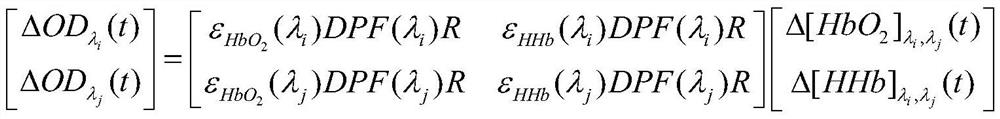A Near Infrared Brain Function Signal Processing Method Based on Differential Path Factor Estimation
A differential path and signal processing technology, applied in medical science, using spectrum diagnosis, diagnosis, etc., can solve the problems of measurement error interference, low measurement and extraction accuracy of near-infrared brain function activity response signal measurement, etc. The effect of high quality inspection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
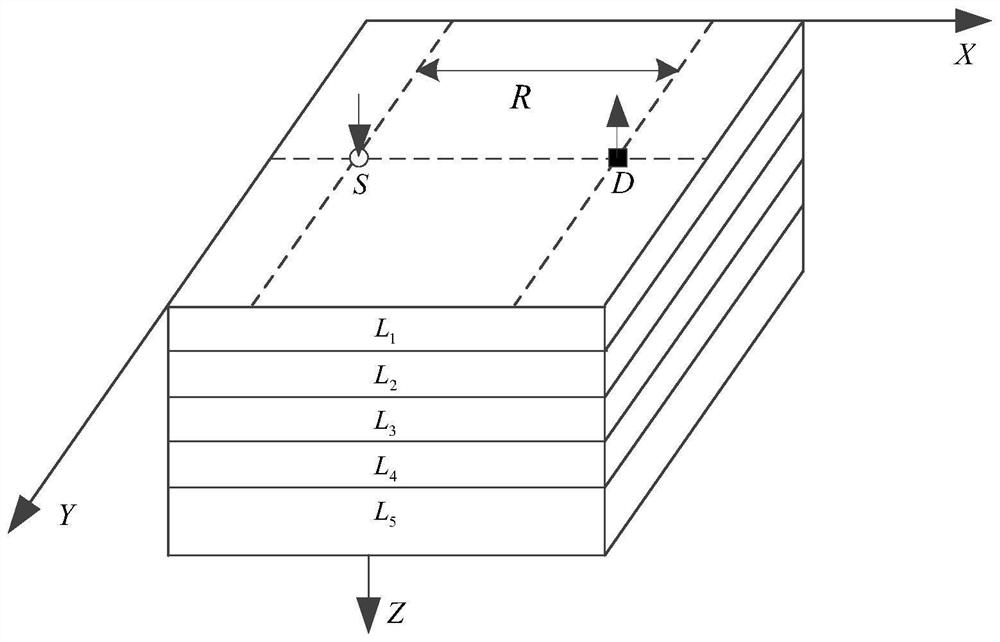
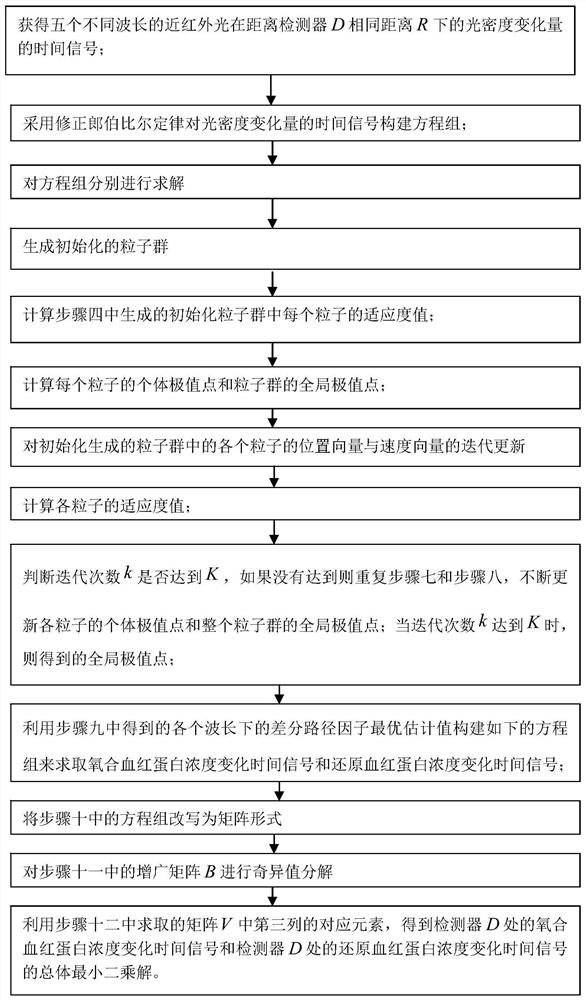
[0068] Embodiment 1: Combining figure 1 , figure 2 This embodiment will be described. The method for processing near-infrared brain function signals based on differential path factor estimation in this embodiment is specifically implemented according to the following steps:
[0069] Step 1: Place a near-infrared probe composed of a five-wavelength light source S and a detector D on the scalp surface of the brain tissue to be tested. The straight-line distance between the five-wavelength light source S and the detector D is R, and the five-wavelength light source S emits The wavelengths of near-infrared light are λ 1 , λ 2 , λ 3 , λ 4 and λ 5 , the detector D is used to obtain the diffuse reflection light intensity in the quiet state of the brain and the diffuse reflection light intensity in the brain-evoked excitation state, so as to obtain the optical density of five different wavelengths of near-infrared light at the same distance R from the detector D Time signal of ...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0125] Embodiment 2: This embodiment differs from Embodiment 1 in that: in step 10, the optimal estimated value of the differential path factor at each wavelength obtained in step 9 is used to construct the following equation system to obtain oxyhemoglobin Concentration change time signal and reduced hemoglobin concentration change time signal;
[0126] The specific equation system can be expressed as follows:
[0127]
[0128] where ε HHb (λ 1 ) is the wavelength of the near-infrared light emitted by the light source S is λ 1 The reduced hemoglobin extinction coefficient at ; ε HHb (λ 2 ) is the wavelength of the near-infrared light emitted by the light source S is λ 2 The reduced hemoglobin extinction coefficient at ; ε HHb (λ 3 ) is the wavelength of the near-infrared light emitted by the light source S is λ 3 The reduced hemoglobin extinction coefficient at ; ε HHb (λ 4 ) is the wavelength of the near-infrared light emitted by the light source S is λ 4 The re...
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0130] Embodiment 3: This embodiment is different from one of Embodiments 1 to 2 in that: in step 13, the corresponding element of the third column in the matrix V obtained in step 12 is used to obtain the Overall least squares solution of the time signal of oxyhemoglobin concentration change and the time signal of reduced hemoglobin concentration change at detector D; respectively expressed as:
[0131]
[0132]
[0133] Among them, Δ[HbO 2 ] TLS (t) is the overall least-squares solution of the oxyhemoglobin concentration change time signal at detector D; Δ[HHb] TLS (t) is the overall least squares solution of the reduced hemoglobin concentration change time signal at detector D.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com