Degradable luminal stent with thermal adhesive composite structure, and preparation method thereof and application thereof
A composite structure and thermal bonding technology, applied in stents, medical science, surgery, etc., can solve the problems of stent structural integrity damage, uneven material degradation, stent collapse, etc., and achieve poor mechanical properties and bond fastness Large, the effect of improving the radial support force
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0036] A method for preparing a degradable luminal stent with a thermally bonded composite structure:
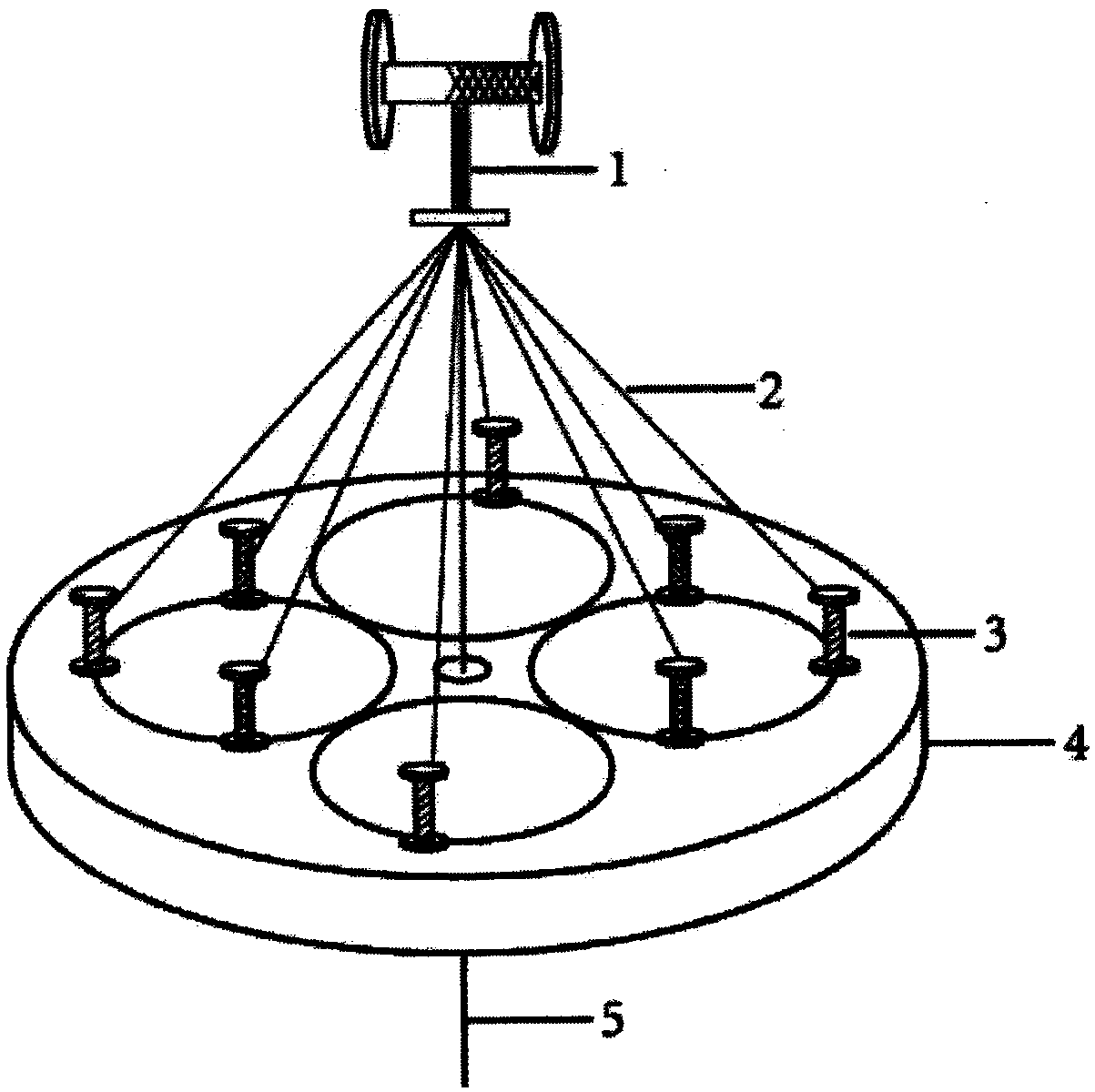
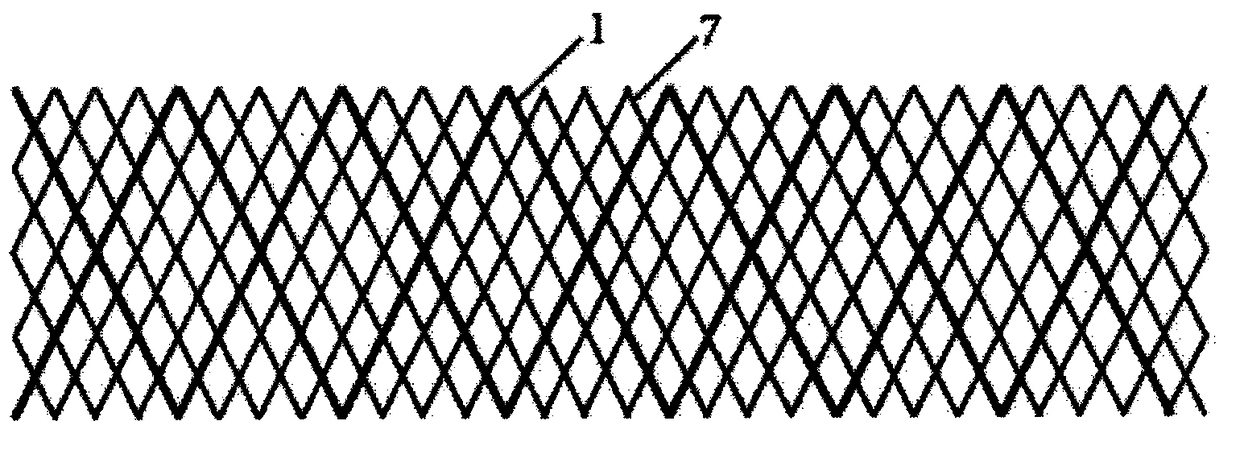
[0037] Step 1: Such as figure 1 As shown, polycaprolactone (PCL) is used as the shell yarn 2 to make four sets of bobbins 3 and placed on the yarn carrier 4 of the knitting machine; the yarn carrier 4 drives the bobbin 3 carried by the yarn carrier 4 to perform the knitting action . The yarn tube 3 carrying the PCL moves in the opposite direction around the poly-p-dioxanone (PPDO) core yarn 5 drawn from the central through hole of the braiding machine track disk to form a braided yarn 1 with a shell core structure. The PCL shell yarn is a multifilament with a diameter of 0.10mm, and the PPDO core yarn is a monofilament with a diameter of 0.30mm. The weaving method used is 8 spindles diamond weaving;
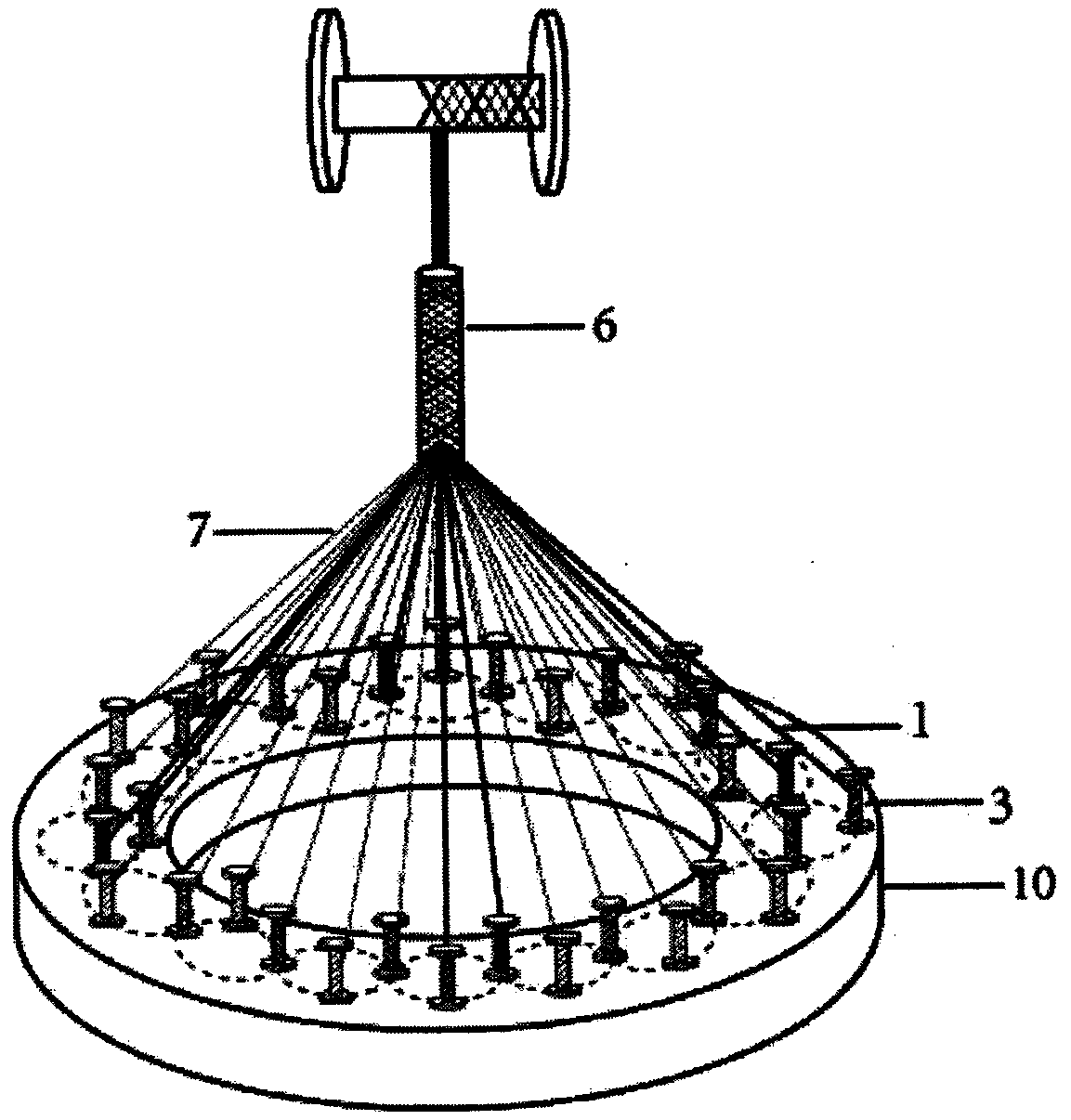
[0038] Step 2: Such as figure 2 As shown, 4 groups of knitting yarns 1 and 20 groups of single-component degradable polymer yarns 7 of PPDO monofilament are made into bobbins 3 an...
Embodiment 2
[0041] A method for preparing a degradable luminal stent with a thermally bonded composite structure:
[0042] Step 1: Such as figure 1 As shown, PLLA is used as the shell yarn 2 to make 8 sets of yarn tubes 3 and placed on the yarn carrier 4 of the knitting machine; the yarn carrier 4 drives the yarn tube 3 carried by the yarn carrier 4 to perform the knitting action. The bobbin 3 carrying PLLA moves in the opposite direction around the polyglycolide (PGA) core yarn 5 drawn from the central through hole of the orbit disk of the braiding machine, so that the twist direction of the shell yarn 2 is positive and antisymmetric with the core yarn 5 as the central axis. , The braided yarn 1 that forms the shell core structure, the PLLA shell yarn 2 is a multifilament with a diameter of 0.05mm, and the PGA core yarn 5 is a monofilament with a diameter of 0.25mm. The weaving method used is 8 spindles regular weaving;
[0043] Step 2: Such as figure 2 As shown, 8 groups of knitting yarns 1...
Embodiment 3
[0046] A method for preparing a degradable luminal stent with a thermally bonded composite structure:
[0047] Step 1: Such as figure 1 As shown, polyglycolide-lactide (PLGA) is used as the shell yarn 2 to make 4 sets of bobbins 3 and placed on the yarn carrier 4 of the knitting machine; the yarn carrier 4 drives the bobbin carried by it to move Implement the knitting action. The bobbins 3 carrying PLGA are equally divided into two groups, around a group of polyglycolide (PGA) core yarns 5 drawn out from the central through hole of the braiding machine track disk to do a reverse movement, so that the twist direction of the shell yarn 2 is centered Yarn 5 is a braided yarn 1 whose central axis is positively and antisymmetrically staggered to form a shell core structure. PLGA shell yarn 2 is a multifilament with a diameter of 0.08mm. PGA core yarn 5 is a monofilament with a diameter of 0.20mm. The weaving method used is 8 Ingot diamond weaving;
[0048] Step 2: Such as figure 2 As...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| The inside diameter of | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Wall thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com