Pseudomonas aeruginosa for increasing yield of rhamnolipid, and construction method thereof
A technology of Pseudomonas aeruginosa and rhamnolipids, which is applied in the biological field, can solve problems such as rhamnolipid difficulties, and achieve the effects of increasing oil utilization capacity, increasing yield, and increasing yield
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
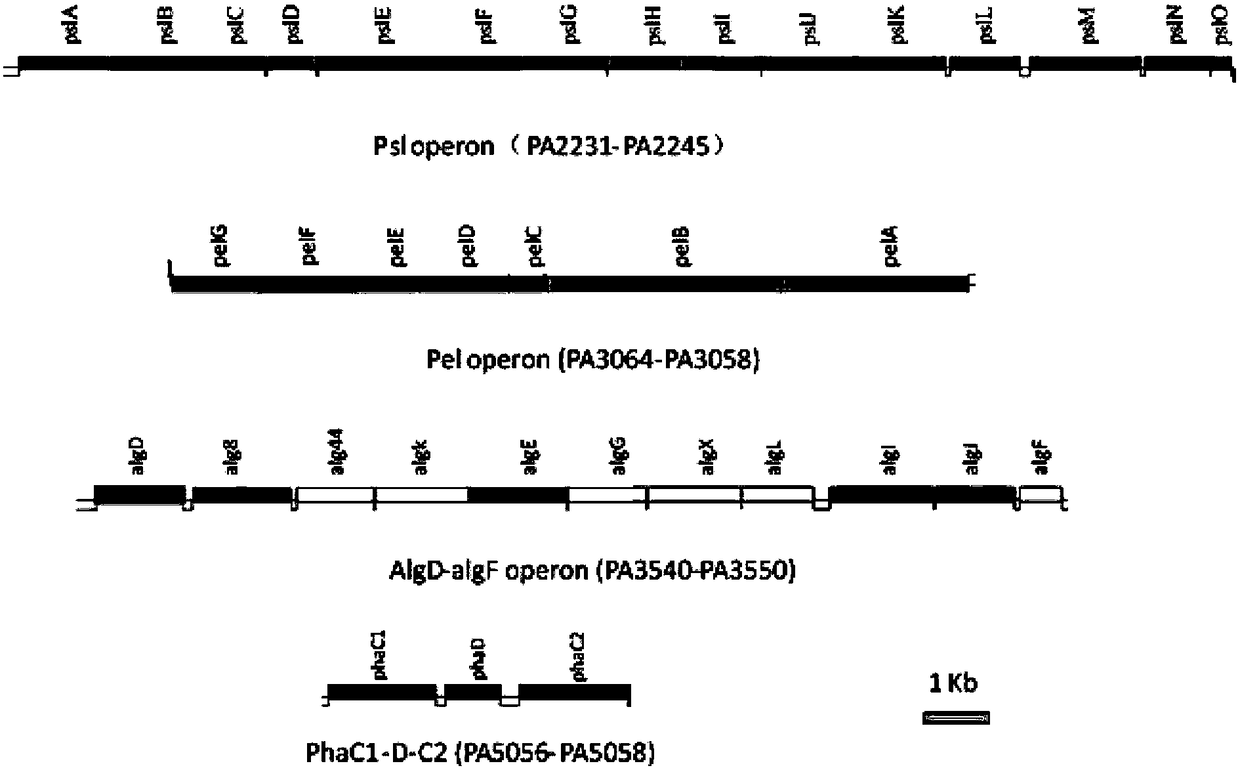
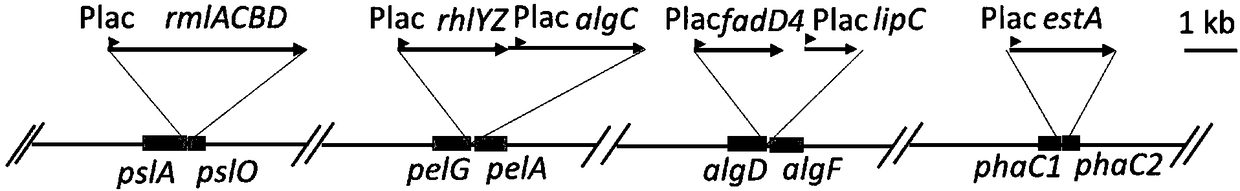
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0061] Embodiment 1, have the construction of the high copy plasmid vector pUCP18 of gentamicin (Gm) resistance
[0062] Primers were designed by analyzing the sequences of the high-copy plasmid vector pUCP18 and the gentamicin resistance cassette, and the primers used to amplify the gentamicin resistance were:
[0063] Gm(NdeI)-F:GTGC CATATG AAGTTCCTATACTTTC (SEQ ID NO. 1)
[0064] Gm(NdeI)-R:CGCTTACT CATATG GAATTCTAGATC (SEQ ID NO. 2)
[0065] The Gm resistance gene was amplified from the pPS856 plasmid as a template, then digested with NdeI, and cloned into the pUCP18 vector that was digested with NdeI and dephosphorylated to obtain the plasmid vector pUCP18Gm with gentamicin (Gm) resistance .
Embodiment 2
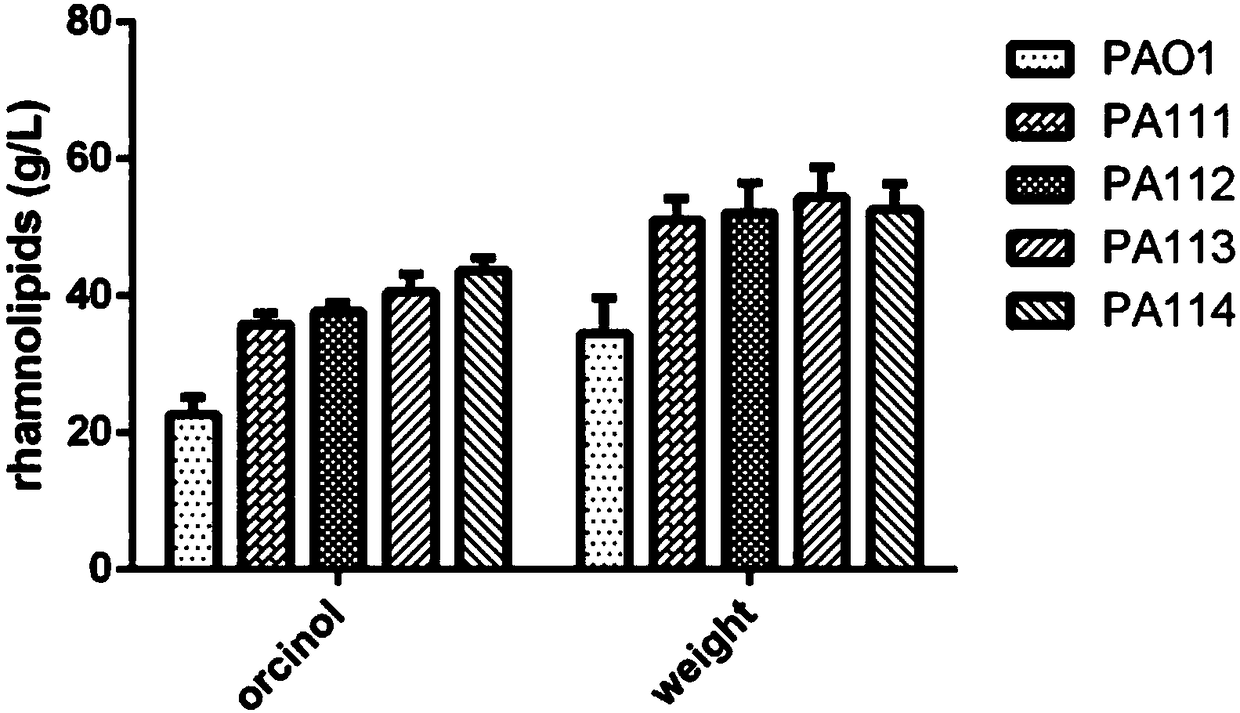
[0066] Example 2. Construction of rmlACBD and rmlBDAC overexpression strains PAO1 / rmlACBD, PAO1 / rmlBDAC and comparison strain PAO1 / pUCP18Gm and determination of rhamnolipid synthesis.
[0067] The rmlBDAC operon in Pseudomonas aeruginosa encodes the enzyme for dTDP-L-rhamnose synthesis. The order of the genes on the chromosome is rmlBDAC, and the promoter before the rmlB gene is affected by the clustering effect and σ s However, in the synthesis of dTDP-L-rhamnose, the sequence of action of the enzyme is RmlA, RmlB, RmlC and RmlD, and RmlA is responsible for transferring thymonucleotide to glucose-1-phosphate to generate dTDP-1 - Glucose, the rate-limiting enzyme for this series of reactions. RmlABCD plays a catalytic role in the dimer form of a dimer, so we also constructed a rmlACBD arrangement under the constitutive promoter, and compared the effects of these two arrangements on the production of rhamnolipids .
[0068] First, the rmlBDAC gene was cloned into the pUCP18Gm...
Embodiment 3
[0077] Example 3, construction of rhlYZ and algC overexpression strains PAO1 / algC, PAO1 / rhlYZ and determination of rhamnolipid synthesis
[0078] RhlYZ, enoyl-CoA hydratase / isomerase, is a group of enzymes recently discovered in Pseudomonas aeruginosa with a transition function in fatty acid degradation, responsible for the direct conversion of fatty acid β-oxidation intermediates into hydroxyacyl- COA (Abdel-Mawgoud, 2014). AlgC protein has two functions of phosphoglucomutase and phosphomannose mutase at the same time, which can convert glucose-6-phosphate and mannose-6-phosphate into glucose-1-phosphate and mannose-1-phosphate respectively, Glucose-1-phosphate generates dTDP-L-rhamnose under the action of RmlABCD. Therefore, it is speculated that the expression of RhlYZ and AlgC has an effect on the synthesis of rhamnolipids.
[0079] First, the rhlYZ and algC genes were cloned into the pUCP18Gm vector, respectively. Using Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 chromosomal DNA as a ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com