Application of corn ZmbZIP107 gene in cultivation of lead stress-resistant plants
A technology of transgenic plants and corn, which is applied in the field of plant response to heavy metal stress, can solve problems such as no lead tolerance, and achieve the effect of huge economic benefit potential and broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
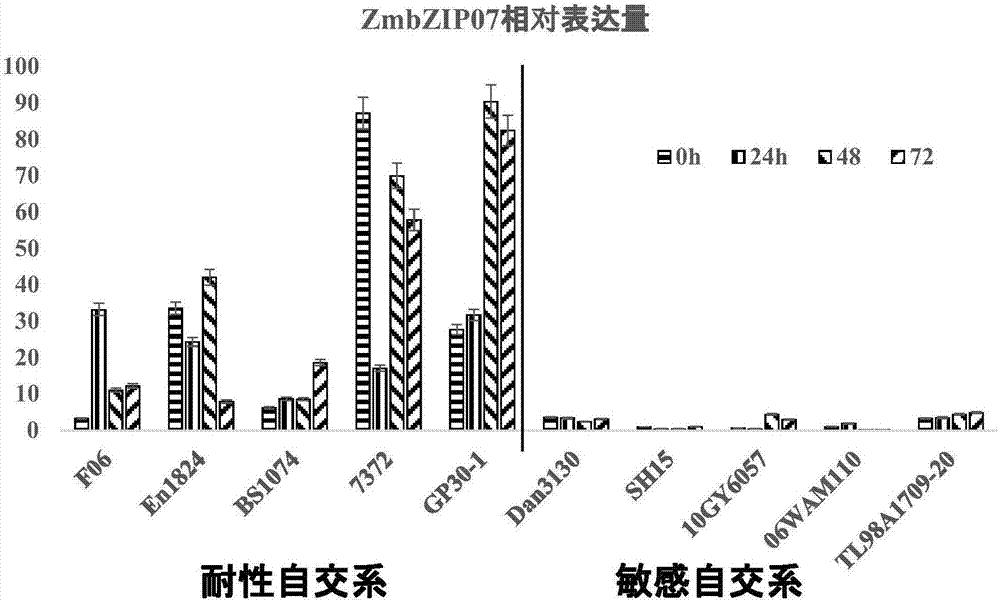
[0017] Example 1. Expression analysis of maize ZmbZIP107 gene under lead stress
[0018] 1-1. Lead stress treatment of maize inbred line materials
[0019] Select the plump 312 corn inbred line seeds and sterilize them with 75% ethanol for 1 min, 10℅ H 2 O 2 Soak the solution for 15 minutes and shake it continuously during disinfection, then rinse with deionized water 3 to 5 times until the residual H 2 O 2 Rinse well, soak in deionized water for 4 hours, and finally germinate with filter paper in the dark at 28°C. After about 2-3 days, transfer the germinated corn to a floating plate, and culture it with Hoagland nutrient solution at 28°C under light (16h) / dark (8h) conditions for hydroponic culture. Change the culture medium twice a week until the seedlings grow. To the three-leaf stage, stress treatment.
[0020] 1-2. Lead stress treatment:
[0021] Select 6 seedlings with the same growth and remove the endosperm and transfer them into a plastic container filled with nutrient solu...
Embodiment 2
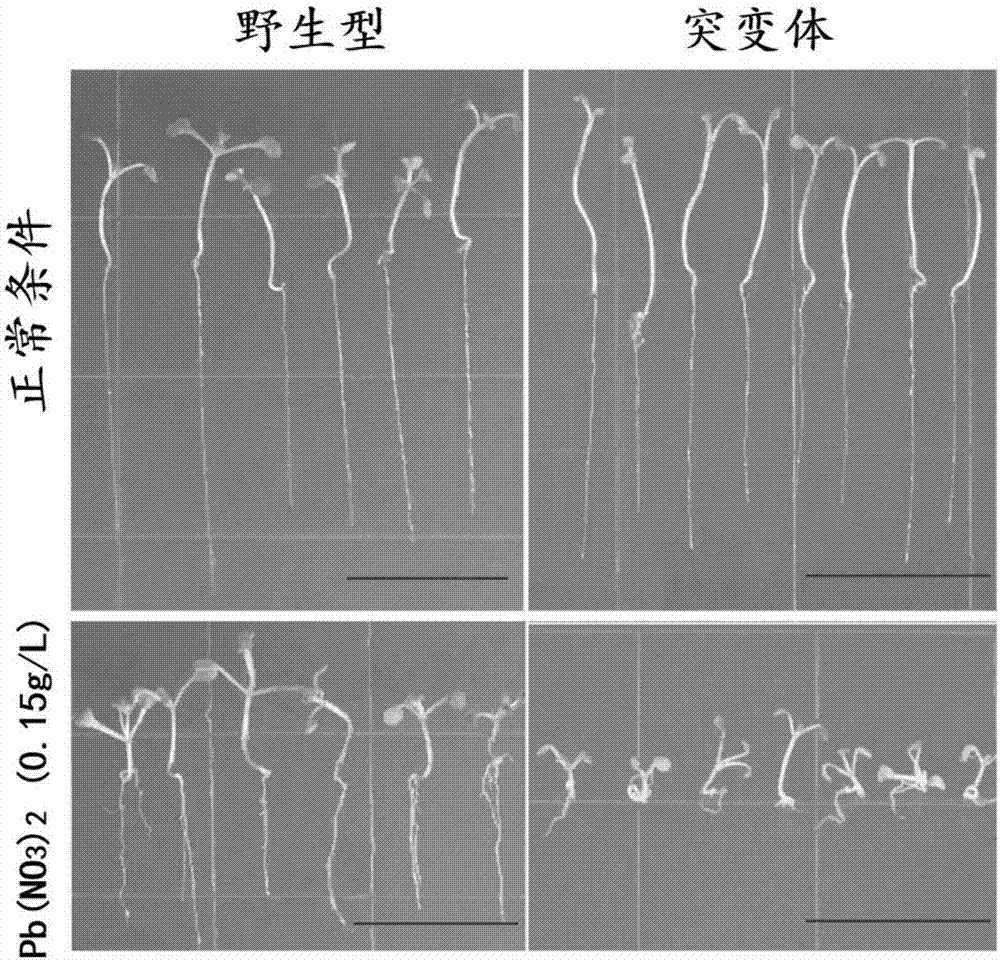
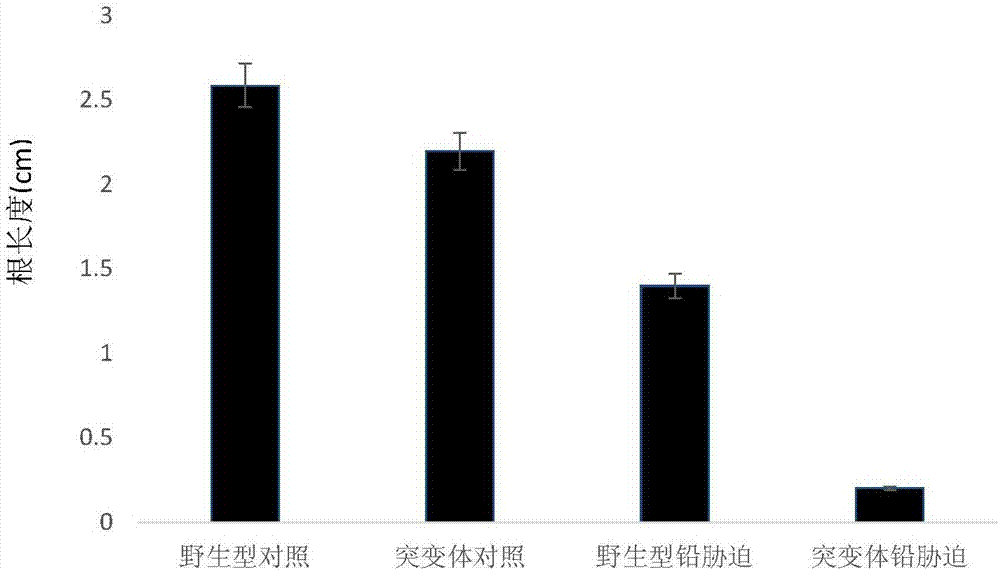
[0043] Example 2. Analysis of lead tolerance of Arabidopsis homologous gene mutant plants
[0044] For the Arabidopsis homologous gene mutant SALK_028204 (ordered from the Arabidopsis TAIR mutant library), first use 75% absolute ethanol to disinfect the mutant and wild-type seeds for 1 min, then disinfect with 1% NaClO for 15 min, and finally with no After washing with bacteria water for 3 to 5 times, sowing them on 1 / 2MS medium and culturing for 7 days, and then transplant wild-type plants and mutant plants at 0g / L and 0.15g / L Pb(NO 3 ) 2 Continue culturing on 1 / 2MS medium, and observe the plant growth after 10 days. The results are as follows figure 2 with image 3 As shown, the growth of mutant plants under normal conditions is not much different from that of wild type. Under lead stress conditions, lead stress obviously inhibits the growth of plant roots, but the growth of mutants is more significantly inhibited. The average root length of wild-type plants was reduced by 45% ...
Embodiment 3
[0046] Example 3. QTL localization verification.
[0047] Using the constructed corn IBM Syn 10DH (B73×Mo17) population of 200 families as the linkage population, the processing method and phenotype identification are the same as 1-2, and then combined with 6618 bin marker genotype data, the QTL mapping results are as follows Figure 4 As shown, a QTL locus related to the total number of roots was detected on chromosome 10, with a phenotypic contribution rate of 5.1%, located in the segment chr10.471~chr10.596.5, and the corresponding physical position on the chromosome is 39.075 Mb ~ 53.375Mb (Maize B73RefGen_v3). The ZmbZIP107 gene falls in the QTL mapping segment, further verifying the importance of this gene in the process of lead stress in maize.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com