Manufacturing method of controllable-temperature microfluidic chip
A technology of microfluidic chips and manufacturing methods, applied in chemical instruments and methods, laboratory containers, laboratory utensils, etc., can solve problems such as limited heat transfer capacity, complex device structure, and increased maintenance difficulty. The effect of high control precision and fast heating and cooling speed
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
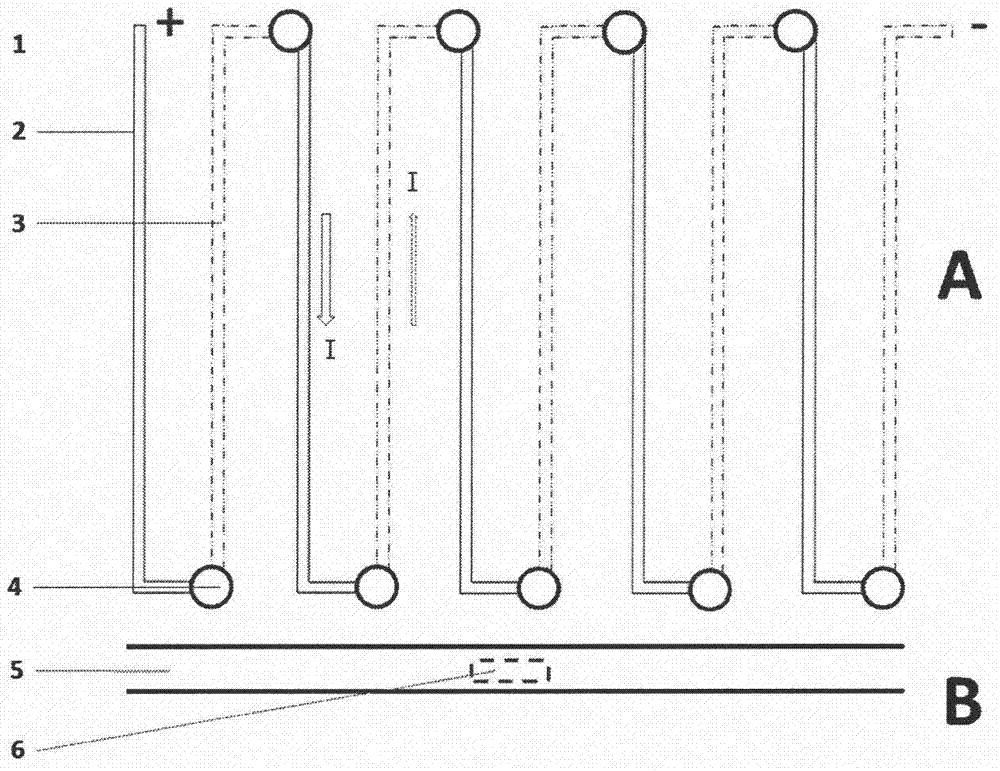
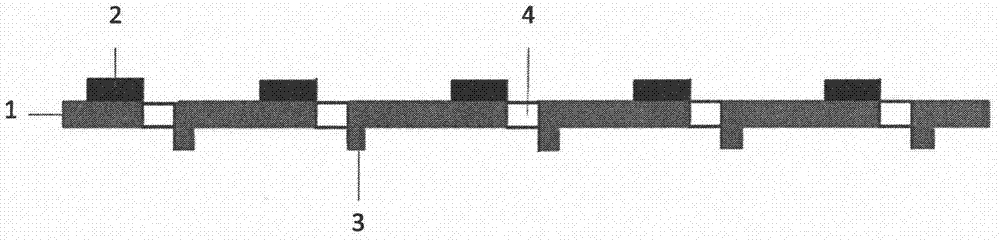
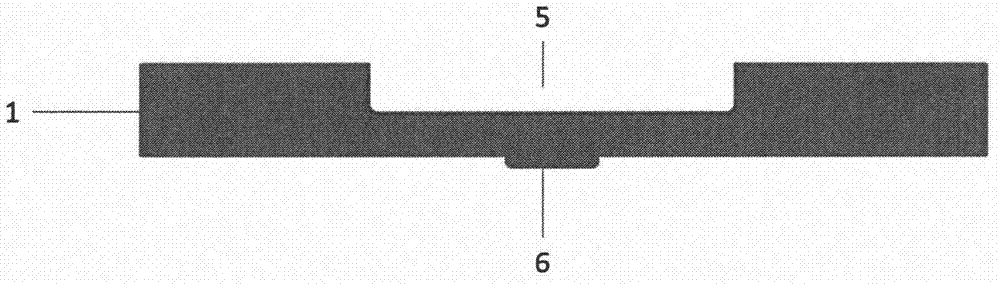
[0025] designed as figure 1 The temperature-controllable microfluidic chip shown has a planned reaction groove area and a temperature-controlled circuit area. The substrate adopts an alumina ceramic substrate, and a reaction groove is processed by laser ablation on one side of the reaction groove area, and a thermocouple temperature measuring probe is printed on the back of the reaction groove. N-type Bi sputtered by mask magnetron sputtering on the front side of the temperature control line area 0.5 Sb 1.5 Te 3 Circuit layer of thermoelectric material, P-type Bi2Te sputtered by mask magnetron sputtering on the back 2.7 Se 0.3 For the circuit layer of thermoelectric materials, through holes are drilled in the line section, and copper is electroplated in the through holes to form an alternating series circuit structure of N-P-N-P..., such as figure 1 When the circuit is connected as shown, the cooling of the reaction tank is realized. The schematic diagram of the cross-se...
Embodiment 2
[0027] designed as figure 1 The temperature-controllable microfluidic chip shown has a planned reaction groove area and a temperature-controlled line area. The substrate adopts a silicon substrate, a groove for reaction is processed by mask photolithography on one side of the reaction groove area, and a thermocouple temperature measuring probe is printed on the back of the reaction groove. On the front side of the temperature control circuit area, the circuit layer of N-type PbTe thermoelectric material is vacuum-evaporated, and the circuit layer of P-type PbSe thermoelectric material is vacuum-evaporated on the back. Through holes are drilled in the line section, and silver is electroplated in the through holes to form Alternating series line structure of N-P-N-P…, such as figure 1 When the circuit is connected as shown, the cooling of the reaction tank is realized. The schematic diagram of the cross-sectional structure of the through hole in the temperature control circuit...
Embodiment 3
[0029] designed as figure 1 The temperature-controllable microfluidic chip shown has a planned reaction groove area and a temperature-controlled line area. The substrate adopts a hard polyimide substrate, and a groove for reaction is processed by hot molding on one side of the reaction groove area, and an NTC temperature measuring probe is printed on the back of the reaction groove. In the temperature control line area, the circuit layer of N-type Bi paste thermoelectric material is screen-printed on the front side, and the circuit layer of P-type BiSb paste thermoelectric material is screen-printed on the back side. After drying, through holes are drilled in the line section. Gold is electroplated in the through hole to form an alternating series circuit structure of N-P-N-P..., such as figure 1 When the circuit is connected as shown, the cooling of the reaction tank is realized. The schematic diagram of the cross-sectional structure of the through hole in the temperature c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com