klhl24 gene mutant and its application
A technology of KLHL24 and mutants, applied in the direction of ligase, enzyme, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of epidermolysis bullosa that need to be further studied
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0054] Example 1 Determination of epidermolysis bullosa pathogenic genes and pathogenic mutations
[0055] 1. Sample collection
[0056] The inventor collected a Chinese Han family with three generations of epidermolysis bullosa (Epidermolysis bullosa) and 4 sporadic patient samples. The family of this patient included 6 members, including 2 EB patients. The proband showed extensive exfoliation of the skin on the abdomen and limbs at birth. After receiving good care, the wound showed atrophic scar epithelium, and physical injury induced blisters and erosions. Recurring episodes, most of which were associated with hypo- or hyperpigmentation, but did not heal spontaneously, with mildly affected oral mucosa and toenail dystrophy, with normal hair growth; the affected daughter of the proband suffered from extensive skin detachment shortly after birth and died of secondary infection without obtaining a DNA sample.
[0057] Therefore, the inventor collected samples from the patien...
Embodiment 2
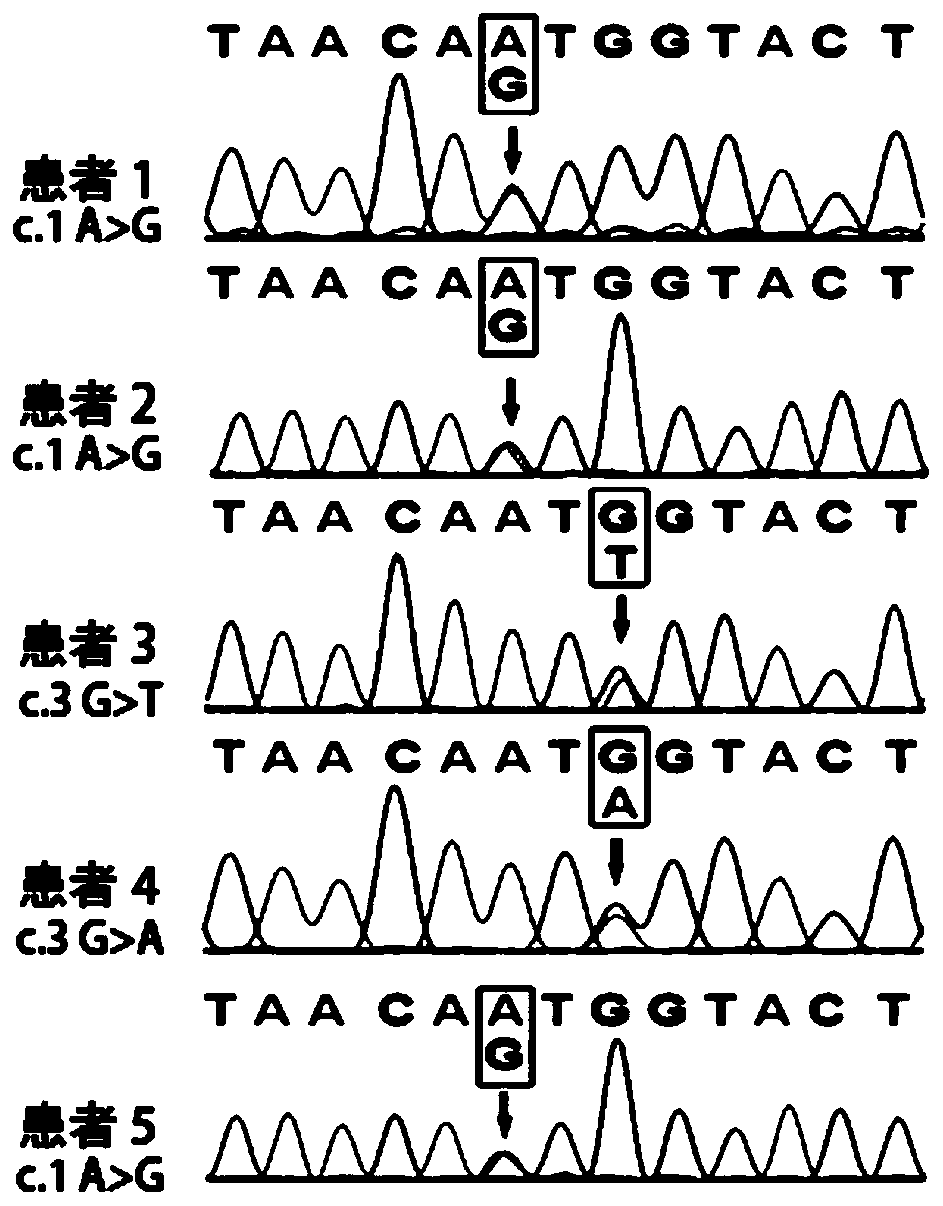
[0073] Example 2 Sanger method sequencing verification
[0074] The KLHL24 gene of 5 patients described in Example 1 (1 family patient, 4 sporadic patients) and normal parents was detected, primers were designed for the sequence of KLHL24, obtained by PCR amplification, product purification and sequencing The relevant sequence of KLHL24, according to whether the sequence determination results belong to the mutant type or the wild type, verifies the correlation between KLHL24 and EB disease. The specific method steps are as follows:
[0075] (1) DNA extraction:
[0076] Genomic DNA was extracted from the peripheral venous blood of 5 patients and normal family members according to the method in Example 1, and the concentration and purity of DNA were measured by a spectrophotometer. The OD260 / OD280 of each sample genomic DNA was between 1.7-2.0. The concentration is not less than 200ng / ul, and the total amount is not less than 30μg.
[0077] (2) Primer design and PCR reaction:...
Embodiment 3
[0084] Example 3 Other biological verification
[0085] 1. Reverse transcription PCR (RT-PCR)
[0086] KLHL24 belongs to the KELCH family of genes, which includes 42 genes. This gene encodes a KELCH protein that shares a highly conserved BTB domain and a BACK domain, and interacts with CUL3 and RBX1 to form a CUL3-RBX1-KELCH ubiquitin ligase complex. The KELCH proteins also share a KELCH domain responsible for the uptake of ubiquitinated substrates, thereby determining the specificity of the ubiquitin ligase E3. Therefore, the inventors determined whether KLH24 is expressed in skin tissue by performing RT-PCR analysis of KLHL24 on cDNA samples of skin and peripheral blood. The specific method is as follows:
[0087] (1) Total RNA was extracted from normal human skin and peripheral blood using Trizol reagent (Invitrogen) and QIAamp RNA BloodMiniKit kit (Qiagen) according to the manufacturer's instructions.
[0088] (2) cDNA was amplified from 50-500 ng of total RNA using Tra...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com