Installation structure and modules
A technology for mounting structures and bumps, which is applied in the assembly of printed circuits with electrical components, semiconductor/solid-state device components, sustainable manufacturing/processing, etc., and can solve the problems of shortened signal wavelength, deterioration of connection reliability, and rising manufacturing costs.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
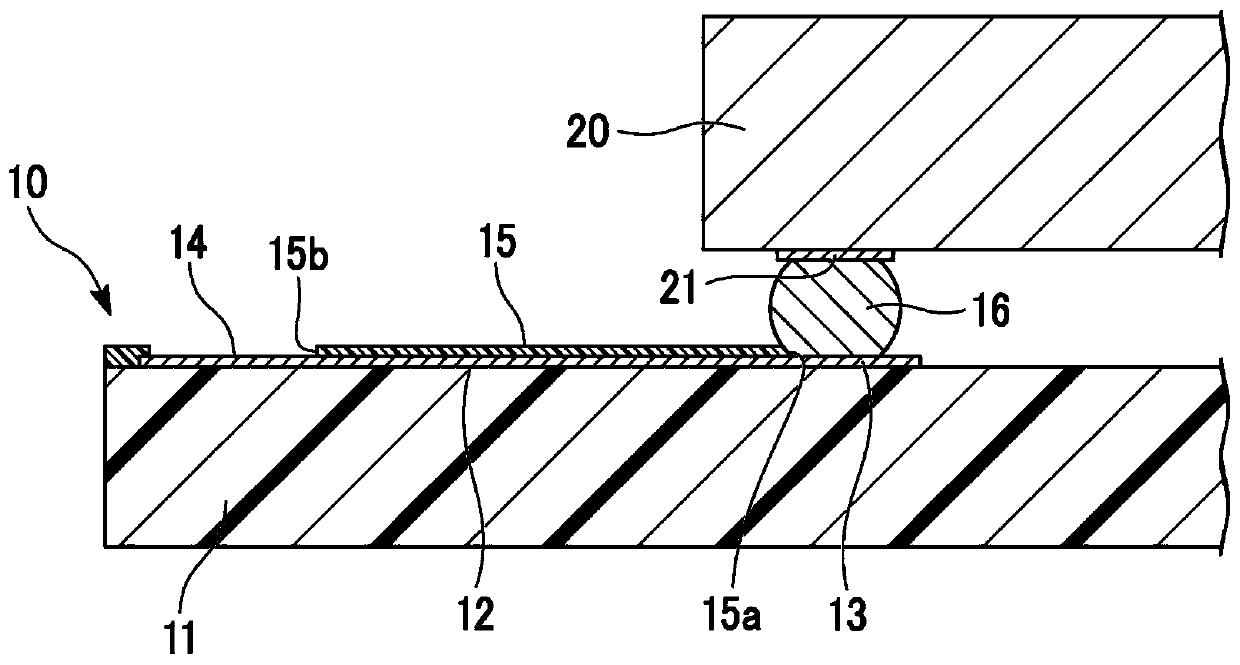
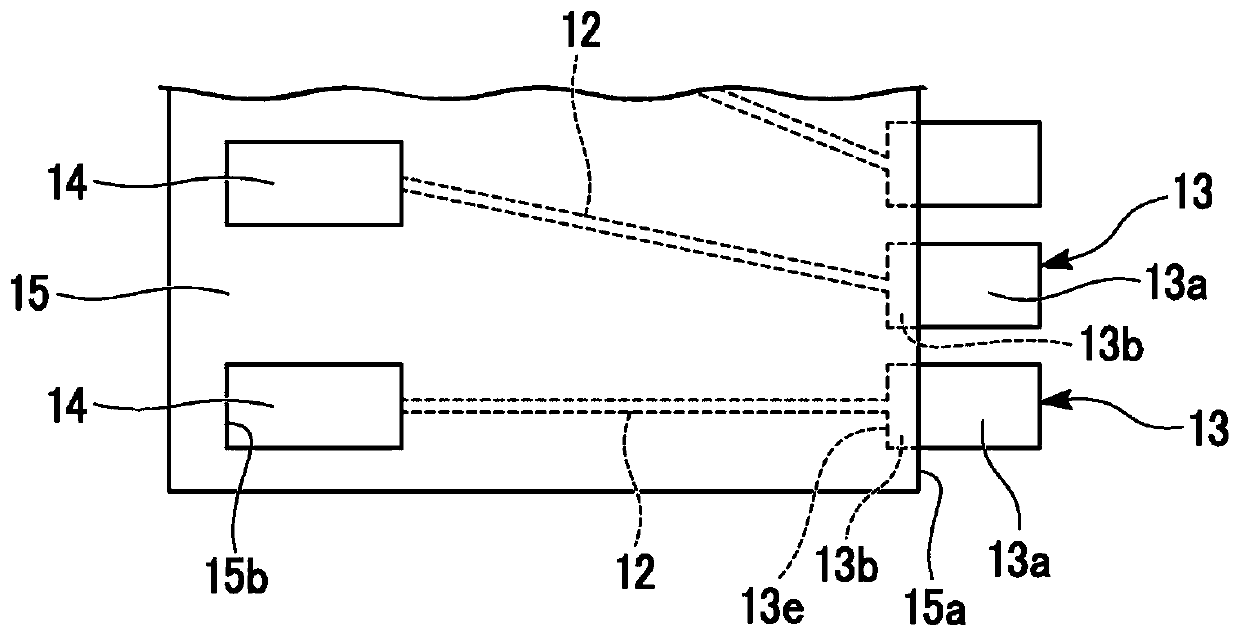
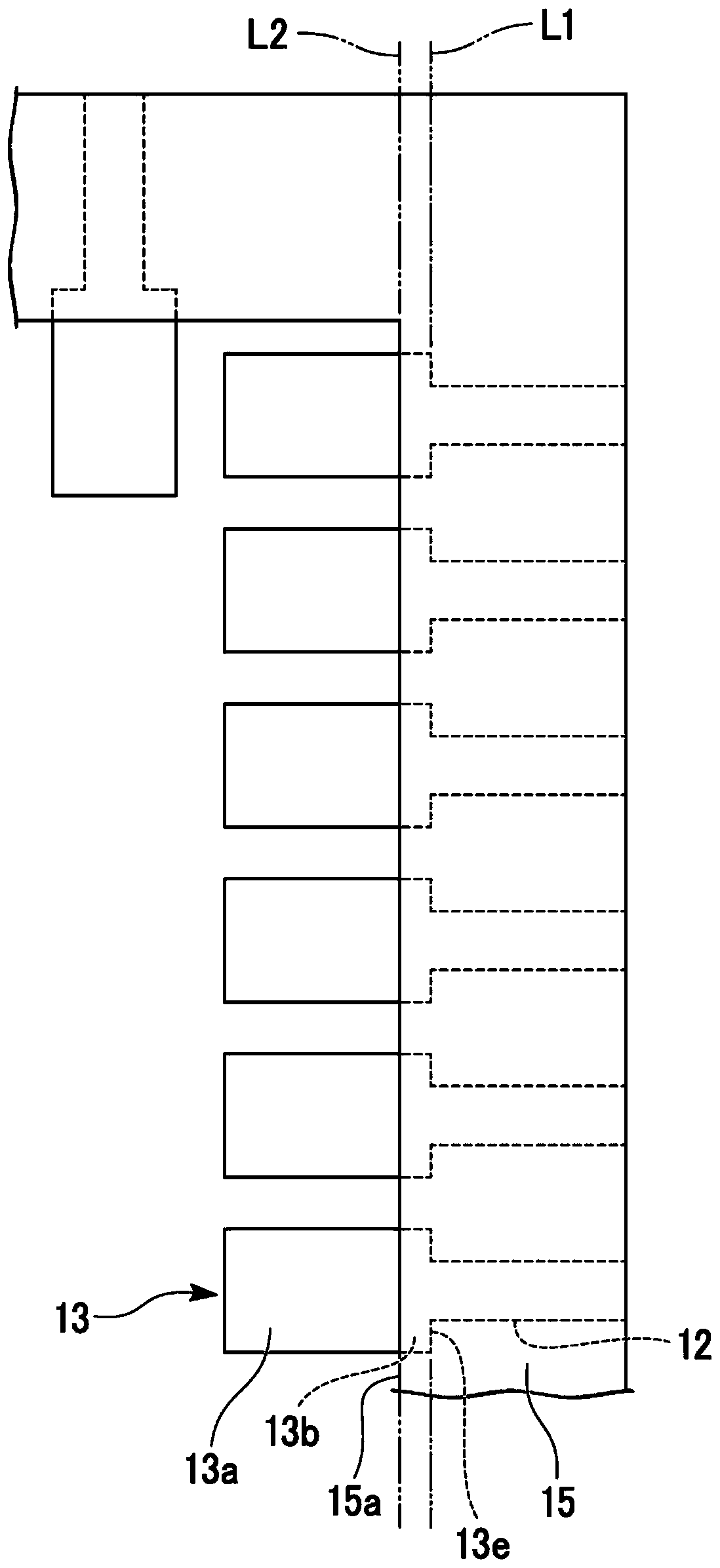
[0059] Figure 3A as well as Figure 3B The mounting structure of Example 1 is shown in . The mounting structure according to the first embodiment constitutes a module structure of an interposer substrate on which ICs are mounted as the semiconductor device 20 . The wiring board 10A of the first embodiment is an interposer substrate, and connects IC terminals (first terminals 21 ) with a narrow pitch of about 100 μm and FPC terminals (third terminals 14 ) with a wide pitch of about 500 μm.
[0060] The photosensitive insulating film 15 completely covers the wiring 12 , but an opening is formed in the photosensitive insulating film 15 inside the end portion 15 a in a region surrounded by the IC I / O terminal (second terminal 13 ). The width of the second terminal 13 (the dimension in the pitch direction, the width of the second terminal 13 in the direction in which the plurality of second terminals are arranged) is, for example, 70 μm. The width of the wiring 12 is, for examp...
Embodiment 2
[0064] Figure 4A as well as Figure 4B The mounting structure of Example 2 is shown in . In the second embodiment, the structure of the wiring board 10B is the same as that of the first embodiment, but the insulating material disposed around the bump 16 is the side filler 18 . The side filler 18 (for example, epoxy-based or the like) is disposed only on the peripheral portion of the lower surface of the semiconductor device 20 where the first terminal 21 and the bump 16 are provided by adjusting the viscosity. A cavity 19 is formed between the semiconductor device 20 and the wiring board 10B (specifically, between the insulating substrate 11 ). In the case of high-frequency transmission applications, there are cases where the transmission loss deteriorates due to the dielectric between the IC and the interposer. By using the side filler 18, a gas (air, etc.) with a low dielectric constant is arranged in the cavity 19, so that the stress relaxation function can be obtained ...
Embodiment 3
[0066] Figure 5A as well as Figure 5B The mounting structure of Example 3 is shown in . The third terminal 14 of the wiring board 10C of the third embodiment constitutes a card edge connector. For the structure directly below the semiconductor device 20, in Figure 5A as well as Figure 5B Although the case of using the same underfill 17 as in Example 1 is exemplified in FIG. 1 , it is also possible to use the side filler 18 like in Example 2. The end portion 15c of the photosensitive insulating film 15 that is in contact with the card edge connector is, for example, linear.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com