A kind of indium phosphide bismuth nitrogen material and its preparation method, laser and detector using the material and its preparation method
A technology of indium phosphorus nitrogen bismuth and laser, which is applied in the field of materials science, can solve the problems of difficulty in doping nitrogen atoms, no way to greatly improve semiconductor performance, narrowing and other problems, and achieves suppression of Auger recombination effect, good semiconductor performance, Increase the effect of spin-orbit splitting
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
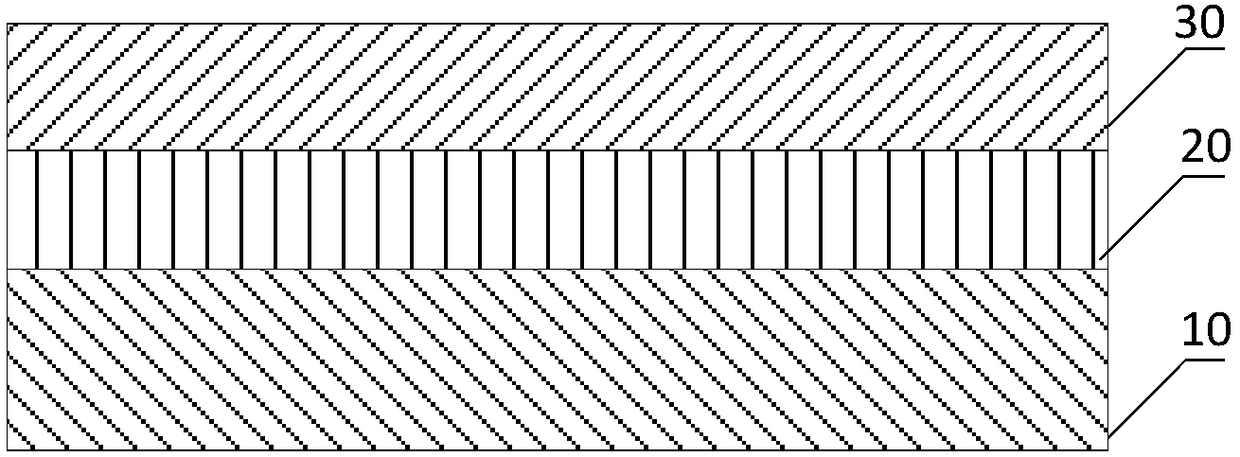
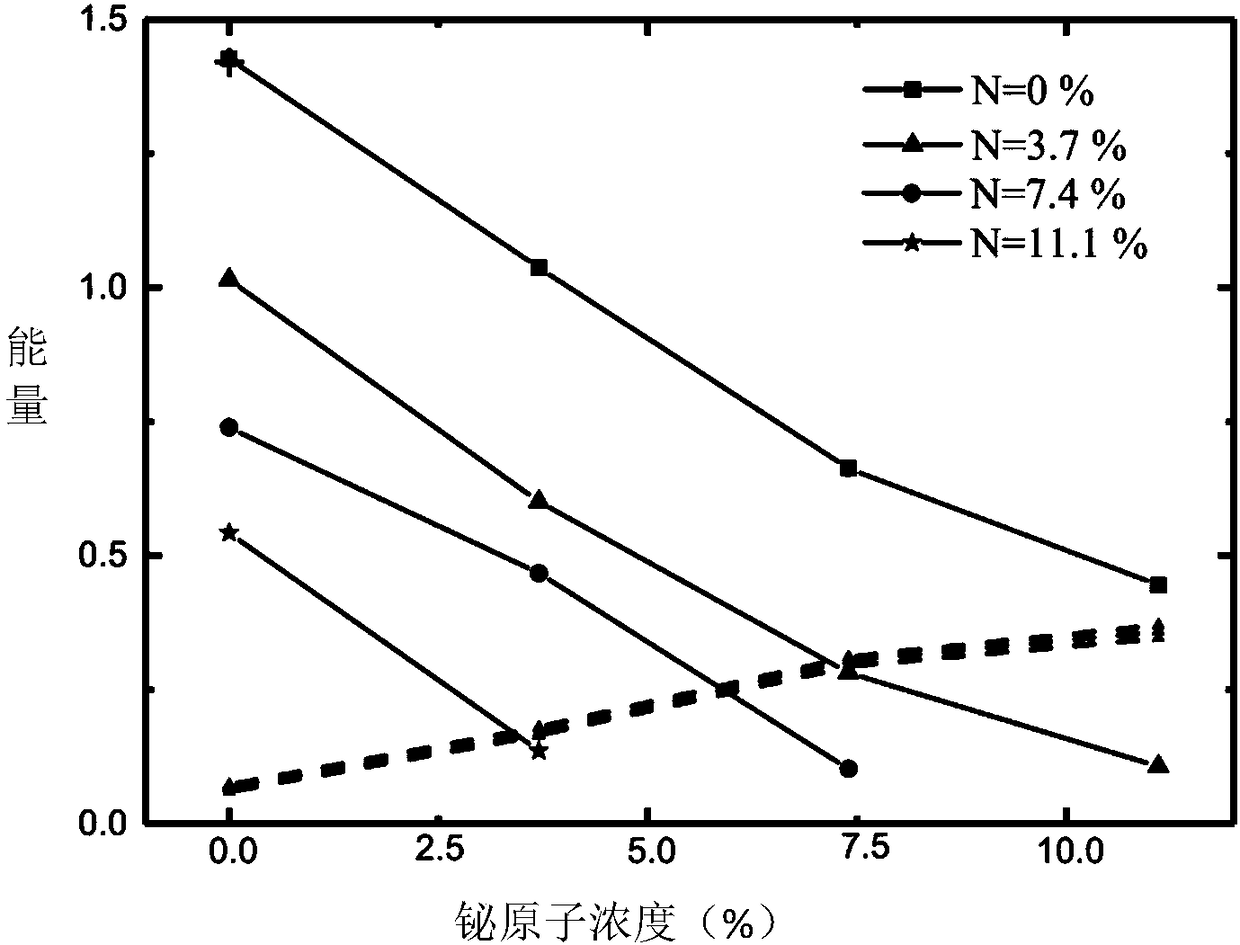
[0069] Please refer to figure 1 , in this embodiment, the indium phosphide bismuth nitrogen material includes: an indium phosphide substrate 10 , an indium phosphide buffer layer 20 and an indium phosphide bismuth nitrogen body 30 . Wherein the indium phosphide buffer layer 20 is disposed on the indium phosphide substrate. The InPBN body 30 is disposed on the InP buffer layer 20 . The chemical formula of indium phosphide bismuth nitrogen body is InP 1-x-y N x Bi y , where x and y are the concentration percentages of nitrogen atoms and bismuth atoms, respectively, and 0<x<11.1%, 0<y<11.1%. In other embodiments of the present application, the indium phosphide substrate may also be other auxiliary substrates.
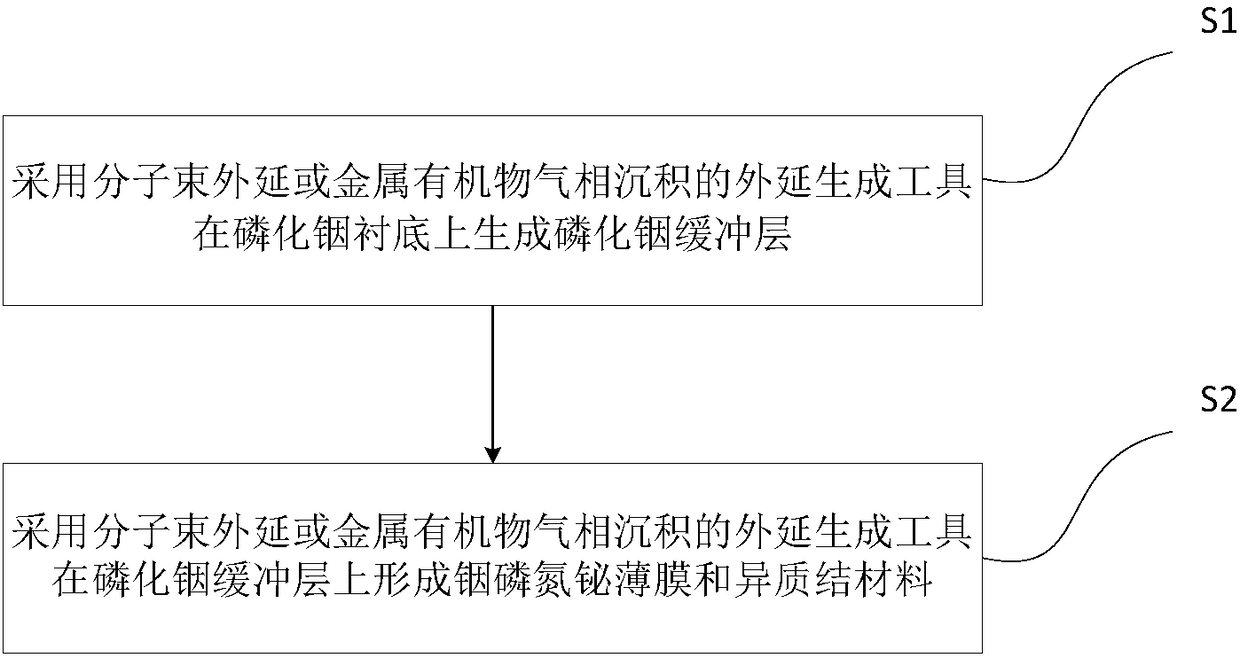
[0070] Please refer to figure 2 , in this embodiment, the preparation method of indium phosphide bismuth nitrogen material comprises the following steps:
[0071] S1: An indium phosphide buffer layer is formed on an indium phosphide substrate by molecular beam epit...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com