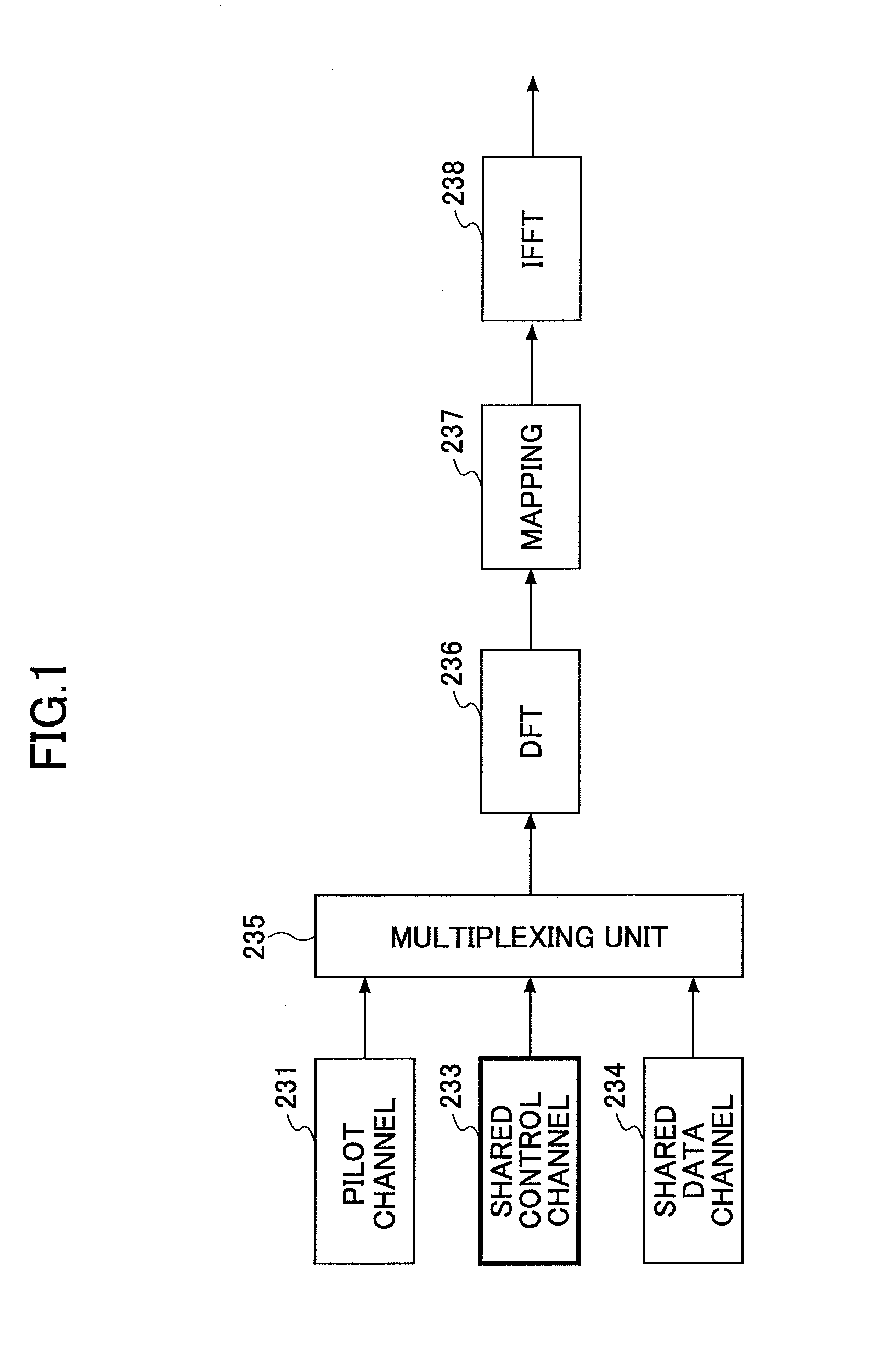
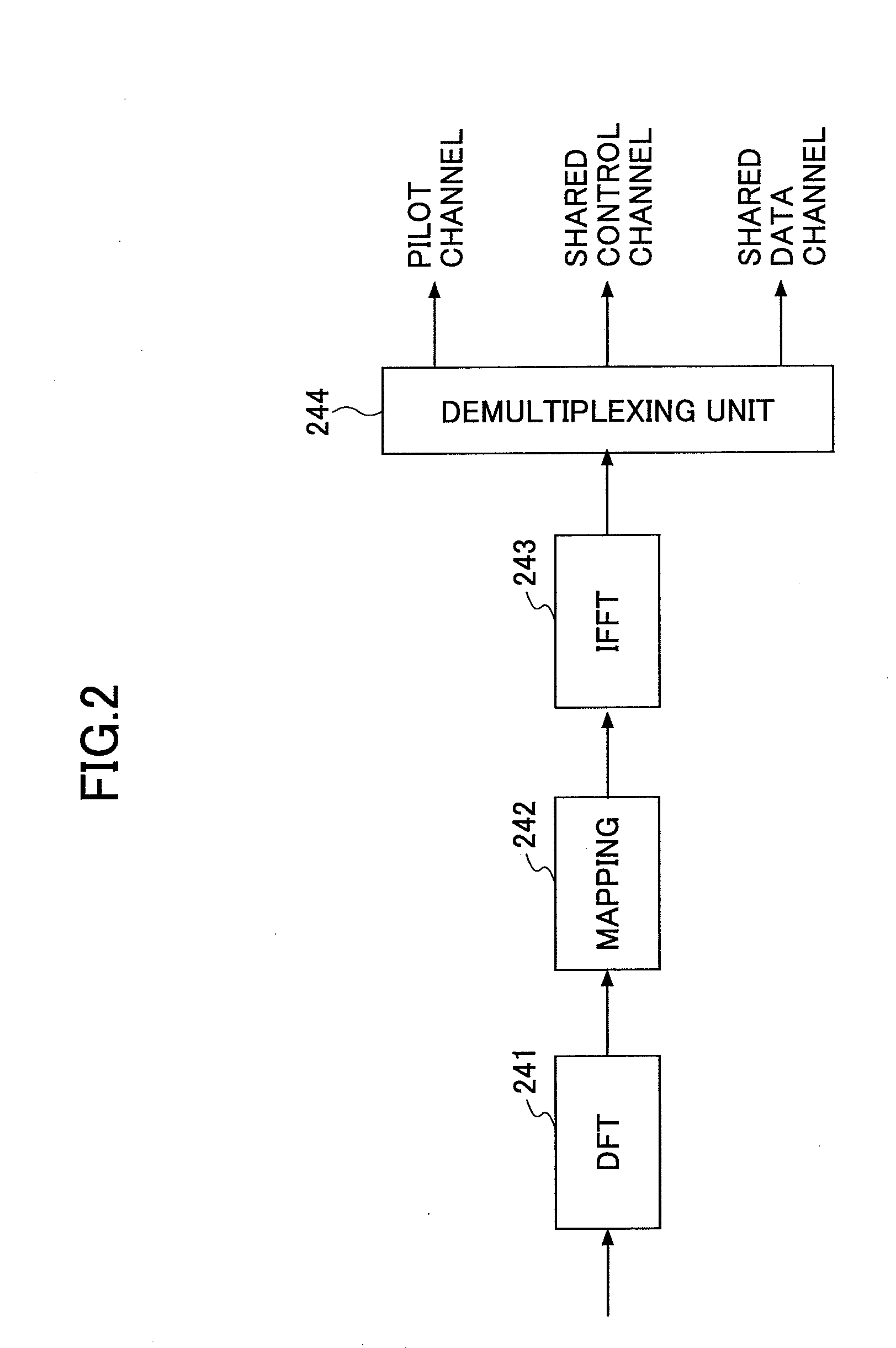
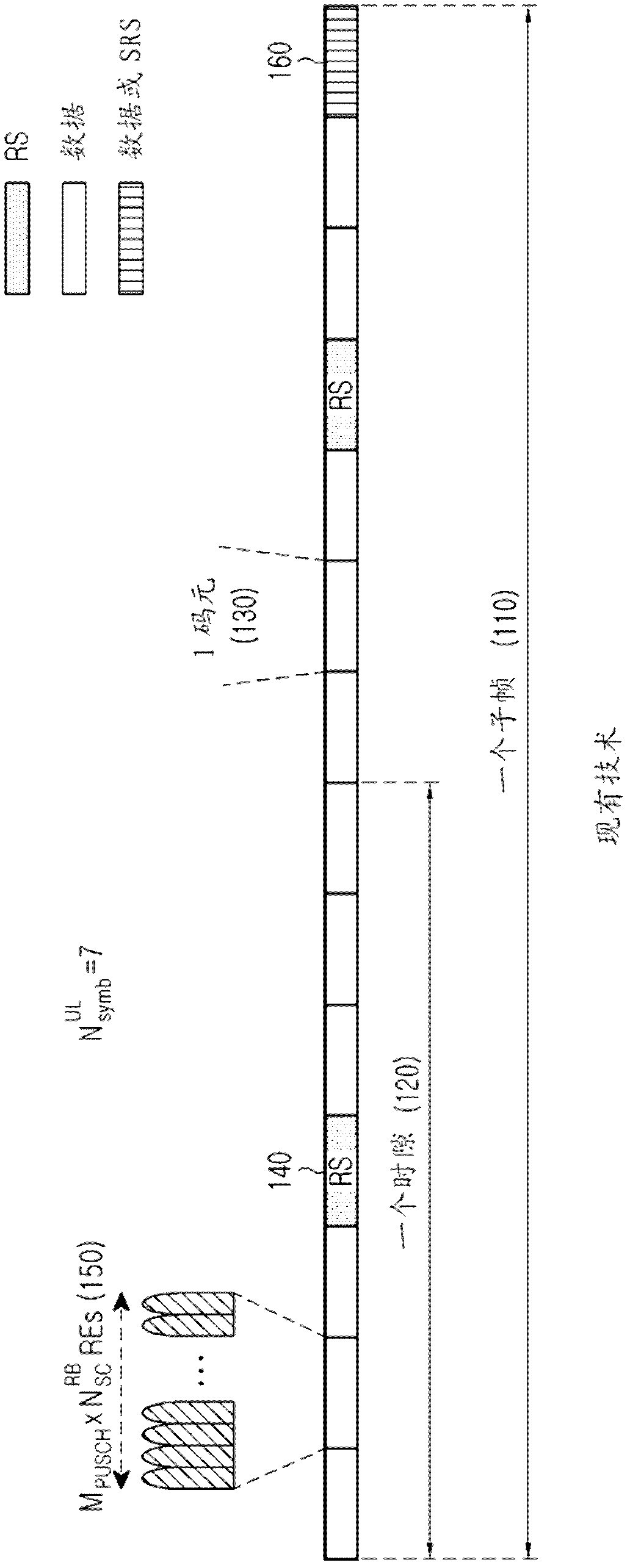
A transmission apparatus used in a mobile communication system adopting a single carrier scheme in an uplink includes: multiplexing means configured to multiplex a pilot channel, a control channel, and a data channel; and transmission means configured to transmit a transmission symbol including at least the pilot channel and the control channel using the uplink. A first pilot channel used for a reception apparatus to measure channel state of the uplink is transmitted using a frequency band over a plurality of resource blocks. A second pilot channel for compensating for a channel transmitted by the uplink is transmitted by a resource block assigned to the transmission apparatus. Control channels of the transmission apparatus and the apparatus other than the transmission apparatus are orthogonalized with each other by a FDM scheme.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
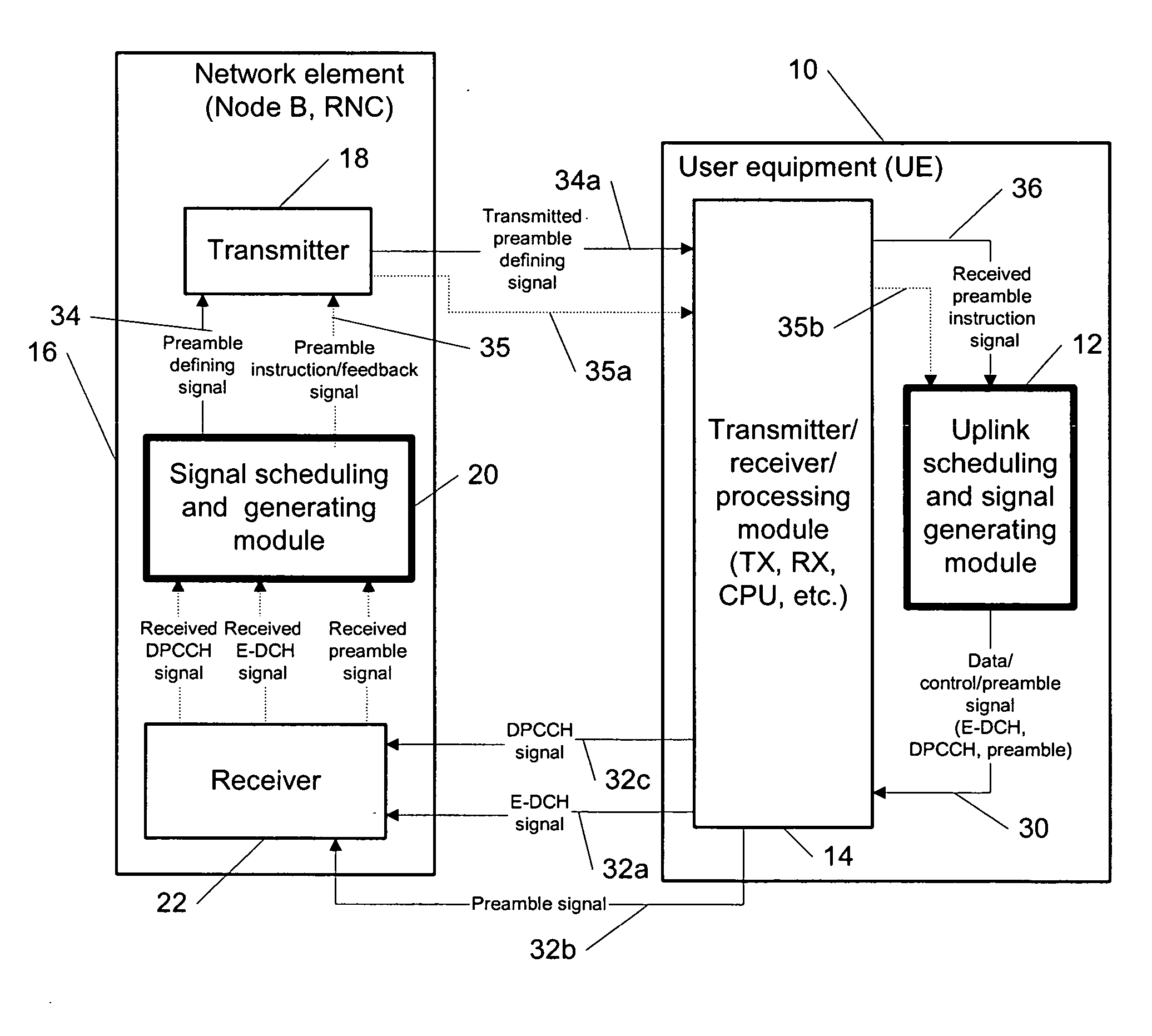
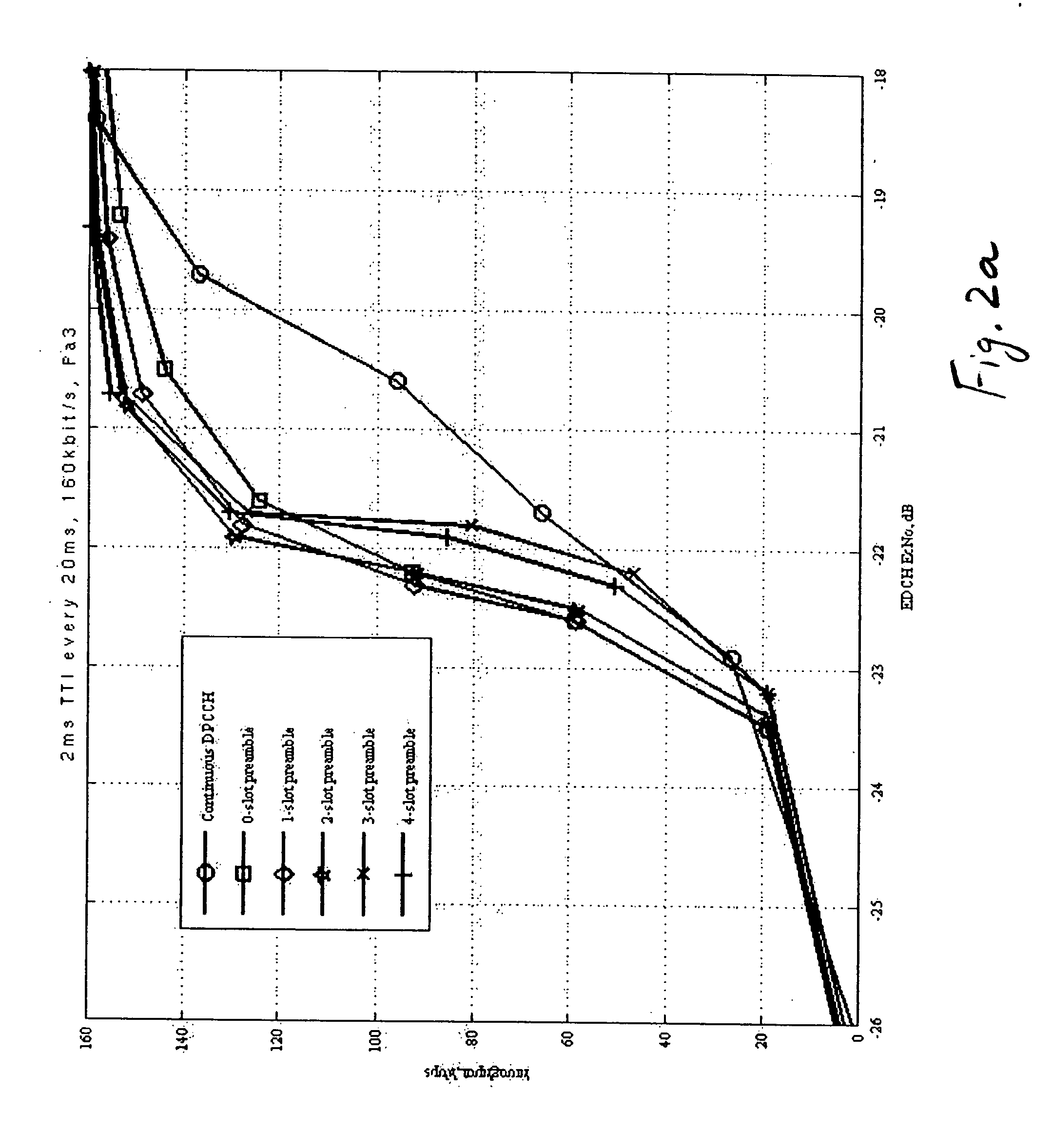
Adaptive preamble length for continuous connectivity transmission
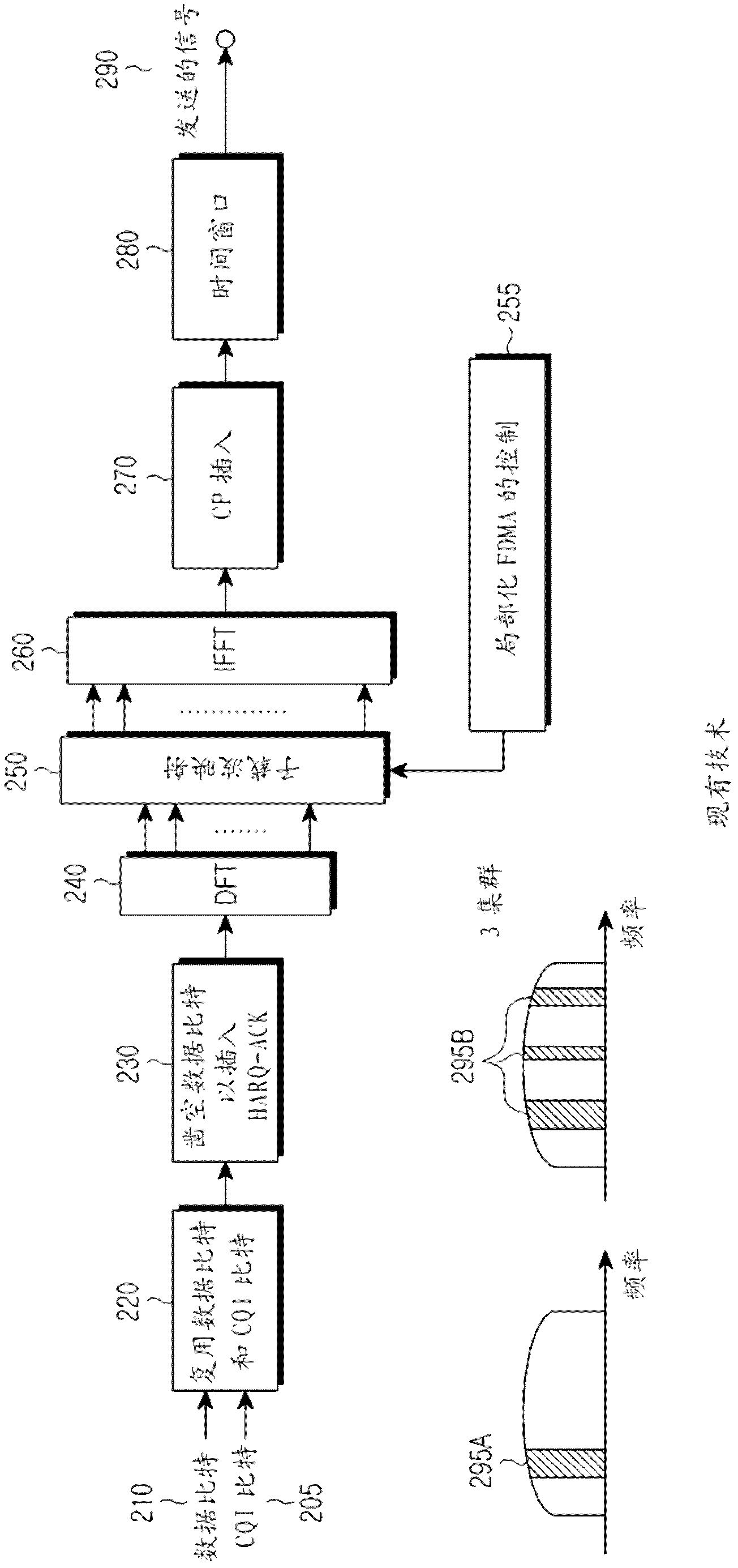
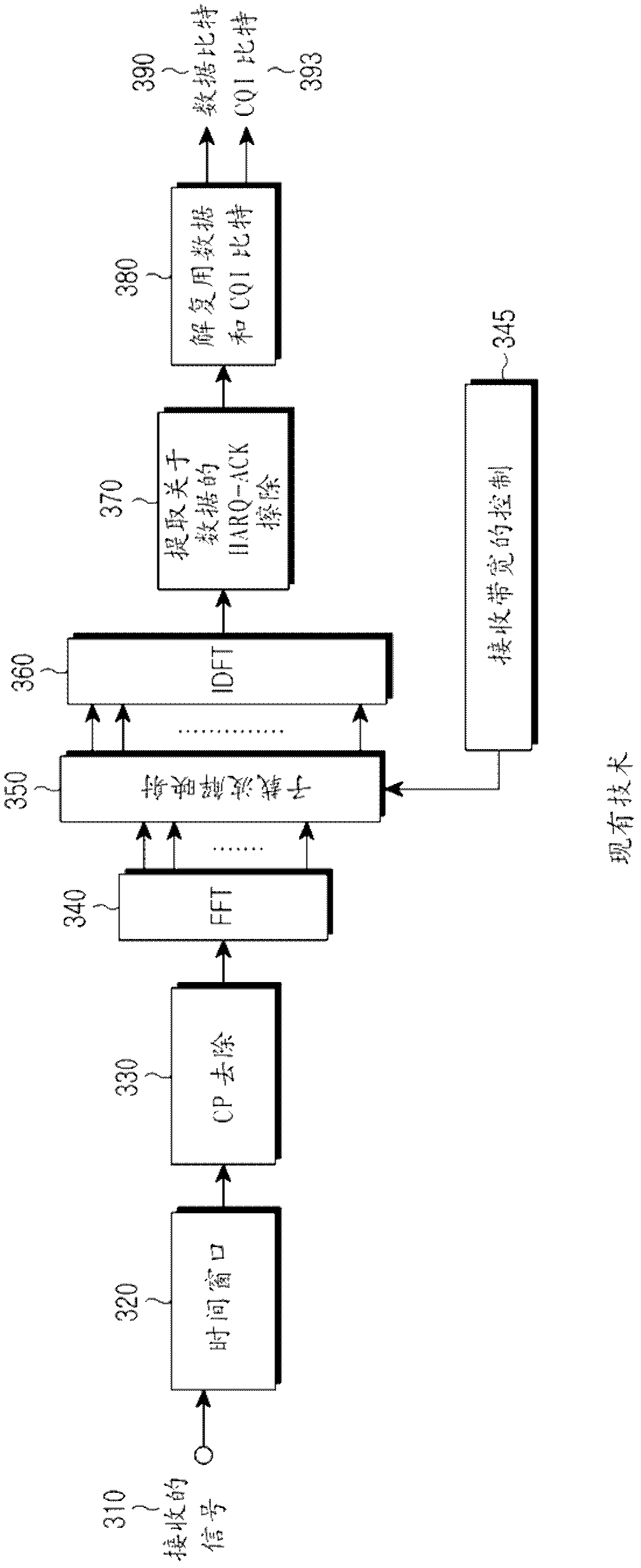
The specification and drawings present a new method, system, apparatus and software product for defining an adaptive preamble length of a preamble for a continuous connectivity transmission using a control channel, e.g., a UL (uplink) dedicated physical control channel (DPCCH), for transmitting the preamble. Such a preamble would reduce the accuracy requirement for the initial power setting after a transmission gap and also help the channel estimation and the synchronization of a data channel, e.g., an enhanced dedicated channel (E-DCH). The preamble length can be optimized and defined using a predetermined criterion depending on: a) a degree of fading of a multipath channel which is used for transmitting data on the data channel and / or b) a throughput relative to a nominal throughput in the data channel.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
AUTOMATIC NoC TOPOLOGY GENERATION
ActiveUS20150036536A1Lower latencyImprove performanceData switching by path configurationDistributed computingTraffic volume
Example implementations described herein are directed to automatically determine an optimal NoC topology using heuristic based optimizations. First, an optimal orientation of ports of various hosts is determined based on the system traffic and connectivity specification. Second, the NoC routers to which the host's port are directly connected to are determined in the NoC layout. Third, an optimal set of routes are computed for the system traffic and the required routers and channels along the routes are allocated forming the full NoC topology. The three techniques can be applied in any combination to determine NoC topology, host port orientation, and router connectivity that reduces load on various NoC channels and improves latency, performance, and message transmission efficiency between the hosts.
Owner:INTEL CORP
Hybrid time division multiplexing and data transport
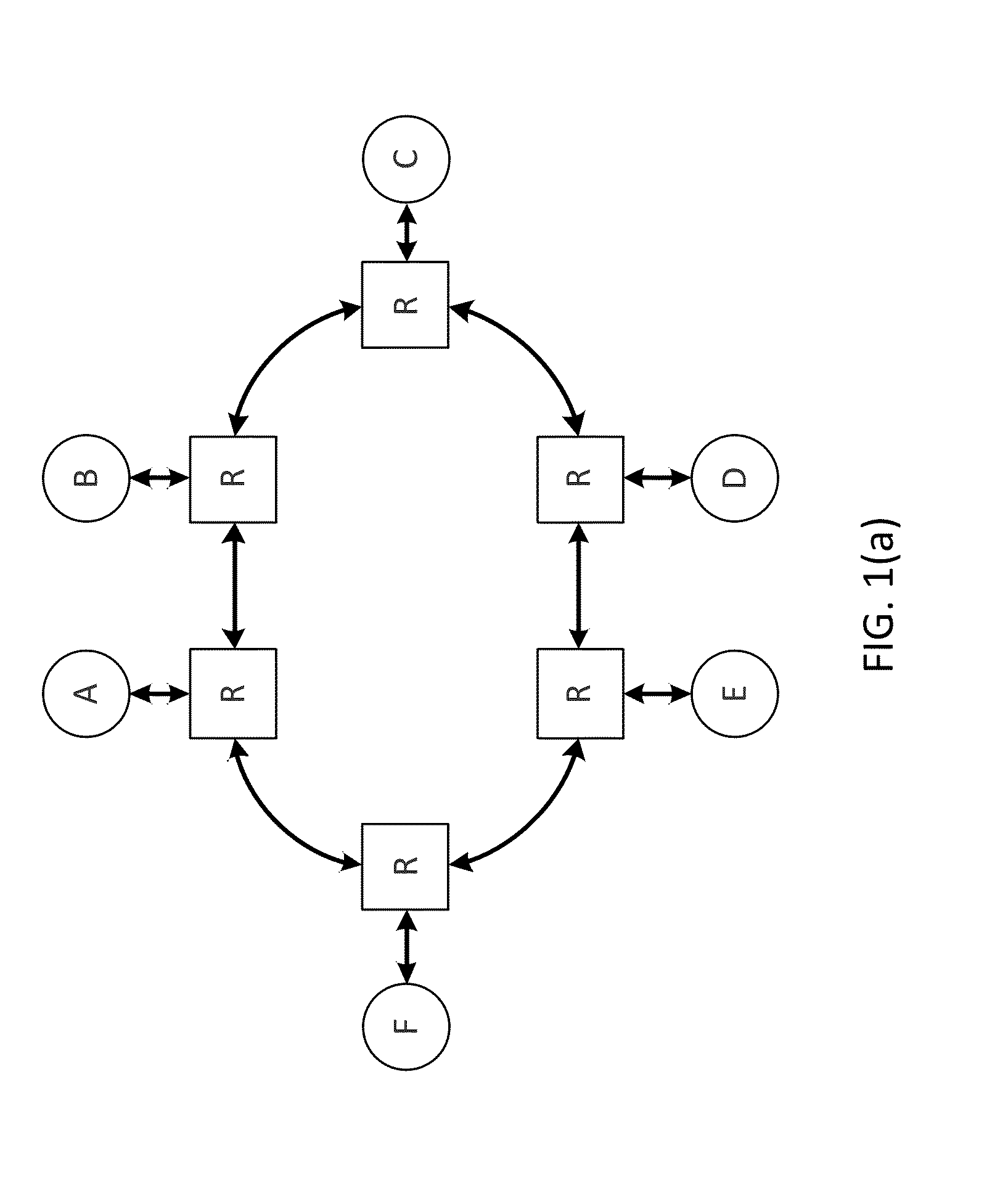
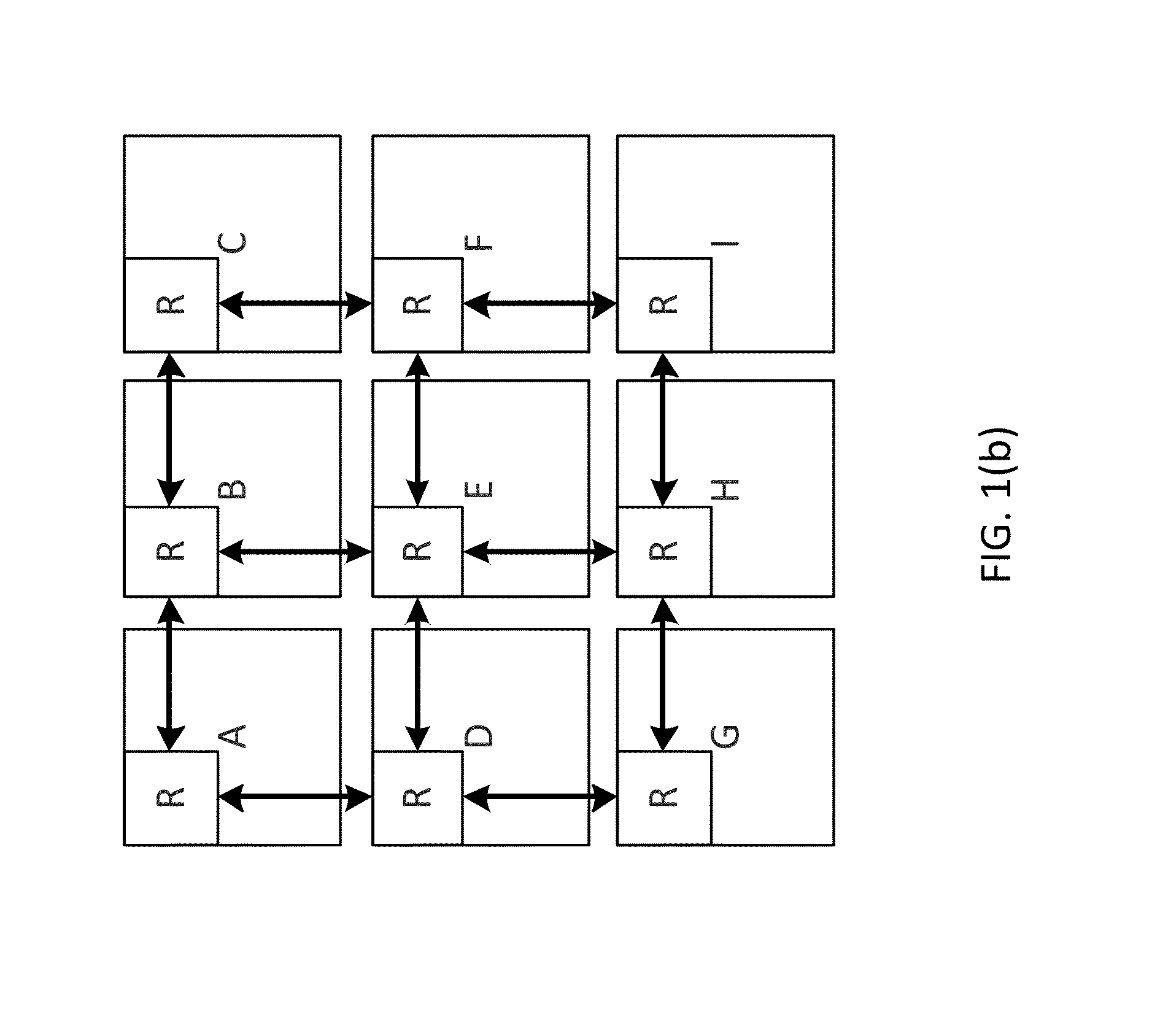
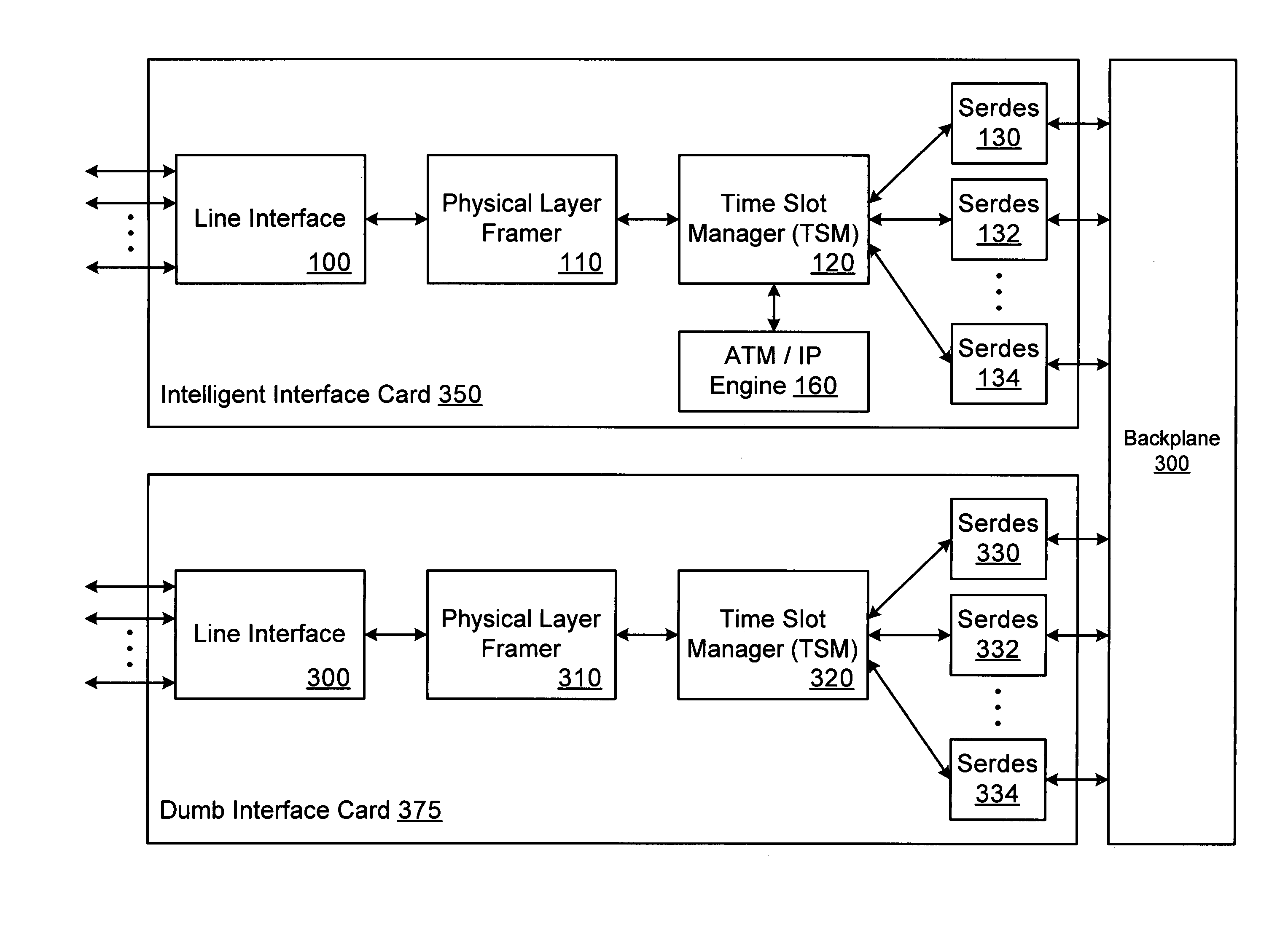
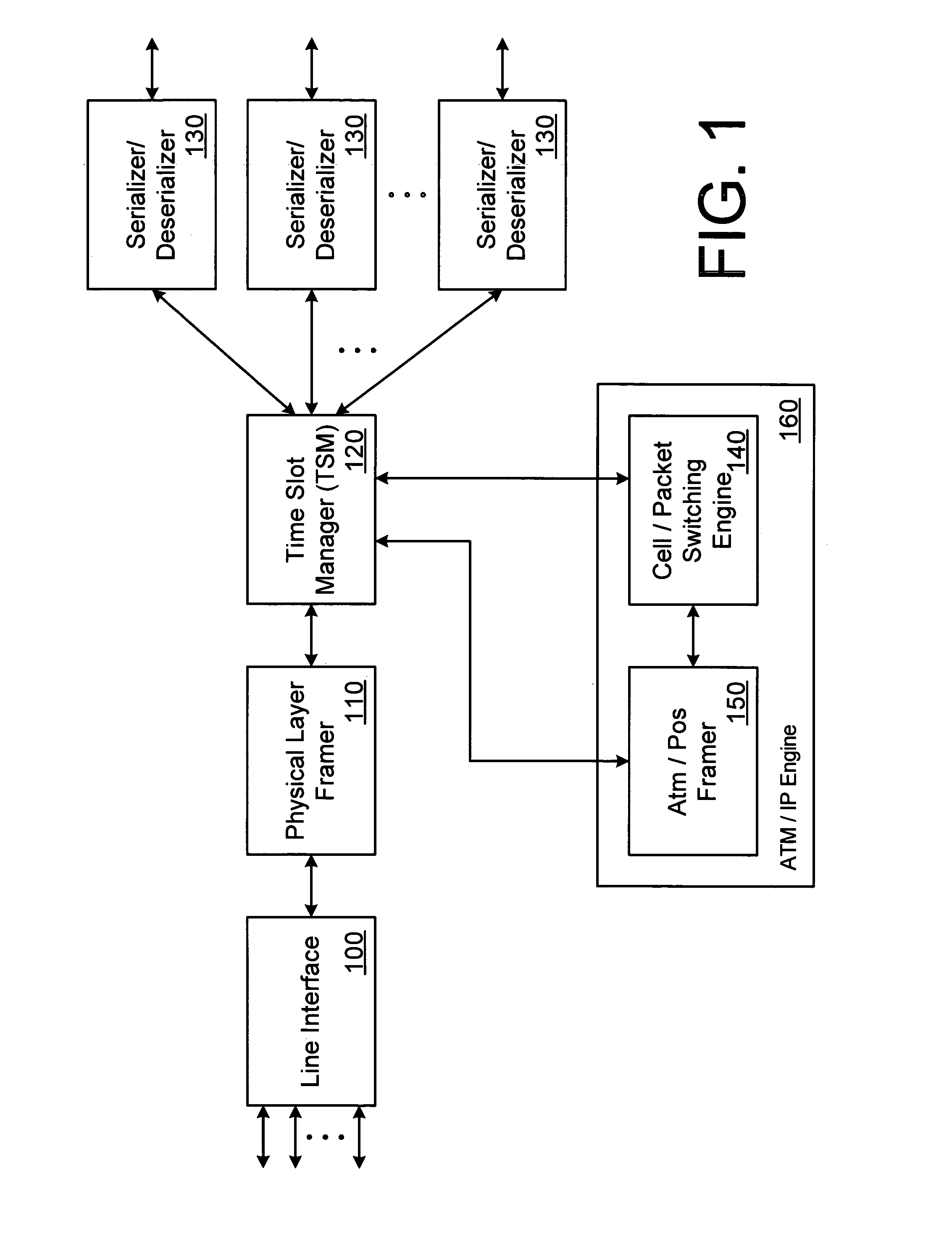
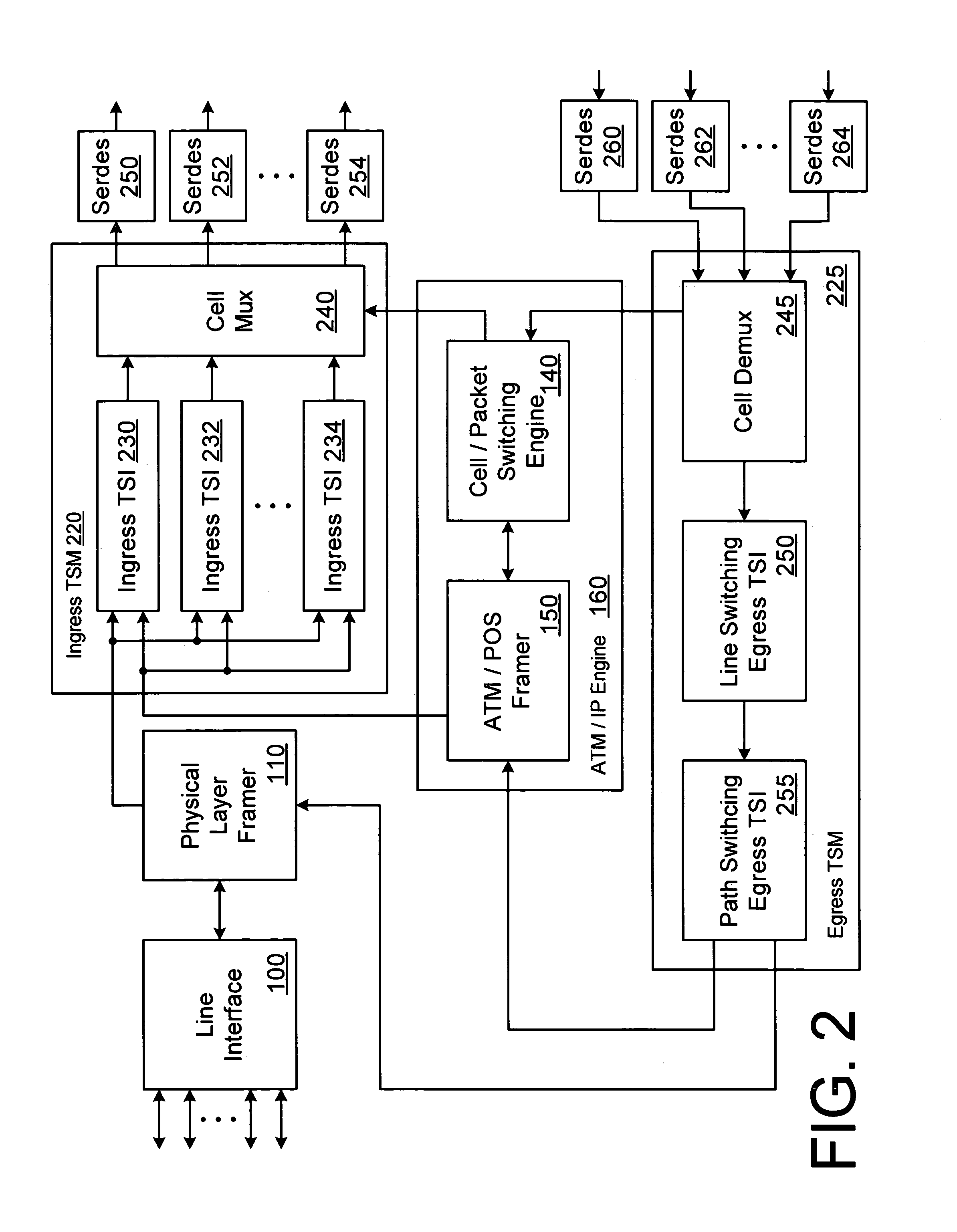
A network switch includes multiple interface cards and a backplane that interconnects the interface cards. The interface cards receive network traffic and perform time and line switching on the data. The network traffic can include a combination of time division multiplexed (TDM) data and network data (e.g., ATM cells, IP packets). In one embodiment, the channels that carry network traffic to the interface cards are pre-configured as either TDM channels or network channels. The channels are processed as appropriate for their respective types by the interface cards. Because both TDM and network traffic can be processed by a single interface card, the number of cards within the network switch can be reduced.
Owner:FORCE10
Method and system for pushing data actively by server
InactiveCN102035893AReduce occupancyReduce performance consumptionTransmissionSpecial data processing applicationsReal-time dataD channel
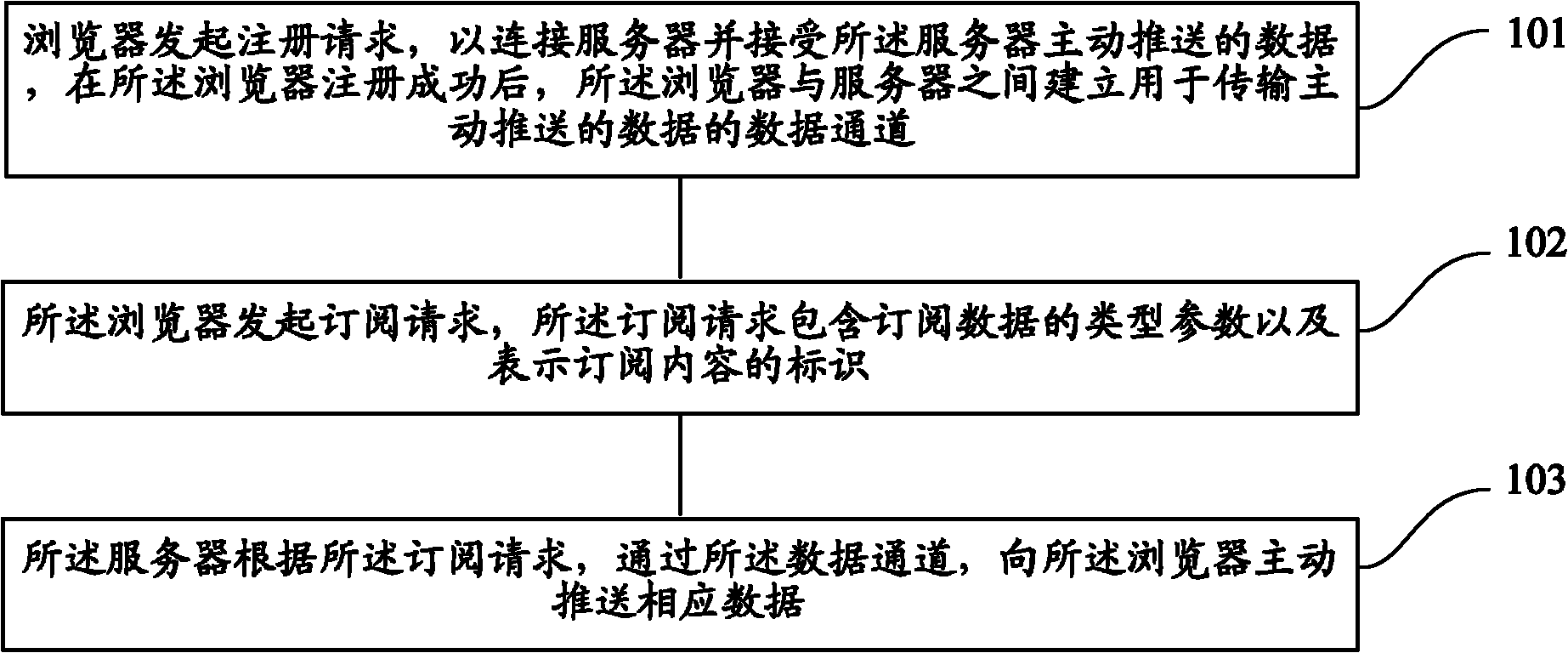
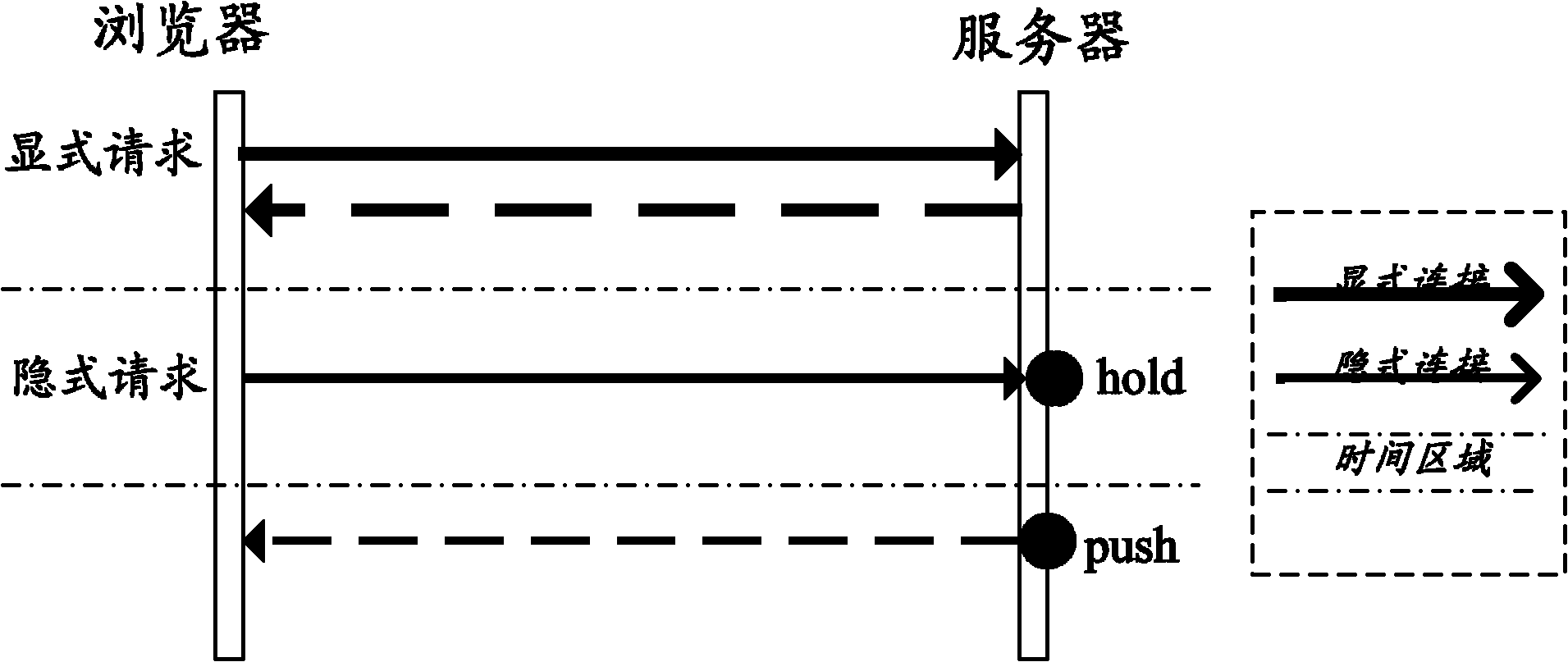
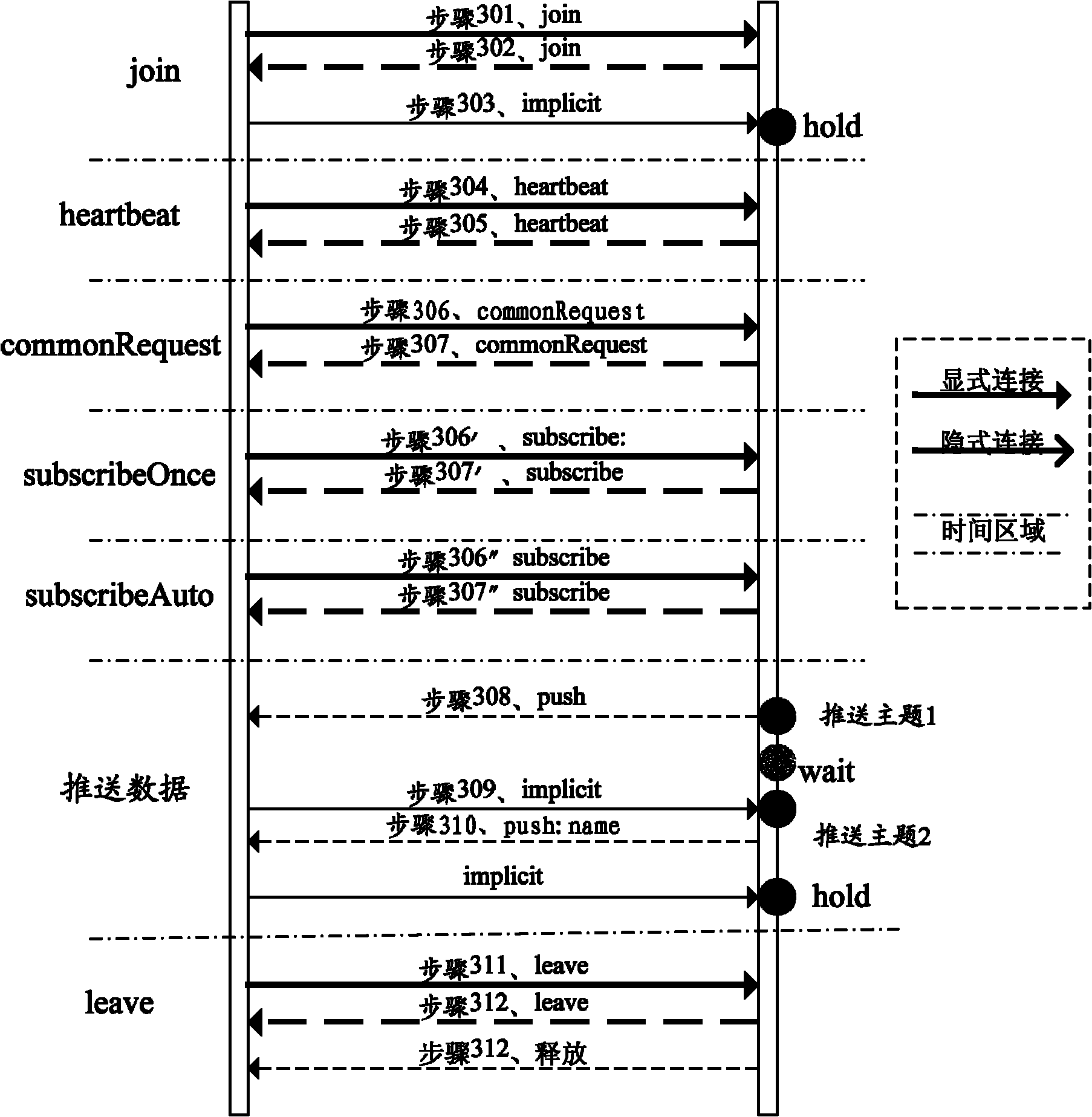
The invention discloses a method and a system for pushing data actively by a server. The method comprises the following steps that: a browser initiates a registering request to be connected the server and receive the data pushed by the server actively, and after the browser is registered successfully, a data channel for transmitting the data pushed actively is established between the browser and the server; the browser initiates a subscription request, wherein the subscription request contains type parameters of subscription data and identifiers for expressing subscription contents; and the server pushes the corresponding data to the browser actively by the data channel according to the subscription request. By the method and the system, the requirement of real-time data pushing of the browser can be met, the concurrency of an application system can be improved, and the performance consumption of the server can be reduced.
Owner:AGRICULTURAL BANK OF CHINA
Method and system for noise dosimeter with quick-check mode and earphone adapter
ActiveUS20070186656A1Rapidly predict noise exposureLow signalVibration measurement in solidsAnalysing solids using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesSound sourcesDisplay device
A noise dosimeter with capability to rapidly predict noise exposure over an extended time period based on a measurement of short duration. Either an acoustic or an electrical earphone adapter provides a convenient means to connect the noise dosimeter to an external sound source. A direct input jack operable to receive at least one audio signal provides a signal to an RMS detector, which provides a DC signal to a two-stage amplifier circuit. The outputs of the amplifiers are provided to a processor having multiple A / D channels. The processor calculates accumulated noise doses and drives a display, which in one embodiment includes a panel of light-emitting diodes. In one embodiment, the dosimeter includes functionality for control of external devices such as sound boards.
Owner:ETYMOTIC RES
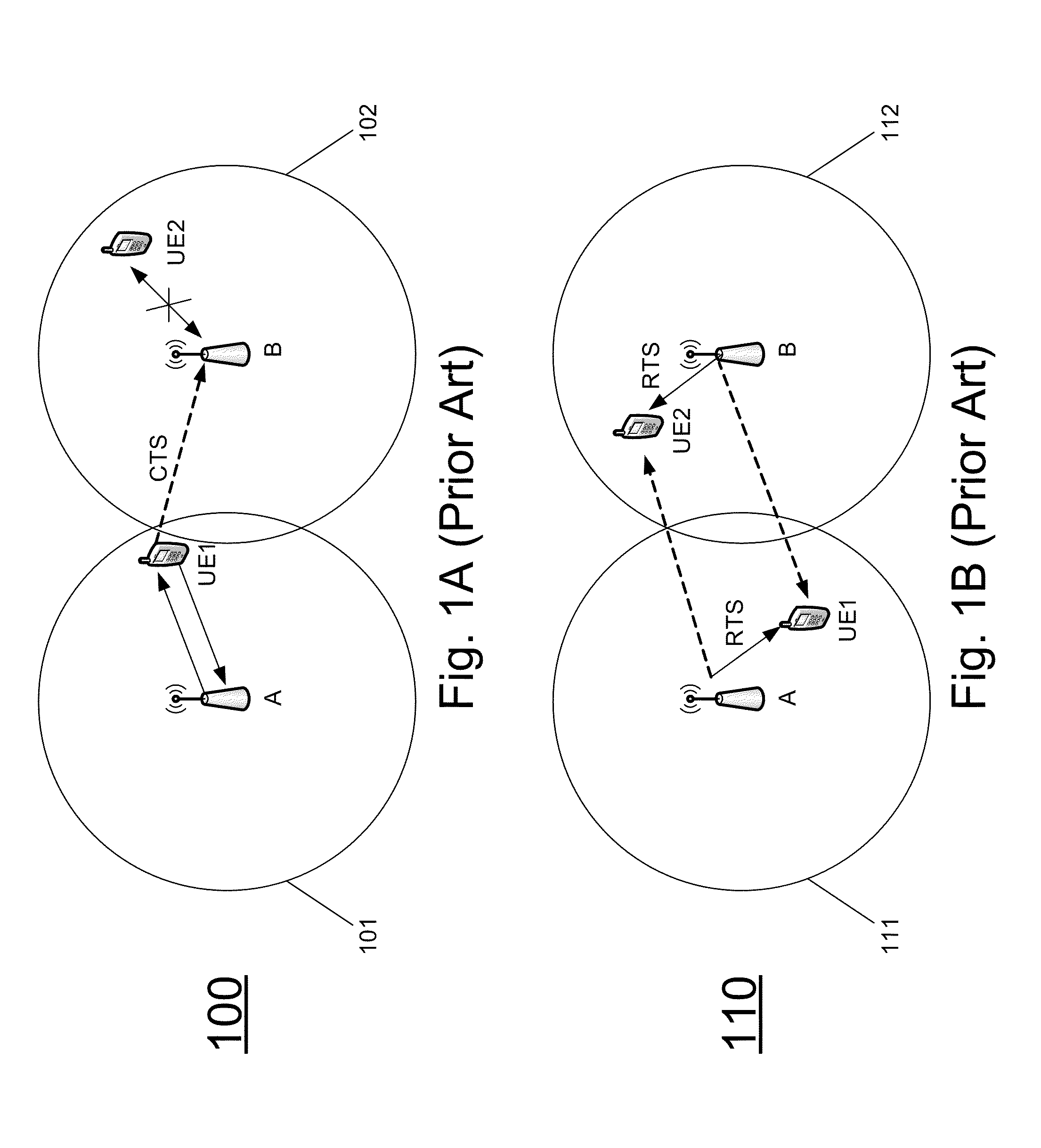
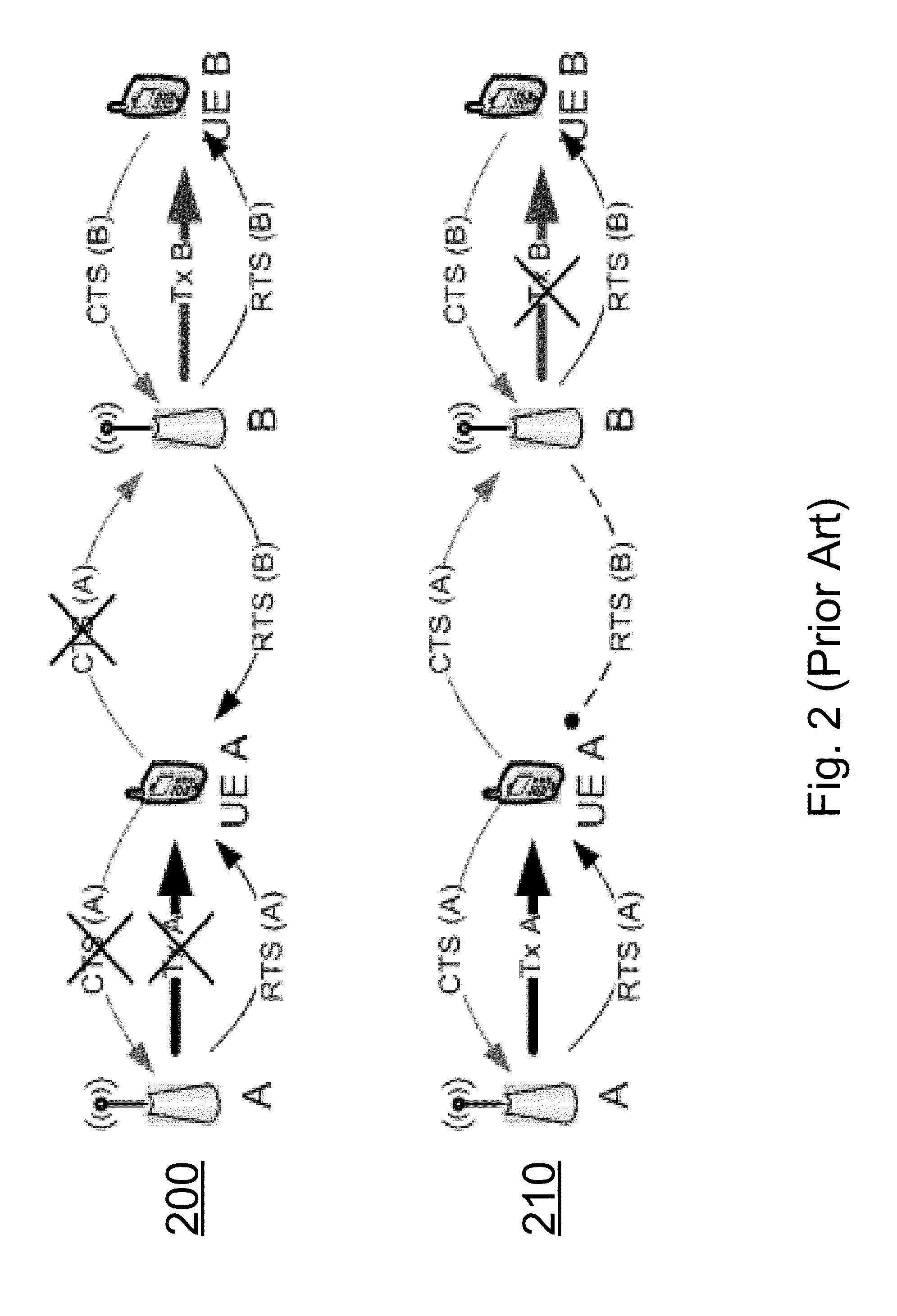
Protocol with improved spatial reuse
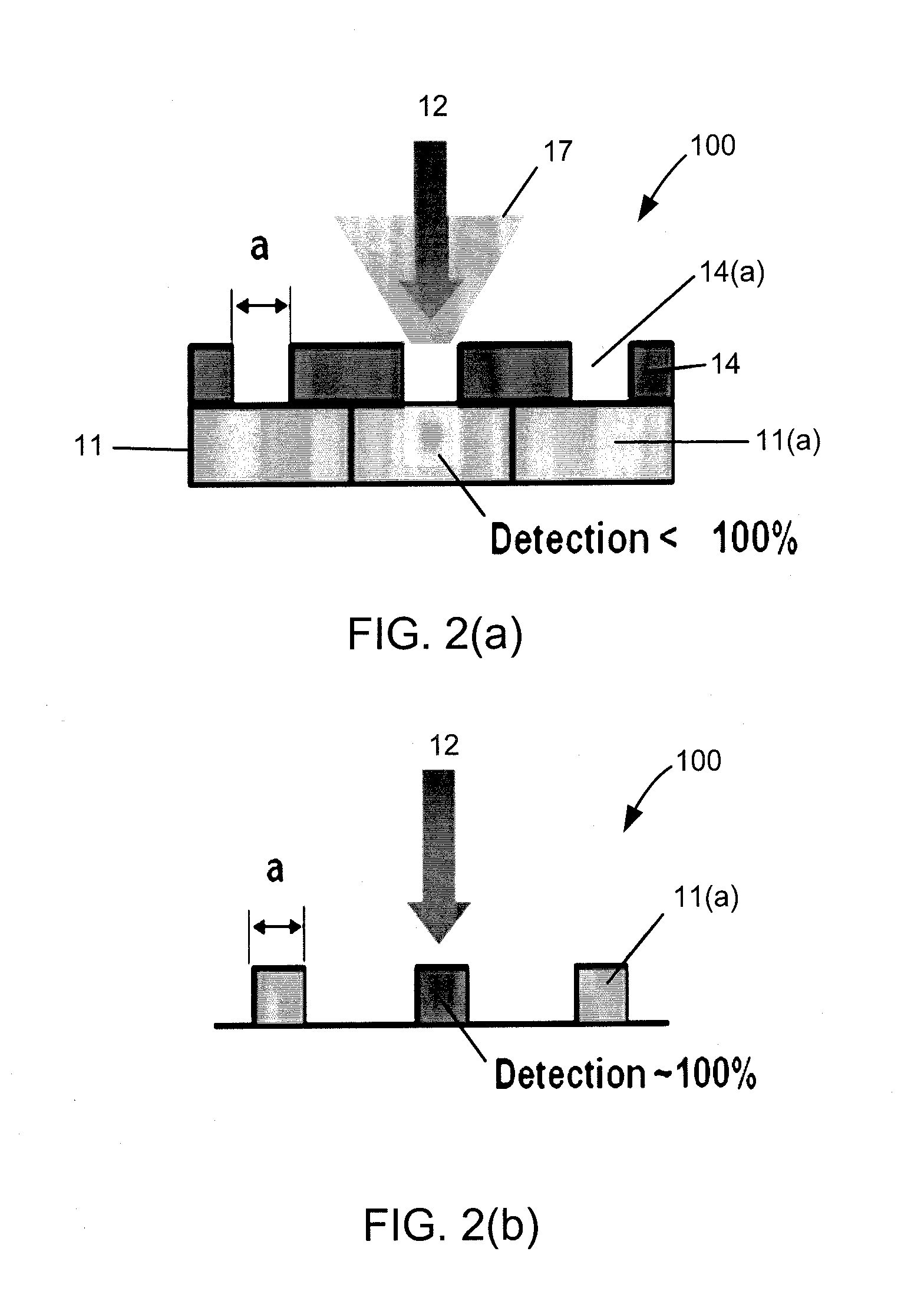
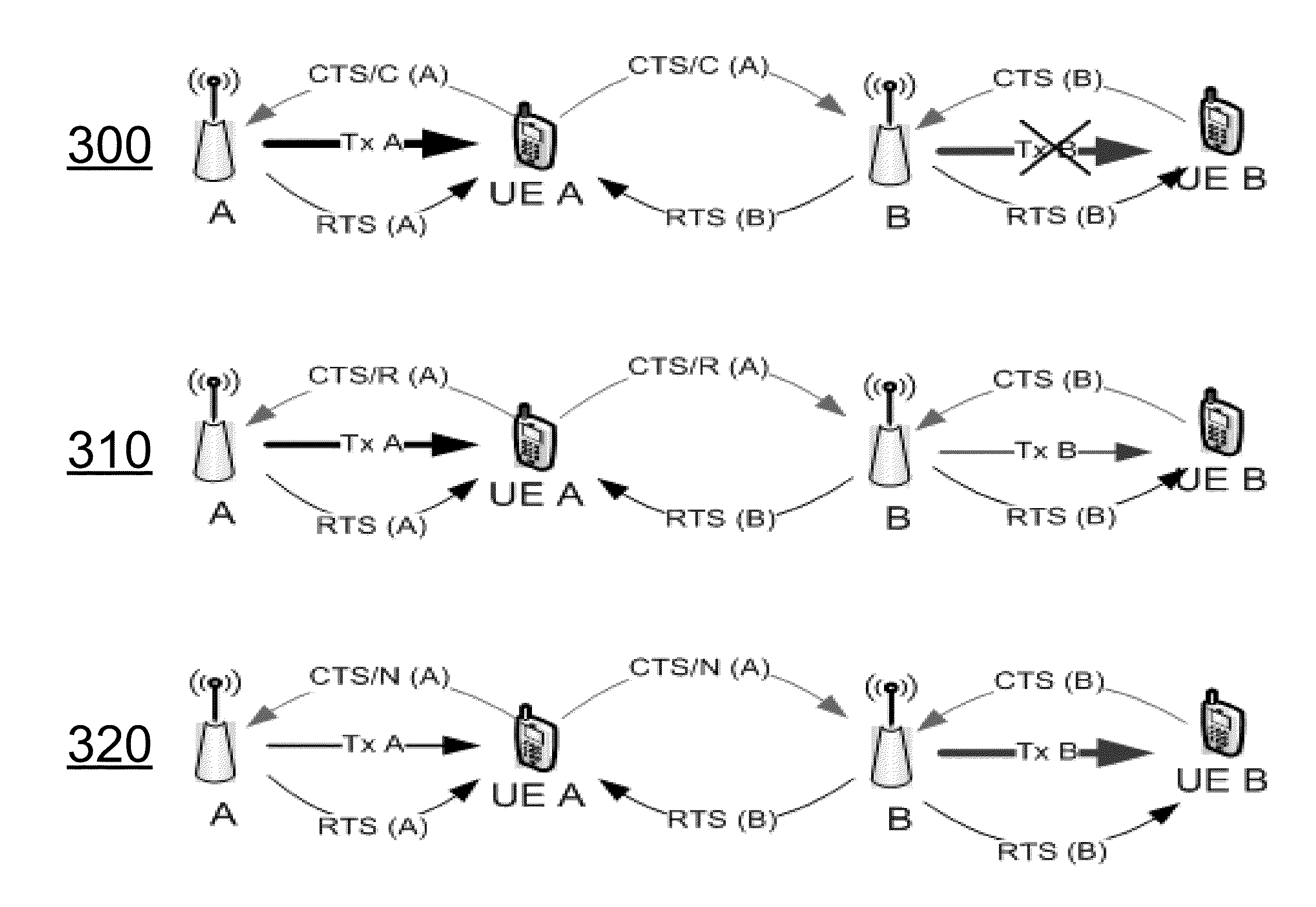
According to an embodiment, a method, apparatus, and computer readable medium can provide an efficient mechanism to improve data rates of nodes suffering high interference without sacrificing performance of nodes that do not need interference-free channels to communicate. A node can receive two or more RTS packets and identify the RTS packet corresponding to its own cell, as well as RTS packets belonging to interferers. Based on the interference level estimated from the RTS packets, the node can decide if the channel needs to be interference-free for the intended transmission or if the current level of interference is acceptable. According to the embodiment, there can be two or more different types of CTS packets. A node can decide which type of CTS packet to transmit based on the information, signal level, interference level, or a combination therein, of at least two RTS channels, and based on measurements performed on these RTS channels, or other channels.
Owner:NOKIA TECHNOLOGLES OY
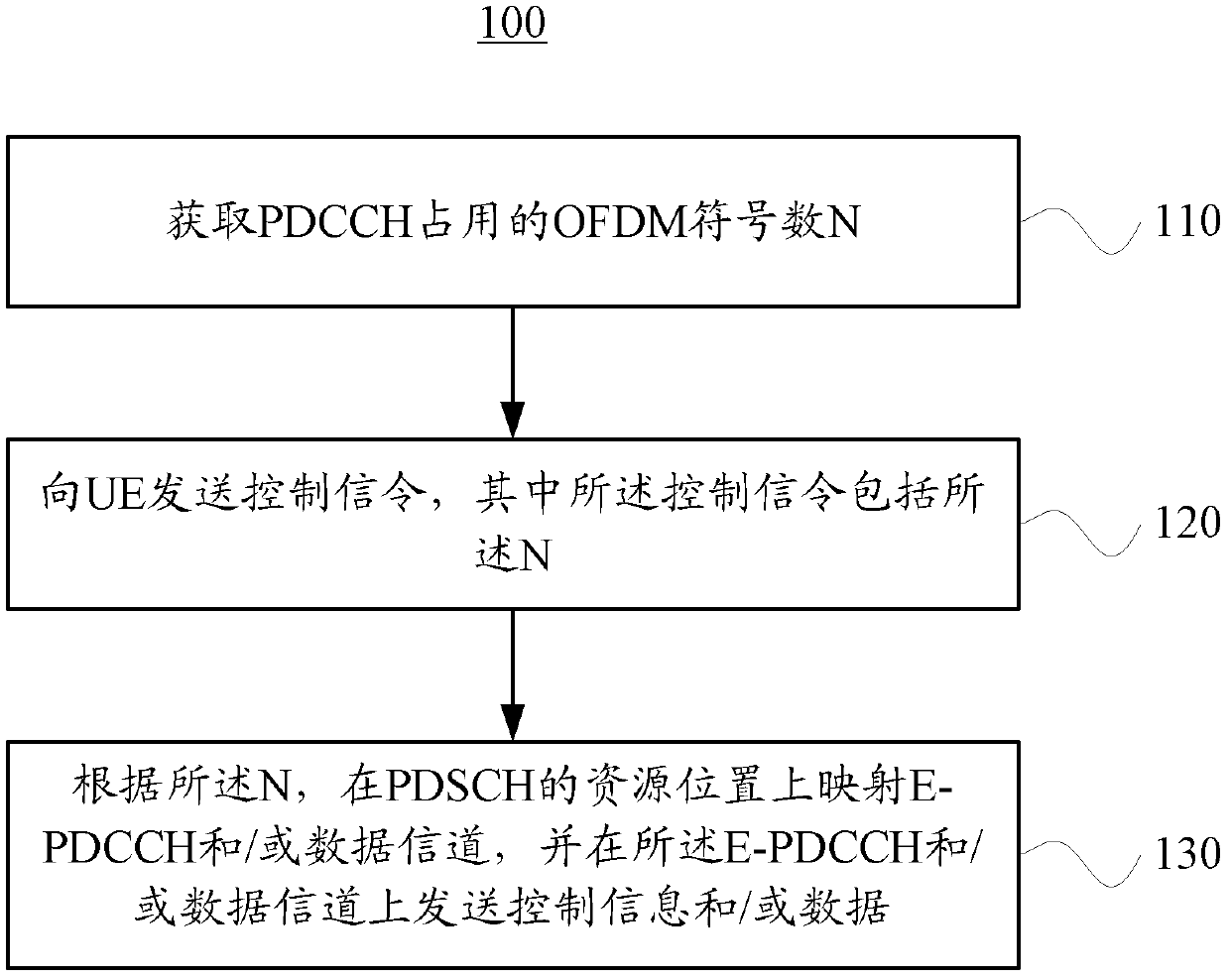
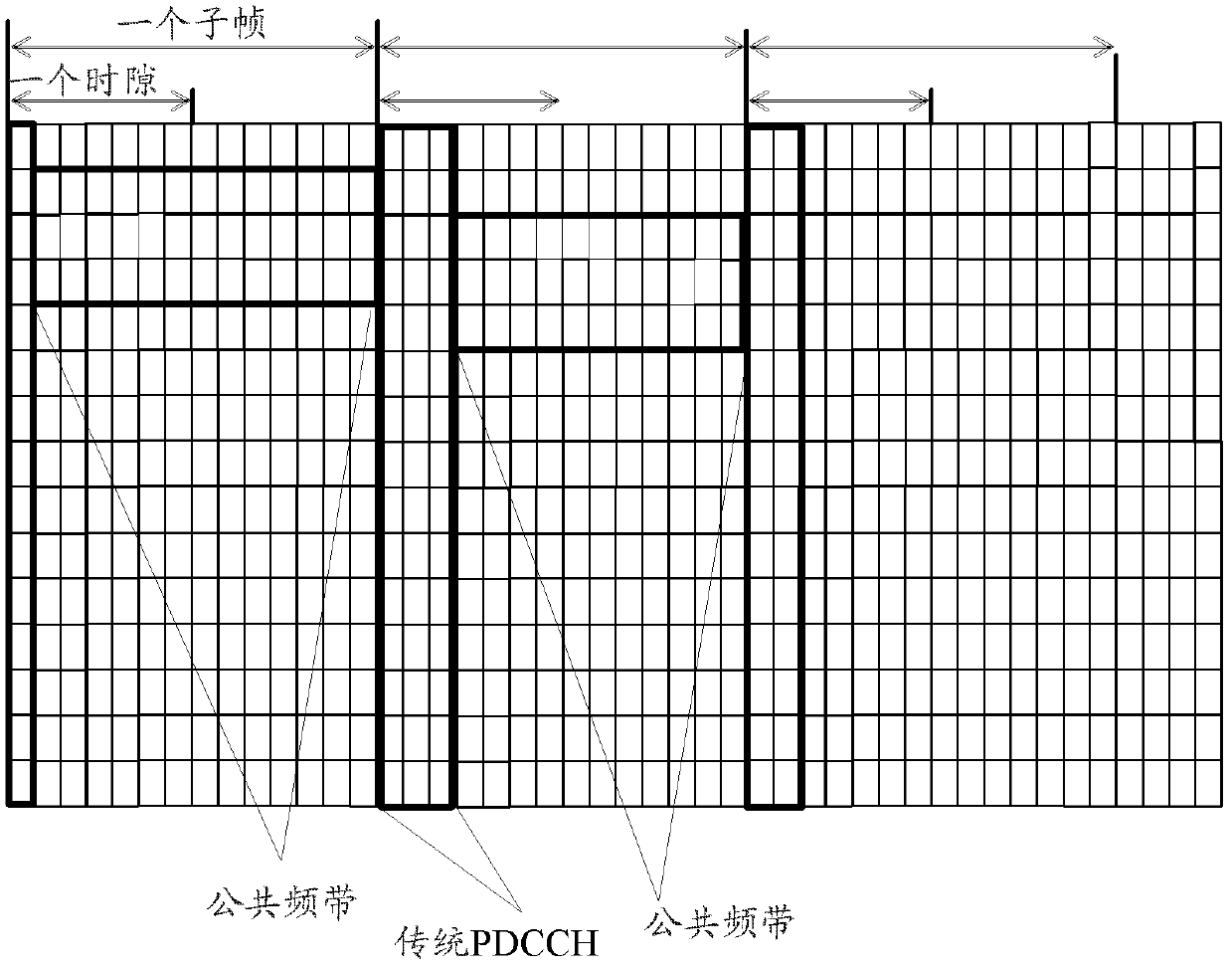
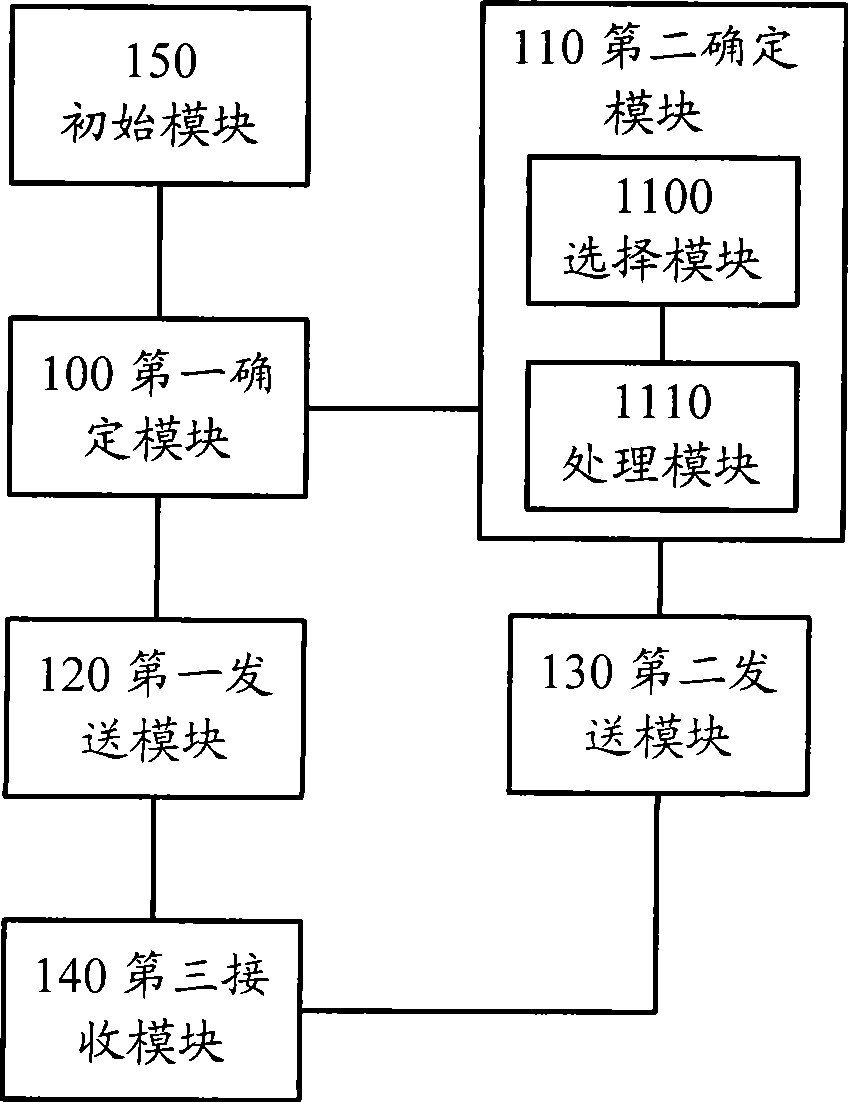
Data transmission method, base station and user equipment
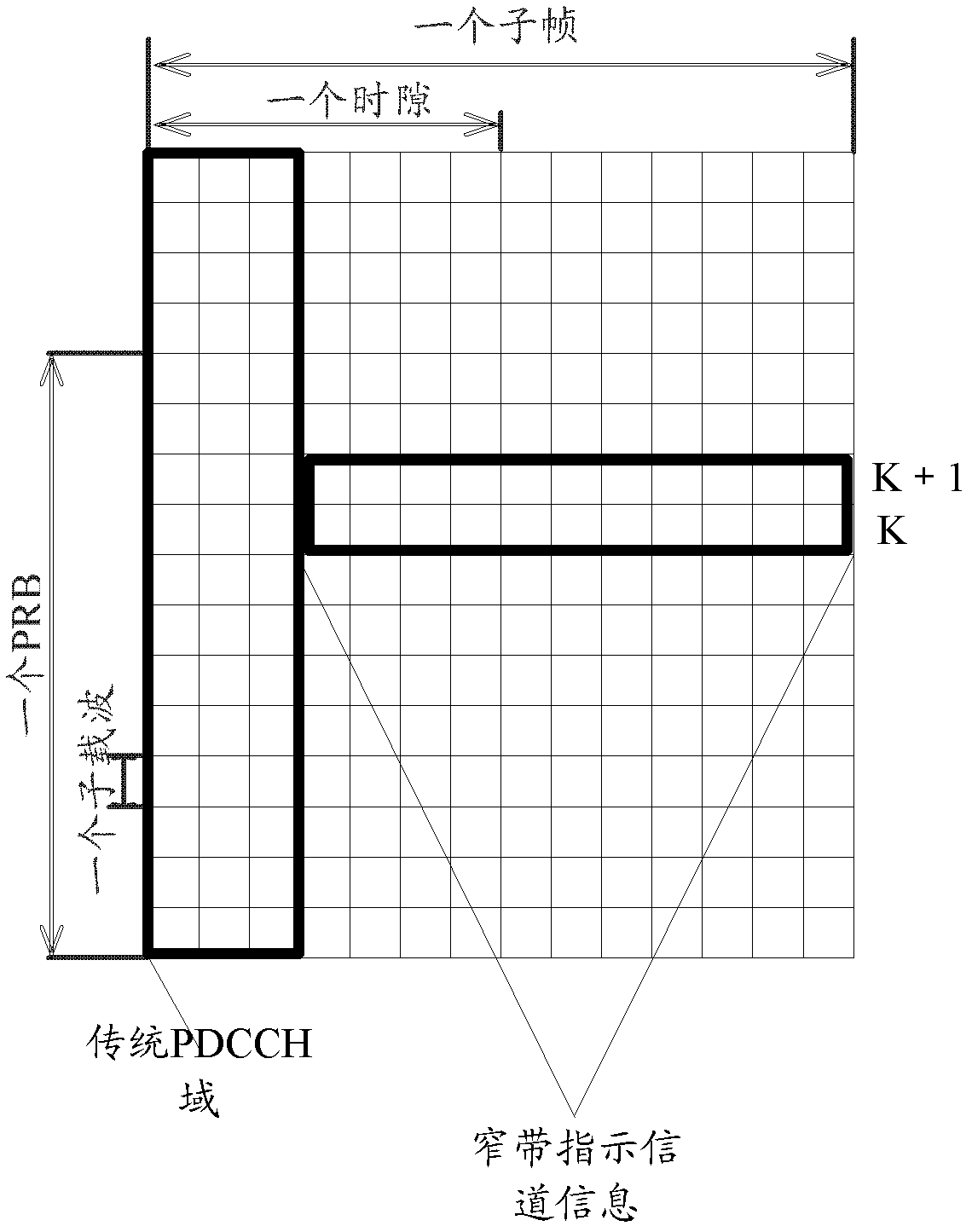
The embodiment of the invention provides a data transmission method which comprises the following steps: obtaining a symbolic number N of orthogonal frequency division multiplexing OFDM occupied by a physical downlink control channel domain; sending a control signaling to the user equipment UE, wherein the control signaling comprises N; and according to the N, mapping an expanded control channel and / or a data channel in a resource position of a physical downlink shared channel PDSCH and sending control information and / or data on the expanded control channel and / or data channel. According to the embodiment of the invention, the UE can obtain the symbolic number N of OFDM occupied by a conventional control channel domain and expands a time frequency domain resource mapping mode of the control channel in the data channel, so that the utilization ratio of the time frequency resources is improved.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
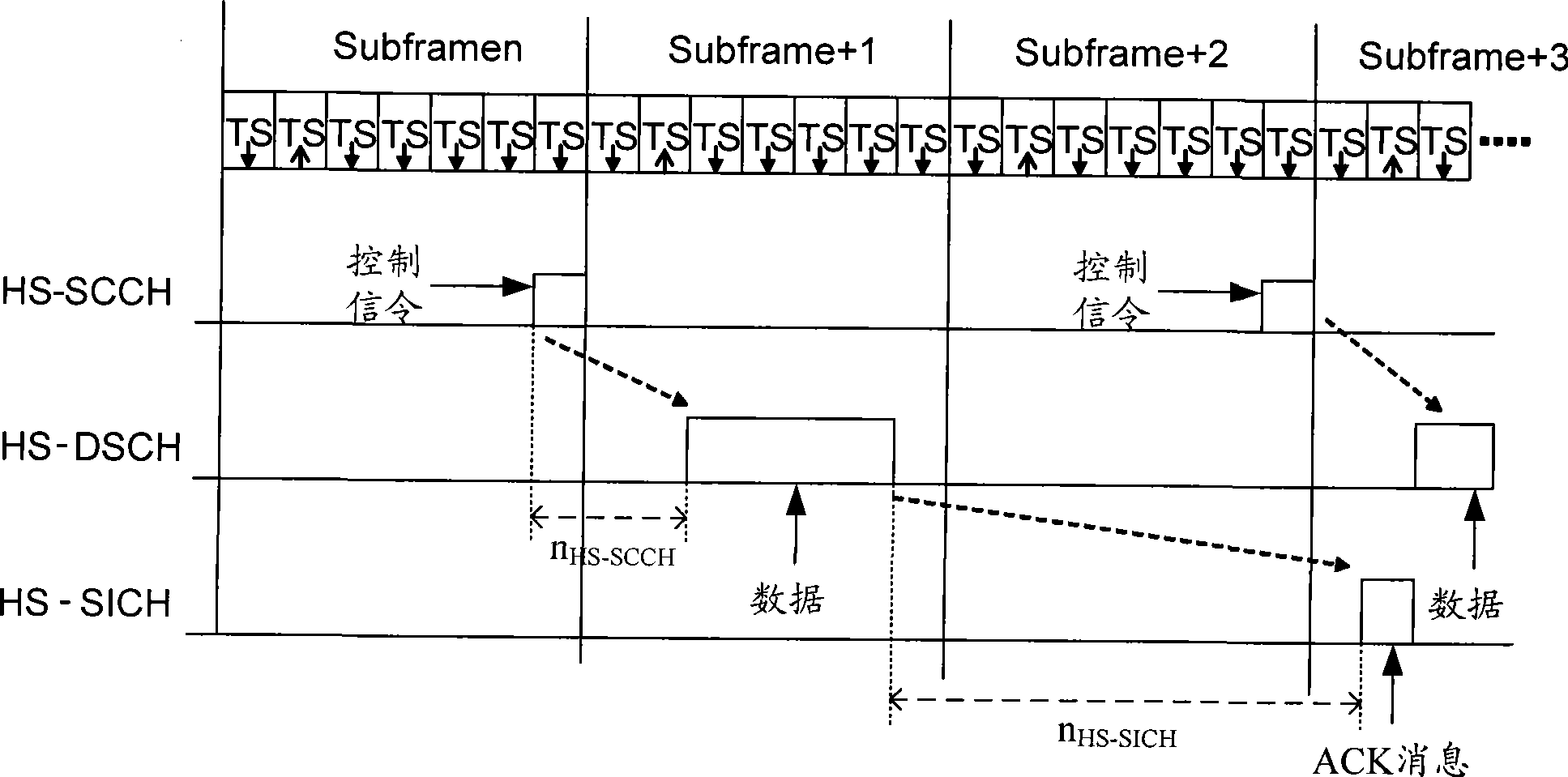
Method, system and apparatus for retransmitting data on high speed shared data channel
ActiveCN101500259AReduce in quantityImprove reliabilityError prevention/detection by using return channelNetwork traffic/resource managementControl signalData transmission
The embodiment of the invention discloses a method for retransmitting data on a high-speed shared data channel, and a system and a device thereof, solving the problem that when the prior art is utilized for carrying out HSDPA operation, an HS-SCCH is needed for transmitting a control signaling at every time when retransmitting data, thus leading the proportion of occupied resources of the control signaling in data transmission to be overlarge and resulting in low utilization rate of wireless resources. The method comprises the steps as follows: a base station determines moments for retransmitting data according to set data transmission interval time and number of times of data retransmission; moments for retransmitting the control signaling are determined according to set signaling and data transmission interval time as well as the number of times of signaling retransmission, wherein the number of times of signaling retransmission is smaller than that of data retransmission; the control signaling containing the information of the number of times of data retransmission is transmitted by the HS-SCCH according to the determined moments for retransmitting the control signaling; and the data is transmitted by an HS-DSCH according to the determined moments for transmitting the data.
Owner:DATANG MOBILE COMM EQUIP CO LTD
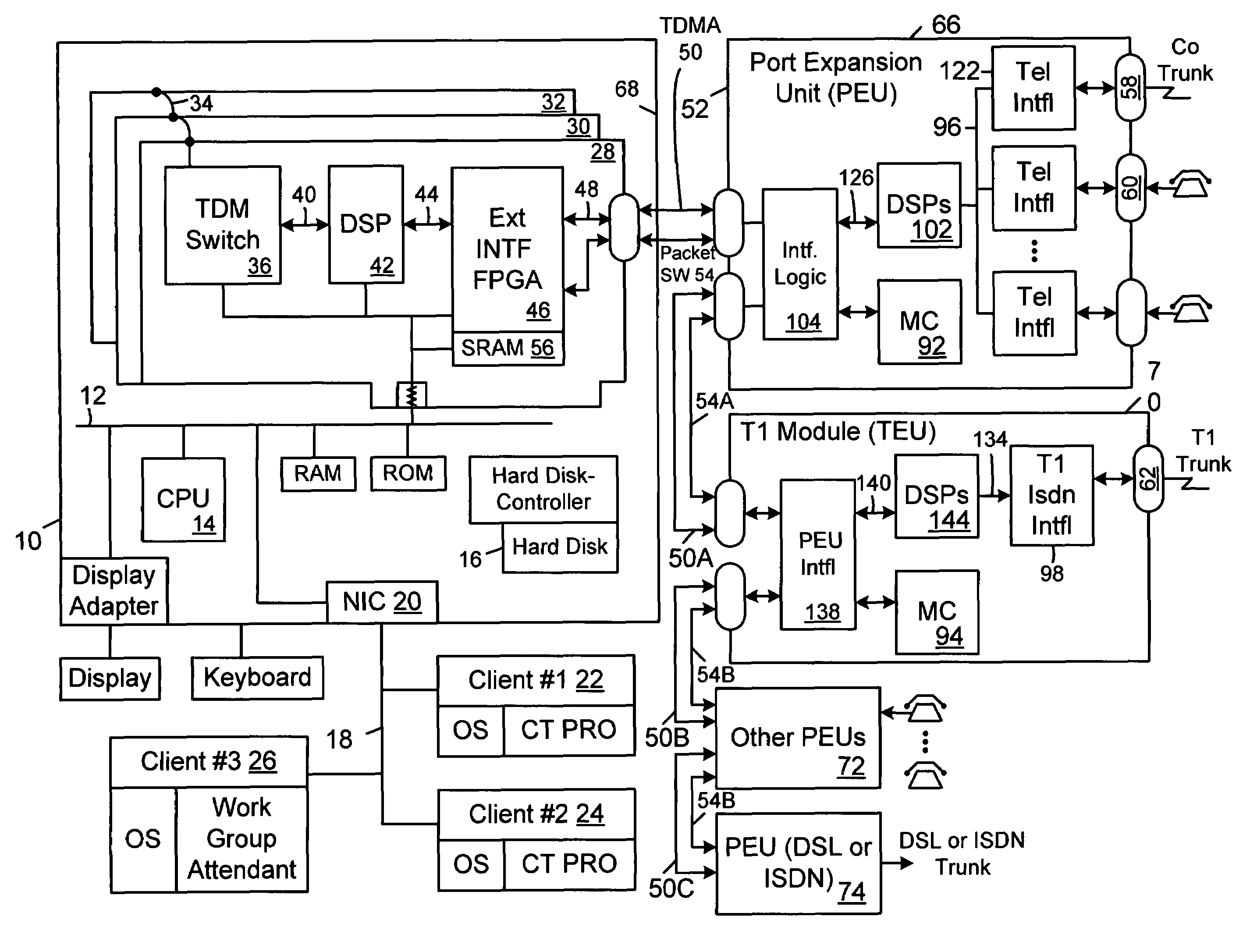
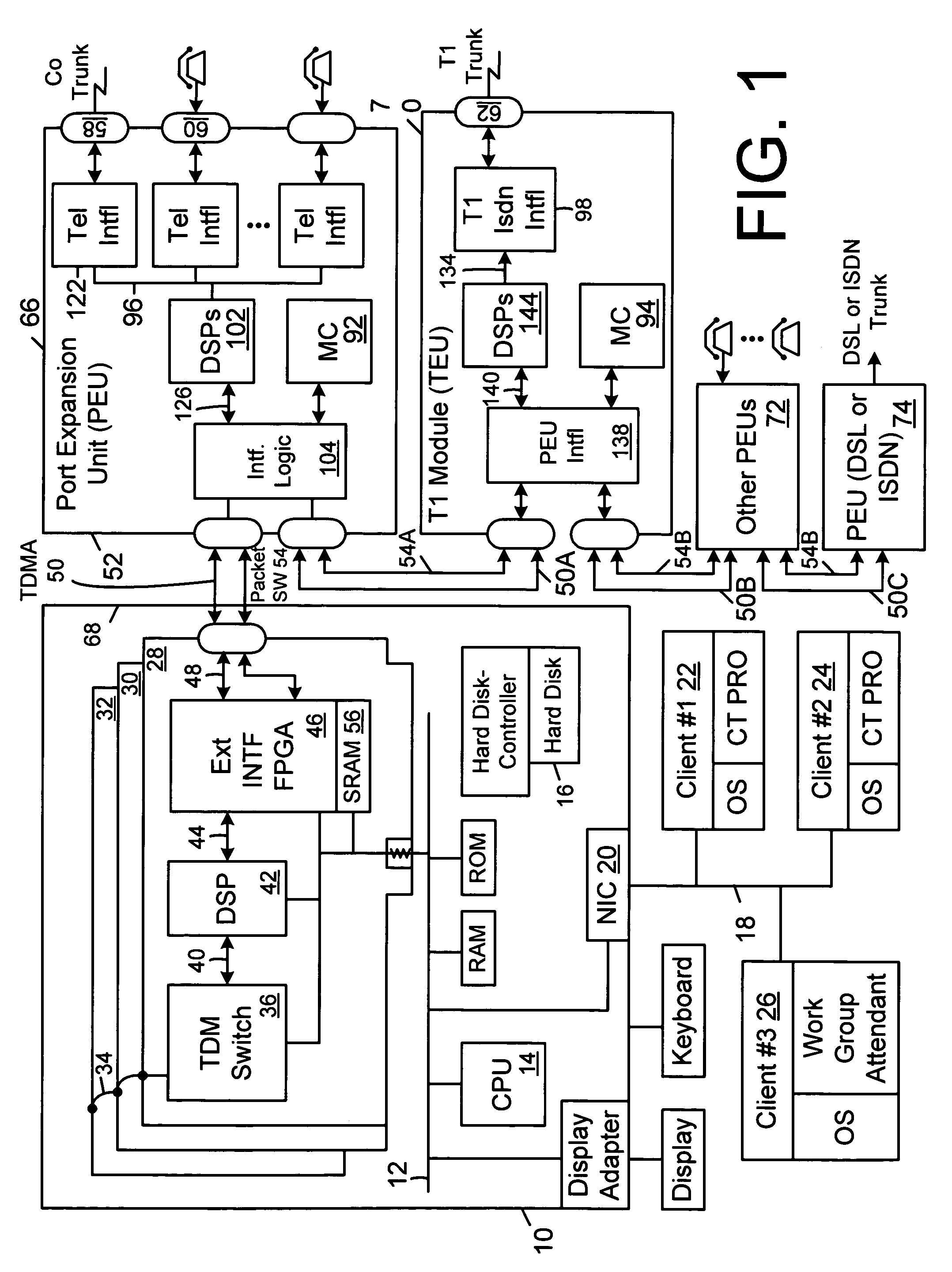
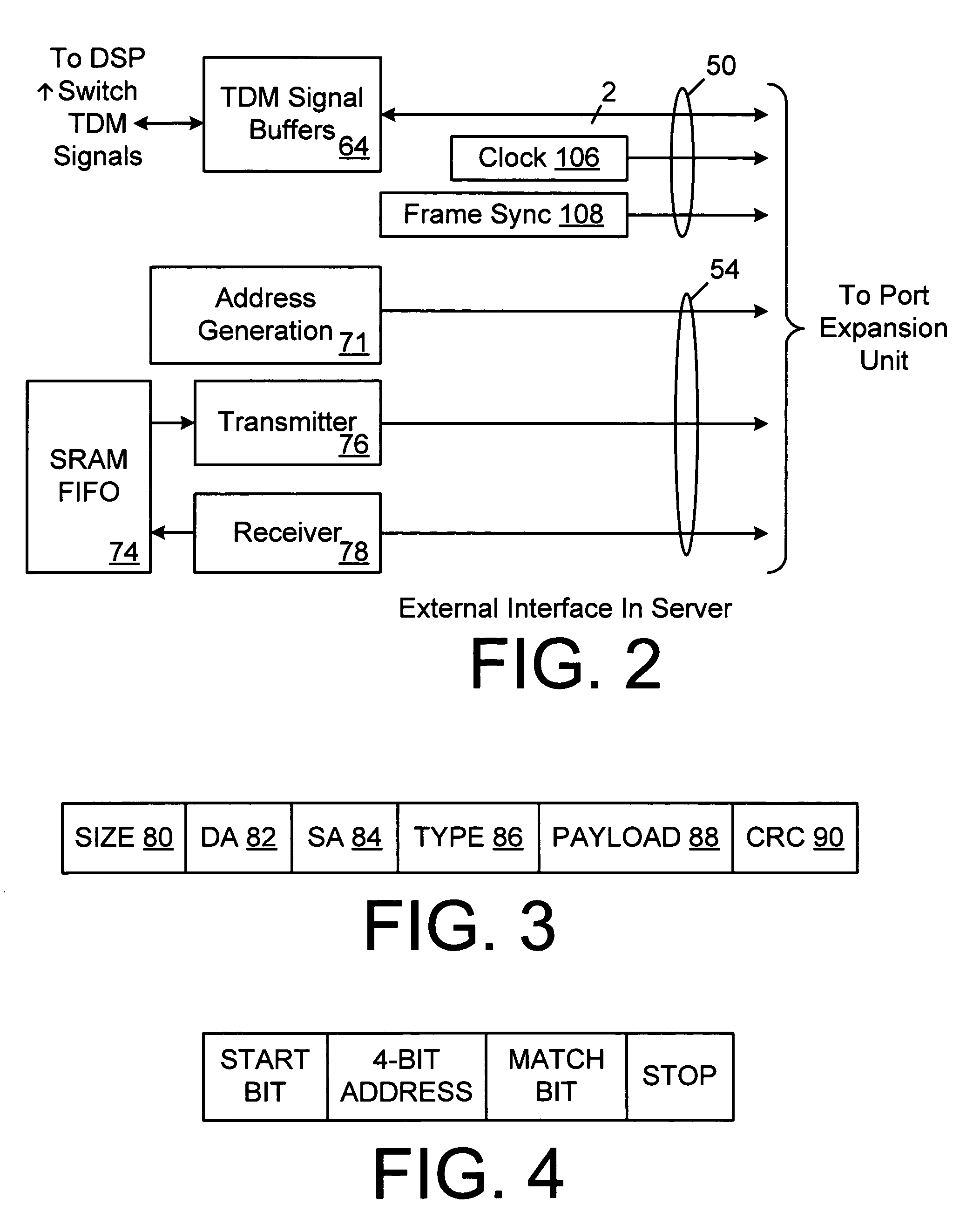
PBX with configurable analog CO line and T1 signalling protocols using packet bus and software switched WAV channels
InactiveUS7023867B1Digital signal processing capabilityImpact on capacityMultiplex system selection arrangementsSpecial service for subscribersMicrocontrollerClient machine
A PBX system using an unmodified personal computer as the host server and using expansion slots to couple one or more switch cards to the system bus, and, optionally including a network interface card to couple the PBX system to other client computers running telephony enabled applications to control the PBX via a local area network. The switch card(s) are each coupled to a chain of one or more port expansion units that do not consume expansion slots. Each PEU contains a DSP and a microcontroller, an FPGA and port interface circuitry to interface to POTS CO lines, extension telephone lines, T1 lines or PRI lines. The personal computer is programmed with a PBX process that controls operations of the overall system and may also be programmed with conventional voice mail applications or integrated voice response and other applications to implement various telephony functions such as recording voice mail or prompt callers to input DTMF tones indicating what they want to do. Each chain of PEUs is coupled to the switch card and the PBX process by a TDMA bus and a packet switched bus. Distributed processing by the DSPs and microcontrollers in the PEUs to do tone generation, tone recognition, and a host of other functions offloads much of the work from the host. The packet switched bus enables easy handling of packetized data in IP packets or other packetized data.
Owner:INTEL CORP
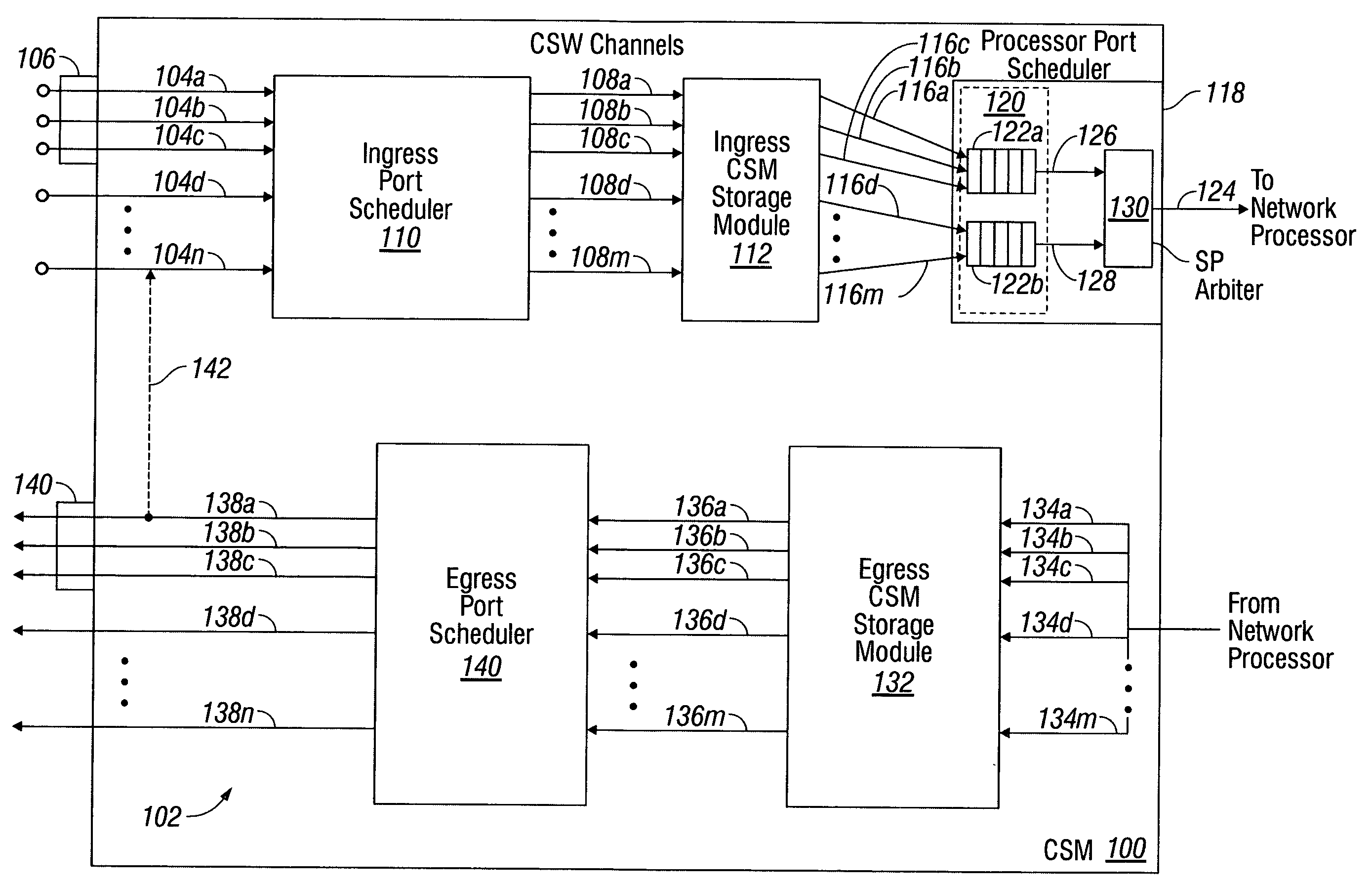
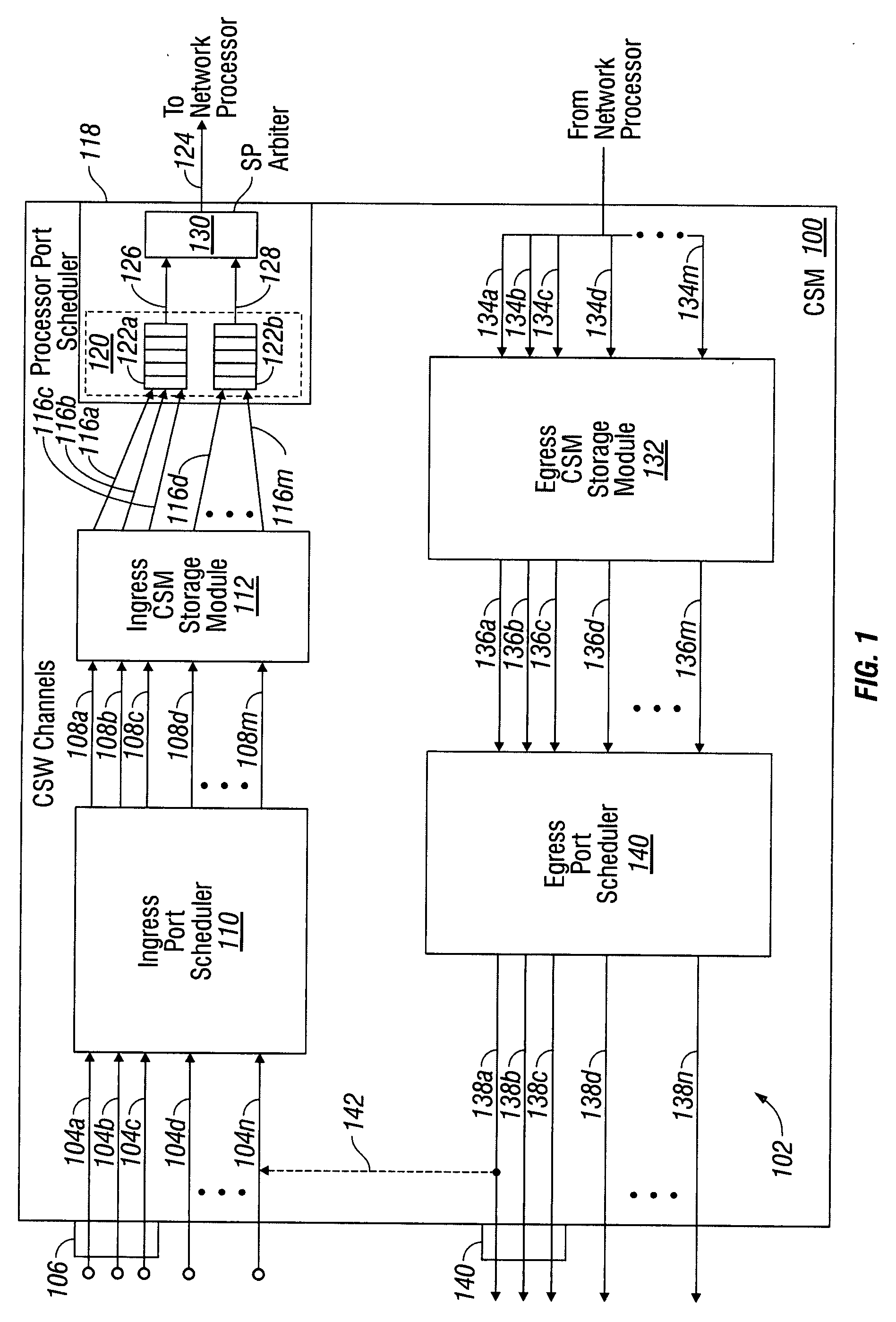
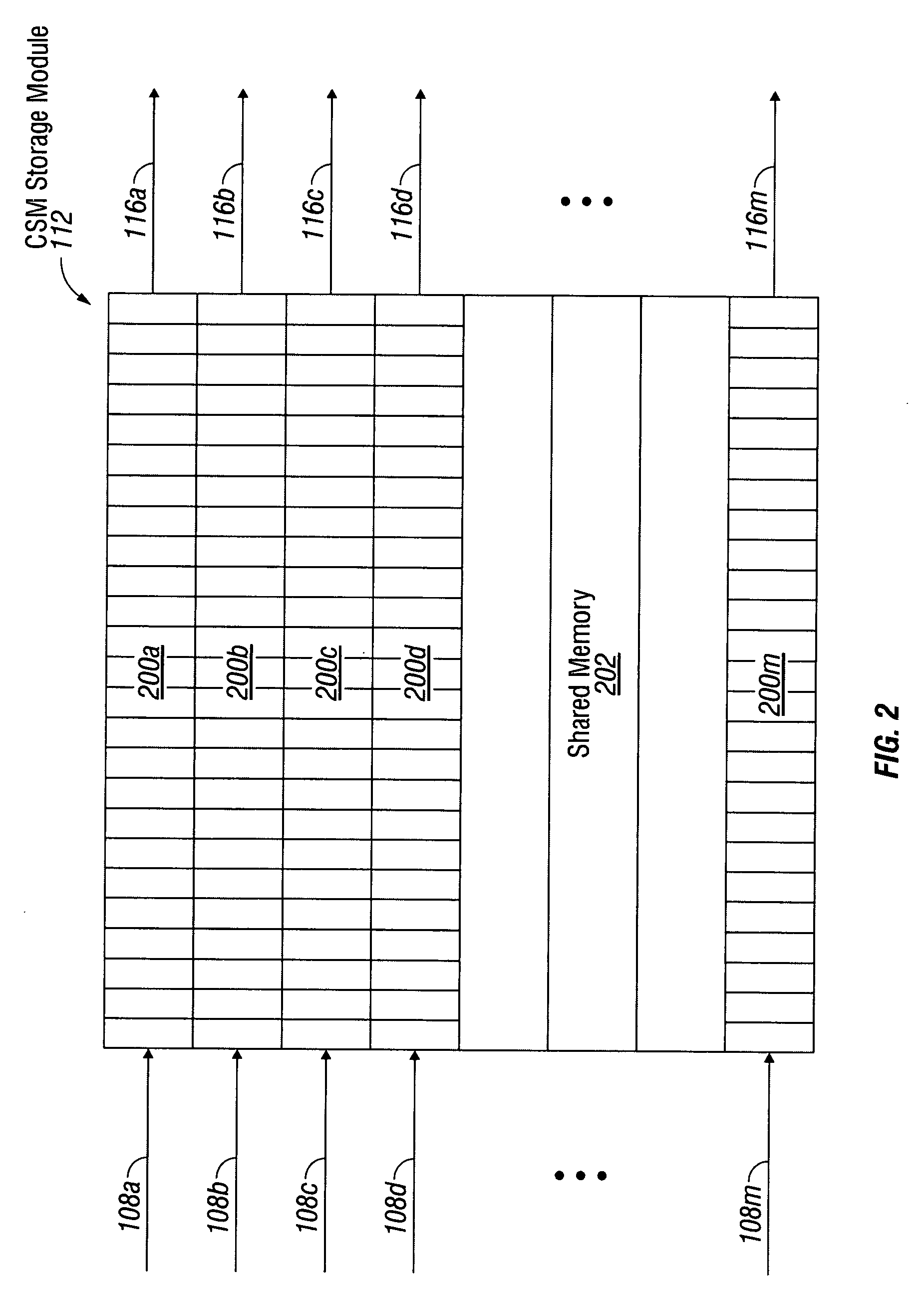
Channel service manager with priority queuing
InactiveUS20080273545A1Eliminate jitterSimple traffic shapingData switching by path configurationRankingPriority queuing
A system and method are provided for prioritizing network processor information flow in a channel service manager (CSM). The method receives a plurality of information streams on a plurality of input channels, and selectively links input channels to CSM channels. The information streams are stored, and the stored the information streams are mapped to a processor queue in a group of processor queues. Information streams are supplied from the group of processor queues to a network processor in an order responsive to a ranking of the processor queues inside the group. More explicitly, selectively linking input channels to CSM channels includes creating a fixed linkage between each input port and an arbiter in a group of arbiters, and scheduling information streams in response to the ranking of the arbiter inside the group. Finally, a CSM channel is selected for each information stream scheduled by an arbiter.
Owner:RPX CORP
Optofluidic microscope device with photosensor array
ActiveUS8314933B2Improve abilitiesPrevent rotationScattering properties measurementsMicroscopePhotoelectric sensor
Owner:CALIFORNIA INST OF TECH
Method and apparatus for communicating maintenance messages and/or test messages of digital subscriber line services
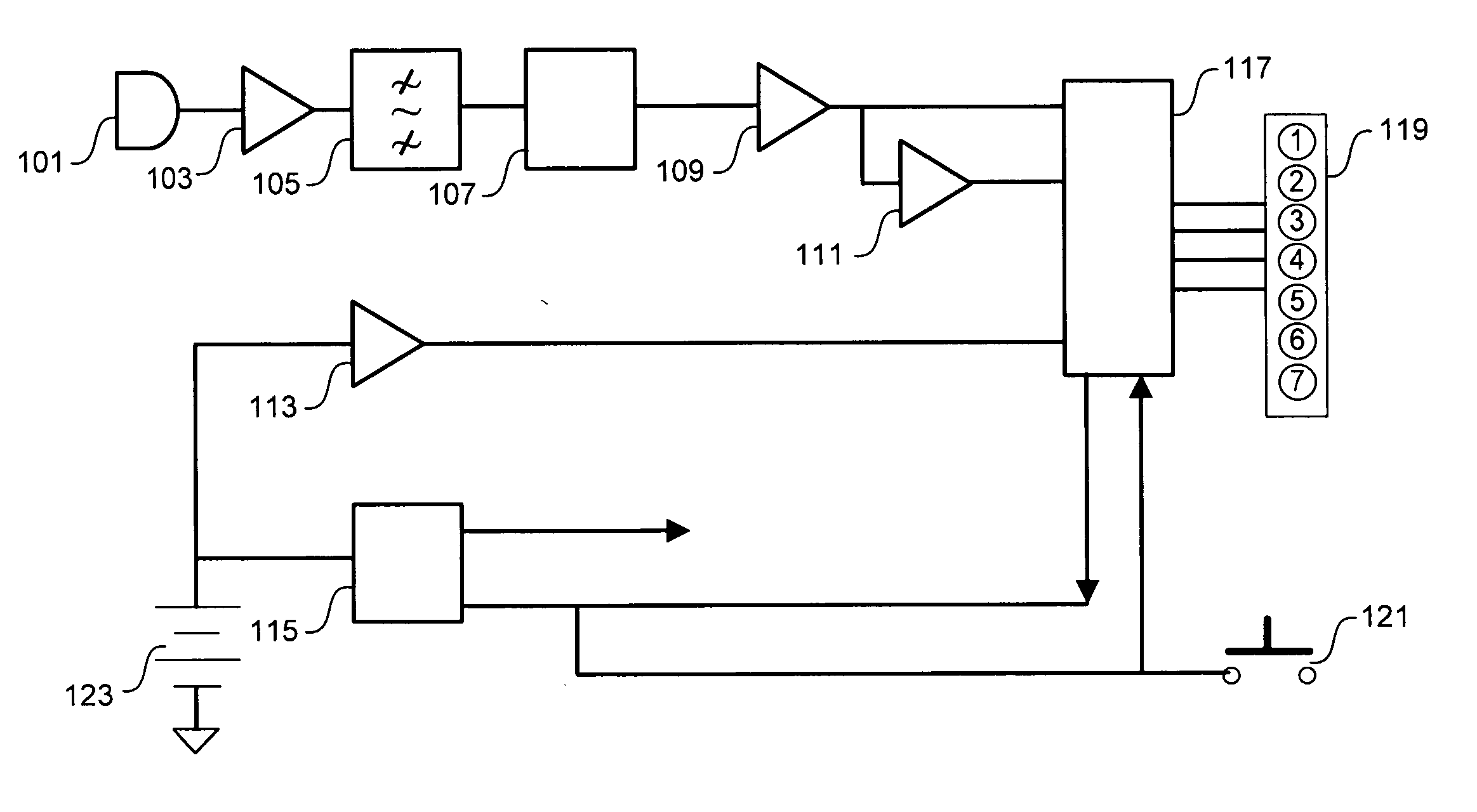
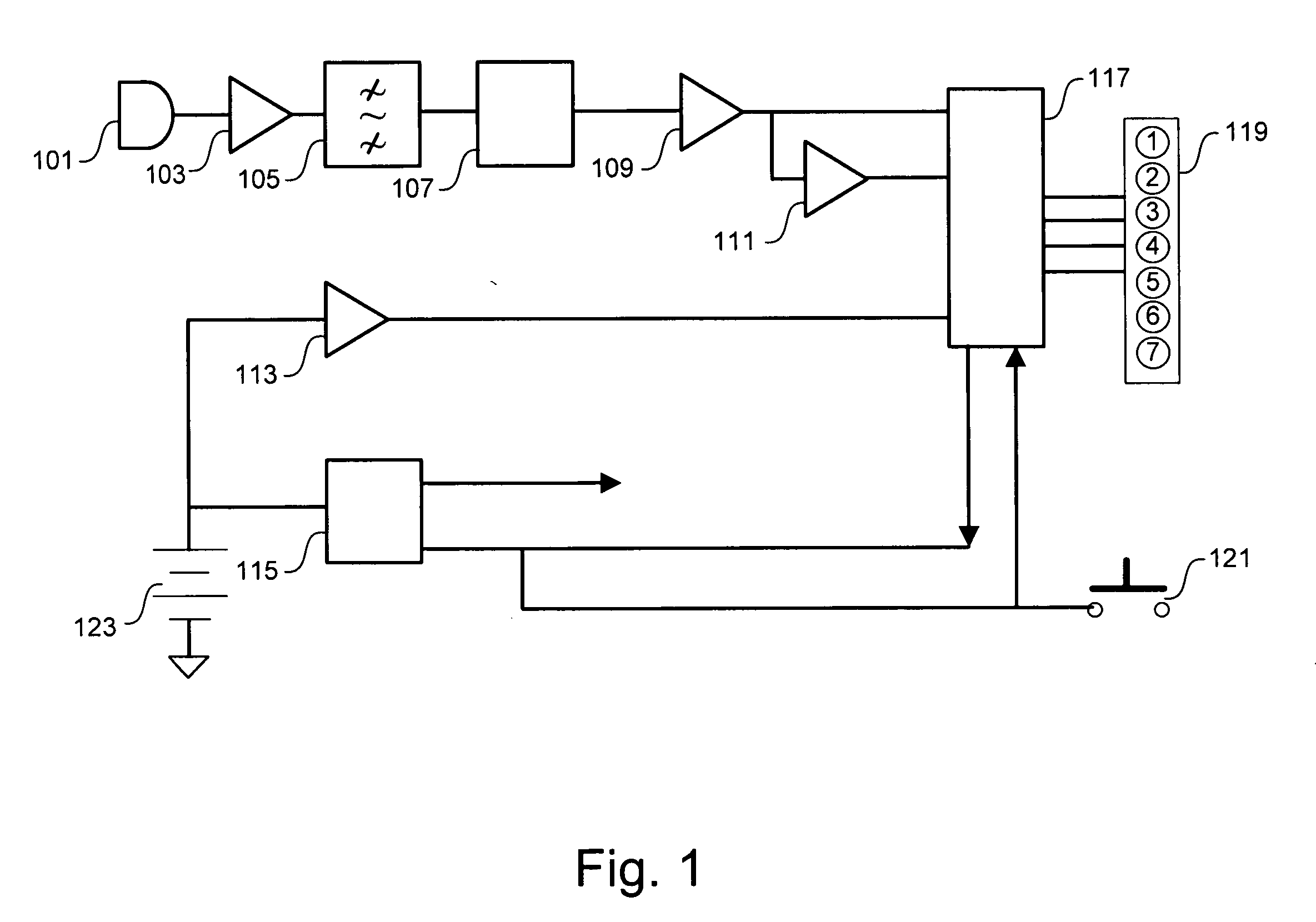
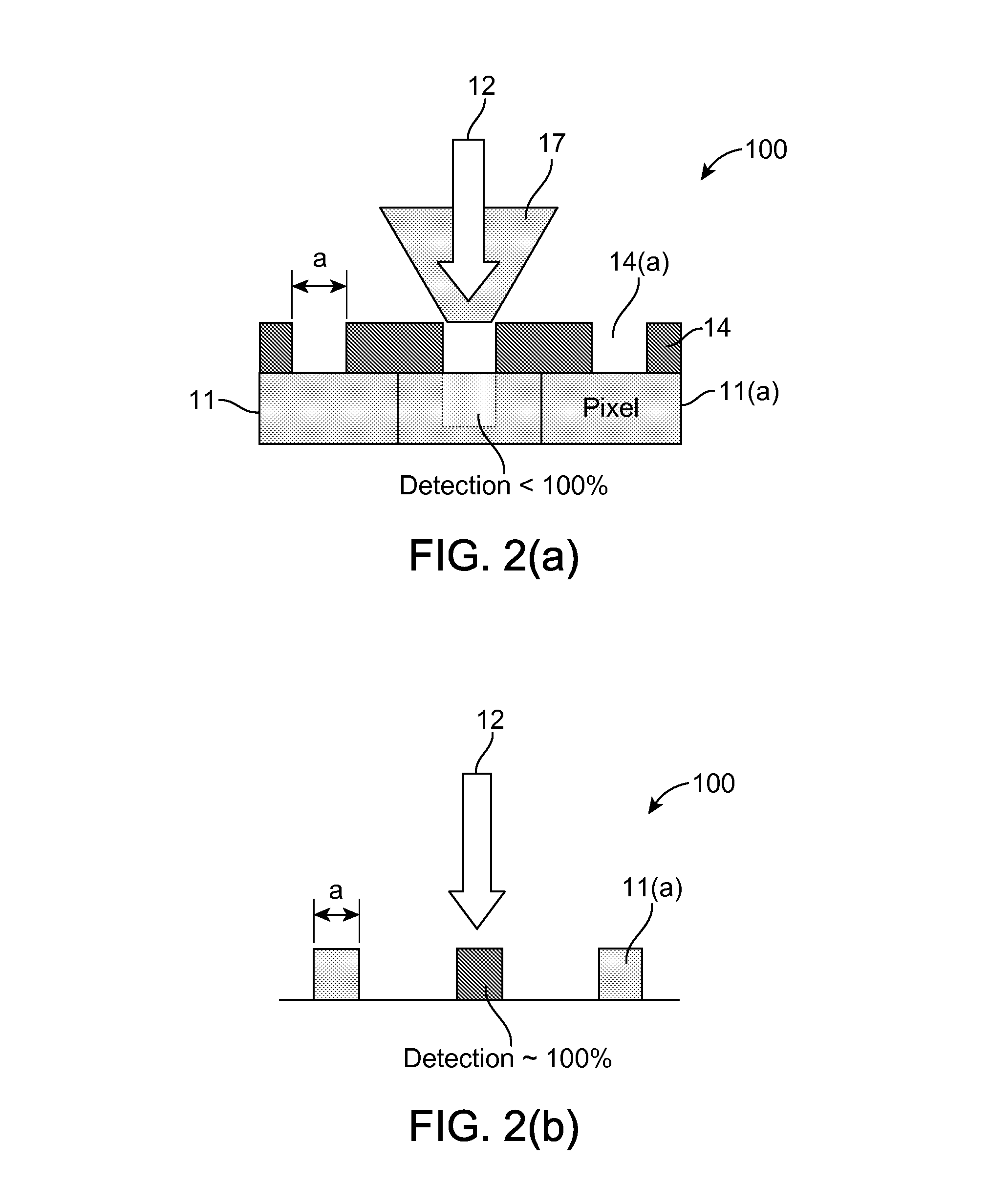
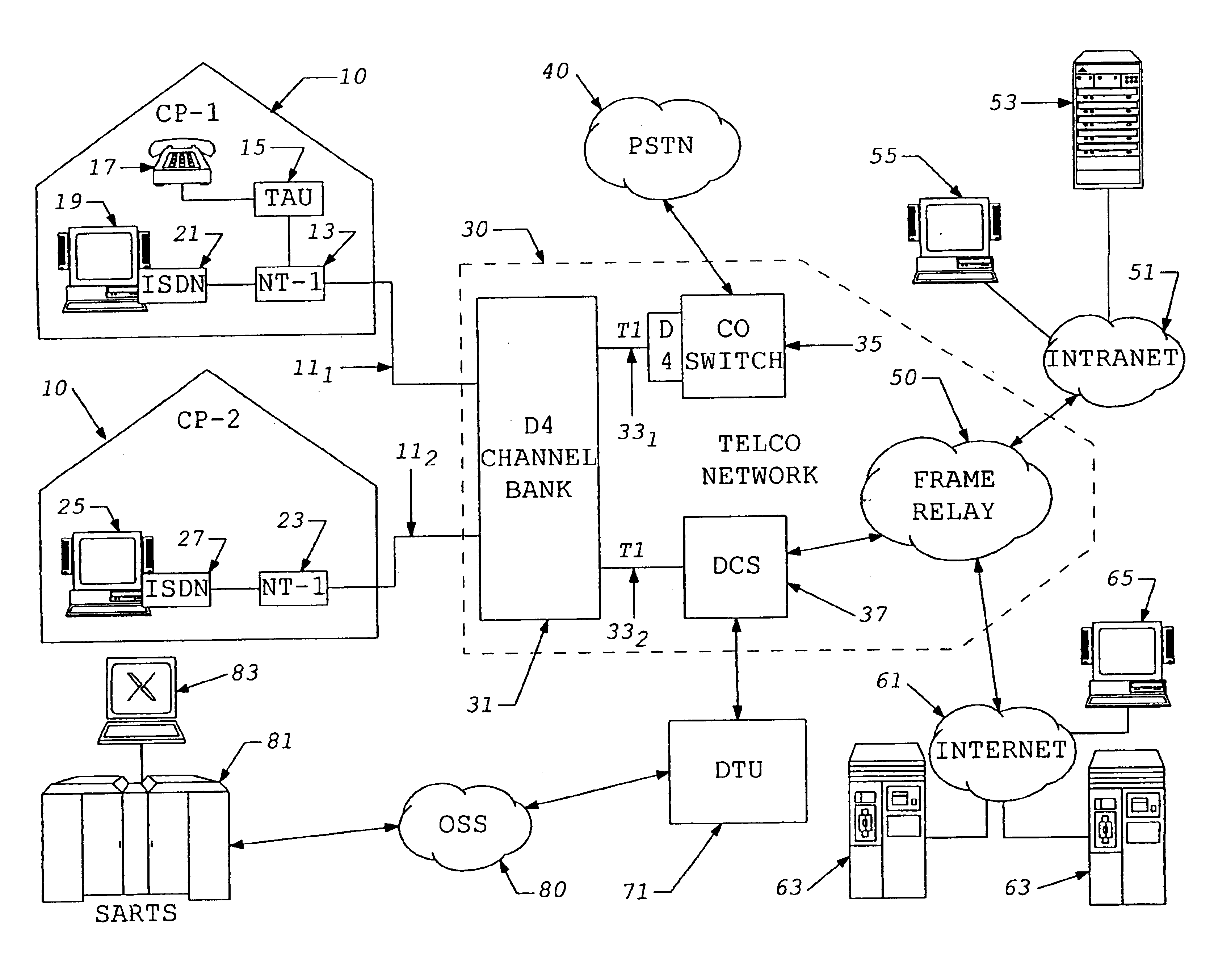
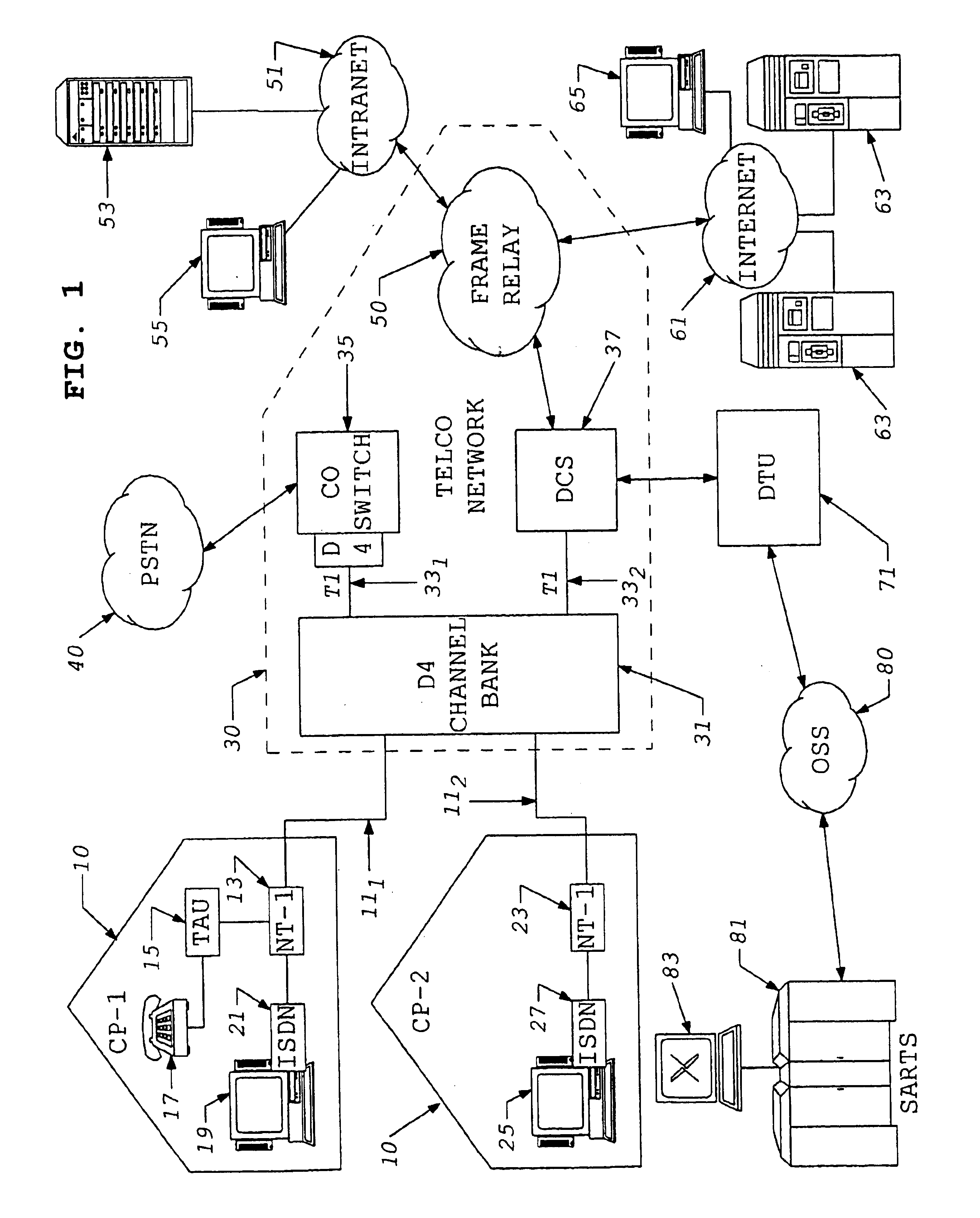
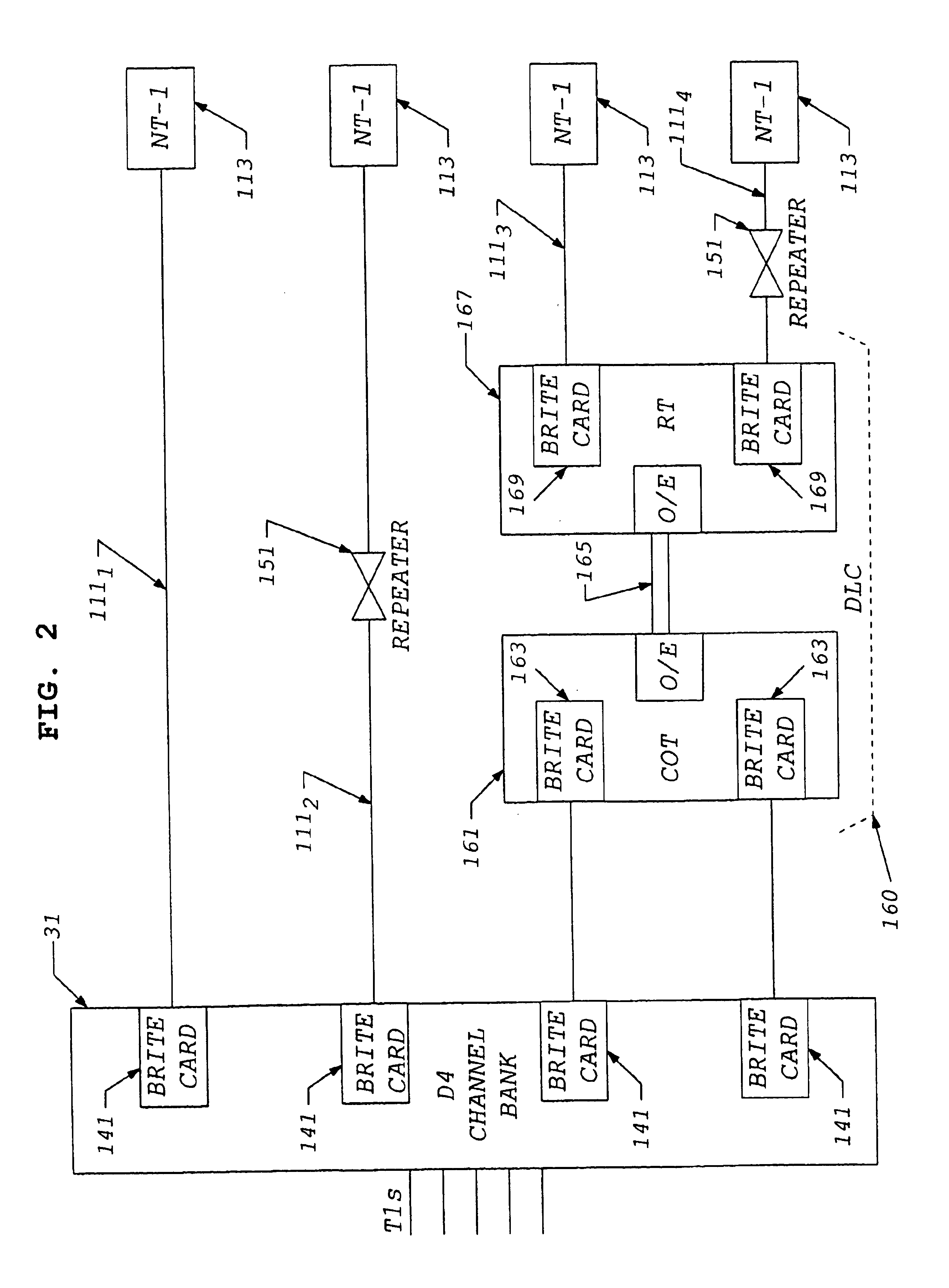
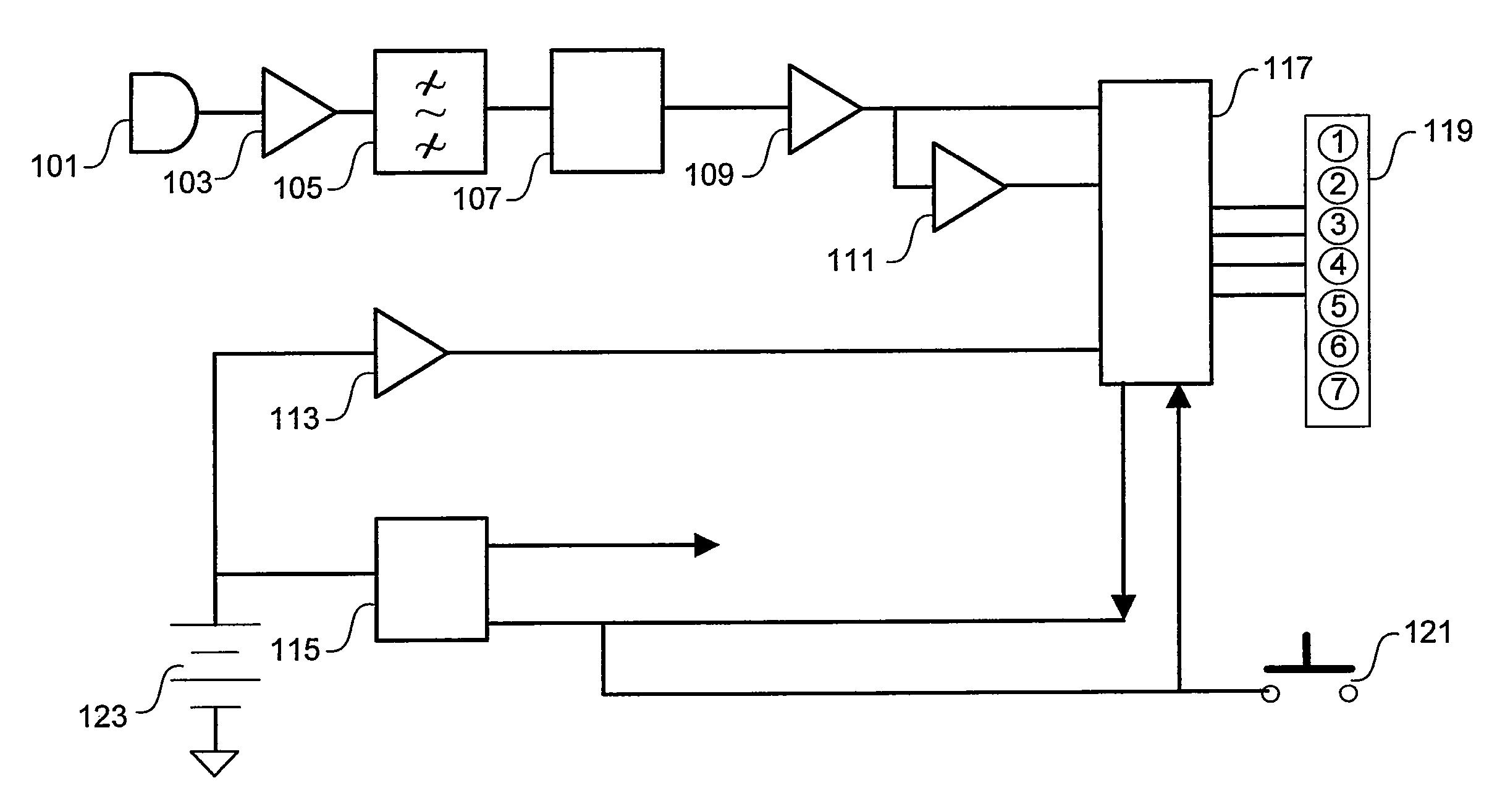
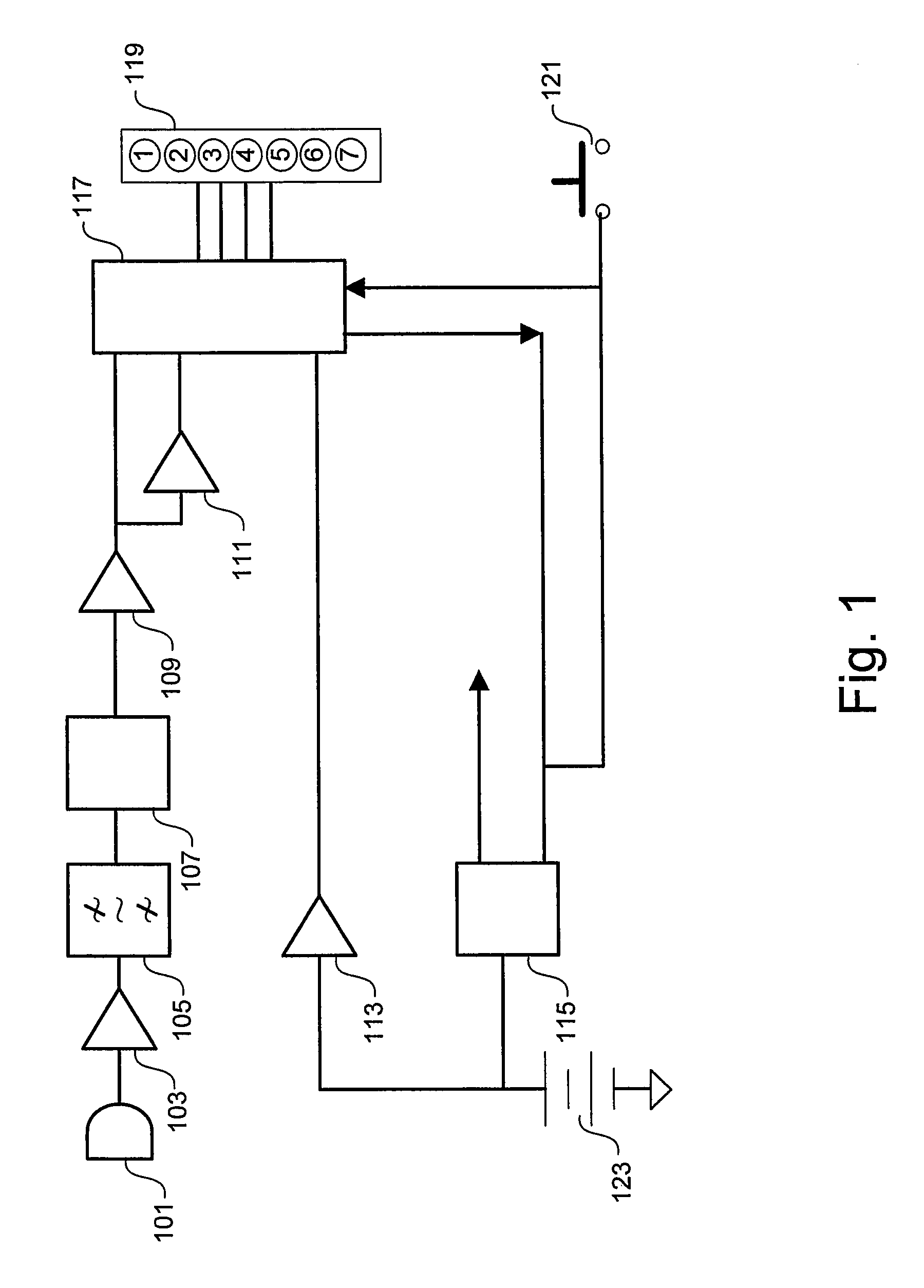
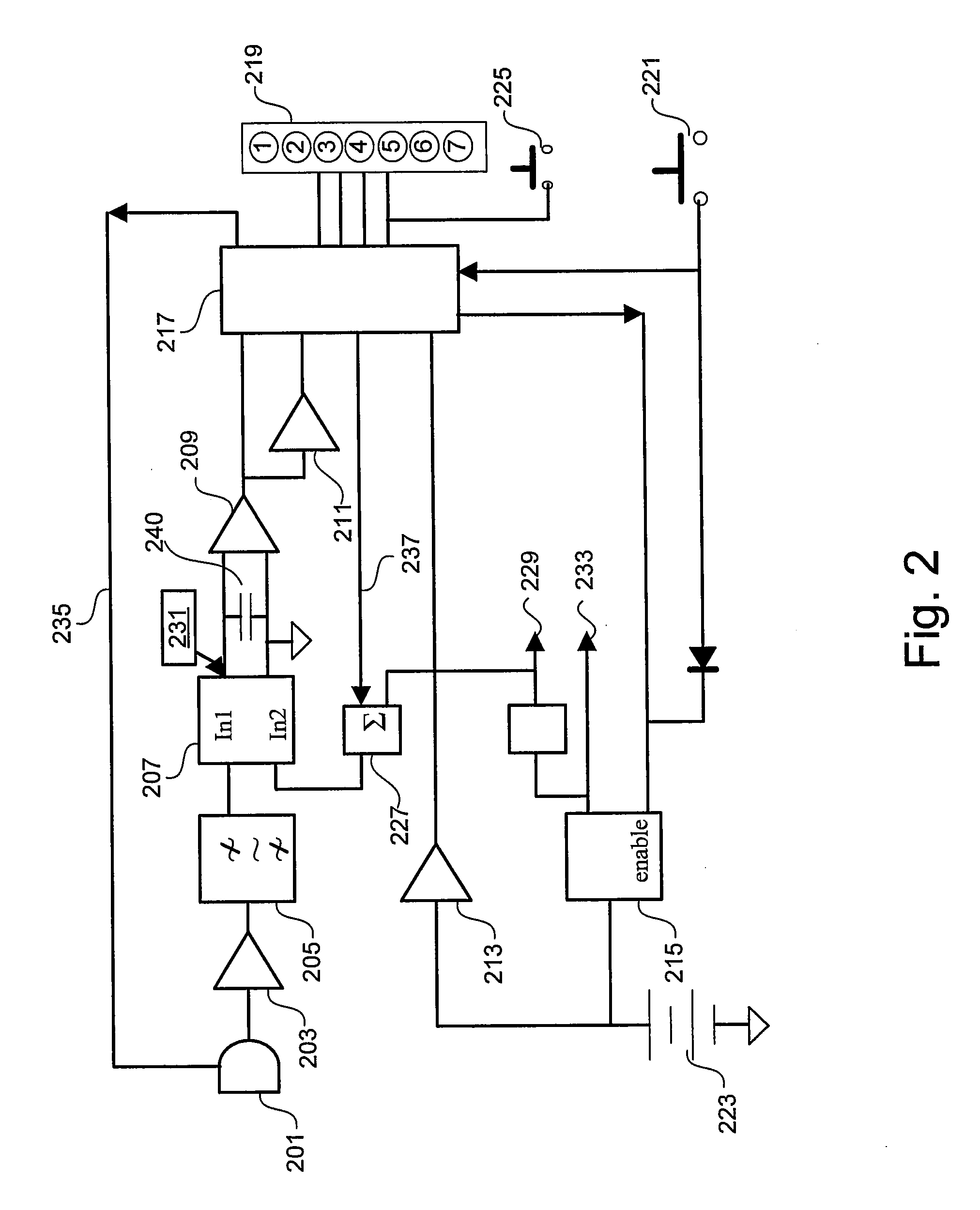
A subscriber's data circuit between channel bank and the customer premises carries fractional T1 bandwidth on a digital subscriber line (DSL) circuit. For example, for an ISDN rate digital subscriber line (IDSL), the circuit between the network termination at the customer premises and a D4 channel bank carries data on two combined B-channels. Such a circuit also carries a D-channel and an embedded operations channel (EOC), in normal ISDN fashion. A data service using such a line circuit, however, only transports the data (combined B-channels) through the network. The D-channel and the EOC are not carried through the network. To facilitate testing of the subscriber's circuit, the carrier operations and testing facilities transmit loop-back commands or the like in band to the channel bank. A command may be addressed to any active node along the subscriber's DSL circuit. The line card serving the subscriber in the channel bank detects the commands, removes the commands from the in-band data and reformats the commands for transmission over the EOC channel. The line card addresses the commands and sends the EOC format commands over the DSL circuit to the appropriate node along the subscriber's line. In response, the node connects the circuit in a loop-back mode, to enable test signal transmission and analysis.
Owner:VERIZON PATENT & LICENSING INC
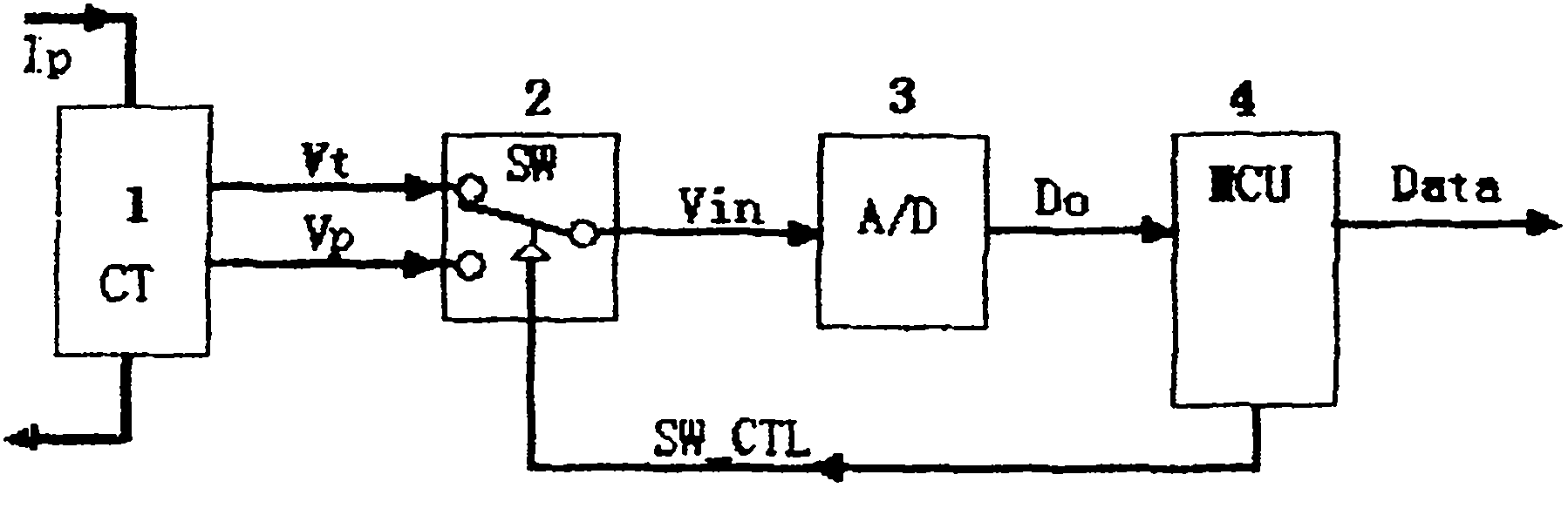
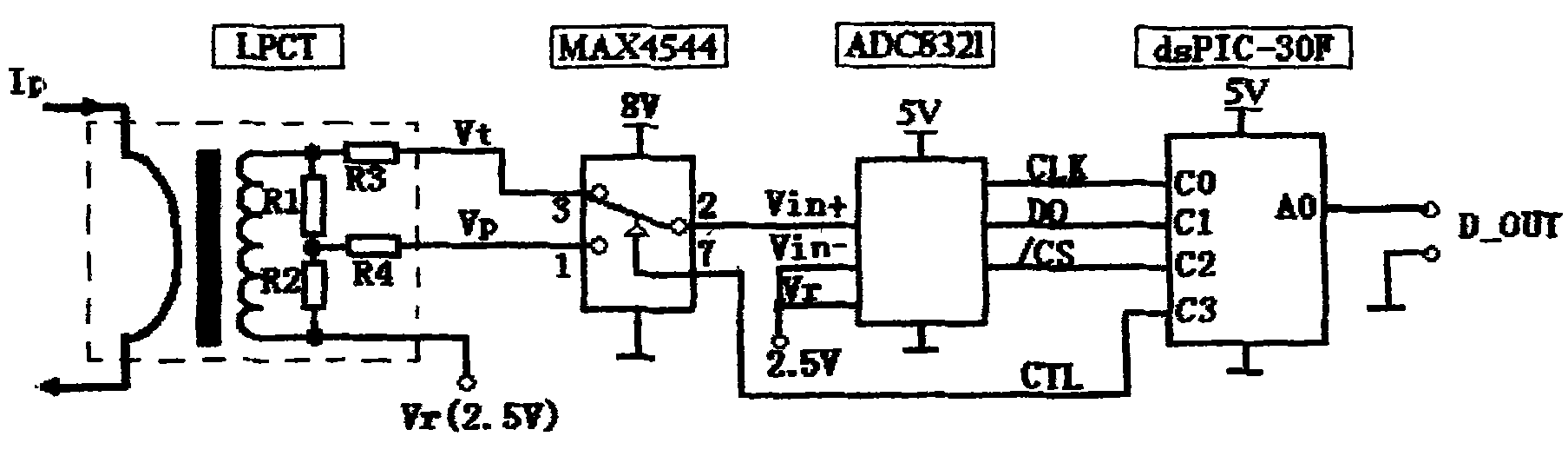
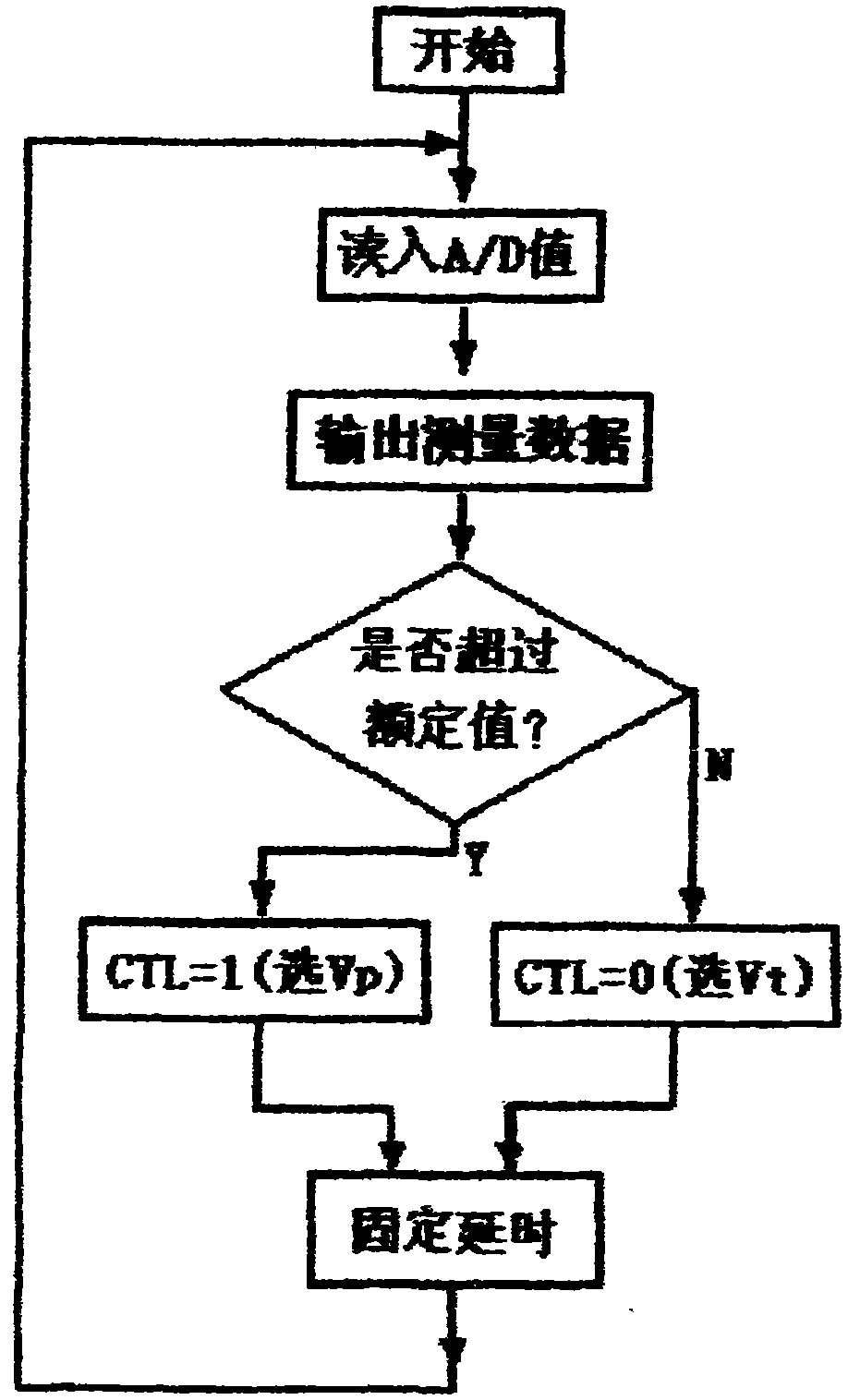
Automatic measurement range switching device of electronic current transformer
InactiveCN102110518AHigh precisionImprove signal-to-noise ratioTransformersInductancesCurrent sensorTransformation ratio
The invention relates to an automatic measurement range switching device of an electronic current transformer, which comprises a current sensor, a single-pole two-throw electronic changeover switch, an A / D converter and a microprocessor. The two outputs with different transformation ratios of the current sensor are both connected with one input end of the electronic changeover switch, the output of the electronic changeover switch is converted to digital quantity through the A / D converter and then read-in by the input end of the microprocessor, and the measurement range control output end of the microprocessor is connected with the changeover control end of the electronic changeover switch. The automatic measurement range switching device provided by the invention can conduct automatic switchover according to the signal variation amplitude; and in case of low current, the A / D converter adopts large measurement input to increase signal-to-noise ratio, and in case of heavy current, the switch is switched to protecting signal input to ensure large A / D input range. Through the use of the automatic measurement range switching device, the electronic current transformer can use the same A / D channel to realize high precision and large-range measurement at the same time, so as to enhance the antijamming capability of small signals.
Owner:西安华伟光电技术有限公司
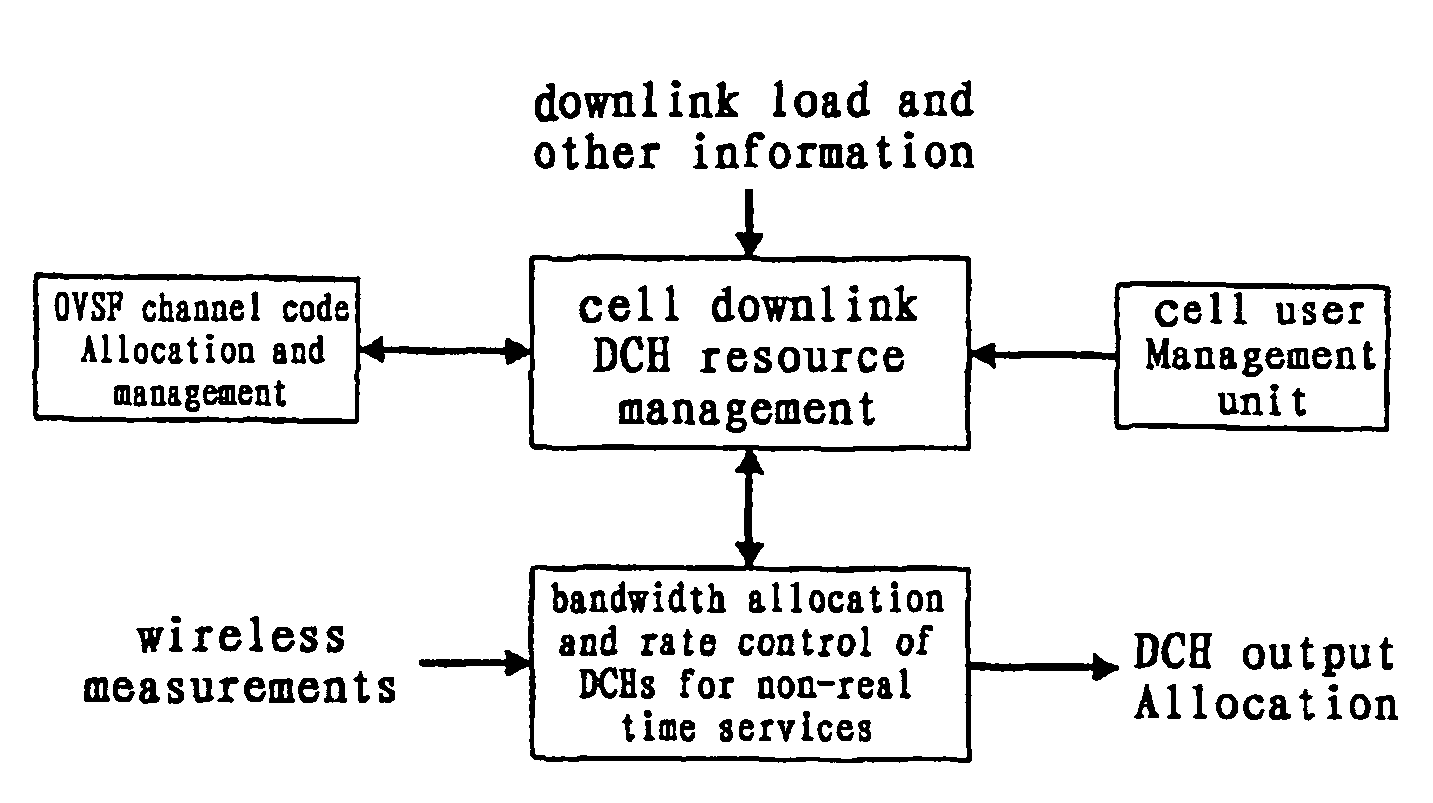
Method of wireless channel resource allocation and rate control in a cdma communication system
InactiveUS7505448B2Increase profitEfficient implementationNetwork traffic/resource managementTime-division multiplexChannel resource allocationWireless resources
The present invention discloses a method for resource allocation and rate control of dedicated channels in a Wideband Code Division Multiple Access (WCDMA) communication system, the method being characterized by comprising: a) the step of determining channel states of downlink DCH channels for non-realtime data services; b) the step of determining states of the users using said downlink DCH channels; and the step of correlating the channel states determined in step a) with the user states determined in step b), and dynamically allocating the DCH channels with certain rates to the users in the different User states according to a wireless measurement result measured by a current transmission channel and based on the priority and fairness requirements. According to the present invention, the method effectively realizes the bandwidth resource allocation and rate control, improves the radio resource availability and provides users, to the maximum extent, with a data service bandwidth as high as possible.
Owner:UT STARCOM (CHINA) CO LTD
Dynamic DCH allocation methodology for packet data services in a wireless communications system
ActiveUS7206286B2Increase data rateQuality is not affectedError preventionTransmission systemsQuality of serviceTime-sharing
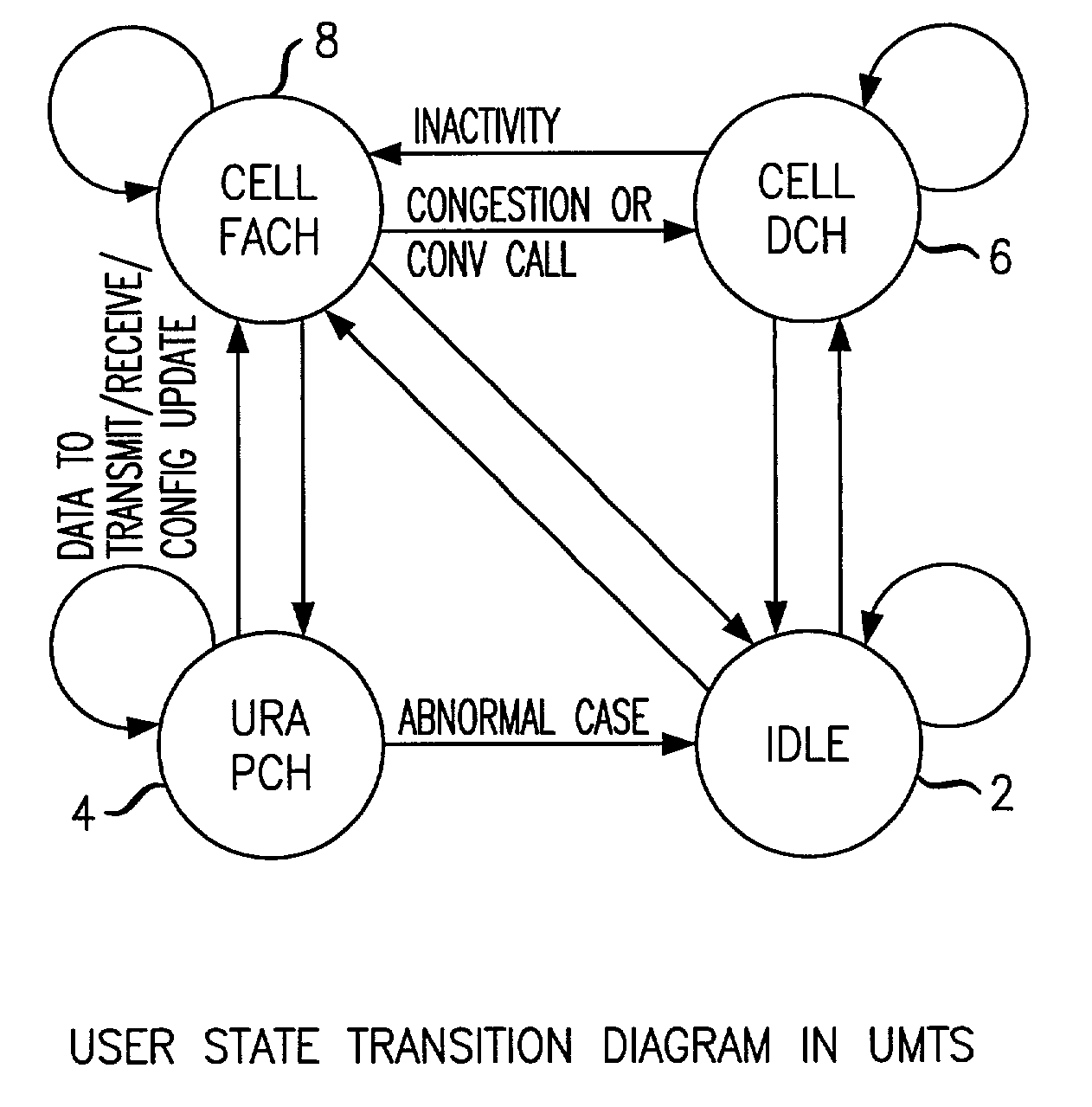
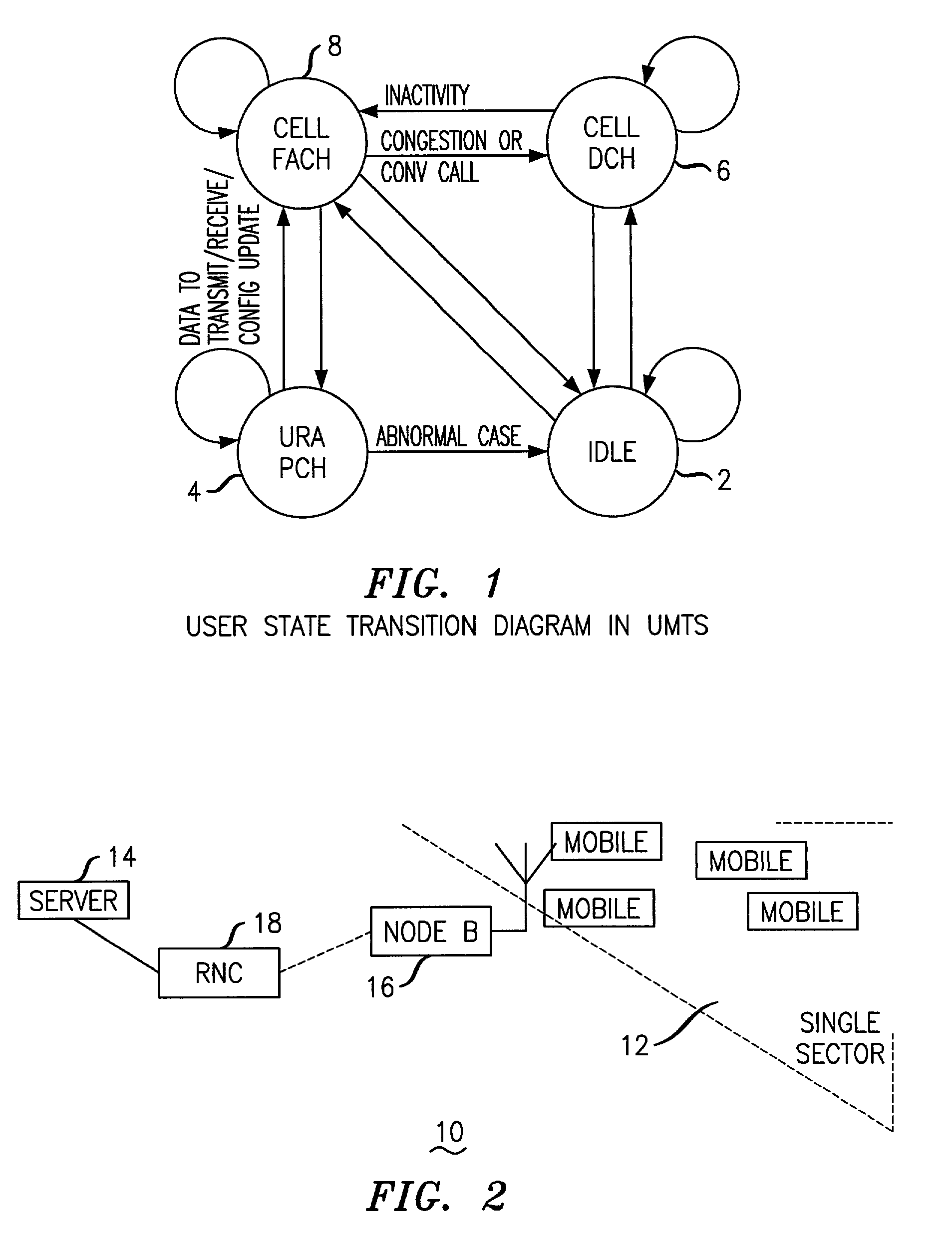
In a UMTS network, each packet data service user requires a dedicated channel (DCH) to transmit at high data rates. However, the number of DCHs available is small due to code and power limitations. Thus many users will have to be allocated the same DCH on a time sharing basis. Such sharing will not impact the quality of service for users whose applications are not delay sensitive and whose traffic generation pattern toggles between transmit and idle states. Such applications include web browsing, FTP sessions and E-mail. The present invention discloses four algorithms that can be used to dynamically allocate DCH channels to a contending user based on the user's need according to its traffic generation. One embodiment of the invention discloses a methodology of allocating user channels for packet data services in a wireless communications network, a first type channel having a given data rate and a second type channel having a lower data rate, including the steps of determining an estimated bandwidth requirement for the packet data services, switching a user to the second channel type from said first channel type if said estimated bandwidth requirement is below a first threshold, and switching a user to the first channel type from said second channel type if the estimated bandwidth requirement is greater than a second threshold. Another embodiment discloses methodology of allocating user channels for packet data services in a wireless communications network, a first type channel having a given data rate and a second type channel having a lower data rate, comprising the steps of providing an inactivity timer per user, and switching from the first channel type to said second channel type depending on a state of said inactivity timer.
Owner:RPX CORP +1
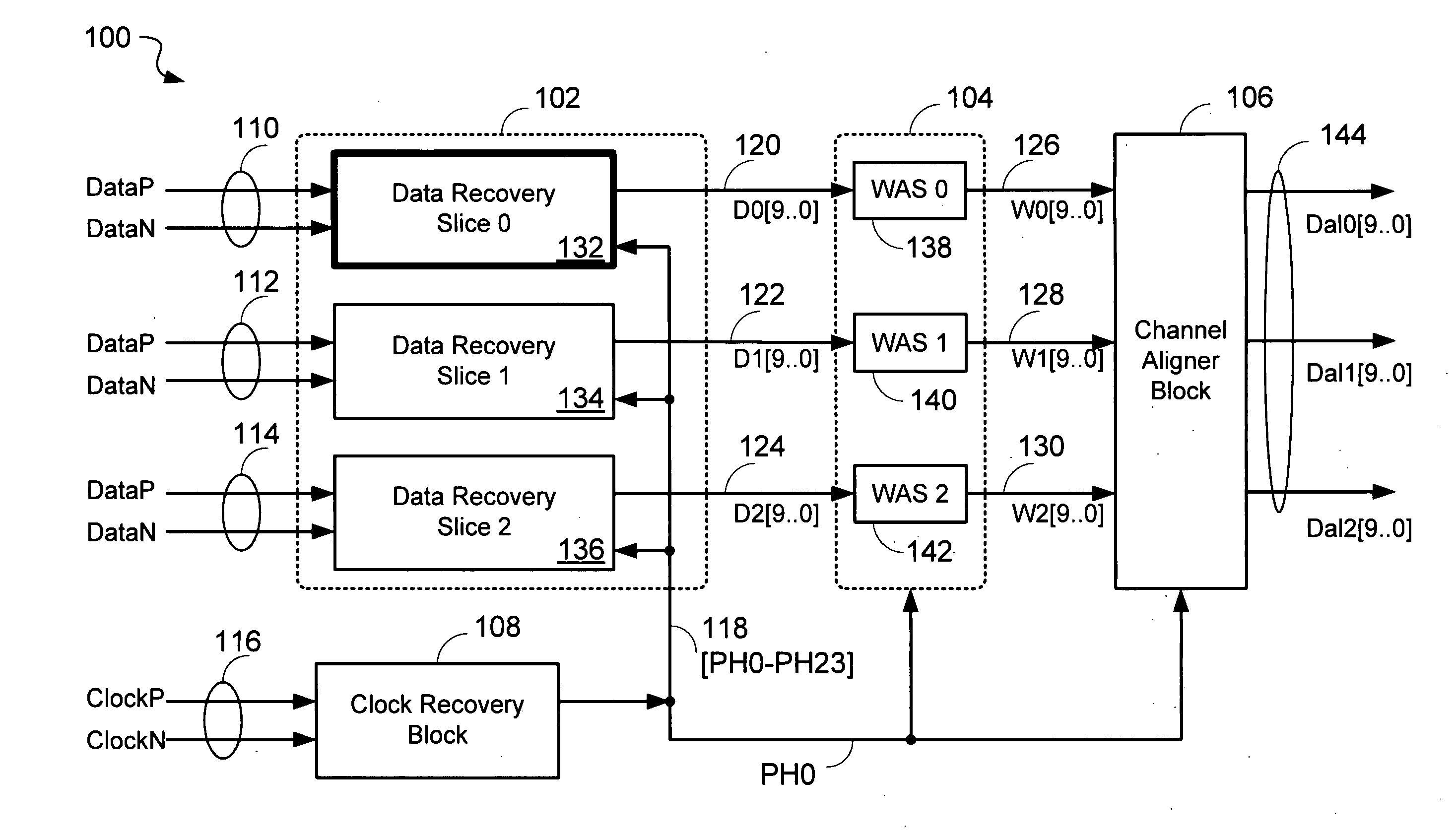
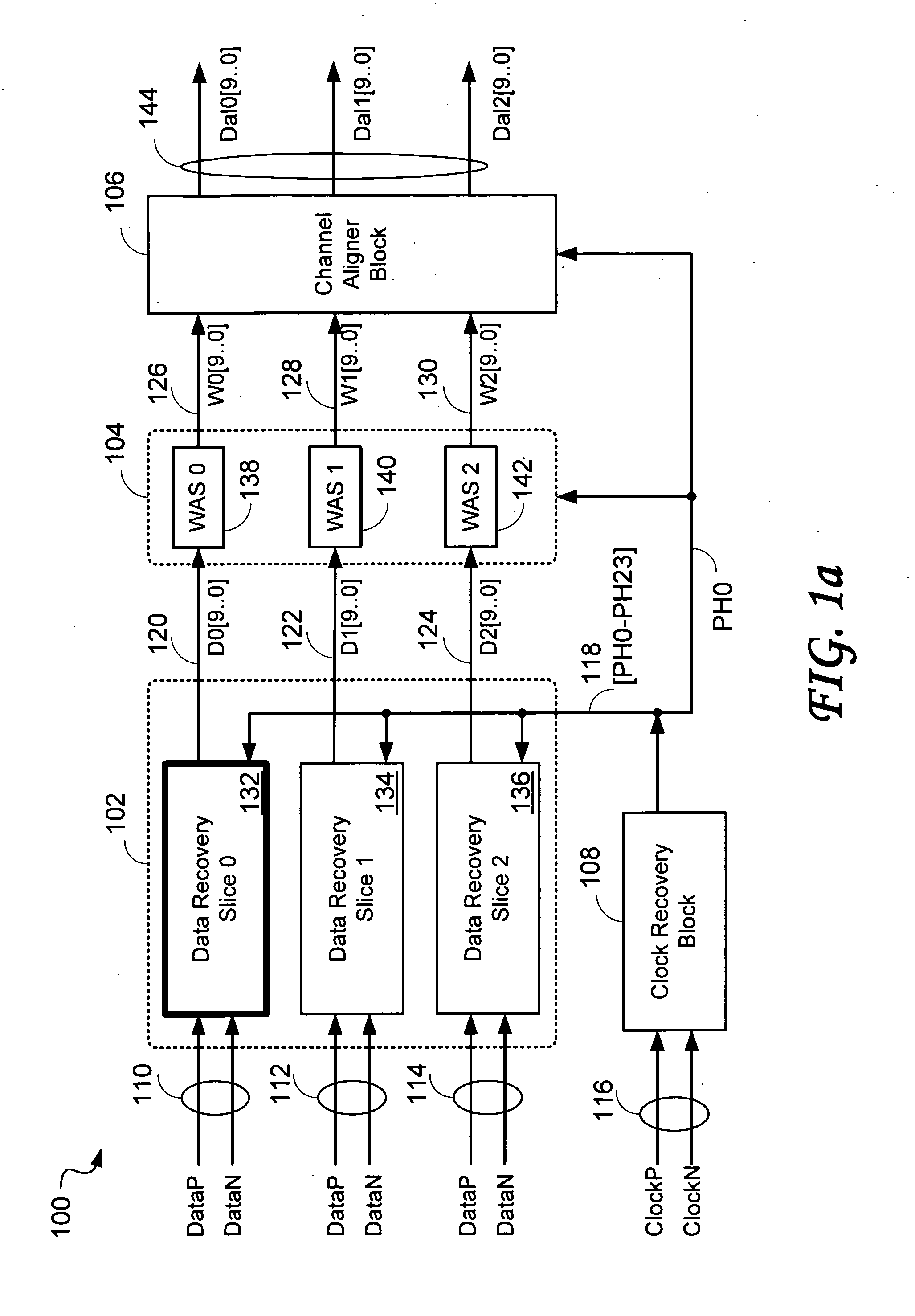
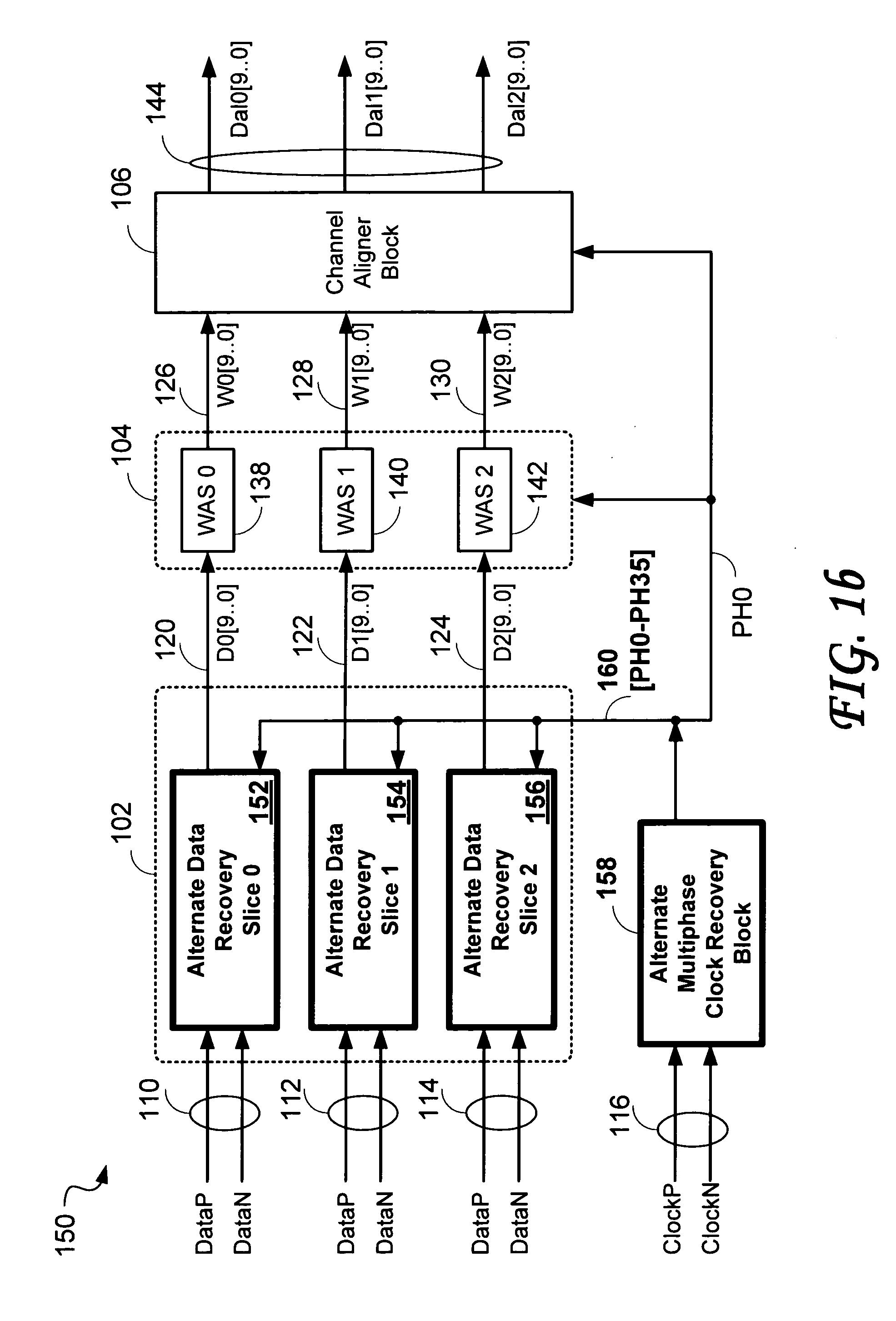
Data recovery system for source synchronous data channels
ActiveUS20090290671A1Easy Data RecoveryReduce distortion problemsModulated-carrier systemsFrequency/rate-modulated pulse demodulationSignal quality24-bit
A high-definition multimedia interface (HDMI) receiver recovers high speed encoded data which are transmitted differentially over data channels of a lossy cable, along with a clock. Inter symbol interference, high-frequency loss, skew between the clock and data channels, and differential skew within a differential signal are compensated by analog circuits which are automatically tuned for best performance by observing the quality of the recovered analog signal. Oversampling is used to provide a 24-bit digital representation of the analog signal for determining the quality of the signal.
Owner:REDMERE TECH
Uplink transmission power control in multi-carrier communication systems
In a communication system wherein a User Equipment (UE) transmits at least two data channels in at least two respective component carriers, a method and apparatus for reducing a transmission power allocated to each of the least two data channels relative to each of a respective nominal transmission power, when a total nominal transmission power for the at least two data channels exceeds a predetermined value are provided. The method includes reducing a transmission power of the first data channel by a first amount; and reducing a transmission power of the second data channel by a second amount, wherein the first amount and the second amount have different values.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Information transferring method between intelligent bi-mode mobile phone and wireless modem
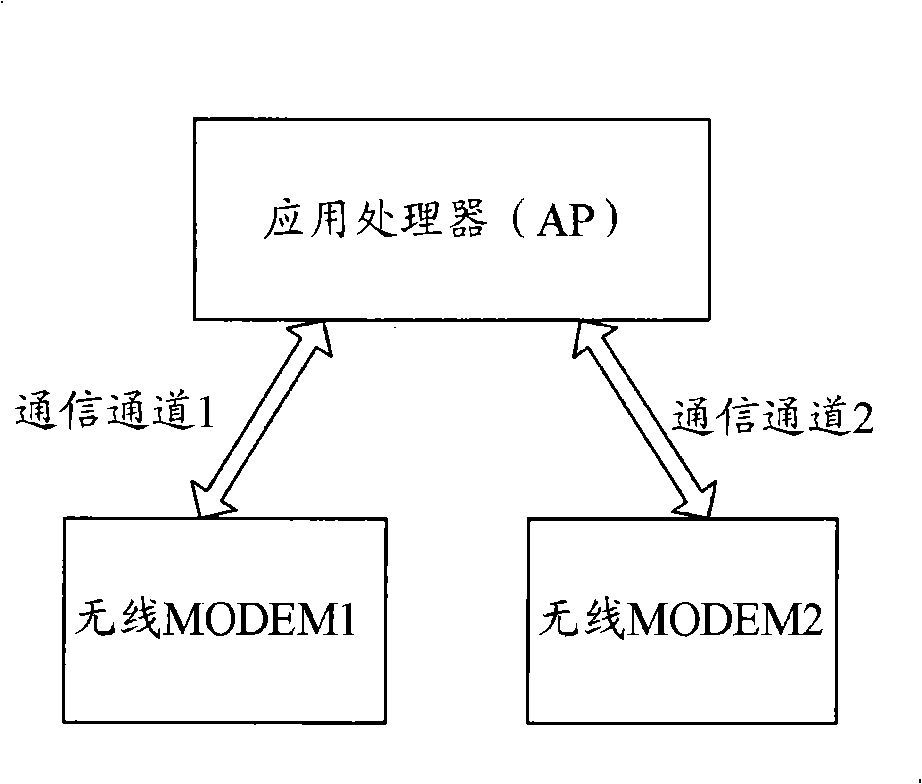
InactiveCN101287221AReduce the burden onImprove collaborationRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsModem deviceInformation transmission
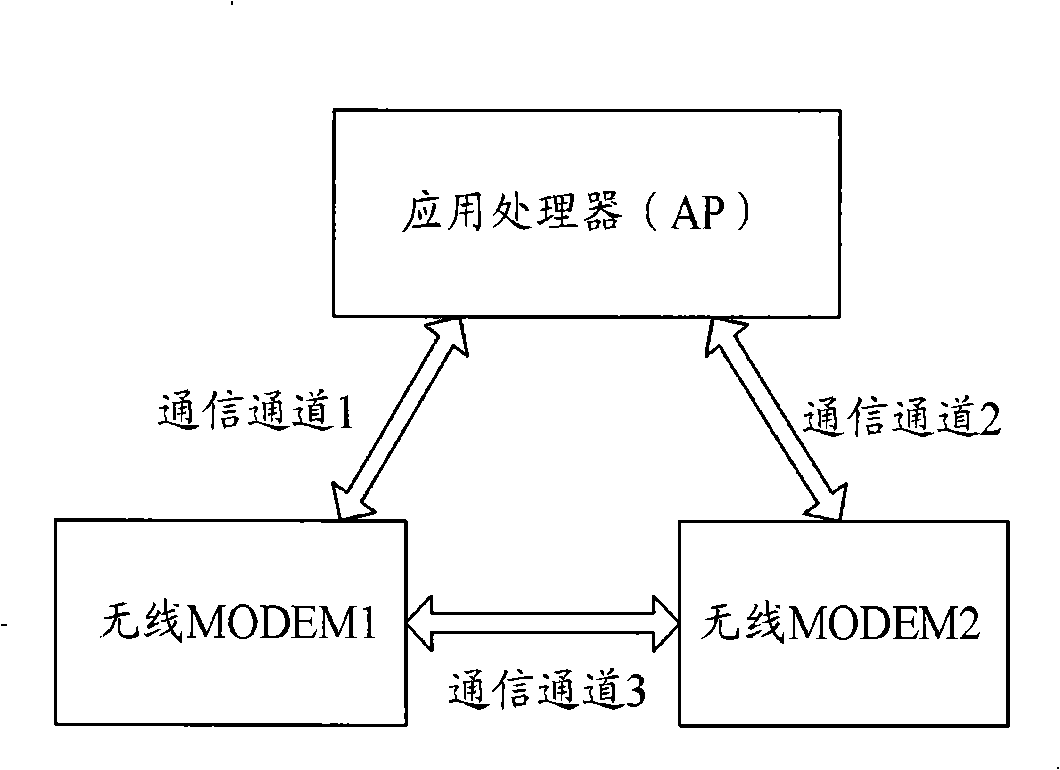
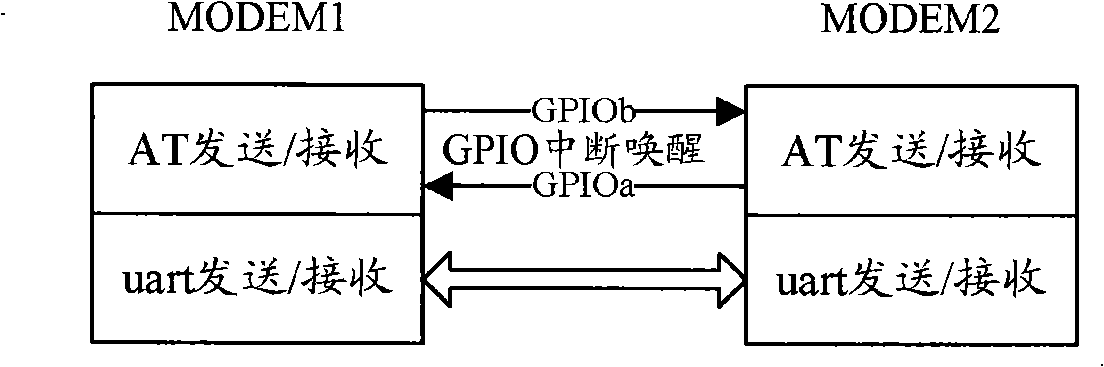
The invention discloses an intelligent dual-mode mobile phone which comprises a first wireless modem and a second wireless modem; a third communication channel is arranged between the first wireless modem and the second wireless modem; the third communication channel is provided with a control channel and a data channel which conducts the data processing through expanded modem instructions. The invention also discloses a method for the information transmission between the wireless modems of the intelligent dual-mode mobile phone. The intelligent dual-mode mobile phone and the information transmission method not only reduce the loading of an application processor (AP) processing the data of the two wireless MODEMs but also reasonably utilize the AP and the processors of the two wireless MODEMs, thereby improving the cooperation capacity of the processor.
Owner:ZTE CORP
Fault reduction realizing method of cluster net communication
InactiveCN1835609AMeet the requirements of rapid emergencyEasy to implementRadio/inductive link selection arrangementsSignal processingMobile phone
The method for solving the problem not capable of making phone call after the base station disconnects to the base station controller and comprises: the control unit of base station detects the transmission link of base station; when deciding a transmission interruption happens, the working mode of base station is set as a fail-soft mode; the signaling processing unit configures the frequency carrier, it includes system information, channel configuration and notice message description; then, the signaling processing unit fills out the received system information into the system message field, and transmits the notice message description on NCH channel; after receiving the notice message description, the mobile phone stays in relevant time slot according to a failure-soft channel ID configured for it in order to initiate or receive the PTT calling.
Owner:HUAWEI TECH CO LTD
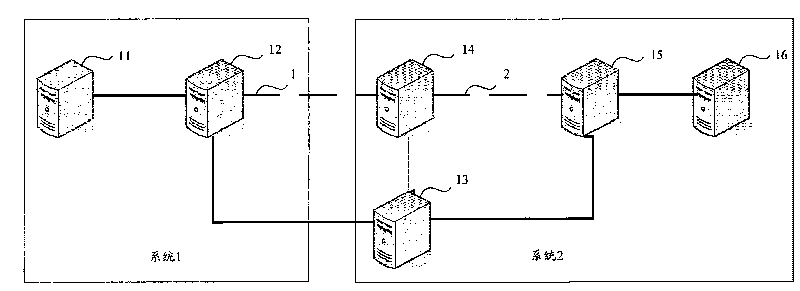
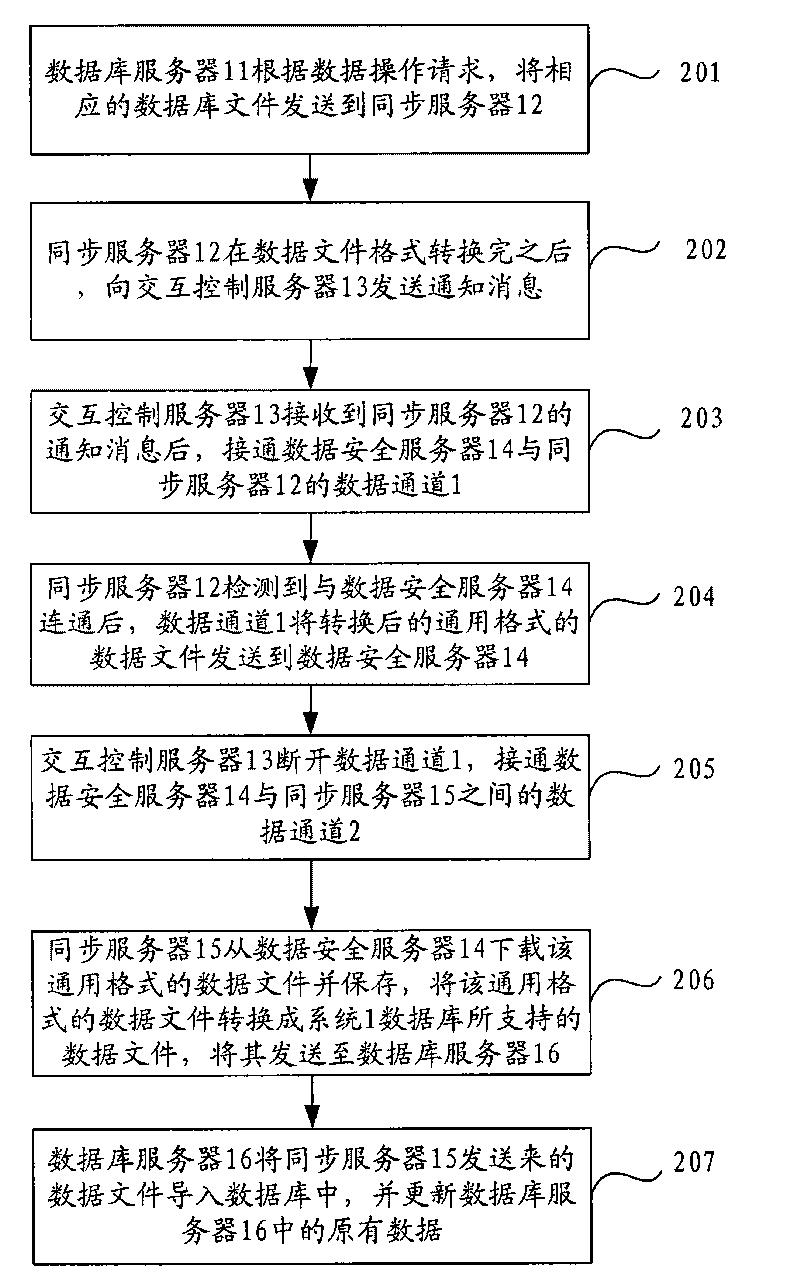
Data transmission method between heterogeneous systems and data transmission system
ActiveCN101754221ARealize two-way data transmissionIncrease flexibilityInformation formatContent conversionCommunications systemData exchange
The invention discloses a data transmission method between heterogeneous systems and a data transmission system, which aims at solving the problem that the data exchange between heterogeneous systems under physical network safety and defence can not be realized in the prior art. The method comprises that: a first communication system communicates with a first data channel between a data entry node of the system and a second communication system, and the data gateway node performs security detection for receiving the data sent by the second communication system through the first data channel; the first communication system disconnects the first data channel and communicates a second data channel between the data entry node and the data processing node of the system, the data processing node converts the format of the data which is received by the second data channel and undergone the security detection to the data format supported by the database of the system, and then saves the data to the database of the system. With the technical scheme of the invention, the data exchange between the heterogeneous systems under the higher data security environment can be realized.
Owner:CHINA MOBILE GROUP SHANDONG
Method and system for noise dosimeter
InactiveUS20070180915A1Vibration measurement in solidsMaterial analysis using sonic/ultrasonic/infrasonic wavesDisplay deviceEngineering
A personal noise dosimeter having functionality for increasing the dynamic range of the device. A microphone provides a signal to an RMS detector, which provides a DC signal to a two-stage amplifier circuit. The outputs of the amplifiers are provided to a processor having multiple A / D channels. The processor calculates accumulated noise doses and drives a display, which in one embodiment includes a panel of light-emitting diodes. A current source injects current into the output of the RMS detector to reduce performance degradation. Functionality detects and accounts for voltage offsets in the dosimeter. The microphone is turned off during offset determination. In one embodiment, the dosimeter includes functionality for control of external devices such as sound boards.
Owner:ETYMOTIC RES
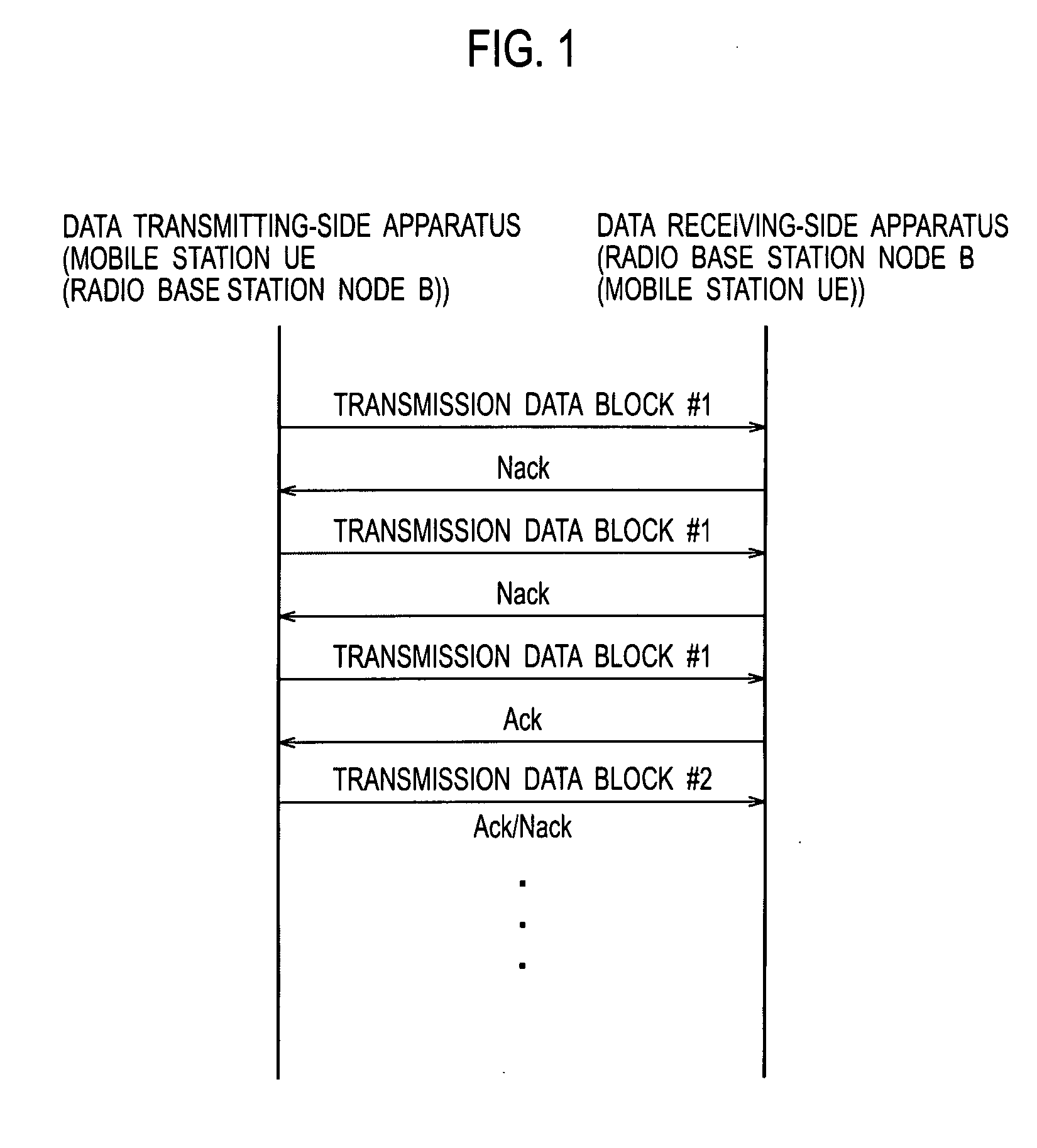
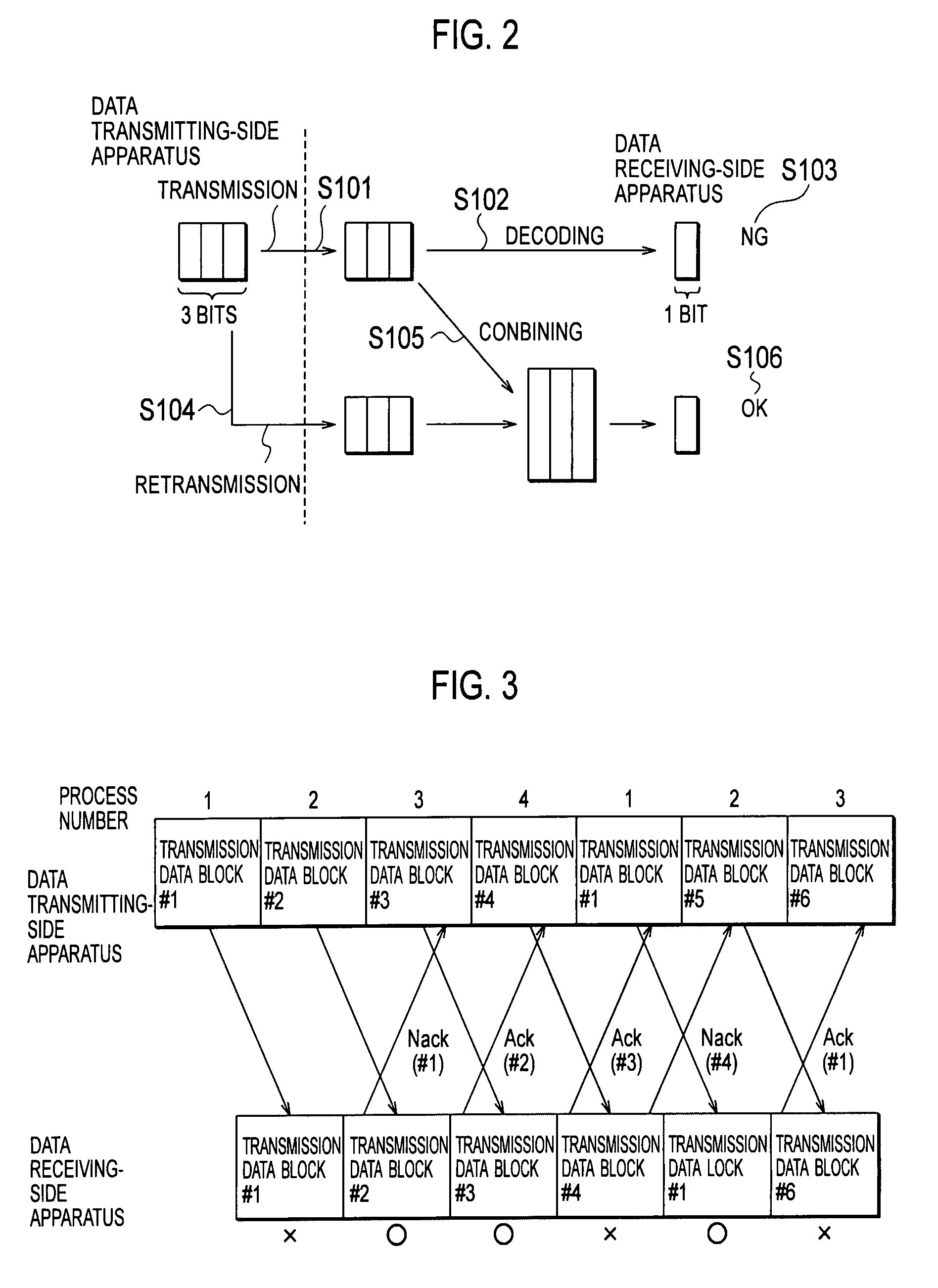
Mobile Communication System, Wireless Line Control Station, Mobile Station, And Wireless Base Station
InactiveUS20080074999A1Increase capacityError prevention/detection by using return channelFrequency-division multiplex detailsControl channelMobile communication systems
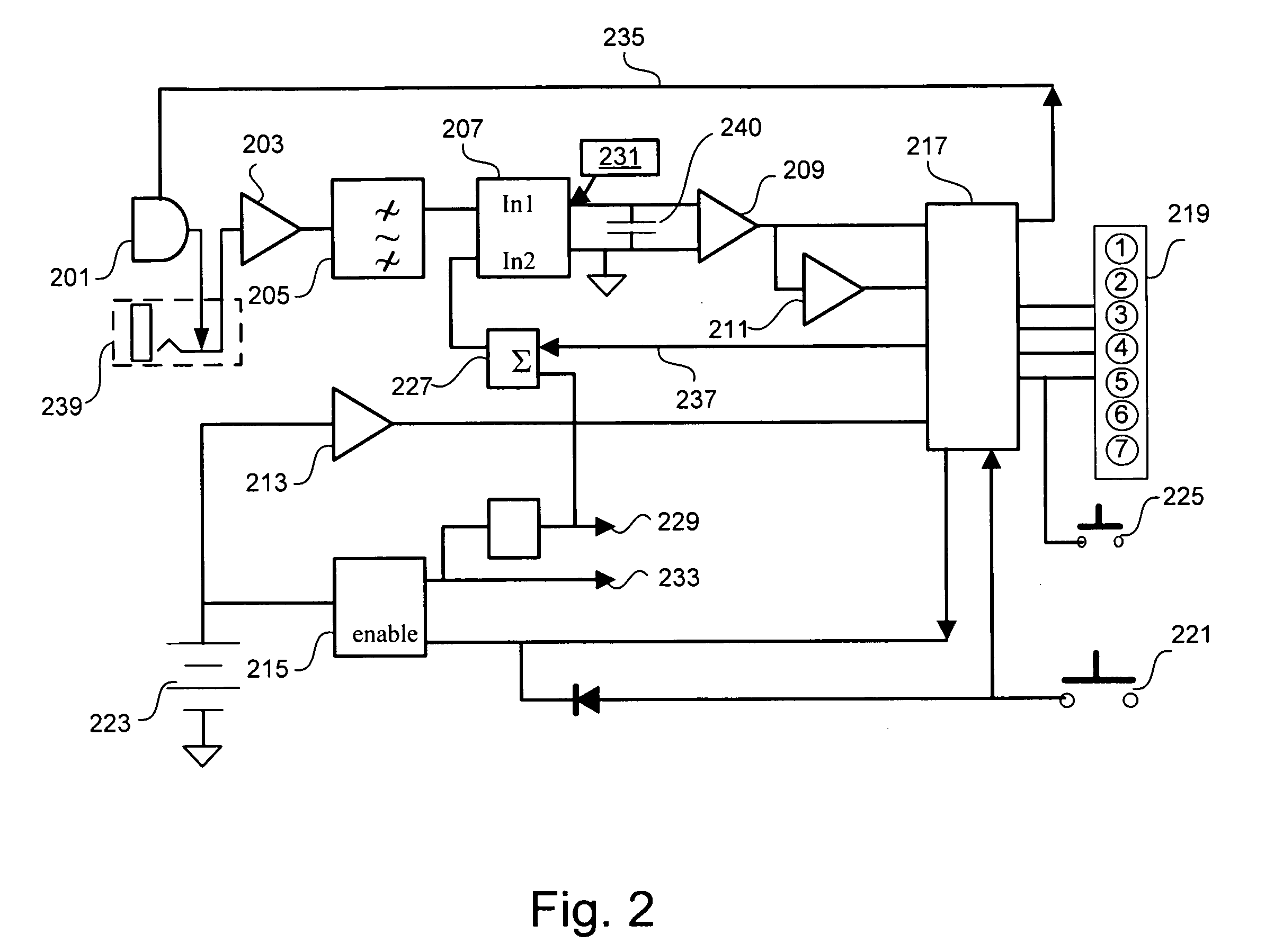
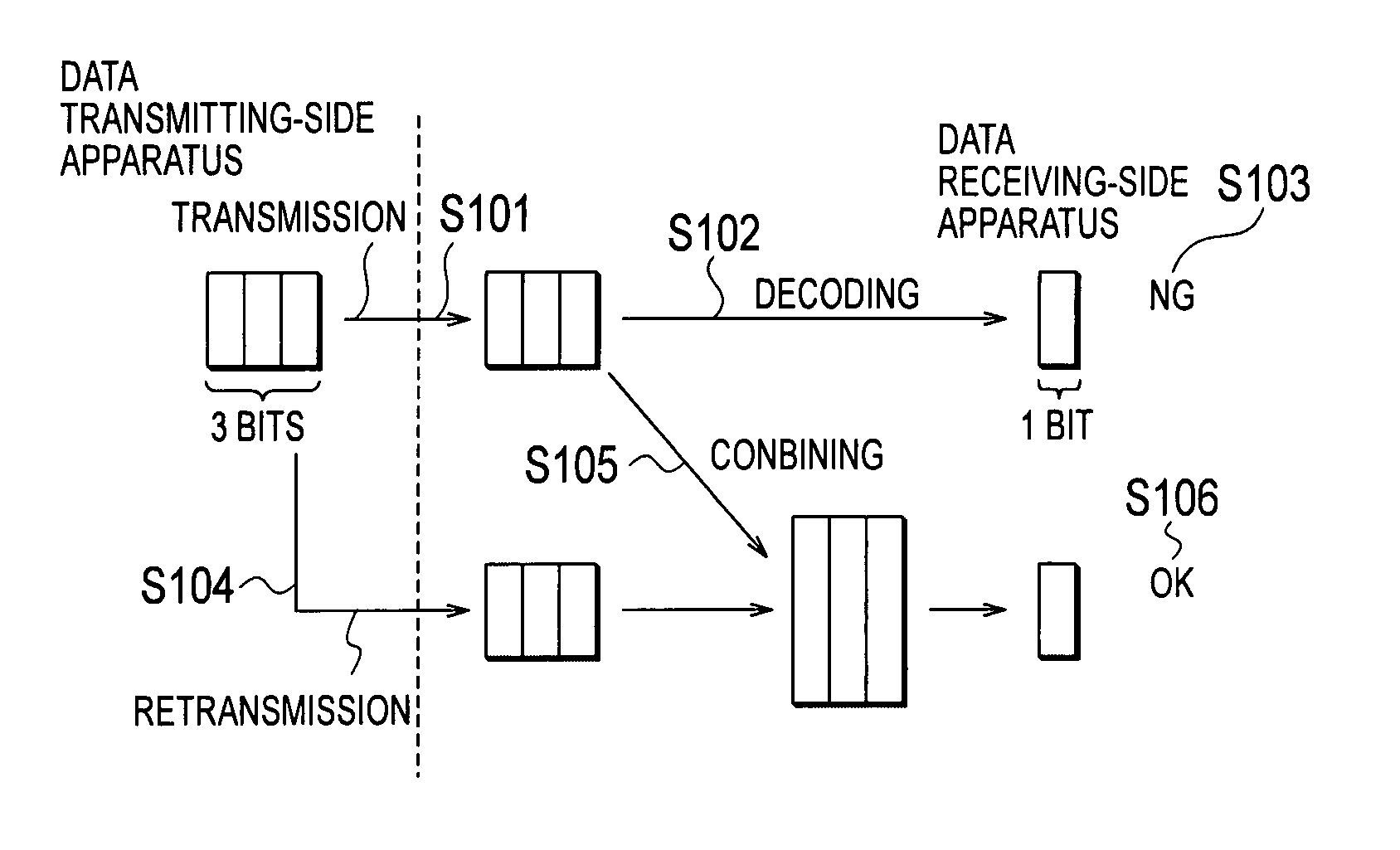
In a mobile communication system according to the present invention, based on a transmission acknowledgement signal transmitted from a data receiving-side apparatus, a data transmitting-side apparatus is configured to retransmit a transmission data block by using a data channel and a control channel, and the data receiving-side apparatus is configured to apply a soft combining to the retransmitted transmission data block. The data transmitting-side apparatus is configured in such a way that the number of retransmissions of the transmission data block can be set to 0.
Owner:NTT DOCOMO INC
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com