CRISPR/Cas9 targeted knockout human intestinal cancer cell RITA gene and specific sgRNA thereof
A colorectal cancer cell-specific technology, applied in the field of sgRNA, can solve the problem that the molecular mechanism of colorectal cancer has not yet been clarified
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
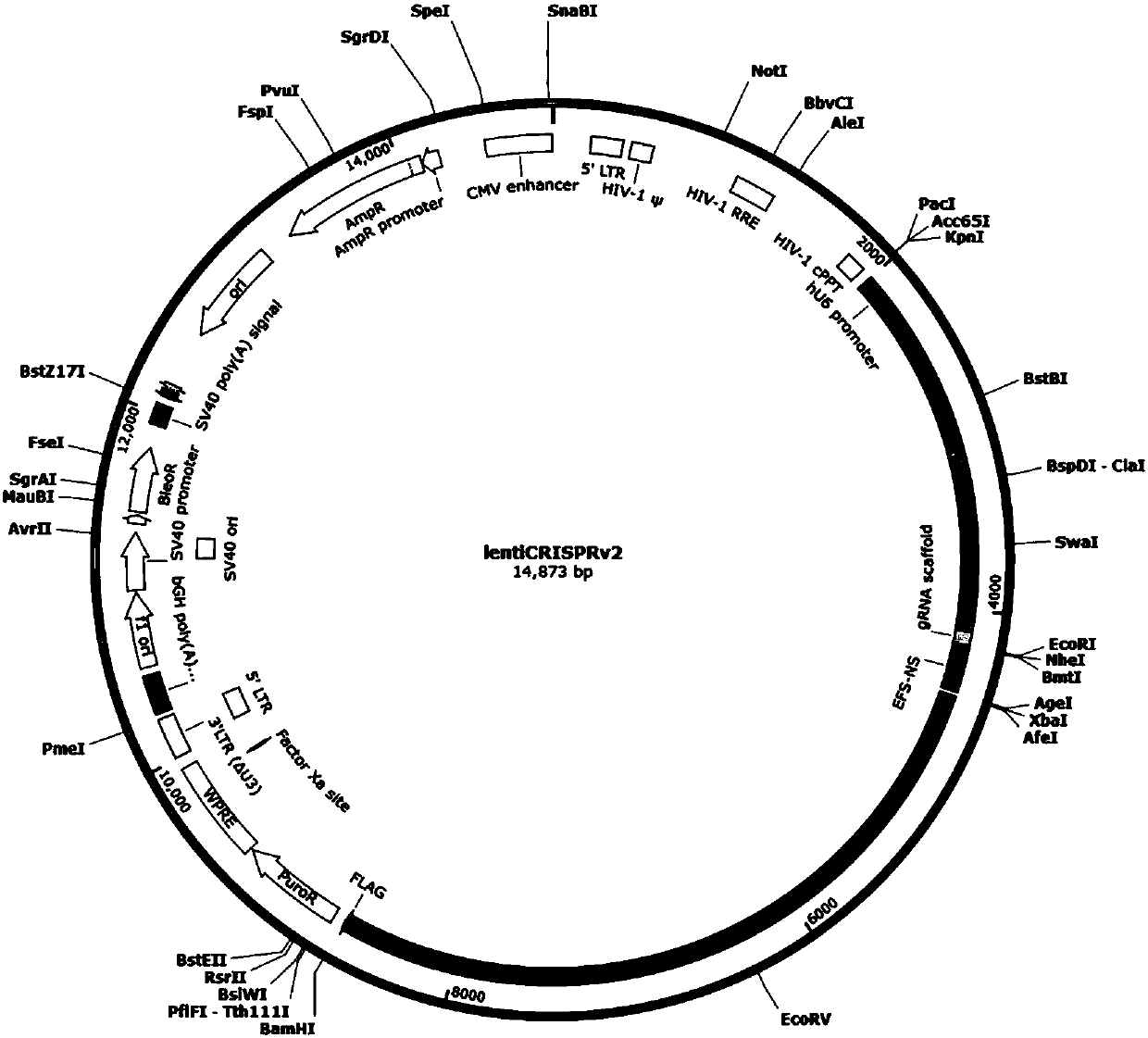
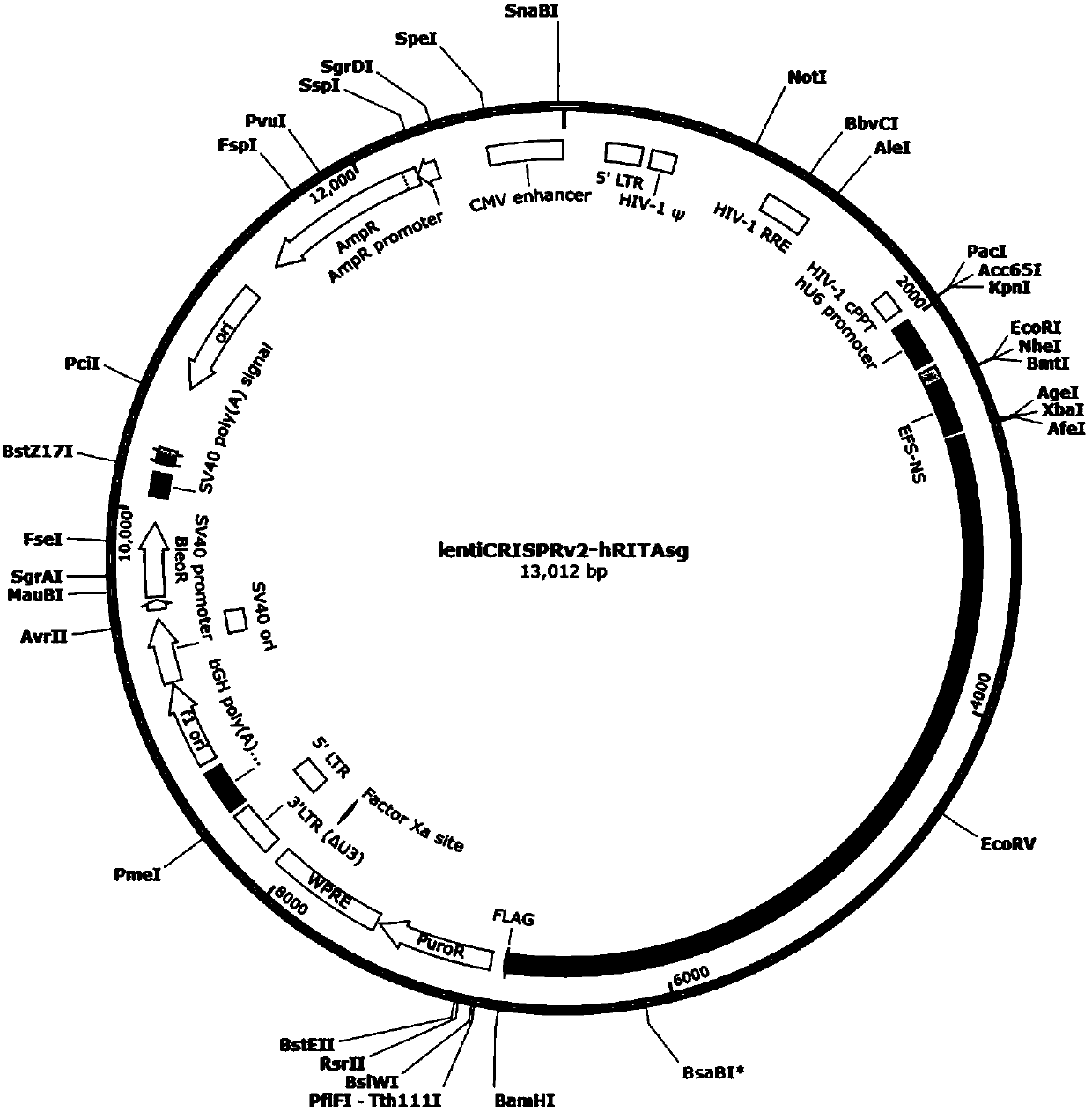
[0044] 1. Construction of knockout RITA plasmids using CRISPR / Cas9 technology
[0045] 1.1 sgRNA oligonucleotide chain synthesis
[0046] Use the CRISPR online design tool (http: / / crispr.mit.edu / ) to design a 20bp sgRNA on the second exon of RITA according to the scoring system, and verify that there are no non-specific genes by BLAST. ACCG is added to the 5′ end of the coding strand template, and AAAC is added to the 3′ end of the non-coding strand template, which is complementary to the cohesive end formed after digestion with BsmBI, and a pair of CRISPR oligonucleotide chains are designed, see Table 1, Table 1 RITA targeting position Dot and sgRNA oligonucleotide sequence.
[0047]
[0048] 1.2 Vector construction
[0049] 1.2.1 Use BsmBI to digest 2 μg Lenti-CRISPRv2 plasmid (purchased from Addgene), 2h, 37°C,
[0050] The enzyme digestion system is:
[0051]
[0052] 1.2.2 Purify the enzyme-digested plasmid product with Jerry Gene Gel Recovery Kit, and operate a...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com