Method of separating and purifying eicosapentaenoic acid ester and docosahexaenoic acid ester via simulated moving bed chromatography
A technology of simulating moving bed and carbopentaenoate, applied in chemical instruments and methods, preparation of carboxylate, preparation of organic compounds, etc., can solve the problems of increasing equipment cost, solvent consumption, complicated SMB separation and purification process, etc. Achieve the effect of saving equipment consumption, reducing costs and saving solvents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
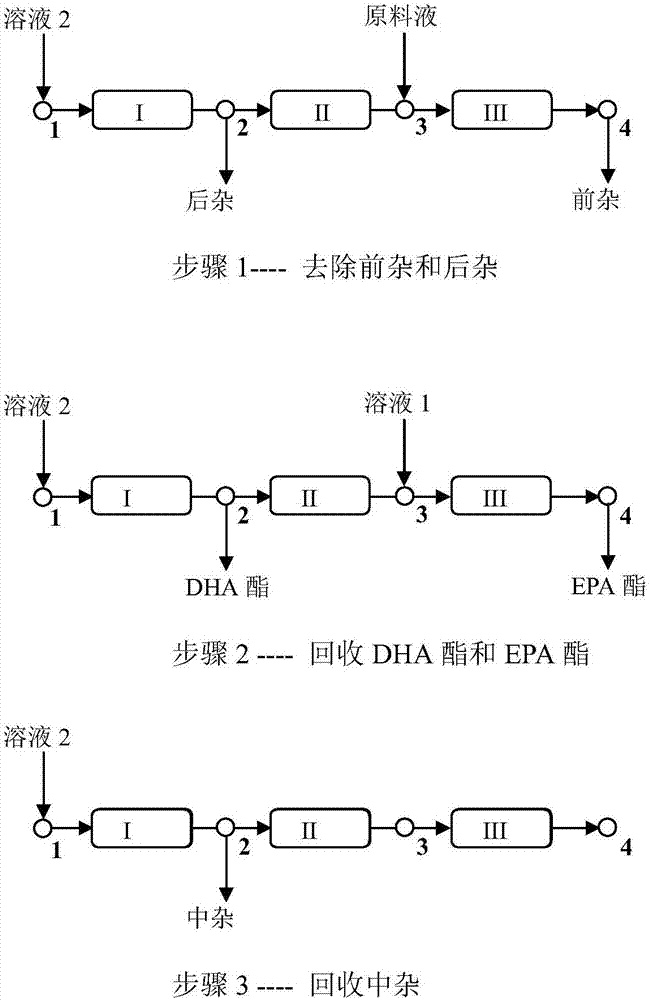
[0044] Embodiment 1 (see figure 1 shown)
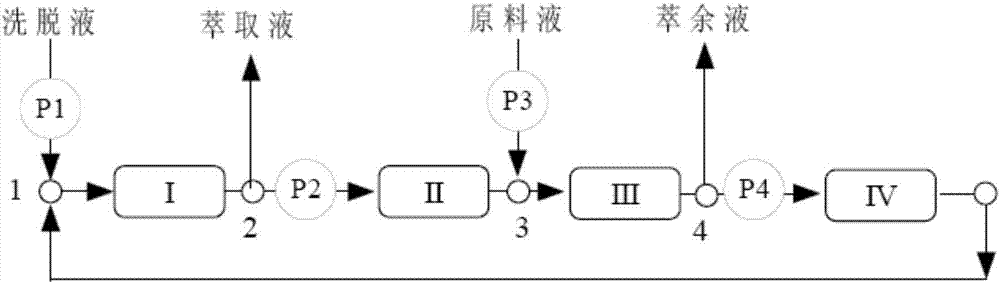
[0045] 2 pillars are arranged in Zone I, Zone II and Zone III respectively. and disable as image 3 The circulating pump P4 in zone IV of the traditional simulated moving bed equipment shown (equivalent to not using zone IV, only an open-loop simulated moving bed with three zones).
[0046] Step 1—removal of pre-impurity and post-impurity feed: the raw material liquid and solution 2 are pumped into the simulated moving bed separation system from the feed port 3 and the eluent inlet 1 at the flow rate of 1mL / min and 4mL / min respectively; II Zone flow control is 3mL / min. Every 5 minutes, the eluent inlet 1 and feed inlet 3 are switched to the next column inlet along the liquid flow direction, while the raffinate outlet 4 and extract outlet 2 flow along the liquid flow direction. Direction moves to the next column exit. The composition of the raffinate and the extract was analyzed by high performance liquid chromatography, and the r...
Embodiment 2
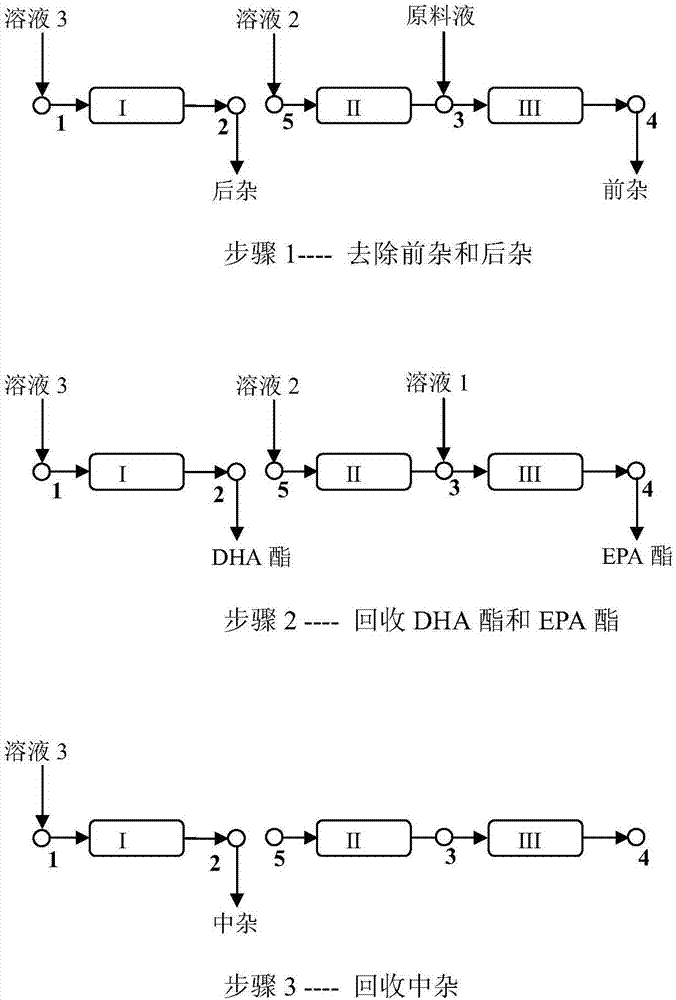
[0050] Embodiment 2 (see figure 2 shown)
[0051] Adopt the simulated moving bed among the embodiment 1, but disconnect the I zone and II zone wherein, solution 2 directly flows into II zone through II zone inlet 5, and wash I zone with pure methanol, and I zone effluent liquid is all collected for the extract. All the other operating conditions and operating steps are the same as in Example 1. The experimental results show that the product separation purity does not change.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com