Electrolyte for micro-electrolytic machining of metal glass
A micro-electrolysis and metallic glass technology, applied in the field of electrolyte, can solve problems such as unstable processing, poor surface quality, and low processing efficiency, and achieve the effects of accelerating charge exchange rate, small environmental impact, and improving processing efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
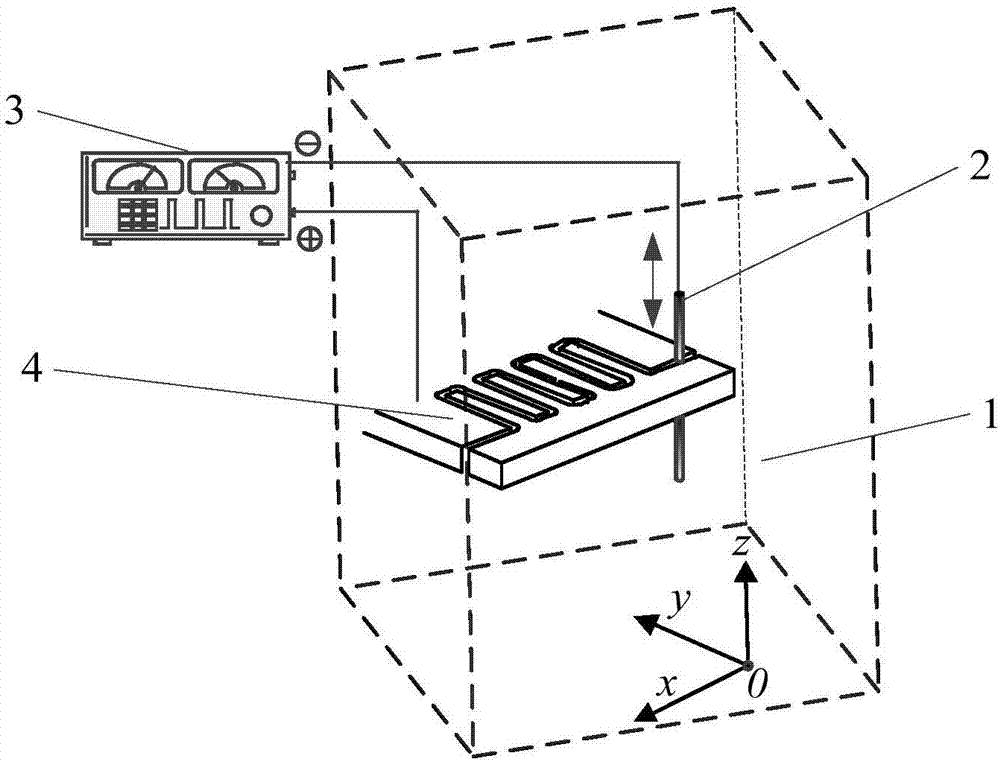
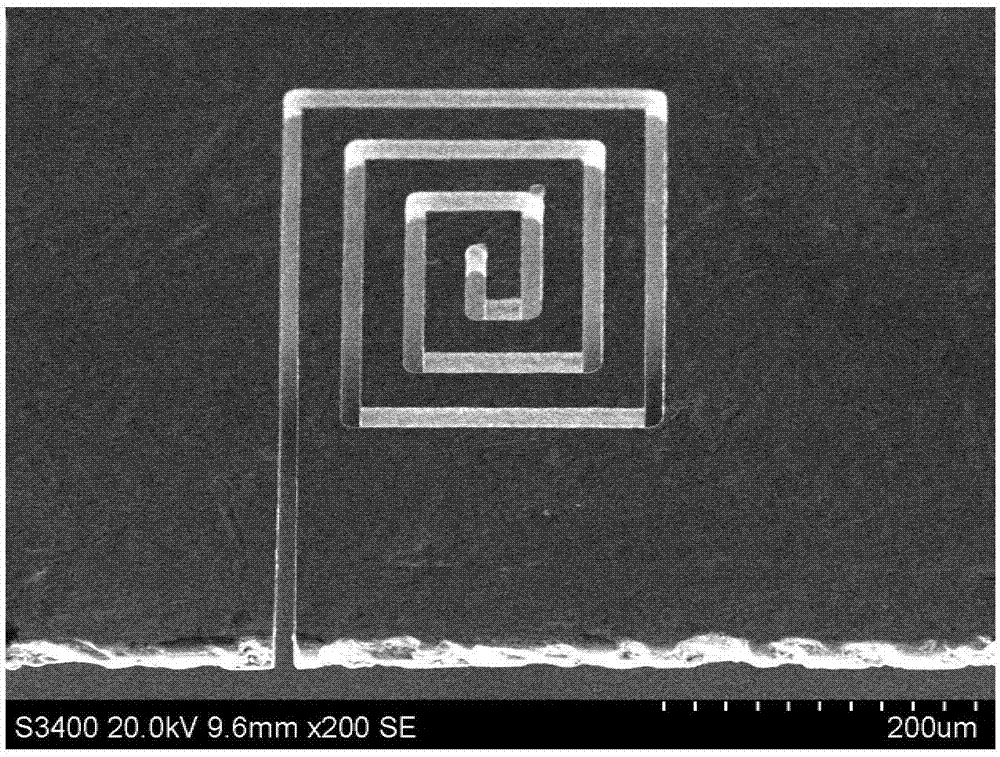
[0032] At room temperature, sulfuric acid and deionized water were mixed at a mass ratio of 0.1:99.9 to form a solution, the mass fraction of the sulfuric acid (5) was 98%, analytically pure, and the deionized water (7) was an industrial standard reagent. Connect the positive pole of the pulse power supply to the nickel-based metallic glass (nickel, chromium, silicon, and boron mass ratio is 72:19:7:2), and the negative pole to the electrode wire, using 5V voltage, 80ns pulse width, 3μs period, and processing speed 0.5 μm / s. The slit width of the processed graphics is 18 μm, the standard deviation of the slit width is 0.2 μm, and the processed surface is smooth, such as Figure 4 shown.
Embodiment 2
[0034] At room temperature, mix sulfuric acid and deionized water at a mass ratio of 1:4 to make a solution, connect the positive electrode of the pulse power supply to nickel-based metal glass (the mass ratio of nickel, chromium, silicon, and boron is 72:19:7:2), and the negative electrode Connect the electrode wire, use 5V voltage, 80ns pulse width, 3μs cycle, and processing speed 0.5μm / s. The slit width of the processed graphics is 25 μm, the standard deviation of the slit width is 0.3 μm, and the surface quality is good, such as Figure 5 shown.
Embodiment 3
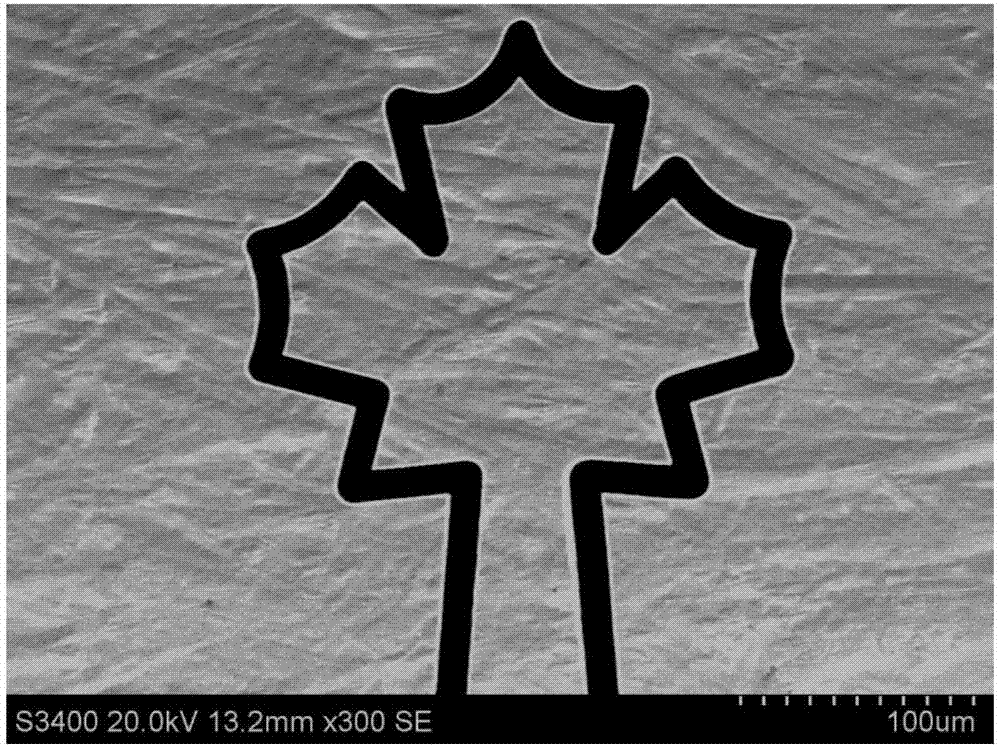
[0036] At room temperature, mix sulfuric acid, hydrogen peroxide, and deionized water at a mass ratio of 0.1:1:98.9 to form a solution, and connect the positive electrode of the pulse power supply to nickel-based metal glass (nickel, chromium, silicon, and boron in a mass ratio of 72:19: 7: 2), the negative electrode is connected to the electrode wire, using 5V voltage, 80ns pulse width, 3μs period, and processing speed 0.5μm / s. The slit width of the processed graphics is 14 μm, the standard deviation of the slit width is 0.2 μm, and the surface quality is good, such as Figure 6 shown.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com