Semi-rigid base material for high grade pavement and preparation method thereof
A semi-rigid base, high-grade technology, applied in the field of pavement base materials, can solve problems such as reducing road construction costs, excessive mining of sand and gravel materials, etc., to reduce road construction costs, solve serious environmental problems, and promote sustainable development.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0032]A method for preparing a high-grade pavement semi-rigid base material, the steps of which are as follows:
[0033] (1) Quicklime and phosphogypsum are mixed and ground; during the mixing and grinding process of phosphogypsum and quicklime, quicklime can absorb part of the water in phosphogypsum, which can greatly increase the fineness of phosphogypsum and make their activity fully exerted;
[0034] (2) The mixed ground material obtained after quicklime and phosphogypsum powder and fly ash, biological coagulation enzyme, iron tailings waste rock and crushed iron tailings waste rock, iron tailings sand are mixed evenly by mass ratio;
[0035] (3) Finally, add cement and polypropylene fiber and mix well.
Embodiment 1
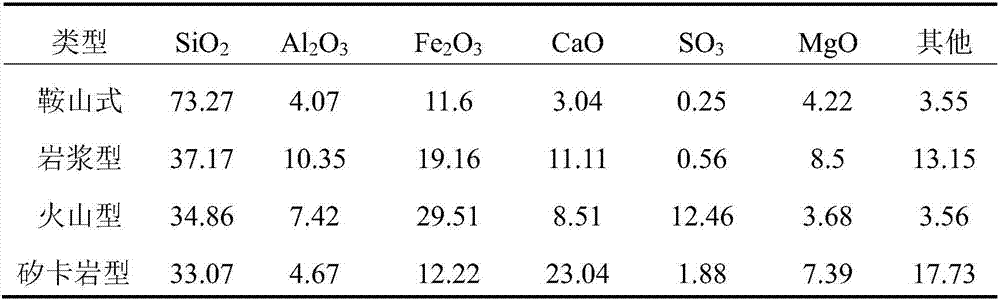
[0037] In a method for comprehensively utilizing Anshan-type iron tailings waste rock and iron tailings sand to prepare high-grade pavement semi-rigid bases, the cement uses 32.5-grade ordinary Portland cement, high-quality quicklime, and the active ingredient of fly ash is greater than 70%, and bio-agglomeration The enzyme product is a dark brown transparent liquid, easily soluble in water, with a density of about 1g / cm 3 Left and right, it is weakly acidic.
[0038] Table 4 shows the chemical composition of Anshan-style iron tailings.
[0039] Table 4 Chemical composition of Anshan-style iron tailings
[0040]
[0041] The method for preparing a semi-rigid base course for high-grade pavement using iron tailings comprises the following steps: mixing quicklime and phosphogypsum for 16 hours and then pulverizing them, adding fly ash, waste iron tailings and crushed iron tailings in proportion Stone, iron tailings sand, biological coagulation enzyme, and then add cement and...
Embodiment 2
[0043] Example 2: Comprehensive stabilization of magmatic iron tailings by using industrial waste phosphogypsum, other inorganic binders and admixtures. Table 5 shows the chemical composition of magmatic iron tailings.
[0044] Table 5 Chemical composition of magmatic iron tailings
[0045]
[0046] Steps: Mix quicklime and phosphogypsum for 16 hours and grind them finely for later use, add fly ash, waste iron tailings and crushed iron tailings waste, iron tailings, biocoagulation enzyme and mix well, then add cement and Polypropylene fibers make the compound. Among them, 7% of fly ash, 9% of quicklime, 8.8% of phosphogypsum, 68% of waste iron tailings and crushed iron tailings, 3% of iron tailings and 4.2% of cement, biocoagulation enzyme accounted for the total amount of the mixture 2%, polypropylene fiber 1.5kg / m 3 .
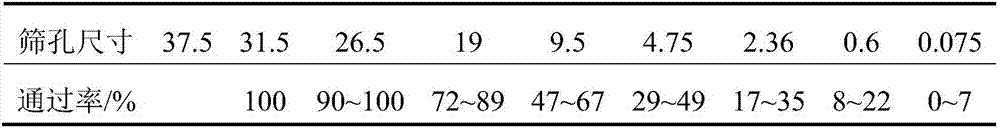
[0047] At this mix ratio, the strength of iron tailings used as pavement base material can meet the specified road use standards for expressways and fi...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Dry density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Unconfined compressive strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com