Patents
Literature
190 results about "Chloronitrobenzene" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Chloronitrobenzene may refer to: 2-Chloronitrobenzene 3-Chloronitrobenzene 4-Chloronitrobenzene
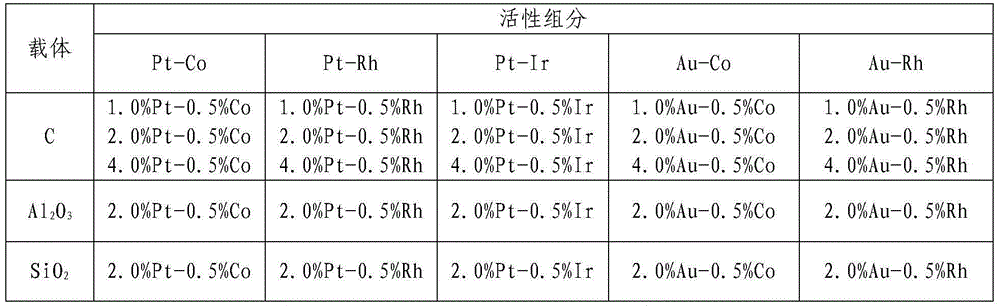
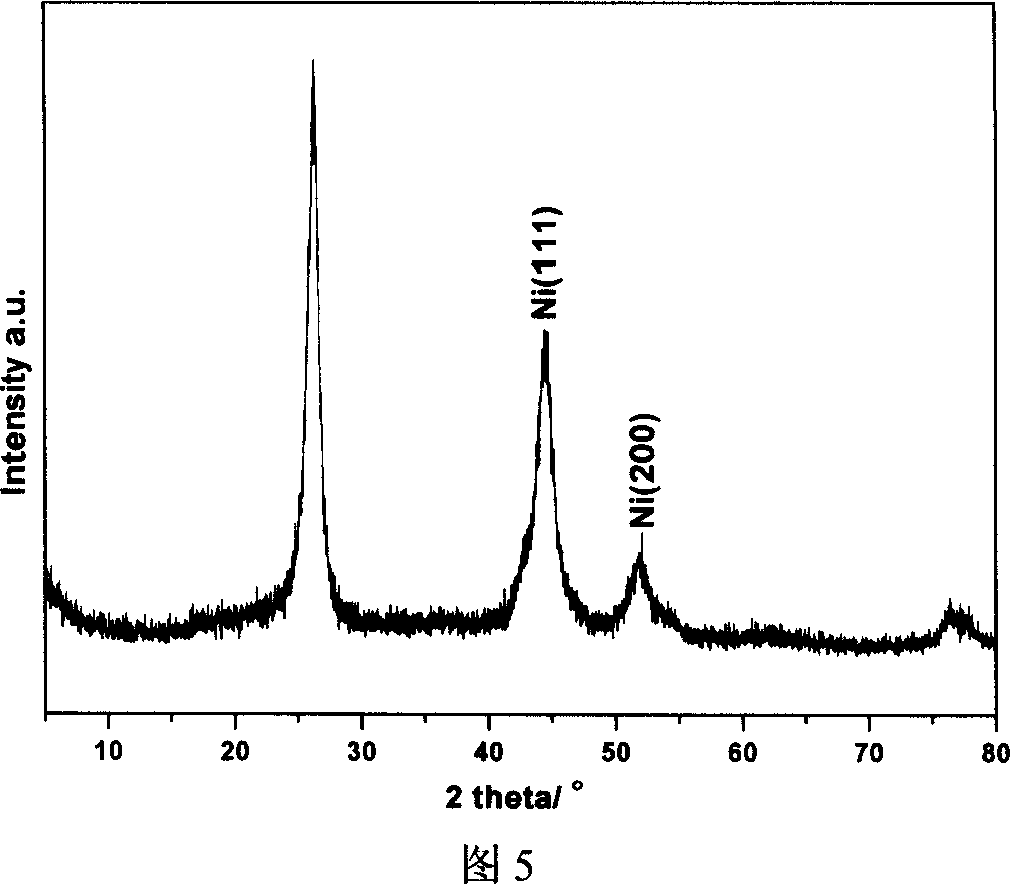
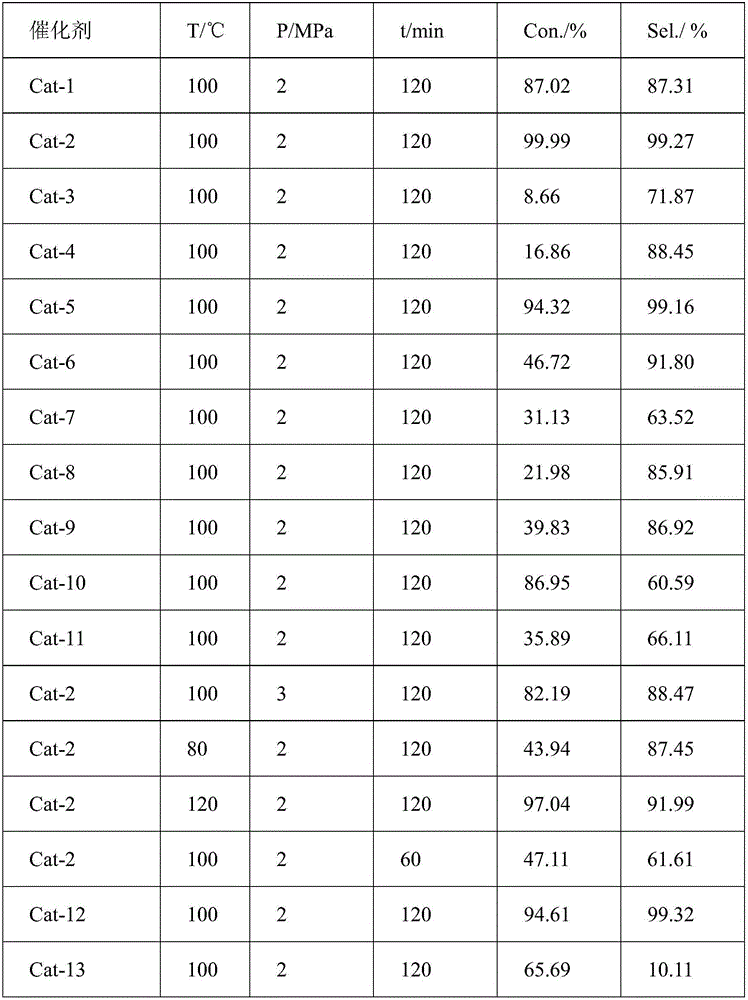
Mesoporous carbon microsphere supported composite catalyst as well as preparation method and application of mesoporous carbon microsphere supported composite catalyst
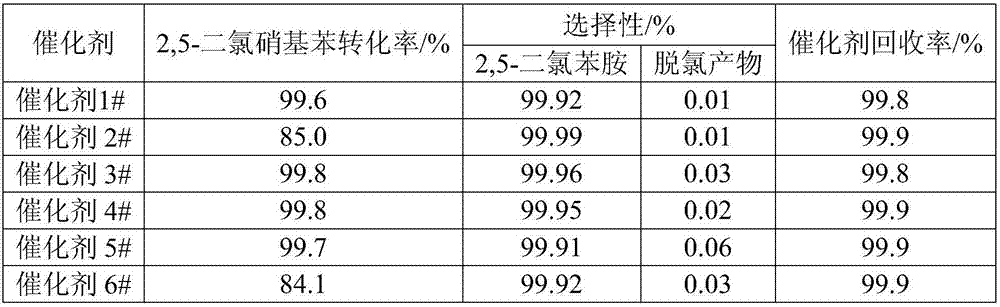
ActiveCN107413335AAvoid uncontrollabilityAvoid stabilityOrganic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationIridiumMicrosphere
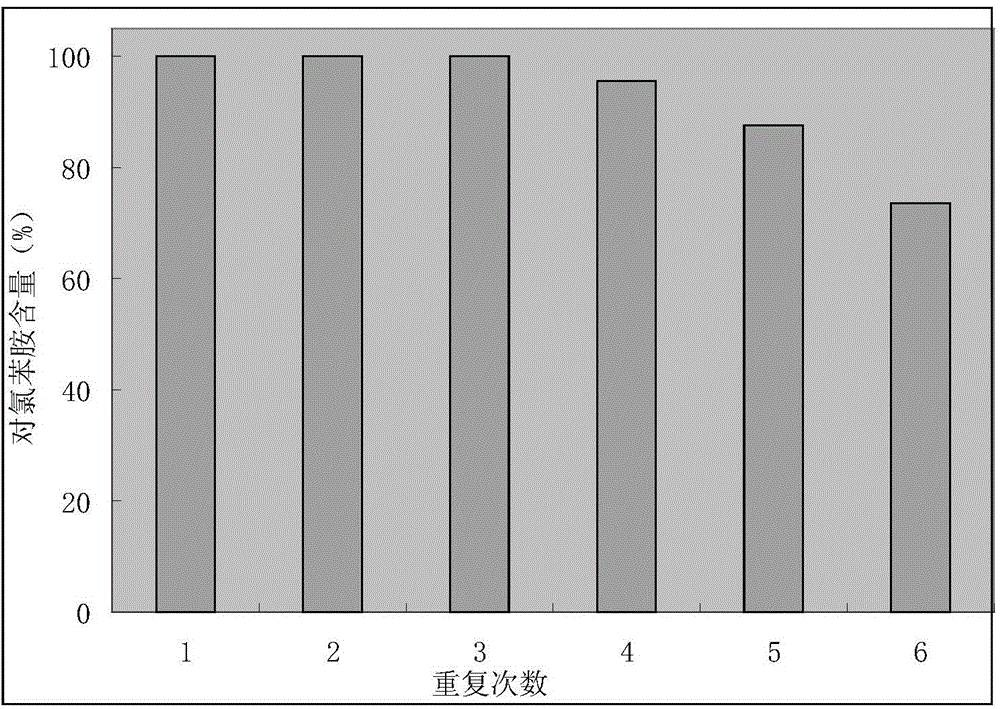
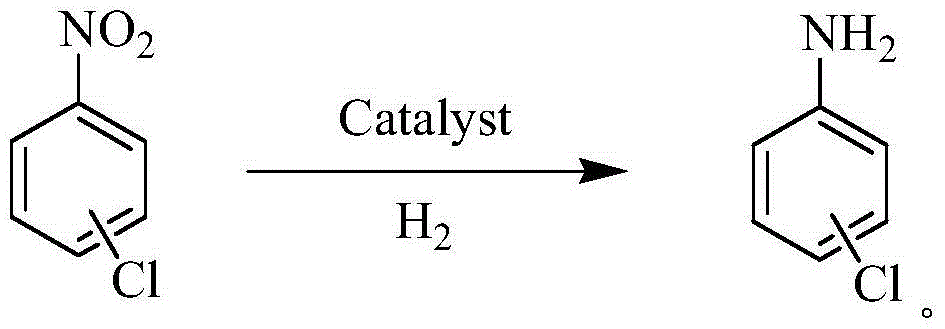
The invention discloses a mesoporous carbon microsphere supported composite catalyst as well as a preparation method and application of the mesoporous carbon microsphere supported composite catalyst. The catalyst is composed of a mesoporous carbon microsphere as well as an active component and a carbon quantum dot which are supported on the mesoporous carbon microsphere; the particle size of the catalyst ranges from 100nm to 1000nm; the active component is one or a combination of several of platinum, palladium, iridium, ruthenium and rhodium; the loads of metals in the active component are as follows: 0wt%-10.0wt% of palladium, 0wt%-10.0wt% of platinum, 0wt%-10.0wt% of iridium, 0wt%-10.0wt% of ruthenium and 0wt%-10.0wt% of rhodium, and not all the loads of palladium, platinum and rhodium are equal to zero; the total load of the active component is 1.0-20%; and the load of the carbon quantum dot is not higher than 30.0wt%. The invention provides the application of the mesoporous carbon microsphere supported composite catalyst to reaction for synthesizing chloroaniline shown as a formula (II) by carrying out selective catalytic hydrogenation on chloronitrobenzene shown as a formula (I) to show that the mesoporous carbon microsphere supported composite catalyst has the characteristics of high conversion rate, high catalytic activity and high stability.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
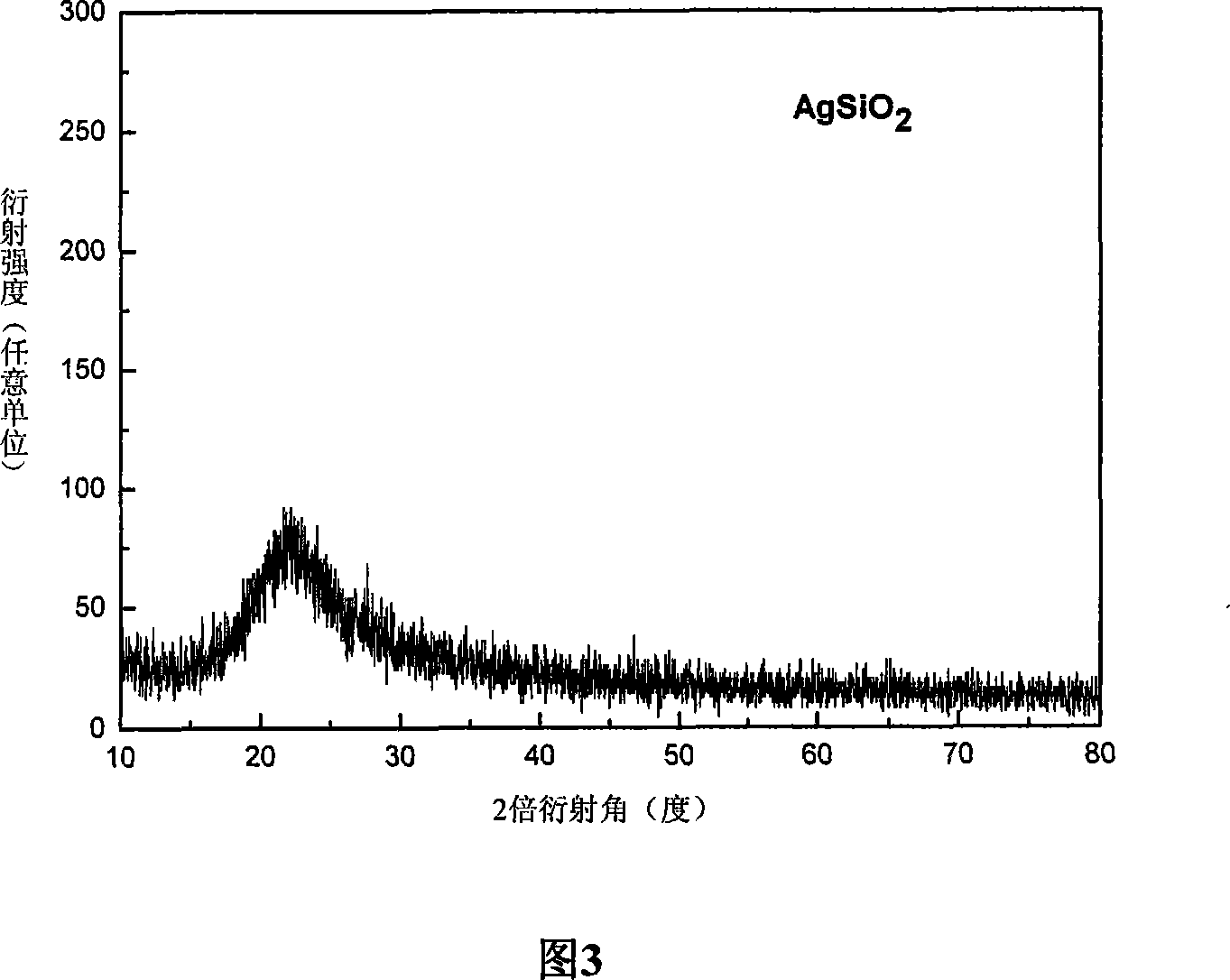
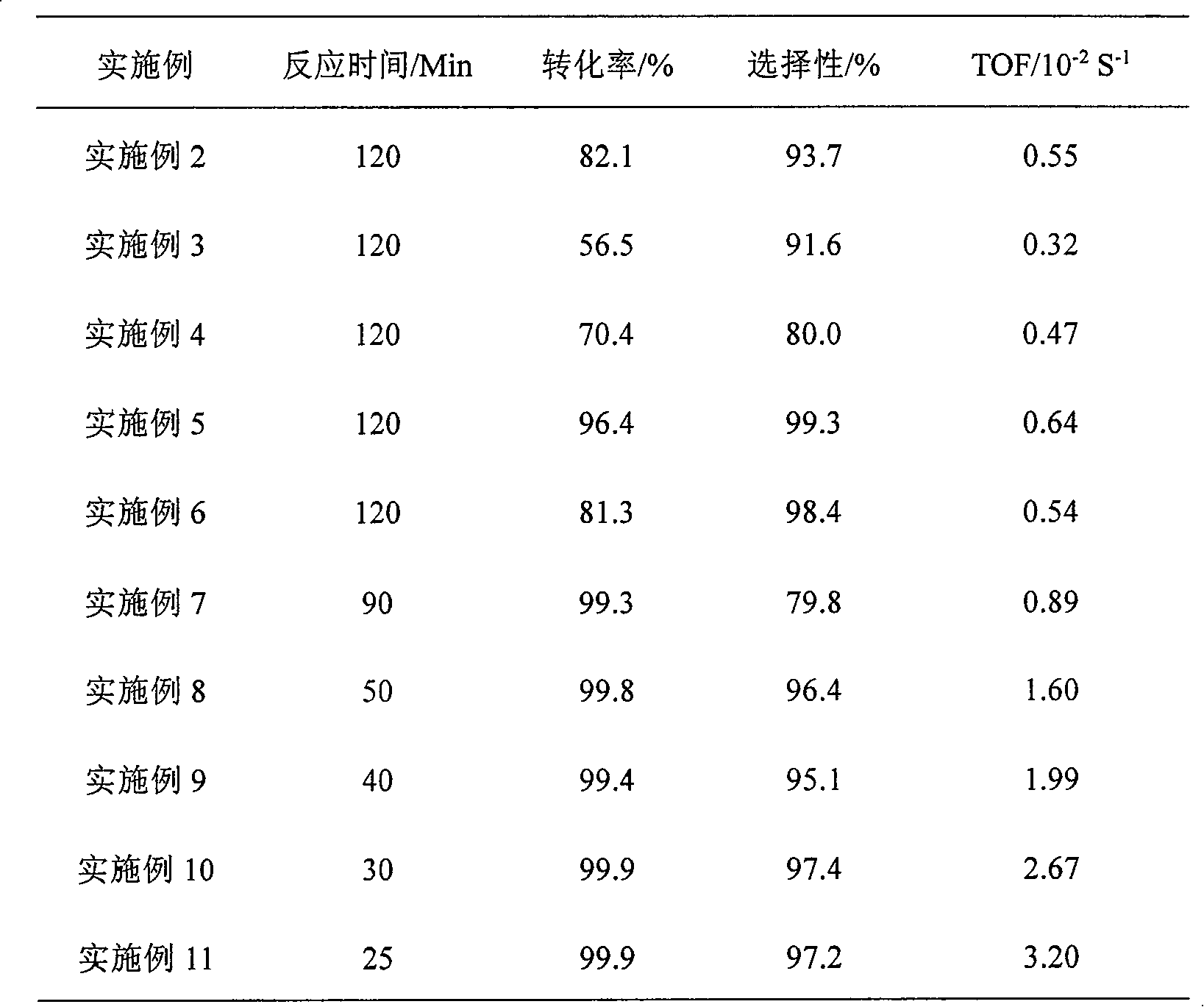
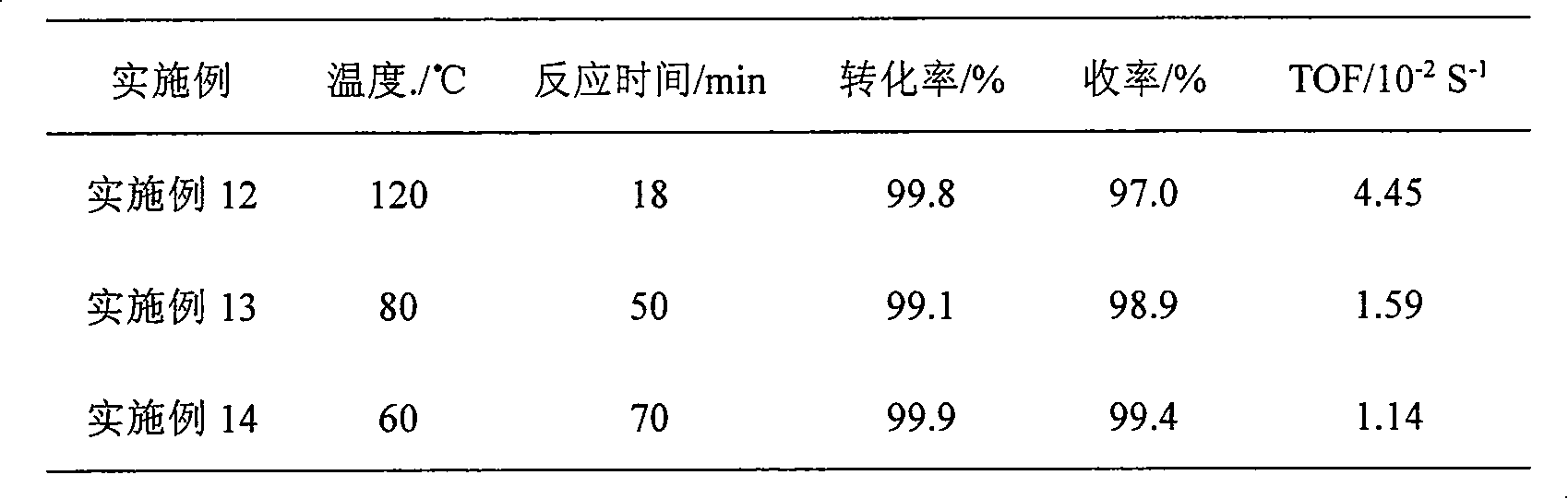
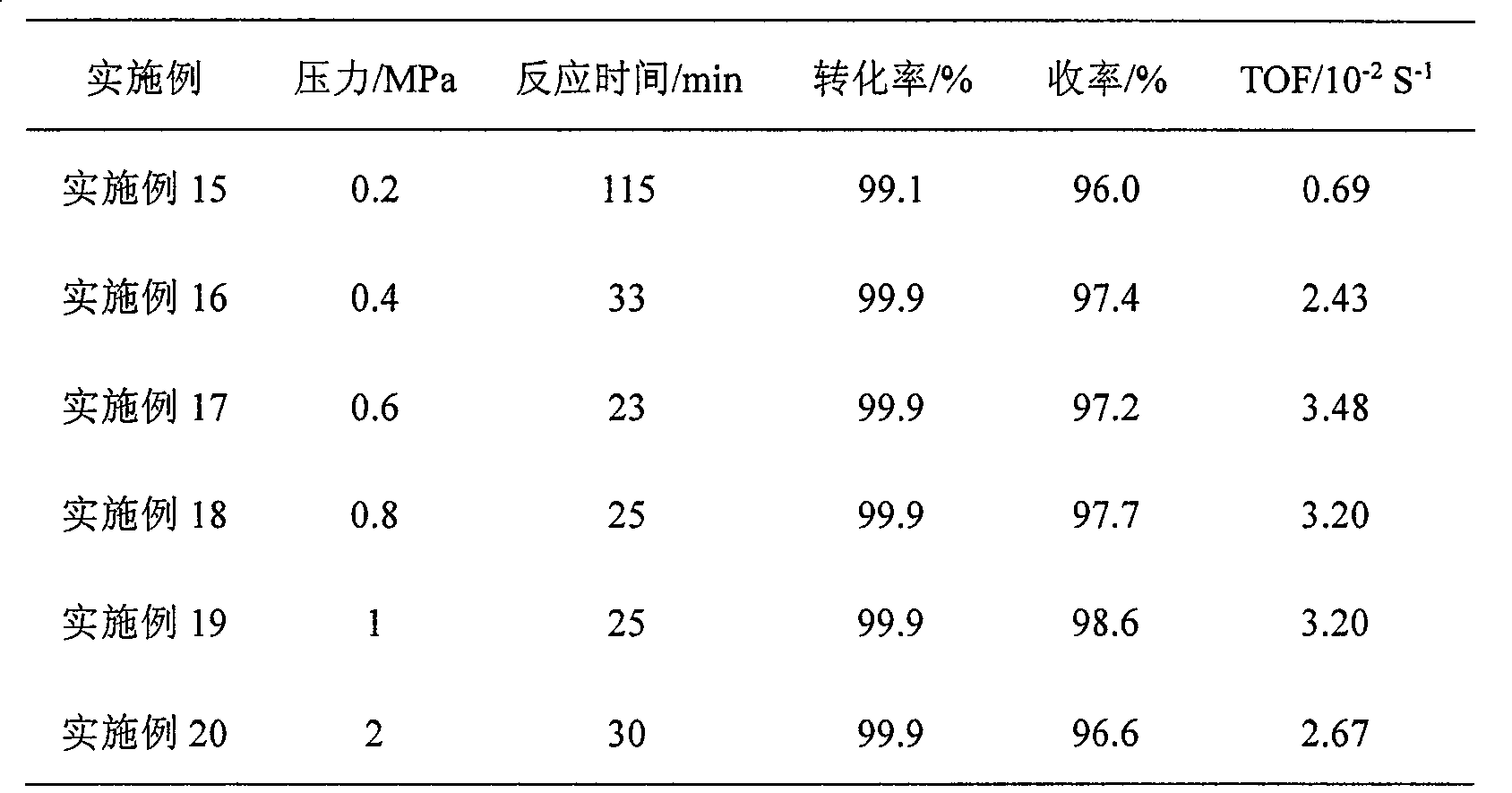
SiO2 supported nanometer silver catalyst, preparing method and applications thereof
InactiveCN101224422ALow costHigh yieldOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationNitro compoundPolyamide
The invention discloses a catalyst for loading silver on SiO2, a preparation method and application in a selective catalytic hydrogenation of chloro-aromatic compounds, nitryl-aromatic ene, nitryl-aromatic aldehydes, nitryl-aromatic ketone, and nitryl-aromatic polyamide. The synthetic method is that tetraethoxysilane and aminopropyl-triethoxysilane are added by weight proportion of 1: 0.1-1: 25 into an ammonia solution containing definite AgNO3, then the solution is stirred to form gelatinate under room temperature and dried under 100-200 DEG C for about 4-12 hours, thus obtaining the catalyst. The synthetic catalyst of the invention solves two problems of current catalytic hydrogenation of aromatic nitro-compounds: (1) a secondary reaction of dechlorination is generated during the hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzenes of aromatic nitro-compounds; (2) the selectivity of reaction is poor when alkene, aldehydes, ketone, nitrile and amide groups coexist.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Method for synthesizing chloro-aniline by chloronitrobenzene selective hydrogenation in alcohol-water system
InactiveCN101195579AFacilitate desorptionHigh activityOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationAlcoholNitrobenzene
Provided is a method for synthesizing chlorophenylamine, which adopts chloronitrobenzene as raw material to react under the temperature of 40-140 DEG C and the pressure of 0.2-4 Mpa and the existence of composite solution of alcohol and water and catalyst, wherein the chloronitrobenzene is selectively hydrogenated to produce chlorophenylamine. The method uses alcohol water as solvent and is directly applied in the chloronitrobenzene which is selectively hydrogenated to produce chlorophenylamine, thereby the method has the advantages of high catalyst activity, milder reaction condition and high the yield.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Pollution-depth degradation method of high-concentration chloronitrobenzene in soil by combination of solubilization and fenton oxidation of mixed surface active agent
ActiveCN103624074AImprove efficiencyReduce adsorption lossContaminated soil reclamationHigh concentrationSurface-active agents
The invention discloses a pollution-depth degradation method of high-concentration chloronitrobenzene in soil by combination of solubilization and fenton oxidation of a mixed surface active agent. The pollution-depth degradation method comprises the following steps: preparing and mixing aqueous solution of sodium dodecyl benzene sulfonate of an anionic surface active agent with certain concentration and a non-ionic surface active agent Tween -80 aqueous solution, putting polluted soil into the solution of the mixed surface active agent, and separating and discharging the solution of the mixed surface active agent after full contact reaction; adding a certain amount of water into the polluted soil after solubilizing treatment, mixing uniformly to prepare soil turbid liquid, and adjusting the pH value of the soil turbid liquid to be acid; adding ferrous sulfate for complete dissolving, then adding hydrogen peroxide slowly for stirring reaction, and after the reaction is finished, standing and discharging the upper-layer aqueous solution after the soil particles are completely sunk to the bottom layer. With the adoption of the surface active agent for solubilization, the pollution-depth degradation method disclosed by the invention has the advantages that high-concentration organic pollution can be economically removed, and the pollutant removing effect can be further optimized by the subsequent fenton oxidation. The pollution-depth degradation method is simple and easy and is suitable for large-scale production and use.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES
Method and catalyst for synthesizing chloroaniline from chloronitrobenzene by virtue of selective catalytic hydrogenation
ActiveCN104418756AEasy to makeHigh catalytic activityOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationHydrogenation processAniline
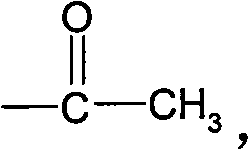
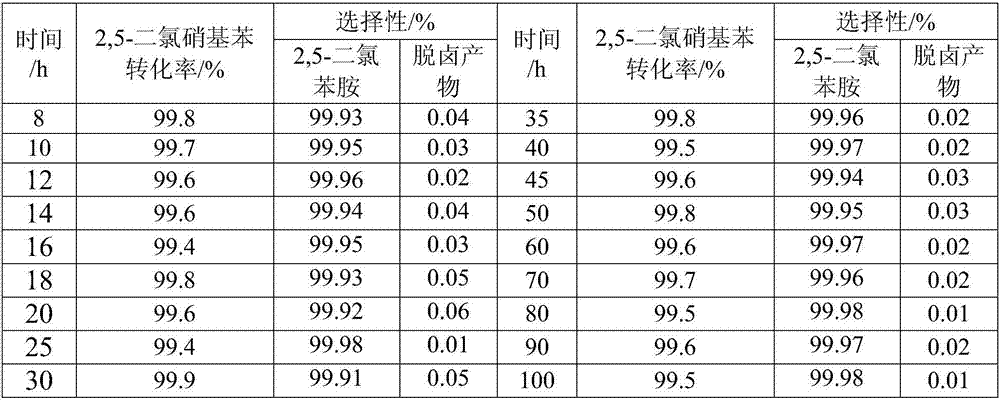
The invention relates to a method for synthesizing chloroaniline and particularly relates to a method and a catalyst for synthesizing chloroaniline from chloronitrobenzene by virtue of selective catalytic hydrogenation. According to the method, a supported noble metal catalyst is utilized, hydrogen serves as a hydrogen source, chloronitrobenzene is subjected to selective hydrogenation in a liquid phase system to generate chloroaniline, and the selective hydrogenation process is presented by the following formula in the specification by virtue of liquid chromatography-mass spectrometric detection. The method is high in efficiency and reaction selectivity, mild in reaction condition and low in cost, and the operation is easily controlled.
Owner:YANTAI INST OF COASTAL ZONE RES CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
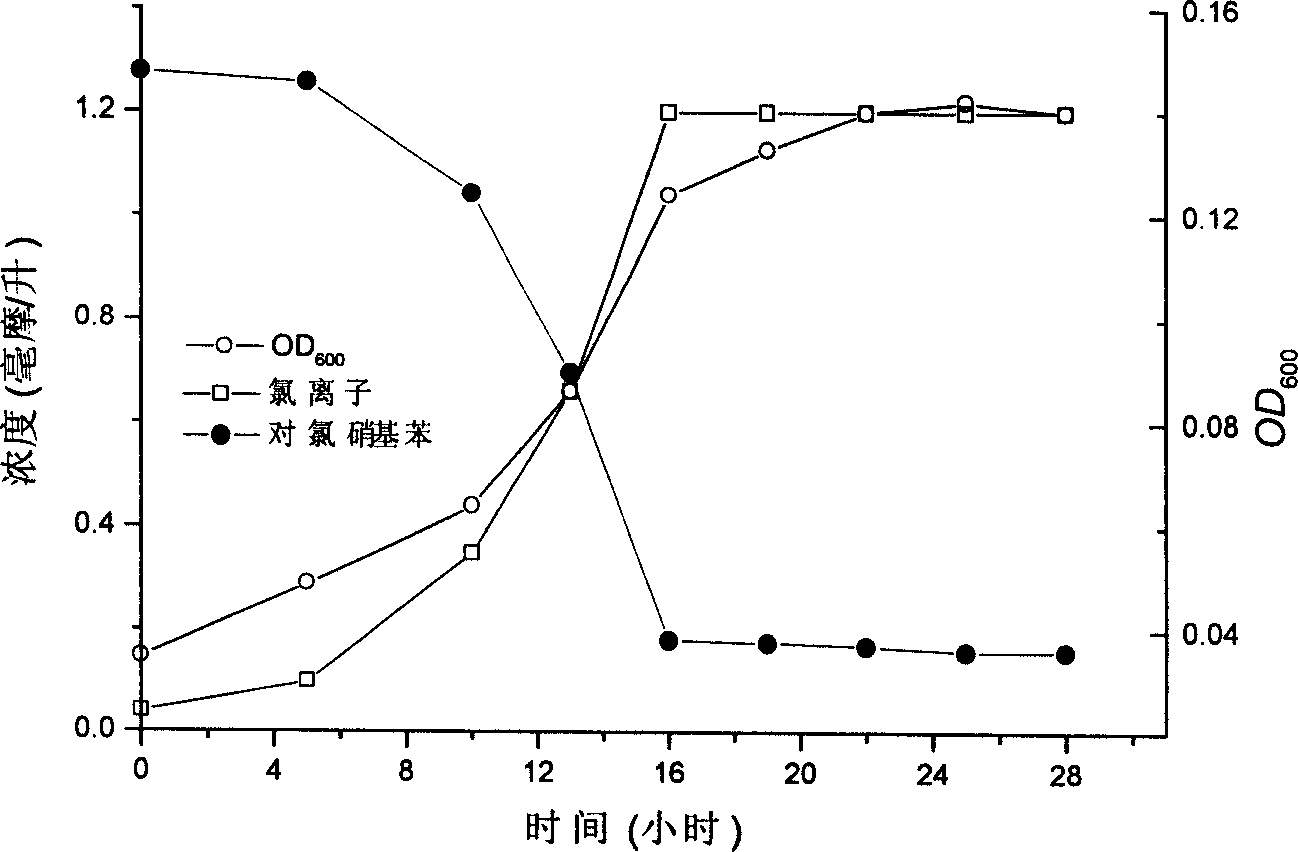
Para-chloro nitrobenzene degrading testosterone coma monad and its use
The present invention relates to one Comamonas testosteroni CNB1CGMCC No. 1028 strain, whose growing cell, cell suspension and immobile cell can degrade para-chloronitrobenzene. The strain can grow with para-chloronitrobenzene as unique carbon source, nitrogen source and energy source, so as to degrade and utilize para-chloronitrobenzene completely. During its growth, the strain first reduces nitro group into hydroxylamine, and produces 2-aminophenol 1, 6-bioxygenase to open the ring of 2-amino-5-chlorophenol into hydrocarbon through meta ring opening. The strain is suitable for the biological treatment of industrial effluent from para-chloronitrobenzene production and the biological repair of para-chloronitrobenzene polluted soil.
Owner:INST OF MICROBIOLOGY - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Prepn of nanometer carbon material supported metal catalyst for hydrogenating chloronitrobenzene to synthesize chloroaniline
InactiveCN101020136AReactiveSimple methodOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationFiberNitro compound
The present invention is preparation process of nanometer carbon material supported metal catalyst for hydrogenating chloronitrobenzene to synthesize chloroaniline. The preparation process includes depositing nanometer carbon material, carbon nanotube or nanometer carbon fiber as carrier in water or polyol solvent to obtain catalyst precursor, and baking in high temperature inertial atmosphere to reduce in reductive atmosphere. The nanometer carbon material supported metal catalyst with metal grains dispersed homogeneously on the surface of nanometer carbon material has high catalytic activity of hydrogenating chloronitrobenzene, simple preparation process, controllable performance and other advantages. The catalyst may be also used for hydrogenating nitro compounds.
Owner:DALIAN UNIV OF TECH
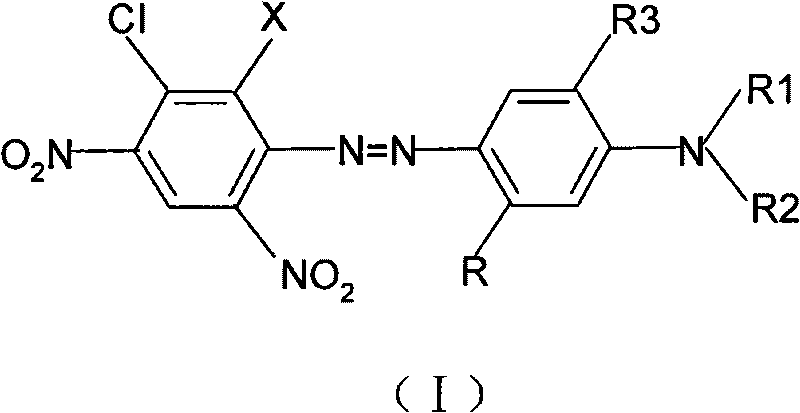
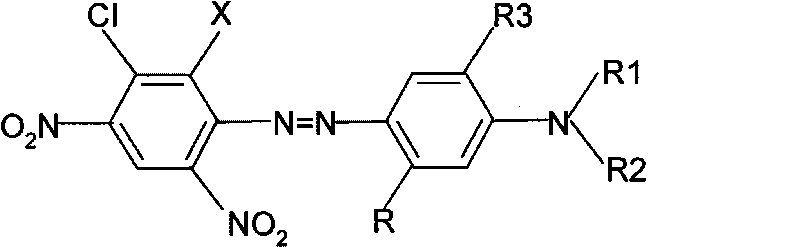
5-chloronitroaniline-containing azoic disperse dyes and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN101735665AImprove wet fastnessGood sublimation fastnessMonoazo dyesDyeing processDisperse dyeHydrogen
The invention provides 5-chloronitroaniline-containing azoic disperse dyes and a preparation method thereof. The structural general formula of the disperse dyes is shown in a formula (I), wherein X is hydrogen or bromine; R is hydrogen, methyl or -NHCO-C1-C4 alkyl; R1 is ethyl, cyanoethyl, phenmethyl, allyl or -CH2CH2OR4, wherein R4 is methyl, ethyl or carbonyl; R2 is independent of R1 but has the definition of the R1; and R3 is hydrogen, methoxyl or ethyoxyl. The 5-chloronitroaniline-containing azoic disperse dyes are characterized in that: a diazonium component contains 2,4-binitro-5-chloroaniline or bromide thereof. The dyes have the advantages of excellent wet fastness and sublimation fastness, are suitable for dyeing terylene and blend fabrics thereof, and have low cost and wide application prospect.
Owner:烟台澳土复合材料有限公司
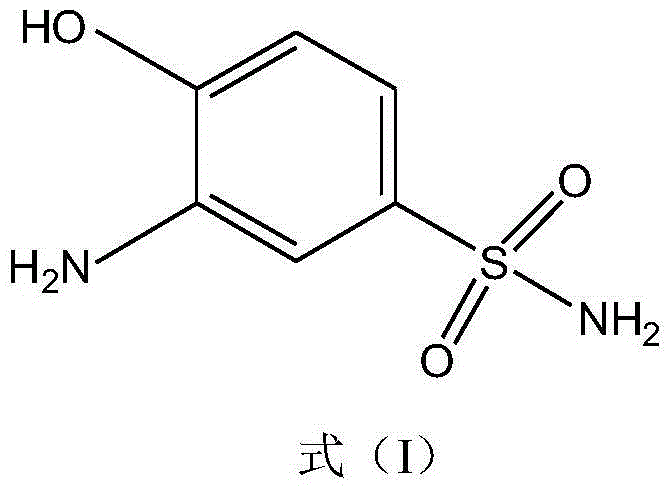
Synthetic method of 2-aminophenol-4-sulfonamide
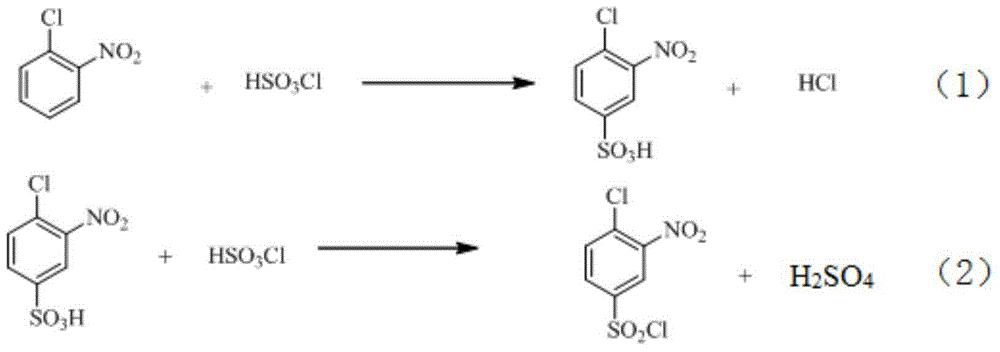
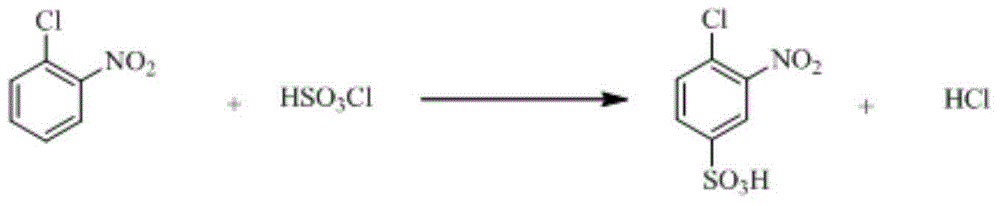
InactiveCN104592064AReduce dosageReduce wasteOrganic compound preparationSulfonic acid amide preparationO-nitrochlorobenzeneChlorosulfuric acid
The invention relates to a synthetic method of 2-aminophenol-4-sulfonamide. The synthetic method comprises the steps of chlorosulfonation, ammoniation, hydrolysis, acidification and reduction, wherein the chlorosulfonation comprises the following two steps: (a) adding chlorosulfonic acid into p-nitrochlorobenzene which serves as a raw material, and carrying out sulfonation reaction to obtain 4-chloro-3-nitrobenzene sulfonic acid; and (b) adding sulfoxide chloride into 4-chloro-3-nitrobenzene sulfonic acid obtained in the step (a), and carrying out chlorination to obtain 4-chloro-3-nitrobenzenesulfonyl chloride. According to the synthetic method, a chlorosulfonation process is improved, and the chlorosulfonation is carried out in two steps, namely p-nitrochlorobenzene is taken as the raw material, is firstly sulfonated by chlorosulfonic acid and is then chloridized by sulfoxide chloride, so that the consumption of chlorosulfonic acid is reduced, the unnecessary wasting is reduced, the production cost is saved, and the yield of products is increased to reach up to 96.88%.
Owner:QINGDAO DOUBLE PEACH SPECIALTY CHEM GRP
Preparation method of supported catalyst for synthesizing chloroaniline through catalytic hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzene
InactiveCN109939713AThe production process is not bigSimple processOrganic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationAsymmetric hydrogenationAniline
The invention relates to a preparation method of a supported catalyst for synthesizing chloroaniline through catalytic hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzene and particularly relates to a preparation method of a nitrogen-doped carbon material supported noble metal catalyst applied to the synthesis of chloroaniline through catalytic hydrogenation. The catalyst has the advantages of high catalytic activity, dechloridation inhibition capacity, long service life and the like, and the prepared chloroaniline product is high in purity.
Owner:JIANGSU YANGNONG CHEM GROUP +2
Preparation method of supported nickel-based catalyst for synthesizing chloroaniline through selective hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzene
InactiveCN106540698AReduce manufacturing costSimple preparation processOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationNickel catalystNickel salt
The invention discloses a preparation method of a supported nickel-based catalyst for synthesizing chloroaniline through selective hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzene. The preparation method comprises the following steps: firstly roasting a carrier, adding the roasted carrier and nickel salt into a solvent for mixing, heating the mixture while stirring, and then dropping a precipitator till the pH value is equal to 6 to 12 to obtain a suspension; carrying out static aging on the suspension obtained in the step (1), filtering and washing the suspension till the filtrate is neutral, drying the filtrate, and roasting in air at the temperature of 200 to 800 DEG C for 2 to 6 hours to obtain a catalyst precursor; and reducing the catalyst precursor under a condition of feeding H2 and N2 mixed gas or feeding H2 at the reducing temperature of 200 to 800 DEG C for 0.5 to 4 hours to obtain the supported nickel-based catalyst for synthesizing chloroaniline through selective hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzene. The catalyst has the advantages of low production cost, simple preparation process, short preparation period and little pollution, is high in reaction performance for synthesizing chloroaniline through selective hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzene, and is low in dechlorination performance.
Owner:NORTHWEST UNIV(CN)
Method for high-selectivity preparation of 3,4-dichloroaniline
ActiveCN103694124AReduce corrosionSolve the problem of hydrogenolysis and dechlorinationOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationPtru catalystNitrobenzene
The invention belongs to the technical field of fine chemical engineering, and relates to a method for preparing 3,4-dichloroaniline from 3,4-dichloronitrobenzene through high-selectivity catalytic hydrogenation. With 3,4-dichloronitrobenzene as raw material and in the presence of a Pt catalyst, 3,4-dichloroaniline is prepared through a catalytic hydrogenation reaction under the pressure of 1.0 MPa-3.0 MPa and at the temperature of 75-120 DEG C. With adoption of the method, the conversion rate of 3,4-dichloronitrobenzene is 100%, the selectivity of 3,4-dichloroaniline is greater than 99.6%, and the dechlorination rate is less than 0.20%. The Pt catalyst is safe to use, and has stable catalytic activity and high selectivity; a dechlorination inhibitor is not required to be added; through introduction of Fe2O3 into the Pt catalyst, a dechlorination phenomenon can be effectively inhibited, and the corrosion of dechlorination to a reaction container during reduction is reduced; and the method is not added with a solvent, overcomes the defect of the addition of the solvent, avoids the problems of pollution of the solvent to the environment and solvent recovery, reduces equipment investment, and reduces production costs.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
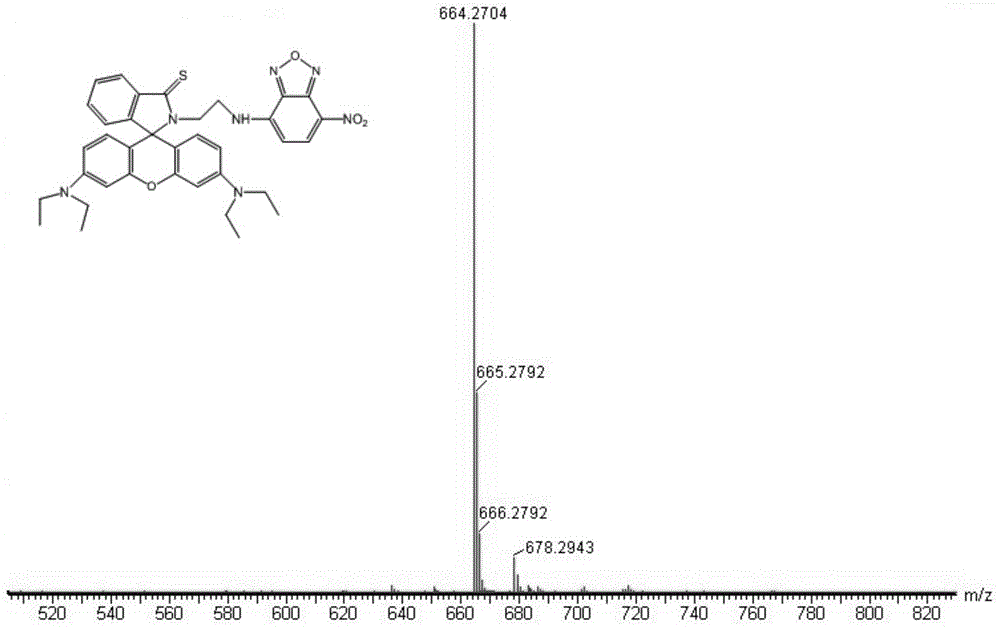
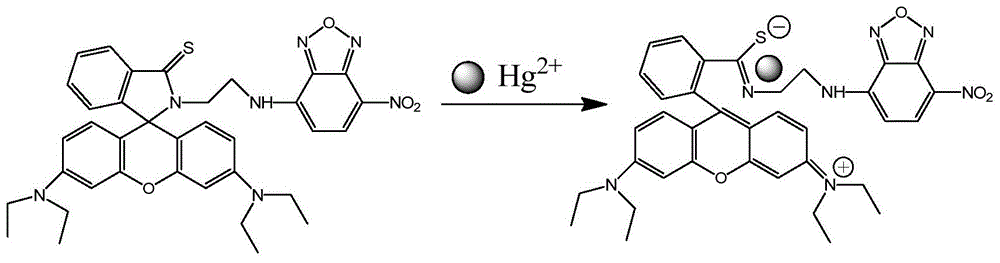
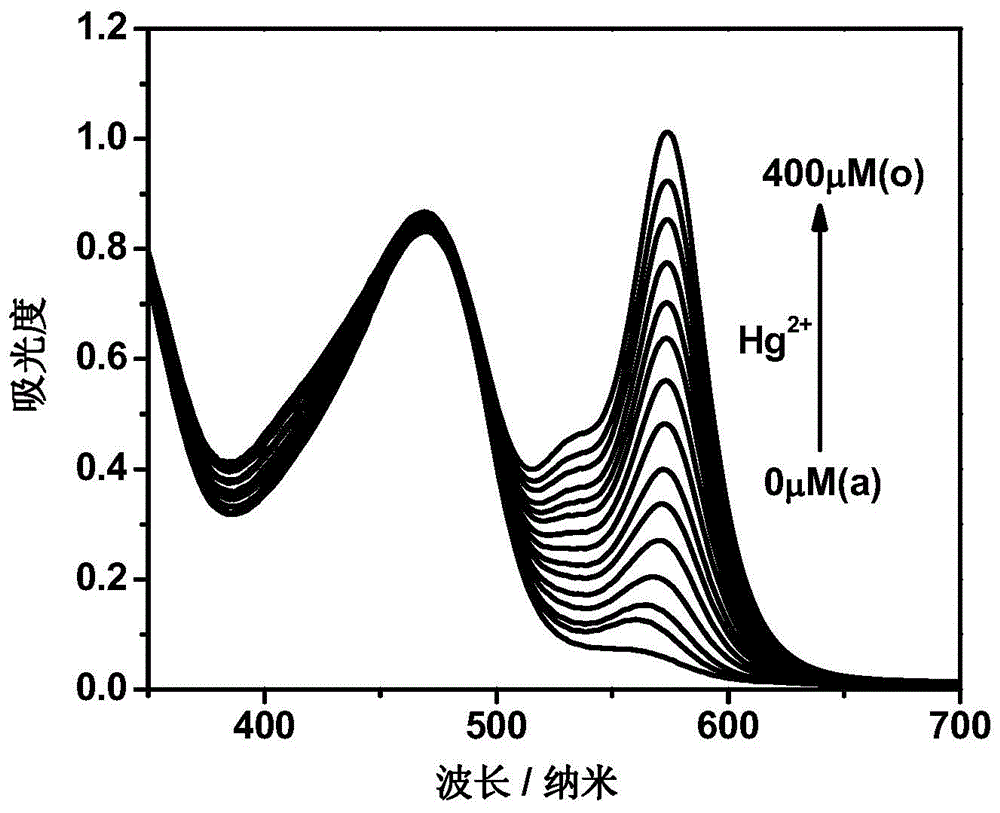
Compound containing rhodamine groups and benzofurazan groups and preparation method and application thereof
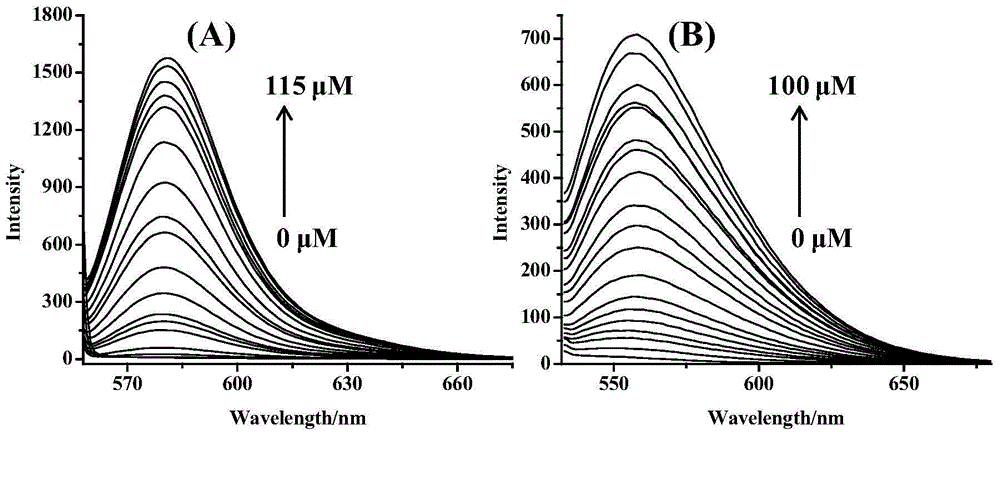
InactiveCN104949949AImprove accuracyEasy to prepareFluorescence/phosphorescenceMercuric ionDiethylenetriamine
The invention discloses a compound containing rhodamine groups and benzofurazan groups and a preparation method and application thereof. The structural formula of the compound is as shown in the specification. The preparation method comprises the following steps: (1) enabling rhodamine B and diethylenetriamine to fully react in a solvent, removing the solvent, and performing preliminary separation and purification; (2) enabling rhodamine B acyl diethylenetriamine and 4-chloro-7-nitrobenzofuroxan to fully react in a solvent, monitoring the reaction process by virtue of TLC, and performing column elution after the reaction is ended, thereby obtaining the product. The method for detecting the concentration of mercury ions or iron ions comprises the following steps: (1) making a standard curve; (2) detecting and recording; and (3) calculating. The invention further discloses an application of the compound serving as an iron ion fluorescence probe or a mercury ion fluorescence probe. The invention also discloses an application of the compound serving as an iron ion specific fluorescence probe or a mercury ion specific fluorescence probe. The compound disclosed by the invention can serve as a specific fluorescence probe for mercury ions or iron ions, is used for detecting mercury ions or iron ions in the solution and is high in accuracy.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA NORMAL UNIVERSITY
Electrochemical coupling upflow anaerobic bioreactor and application method
ActiveCN103771583AReasonable structureStable structureWater/sewage treatment by electrochemical methodsTreatment with anaerobic digestion processesElectron donorElectrochemistry
The invention relates to an electrochemical coupling upflow anaerobic bioreactor and an application method. The electrochemical coupling upflow anaerobic bioreactor comprises an upflow anaerobic bioreactor cylinder, a biological electrode system and a constant-temperature water-bath system, wherein the biological electrode system is used for supplying electron donors to a microorganism system in the upflow anaerobic bioreactor cylinder, and the constant-temperature water-bath system is used for providing constant-temperature water bath to the upflow anaerobic bioreactor cylinder; a sludge area of the upflow anaerobic bioreactor is provided with a pair of biological electrodes with adjustable electrode area and adjustable inter-electrode distance, the biological electrodes are connected with a direct-current power supply outside a bioreactor main body through a metal conducting wire, and electrode voltage, loop current and cathode potential are monitored and controlled through the direct-current power supply and an electric gauge, which are connected with the outside of the bioreactor main body. By adopting the electrochemical coupling uupflow anaerobic bioreactor, the granulation of the anaerobic sludge can be accelerated, the bioreactor can be rapidly started, and chloronitrobenzene can be stably degraded; moreover, the electrochemical coupling upflow anaerobic bioreactor is reliable in structure, easy to machine, small in energy consumption and stable in running.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for synthetizing 3,5-dichloroaniline
InactiveCN103508901AReduce pollutionWith sustainable developmentOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationO-nitrochlorobenzeneChlorobenzene
The invention discloses a method for synthetizing 3,5-dichloroaniline by using industrial production residues, namely meta-position oil, of p-nitrchlorobenzene and ortho-nitrochlorobenzene by two steps of chlorination and reductive dechlorination. The method adopts the following technical scheme: adding an organic solvent to nitrochlorobenzene meta-position oil as a raw material, directly producing a quintozene mixture by one-step chlorination under the effect of a catalyst, reacting for 0.5-10 hours under the condition of 10-180 DEG C, and then cooling to 30 DEG C; filtering out quintozene, and putting into an autoclave after washing into a neutral state by hot water; carrying out dechlorination reduction reaction under the effects of an organic solvent and the catalyst, wherein the reaction temperature is 60-200 DEG C, the reaction pressure is 1-20 MPa, and the reaction time is 1-20 hours; cooling to room temperature after the reaction is ended; leading in oxygen or air to stir after blowing off; filtering and distilling under reduced pressure to remove the solvent, so as to obtain the product 3,5-dichloroaniline, wherein the yield is 80-90%. Waste materials are changed into precious materials by a synthetic route adopted by the technology disclosed by the invention; the target of zero emission is achieved; the method has the advantages of sustainable development, energy conservation and consumption reduction, and small environmental pollution.
Owner:CHINA PETROLEUM & CHEM CORP +1
Preparation method for catalyst used for preparation of chlorinated arylamines through catalytic hydrogenation
ActiveCN107970967APrevent restoreEvenly distributedPhysical/chemical process catalystsOrganic compound preparationBenzeneAmmonium compounds
The invention relates to a preparation method for a catalyst used for preparation of chlorinated arylamines through catalytic hydrogenation, and specifically to a preparation method for a supported noble metal complex catalyst and an application of the supported noble metal complex catalyst in preparation of the chlorinated arylamines like o-chloroaniline, 3,4-dichloroaniline and 2,5-dichloroaniline through catalytic hydrogenation. The invention provides a preparation method for a carbon-supported catalyst (Pt-N / C or Pd-N / C for short, wherein N represents one or more selected from the group consisting of inorganic ammonium compounds) which is obtained through an action of noble metal and an inorganic ammonium compound; and the catalyst is used for preparation of the chlorinated arylaminesthrough catalytic hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzene. The preparation processes for the catalyst and the chlorinated arylamines have the following main advantages: 1, little difference is generated between preparation processes of the catalyst and ordinary noble metal carbon-supported catalysts, and the preparation processes are simple; 2, continuous addition of an auxiliary agent is not needed in the process of preparation of the chlorinated arylamines through catalytic hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzene by utilizing the catalyst; 3, the catalyst has stable activity and low dechlorination amount in the process of hydrogenation; and 4, no solvent is used in the process of hydrogenation, and production capacity is improved.
Owner:JIANGSU RUIXIANG CHEM +1
Alpha-amylase detection reagent and application thereof
ActiveCN105021543AThe measurement result is accurateReduce mistakesColor/spectral properties measurementsLaboratory orderMedical laboratory
The present invention belongs to the field of medical laboratory technology, and in particular relates to an alpha-amylase detection reagent and application thereof. The reagent comprises a reagent R1 and a reagent R2; the reagent R1 is mainly composed of an MES buffer, NH4Cl, CaCl2, a surfactant and a preservative; the R2 reagent consists of an MES buffer, a 2-chloro-4-nitrobenzene-maltotriose and a preservative. The alpha-amylase detection reagent provided by the invention does not contain NaN3, does not lead to alpha-amylase allosterism in the determination process, and can reduce the error in measurement results; at the same time, the test does not need additional tool enzyme, and has short delay time; the test results have good repeatability and stability. Therefore, the invention is conducive to the clinical application of alpha-amylase detection reagent.
Owner:郑州金域临床检验中心有限公司
Supported nickel catalyst for synthesizing chlora aniline by hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzene and its preparation method thereof
InactiveCN1762588ALow costSimple preparation processCatalyst carriersOrganic compound preparationNickel catalystHydrogen
The invention relates to a carrier nickel-base catalyst used to hydrogenate the chloronitrobenzene to synthesize chloroaniline, which comprises silicon dioxide, titania or zirconia as carrier, wherein 10~40% nickel. The preparation process comprises: drying, dipping, calcining, reducing, and activating. The advantages of this invention include: low cost, simple process, little pollution, and well reaction performance.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Bioelectrochemical system and UASB coupled wastewater treatment device and method thereof
ActiveCN106946405AStart fastPromote reductive conversion degradationTreatment by combined electrochemical biological processesWater contaminantsGibbs free energySludge
The invention discloses a cathodic potential regulation-based bioelectrochemical coupled upflow anaerobic biological reaction device and a use method thereof. In the device, an annular electrode is arranged in the sludge layer of an upflow anaerobic bioreactor, and a bioelectrode system provides electrons with high energy for microorganisms nearby a cathode in the cylindrical shell of the upflow anaerobic bioreactor in order to carry out pollutant degradation. A reference electrode is fixed nearby the biological cathode through a fastening bolt, is connected with an online detector and a computer through leading wires, and is used for the real-time monitoring of the cathodic potential of the biological cathode of the coupling reactor. A potential difference needed by the reaction is calculated through a Nernst equation according to Gibbs free energy needed by the degradation of different pollutants, and the applied voltage of the bioelectochemical system is adjusted to control the cathodic potential to be slightly below the range of the potential difference in order to achieve low-energy consumption and high-efficiency degradation of chloronitrobenzene and other non-degradable organic pollutants.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
Method for preparing chloroaniline by catalysis hydrogenation
InactiveCN101735073AInhibition of dechlorination is obviousHigh reactivityOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationProduction rateAlcohol
The invention discloses a method for preparing chloroaniline by catalysis hydrogenation, comprising the following steps: by using chloronitrobenzene as material, alcoholic solution as solvent, and Ni-B amorphous alloys as a catalyst and a dechlorination inhibitor, introducing H2 for catalytic hydrogenation-reduction reaction to obtain the chloroaniline. The Ni-B amorphous alloy in the invention is a catalyst and has relatively high reactivity and selectivity, the selectivity of chloroaniline is greater than 99%, and the production rate of chloroaniline is high; and the function of inhibiting dechlorination of amines is obvious, and the amount of dechlorination is less than 0.5%.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF SCI & TECH
Preparation method of 2,5-dimethoxyl-4-chloroaniline
ActiveCN103265441AGood choiceNot prone to spontaneous combustionOrganic compound preparationChemical recyclingPtru catalystMetal catalyst
The invention relates to a preparation method of 2,5-dimethoxyl-4-chloroaniline. The method comprises the following steps: performing hydrogenation reduction reaction on 2,5-dimethoxyl-4-chloronitrobenzene used as a raw material and hydrogen in a solvent in the presence of a catalyst and a dechlorination agent to generate the 2,5-dimethoxyl-4-chloroaniline, wherein the catalyst is a supported metal catalyst which consists of carrier carbon, and first and second metals loaded on the carrier carbon. The first metal is selected form one or two of Pd and Pt, while the second metal is selected from one or two of Ru and Rh. The dechlorination agent is morpholine or ammonium metavanadate; after reaction, filtering the catalyst and packaging for the next batch; cooling the filtrate and separating out crystals; and filtering white crystals to obtain the 2,5-dimethoxyl-4-chloroaniline. The preparation method provided by the invention is low in production cost, good in safety and less in three-waste discharge, and the target product obtained is good in quality.
Owner:XIANGSHUI HENRYDA TECH CHEM
Preparation for medicinal intermediate 6-chloro-5-fluroindole for synthesizing anti-cancer medicament
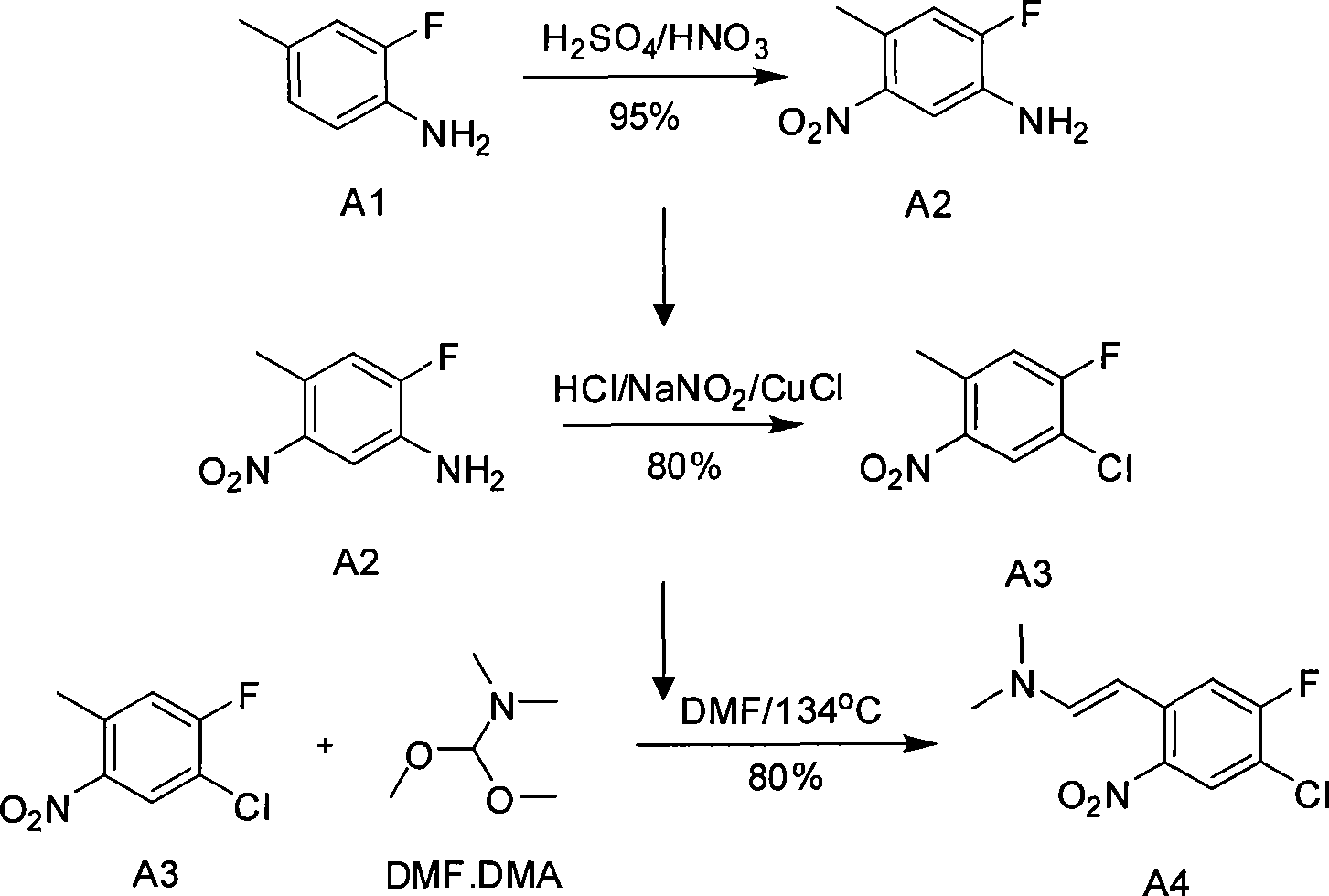
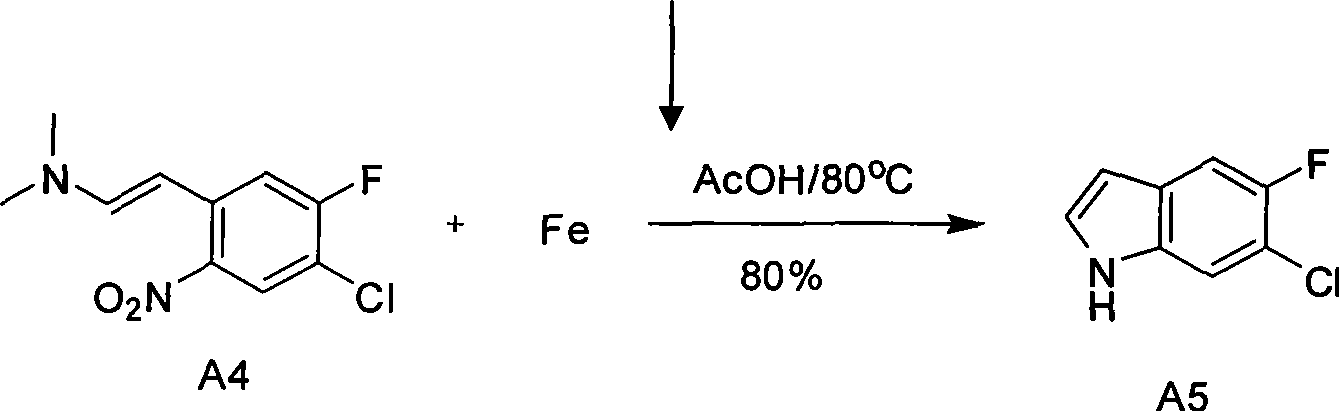
The invention relates to preparation for a medicinal intermediate 6-chloro-5-fluroindole for synthesizing an anti-cancer medicament, which comprises the following steps that: firstly, 3-fluro-4-aminotoluene reacts in a concentrated sulfuric acid system, the pH value is adjusted to be neutral after the reaction, and the mixture is filtered to obtain 3-fluro-4-amino-6-nitrotoluene; secondly, a sodium nitrite solution and cuprous chloride are added in the concentrated sulfuric acid system, and the mixture is diluted by clear water to obtain 3-fluro-4-chloro-6-nitrotoluene; thirdly, the 3-fluro-4-chloro-6-nitrotoluene and N, N-dimethyl formamide dimethylacetal react in a molecular sieve drying DMF system to obtain 2-(methylamino) ethylene-4-fluro-5-chloronitrobenzene; and finally, iron powder is added into an acetic acid system, and after the reaction, the mixture is recrystallized by using a mixed system containing petroleum ether to obtain the white 6-chloro-5-fluroindole. The method has the advantages of simple operation, environmental friendliness, high purity and low cost, and is suitable for industrialized production.
Owner:上海泰坦科技股份有限公司
Ex-situ remediation method suitable for chloronitrobenzene type polluted ground water
ActiveCN103626277ALow toxicityPromotes Oxygen RemovalWater/sewage treatment by reductionWater/sewage treatment by oxidationChemical oxygen demandIron reduction
The invention discloses an ex-situ remediation method suitable for chloronitrobenzene type polluted ground water. The method comprises the following steps: filtering polluted water to remove mechanical impurities, and then, adding reducing iron powder and stirring for reaction, wherein additive amount of the reducing iron powder is 30-40% of COD (Chemical Oxygen Demand) content, and reducing chloronitrobenzene with zero-valent iron to generate ferrous ions Fe<2+> and phenylamine; 3-5 days later after reduction reaction, adding FeSO4.7H2O of which the additive amount is 30% of COD content, and stirring to realize miscibility; gradually adding H2O2 with mass concentration of 30% into a reaction solution to realize oxidizing reaction according to the additive amount of 3-5 times of COD content, and oxidizing the ferrous ions into ferric ions; after the oxidizing reaction, adding Ca(OH)2 according to the amount of 0.1-0.2% of mass of polluted water solution, and regulating pH to 6-9; and finally, removing sediment by virtue of filtering and separating. The ex-situ remediation method uses a zero-valent iron reduction treatment method and a Fenton's reagent oxidizing treatment method in combination, has an obvious remediation effect on the chloronitrobenzene type polluted ground water, and has high pollutant removal rate.
Owner:SHANGHAI ACADEMY OF ENVIRONMENTAL SCIENCES
Electrocatalytic dechlorination method for parachloronitrobenzene
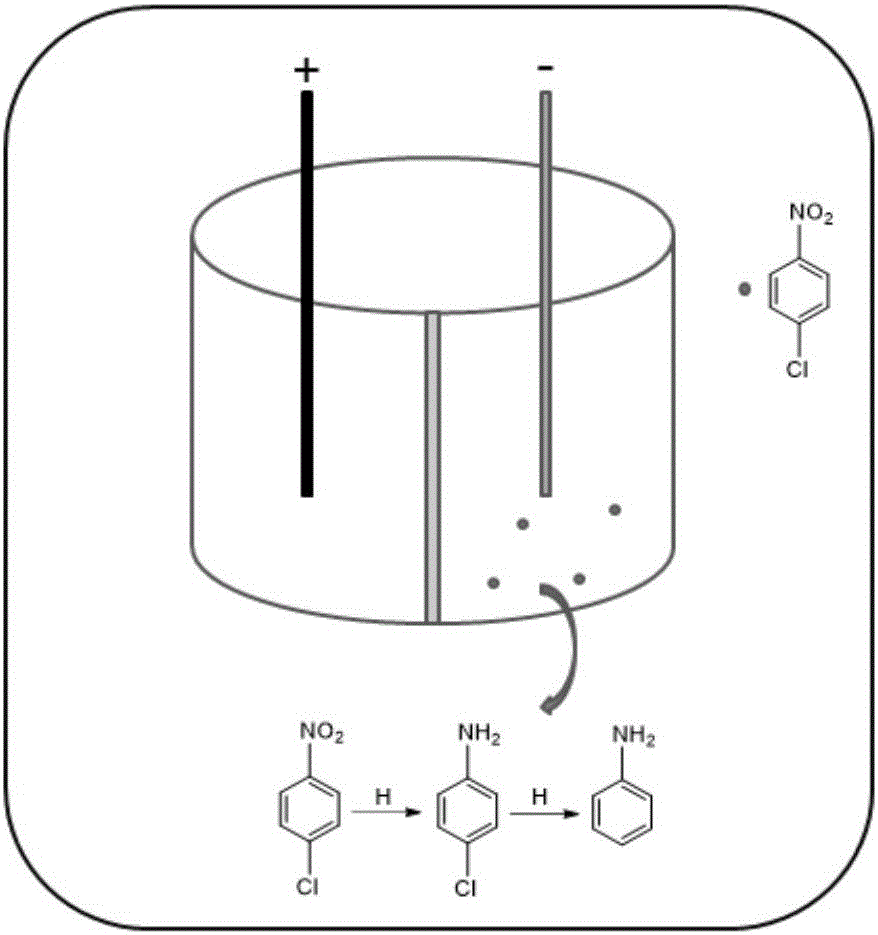
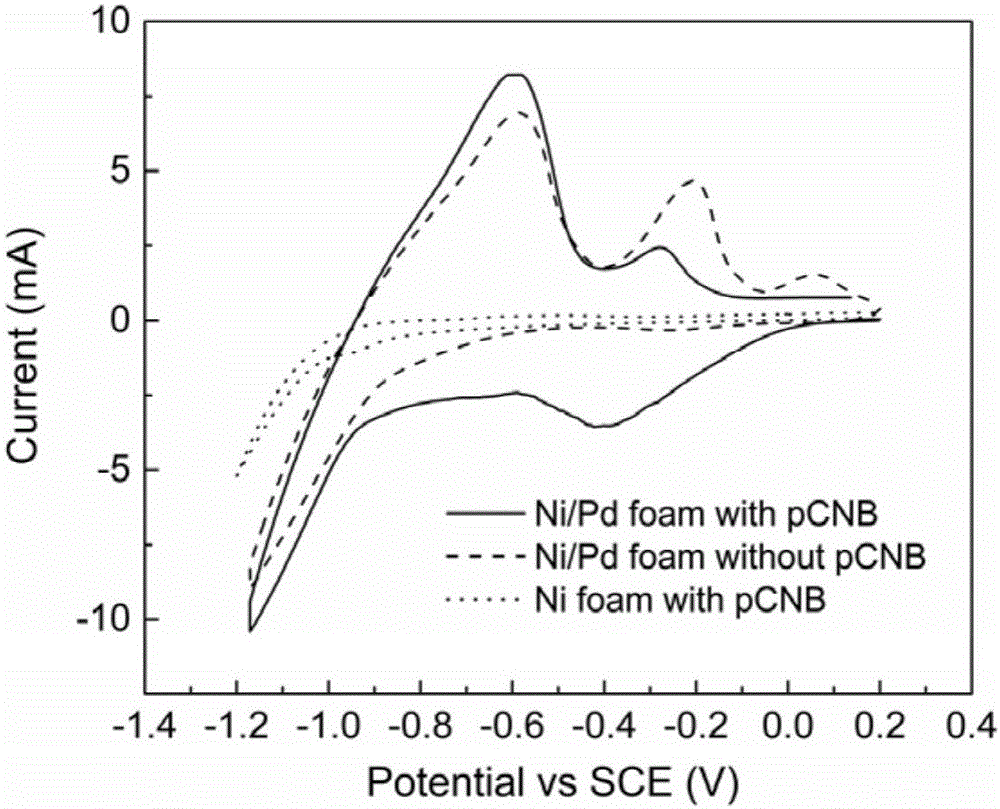
InactiveCN105712447AAchieve one-time removalGood dechlorination effectWater contaminantsWater/sewage treatmentChemical treatmentNitrobenzene
The invention discloses an electrocatalytic dechlorination method for parachloronitrobenzene. The method comprises the following steps: loading precious metal palladium on a foam nickel material with a three-dimensional structure by an impregnation method to obtain a cathode of an electrocatalytic reactor; and introducing parachloronitrobenzene-containing wastewater into the electrocatalytic reactor to fill the whole reactor, wherein electrochemical treatment is started under constant current, the parachloronitrobenzene experiences a reduction reaction in a cathode chamber and is reduced into parachloroaniline under the effect of hydrogen radical, and then a dechlorination effect can be realized to form aniline due to the excellent performance of the palladium-containing foam nickel electrode. In the invention, metal reduction is replaced by electrocatalytic reduction, the problems of easy passivation and low mass transfer efficiency of metals are solved, the difficulty in dechlorination of parachloronitrobenzene in the traditional electrode is overcome, and the chlorine group of chloronitrobenzene is effectively removed.
Owner:NANJING UNIV
Lipid droplet targeting fluorescent probe and synthesis method and application thereof
ActiveCN112321527AAggregation-induced quenchingHigh sensitivityOrganic chemistryFluorescence/phosphorescenceFluoProbesFluorescence
The invention discloses a lipid droplet targeting fluorescent probe and a synthesis method and application thereof. The synthetic method comprises the following steps of enabling a triphenylamine phenylboronic acid compound and 4-chloro-7-nitrobenzo-2-oxa-1, 3-diazole to react for 10-50 h in an organic solvent at the temperature of 60-120 DEG C under the protection of inert gas and the action of acatalyst and alkali, cooling the reaction product to the room temperature, adding dichloromethane, filtering, decompressing to remove the solvent, separating and purifying the product, and drying theproduct. The fluorescent probe provided by the invention has no fluorescence in an aqueous solution, basically has no fluorescence in an organic solvent, has very strong fluorescence in grease, and can specifically target lipid droplets in cells.
Owner:WEST CHINA HOSPITAL SICHUAN UNIV
Process for the Preparation of 11-(4-[2-(2-Hydroxyethoxy)Ethyl]-I-Piperazinyl)Dibenzo[b,f][I,4]Thiazepine
InactiveUS20070225494A1MinimizationImprove productivityNervous disorderOrganic chemistryOrganic solventThiazepine
Disclosed is a process for the preparation of 11-(4-[2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)ethyl]-1-piperazinyl)-dibenzo[b,f][1,4]thiazepine. In the process, low-priced 2,2′-dithiosalicylic acid as starting material is subjected to bond formation reaction with 1-chloro-2-nitrobenzene in a basic aqueous solution, a nitro group reduction reaction is conducted, cyclization and chlorination reactions are simultaneously carried out in the presence of a equivalent amount of halogenating agent, a reaction with piperazine is continuously conducted without separation, and a reaction with 2-haloethoxyethanol is conducted, thereby it is possible to economically producing Quetiapine, that is, 11-(4-[2-(2-hydroxyethoxy)ethyl]-1-piperazinyl)-dibenzo[b,f][1,4]thiazepine, in an environmentally friendly manner. Particularly, the process is advantageous in that economic efficiency is assured because of use of the low-priced starting material, use of an organic solvent is minimized because a reaction is conducted in an aqueous solution, and it is possible to achieve the environmentally friendly and economical process having high commercial usefulness because the number of reaction steps of the process is reduced and because generation of acidic waste is minimized.
Owner:SK BIOTEK
Catalyst for liquid phase hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzene and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102091622AExcellent catalytic activityExcellent catalytic selectivityOrganic compound preparationCatalyst activation/preparationUltrasonic assistedAlloy
The invention discloses a catalyst for liquid phase hydrogenation of chloronitrobenzene and a preparation method thereof. The invention is characterized in that the catalyst consists of amorphous alloy NiB, wherein the mass percentage of Ni is 10 to 80 percent and the mass percentage of B is 20 to 90 percent. The preparation method is an ultrasonic wave-assisted liquid phase reduction method, and comprises the following steps: (1) preparing solution; (2) forming a precipitate; and (3) washing precipitate and storing. The invention has the advantages that: the catalyst has high activity and selectivity; and when the catalyst is used, the chloronitrobenzene conversion rate is over 99 percent and the dechloridation rate is below 4 percent.
Owner:CHINA NAT ACAD NANOTECH & ENG
Pt-Fe/C catalyst as well as preparation method and application thereof
PendingCN109225258ASimple preparation stepsEvenly dispersedOrganic compound preparationAmino compound preparationReaction temperatureSolvent
The invention discloses a Pt-Fe / C catalyst as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The catalyst is composed of an active component and a carrier, wherein the active component is platinum, iron and oxide of iron; the carrier is active carbon; Pt accounts for 0.5-3% of the total mass of the catalyst, and a Fe / Pt mass ratio is (0.5 to 4) : 1. The preparation method of the catalyst comprises the following preparation steps: preparing a platinum-iron active component impregnation solution, performing equal-volume loading, performing in-situ reduction, washing and drying. The catalyst is used for preparing chloroaniline by chloronitrobenzene hydrogenation though a no-solvent method; dechloridation can be effectively restrained in case of not adding a dehalogenation inhibitor, and the advantages of good reaction activity and high selectivity are achieved. Under the conditions of no solvent and auxiliaries, the dosage of the catalyst is 0.8% of the mass of chloronitrobenzene,the reaction temperature is 90 DEG C, hydrogenation pressure is 1.0 MPa, reaction can be completed with two hours, and dechlorination amount is less than 0.1%.
Owner:CHENZHOU GAOXIN PLATINUM +1
Preparation method of colorimetric mercury ion sensor based on rhodamine derivative and application
ActiveCN104530064AHigh sensitivityReduce cost inputOrganic chemistryColor/spectral properties measurementsColorimetric sensorSolvent
The invention discloses a preparation method of a colorimetric mercury ion sensor based on a rhodamine derivative and application. The colorimetric sensor is a novel colorimetric sensor prepared by taking rhodamine B, quadrol, Lawesson reagent and 4-chloro-7-nitrobenzofuran as raw materials. Mercury ions can be subjected to high-selectivity and high-sensitivity detection by the colorimetric sensor in a mixed solvent of acetonitrile and water. Compared with the existing mercury ion detection technology, the novel colorimetric sensor is simple in synthetic route, low in invested cost and simple in used detection device, is suitable for amplification synthesis and actual production application and has great application prospect in technical fields of analytical chemistry, environmental sciences, life sciences and the like.
Owner:HUNAN UNIV OF SCI & TECH
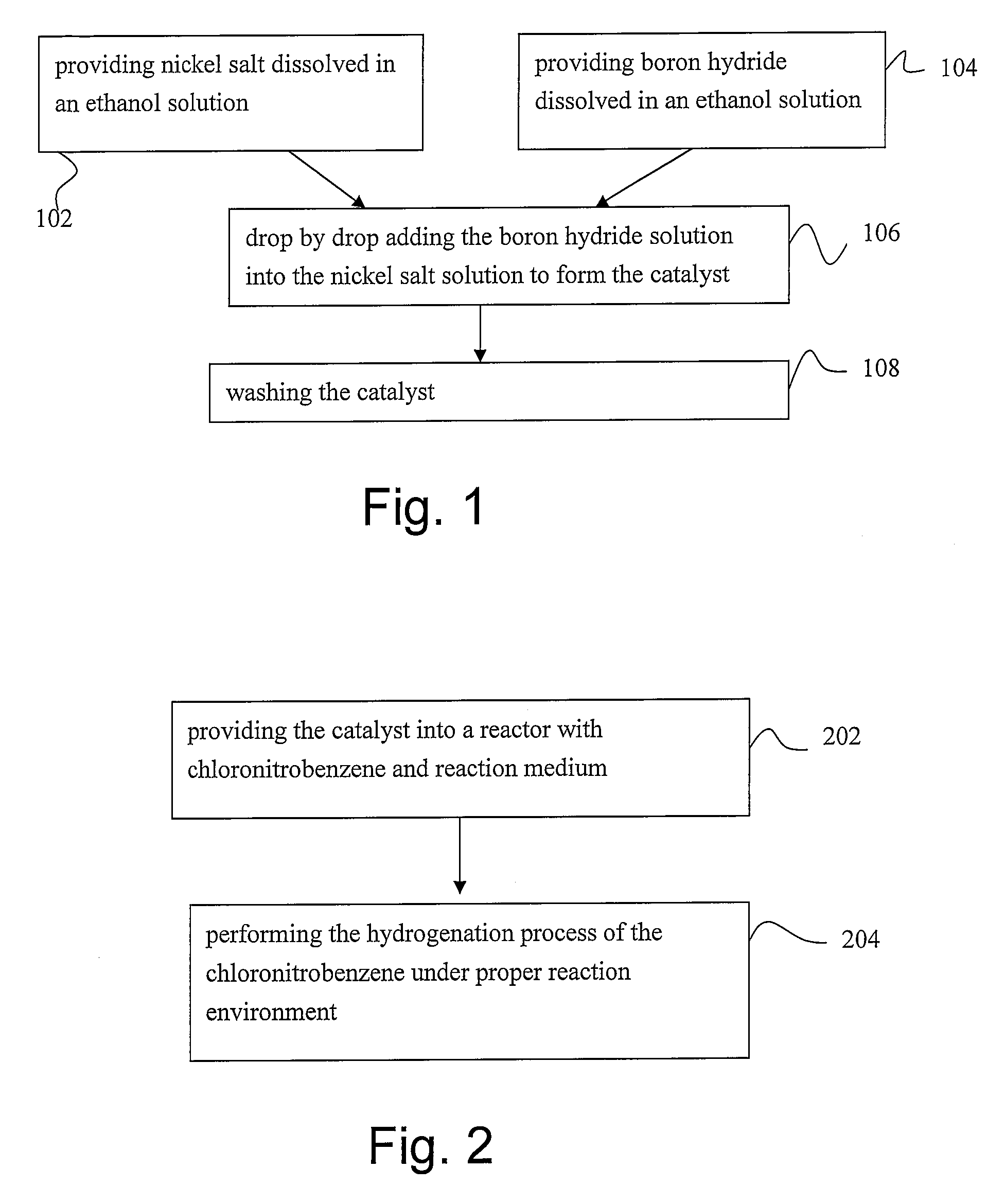
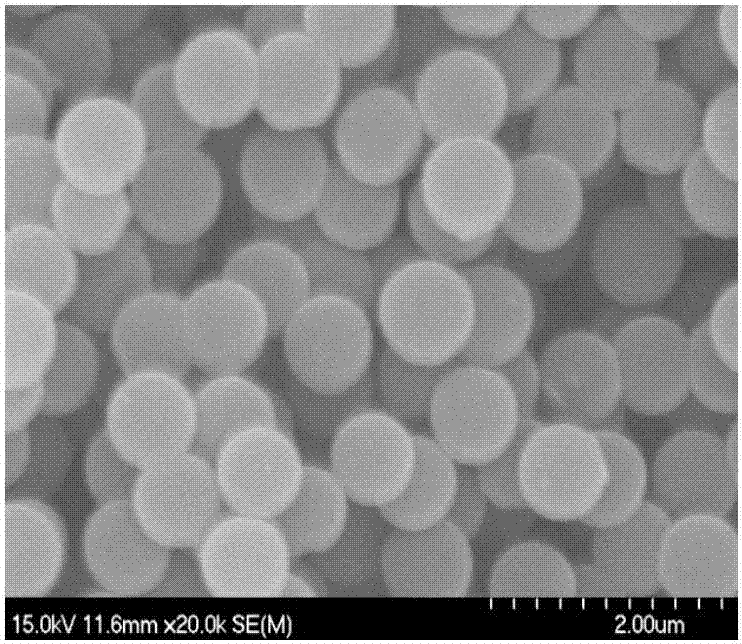
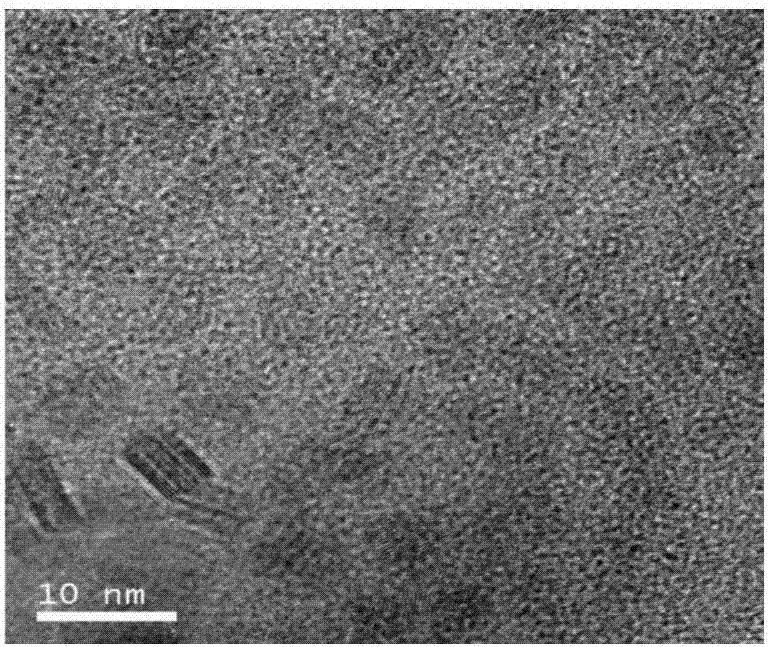
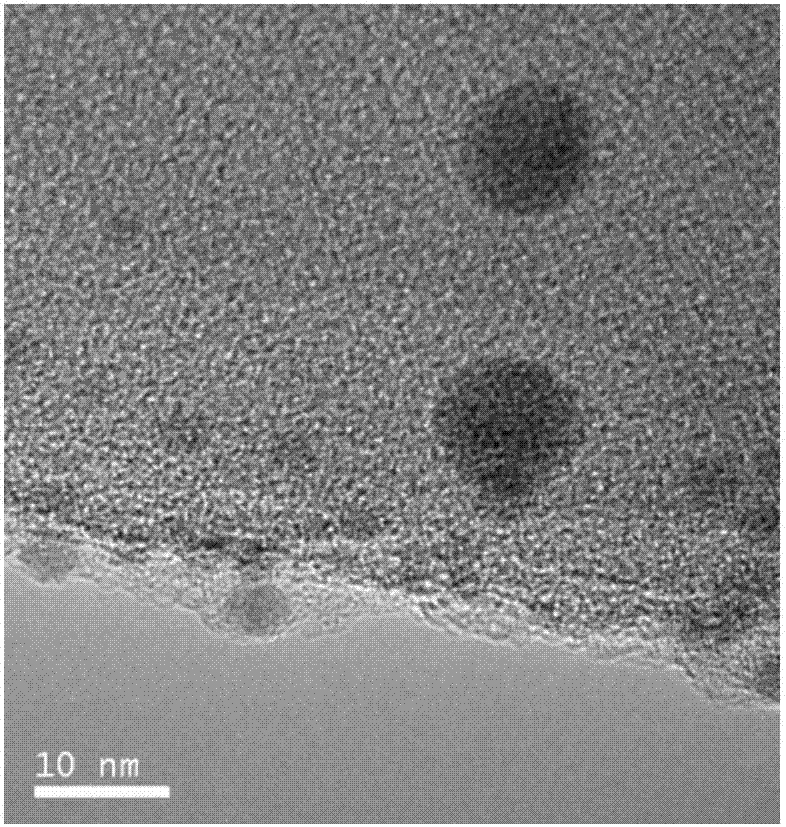
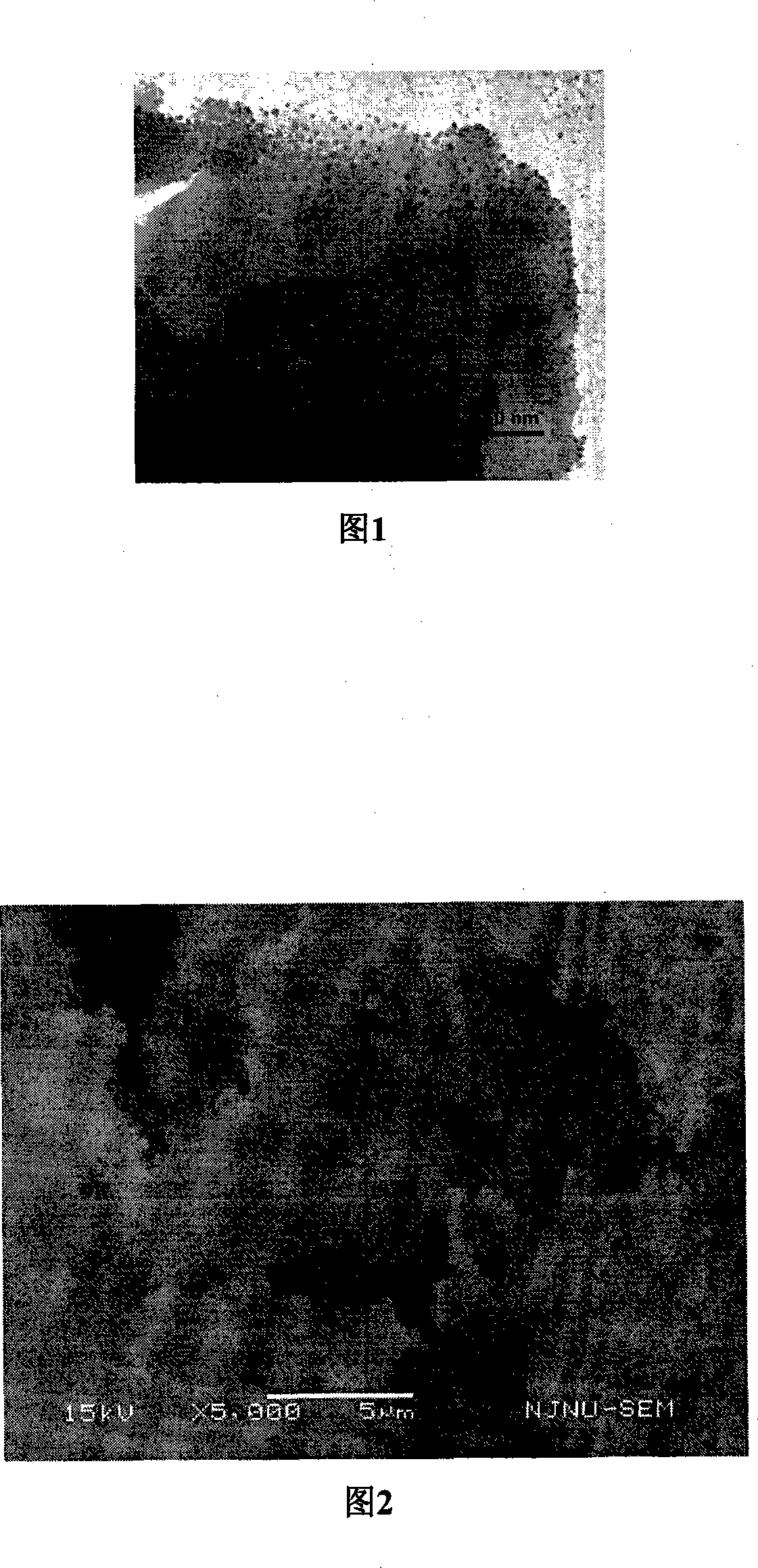
Hydrogenation process of chlorinated nitrobenzene
ActiveUS7381844B2Small diameterIncrease surface areaMaterial nanotechnologyOrganic compound preparationCarbon numberNickel catalyst
A hydrogenation process of chloronitrobenzene. The hydrogenation process comprises the steps of producing a nanosized boron-containing nickel catalyst, wherein a ratio of the amount of the boron atom to the amount of the nickel atom in the nanosized boron-containing nickel catalyst is of about 0.1-0.9. Then, the nanosized boron-containing nickel catalyst is placed into a reactor with a chloronitrobenzene an alcohol solvent having carbon number less than four per molecule and a hydrogenation process is performed to hydrogenating the chloronitrobenzene in hydrogen with a reaction pressure of about 5-40 atm and a reaction temperature of about 40-150° C.
Owner:NAT CENT UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com

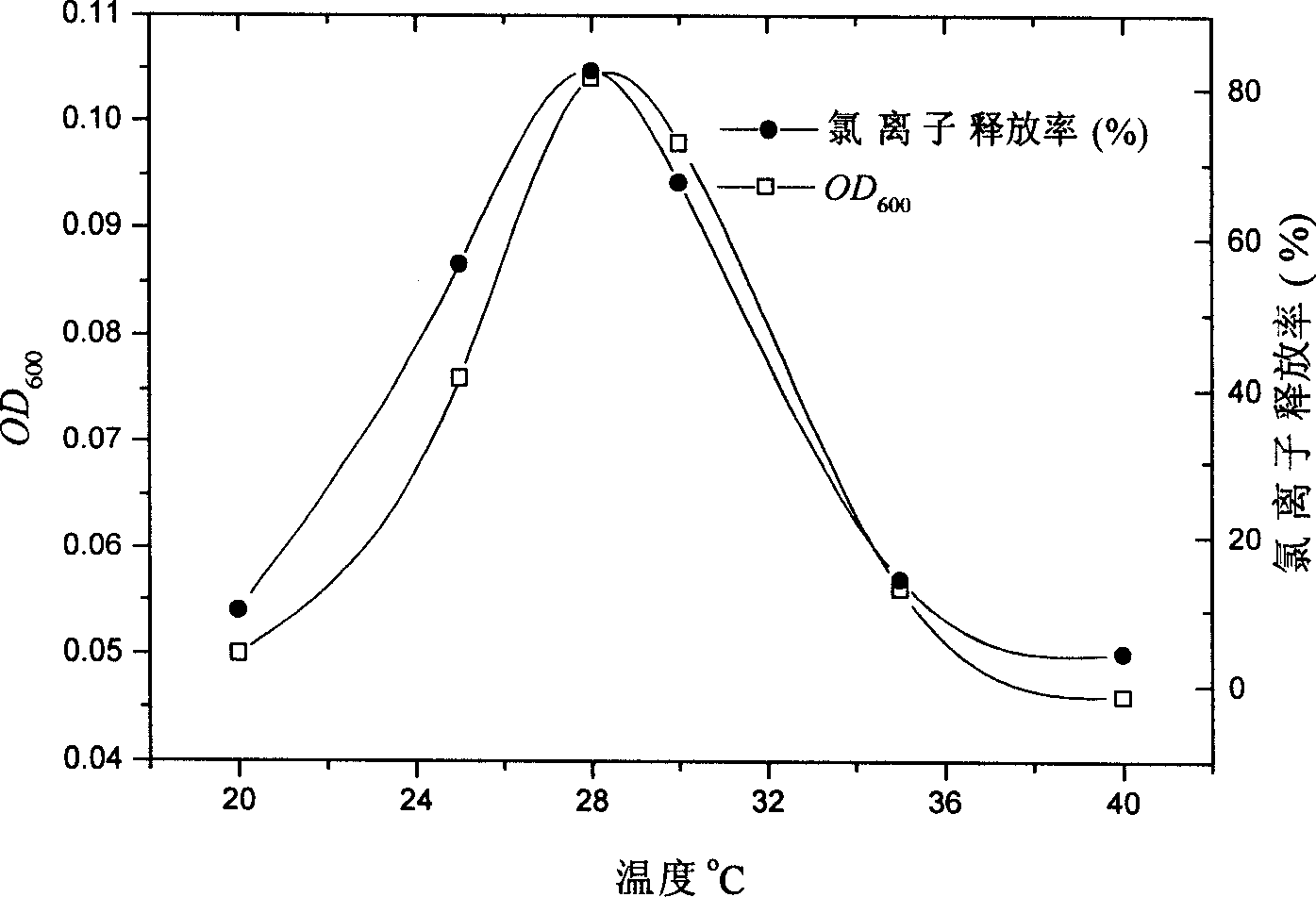
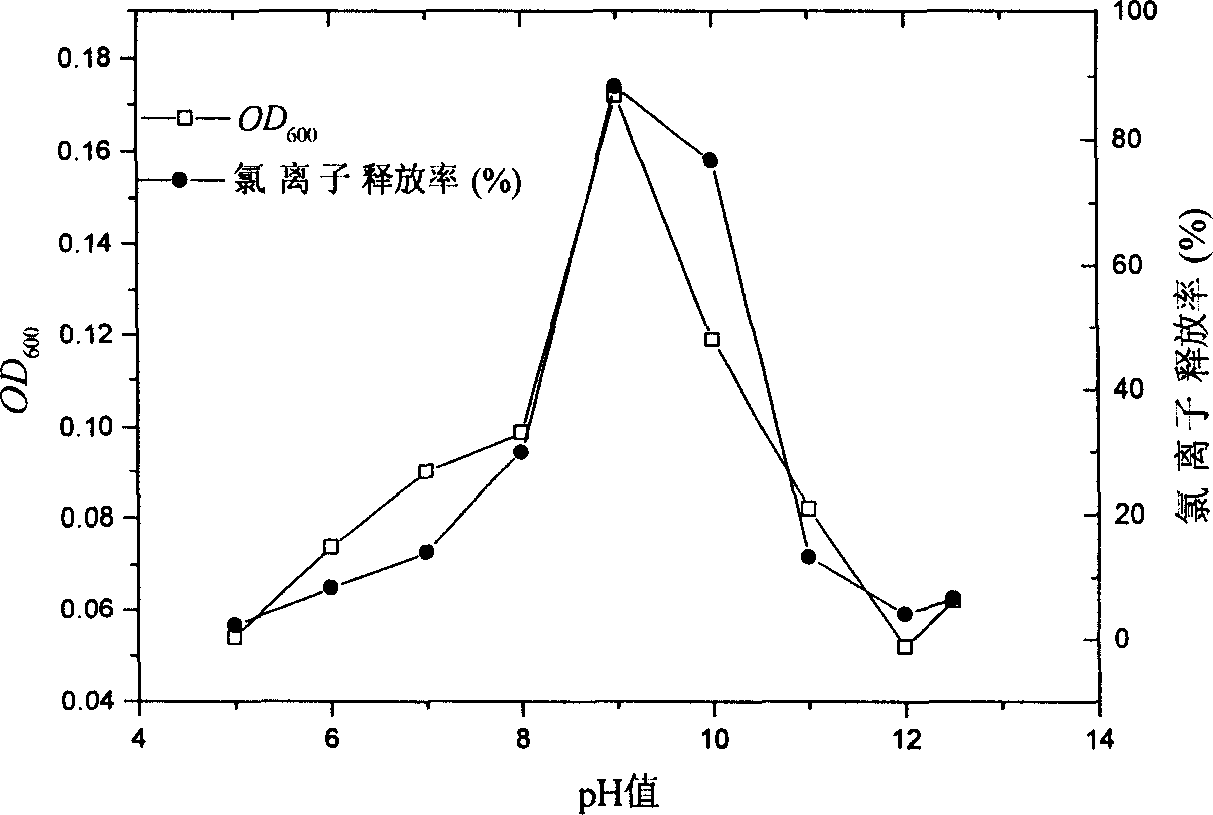

![Process for the Preparation of 11-(4-[2-(2-Hydroxyethoxy)Ethyl]-I-Piperazinyl)Dibenzo[b,f][I,4]Thiazepine Process for the Preparation of 11-(4-[2-(2-Hydroxyethoxy)Ethyl]-I-Piperazinyl)Dibenzo[b,f][I,4]Thiazepine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/6d36962c-963c-4422-b2f6-648f84065f1f/US20070225494A1-20070927-C00001.png)
![Process for the Preparation of 11-(4-[2-(2-Hydroxyethoxy)Ethyl]-I-Piperazinyl)Dibenzo[b,f][I,4]Thiazepine Process for the Preparation of 11-(4-[2-(2-Hydroxyethoxy)Ethyl]-I-Piperazinyl)Dibenzo[b,f][I,4]Thiazepine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/6d36962c-963c-4422-b2f6-648f84065f1f/US20070225494A1-20070927-C00002.png)
![Process for the Preparation of 11-(4-[2-(2-Hydroxyethoxy)Ethyl]-I-Piperazinyl)Dibenzo[b,f][I,4]Thiazepine Process for the Preparation of 11-(4-[2-(2-Hydroxyethoxy)Ethyl]-I-Piperazinyl)Dibenzo[b,f][I,4]Thiazepine](https://images-eureka.patsnap.com/patent_img/6d36962c-963c-4422-b2f6-648f84065f1f/US20070225494A1-20070927-C00003.png)