Method for remediating nickel and chlorinated organic compound combined polluted environmental water
A technology for chlorinated organic compounds and complex pollution, applied in water pollutants, chemical instruments and methods, water/sewage treatment, etc., to achieve the effects of promoting dispersion, increasing reaction sites, and improving reduction efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
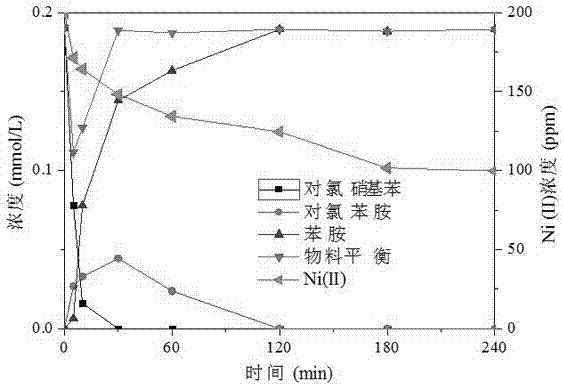
[0025] Bentonite-loaded nanometer zero-valent iron and zero-valent iron respectively repair Ni(II) (200mg / L) and chloronitrobenzene (30mg / L) composite polluted water (pH 6) comparison, according to the following steps:
[0026] (1) in N 2 Under protection, 0.5g / L sodium bentonite, 0.05mol / L FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O and 0.1mol / L NaBH 4 Mix and stir for 4 hours, wash with deoxygenated water and ethanol, and vacuum freeze-dry to prepare bentonite-supported nano-iron.
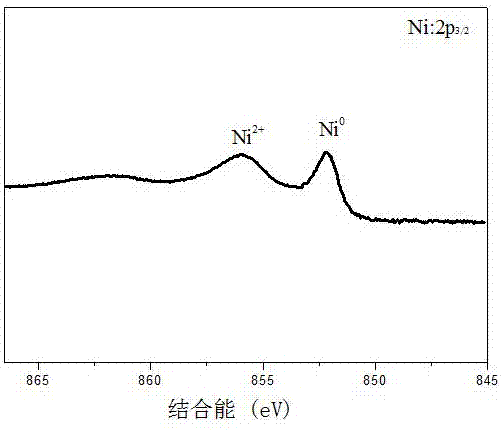
[0027] (2) Weigh the bentonite-loaded zero-valent iron (30mg iron content) prepared in step (1) and the zero-valent iron containing the same amount of Fe and add them to the solution containing 200mg / L Ni(II) and 30mg / L chlorinated In the complex pollution wastewater of nitrobenzene (pH adjusted to 6), in N 2 Under protection, shake the reaction for 2 hours (150 rpm, 25°C). After the reaction, the concentration of residual Ni(II) and other products and concentrations in the wastewater were determined by atomic absorptio...
Embodiment 2
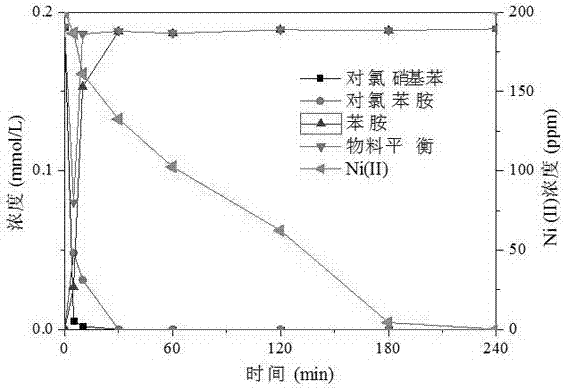
[0029] Bentonite-loaded nano-zero-valent iron repairs Ni(II) (100mg / L) and dichlorophenol (20mg / L) composite polluted water (pH 6), according to the following steps:
[0030] (1) in N 2 Under protection, 0.5g / L sodium bentonite, 0.05mol / L FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O and 0.1mol / L NaBH 4 Mix and stir for 2 hours, wash with deoxygenated water and ethanol, and vacuum freeze-dry to prepare bentonite-loaded nano-iron.
[0031] (2) Weigh the bentonite-loaded zero-valent iron (60 mg iron content) prepared in step (1) and add it to the composite polluted wastewater containing 100 mg / L Ni(II) and 20 mg / L dichlorophenol (pH adjusted to 6 ), at N 2 Under protection, shake the reaction for 4 hours (150 rpm, 25°C). After the reaction, the concentration of residual Ni(II) and other products and concentrations in the wastewater were determined by atomic absorption spectroscopy and high performance liquid chromatography, respectively. The results show that after 60 minutes of reaction, dichlorophenol...
Embodiment 3
[0033] The comparison of bentonite-loaded nano-zero-valent iron repairing Ni(II) (80mg / L) and dichloroethane (30mg / L) composite polluted water (pH 6) was carried out according to the following steps:
[0034] (1) in N 2 Under protection, 0.5g / L sodium bentonite, 0.05mol / L FeSO 4 ·7H 2 O and 0.1mol / L NaBH 4 Mix and stir for 2 hours, wash with deoxygenated water and ethanol, and vacuum freeze-dry to prepare bentonite-loaded nano-iron.
[0035](2) Weigh the bentonite-loaded zero-valent iron (40mg iron content) prepared in step (1) and zero-valent iron containing the same amount of Fe, and add them to the solution containing 80mg / L Ni(II) and 30mg / L dichloro In the complex pollution wastewater of methane (pH adjusted to 6), the N 2 Under protection, shake the reaction for 4 hours (150 rpm, 25°C). After the reaction, the concentration of residual Ni(II) and other products and concentrations in the wastewater were determined by atomic absorption spectroscopy and gas chromatogra...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle size (mesh) | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com