A kind of method that the photocatalytic material containing indium phosphide doped modified tio2 catalytically degrades antibiotic waste water
A photocatalytic material, indium doping technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, catalyst activation/preparation, physical/chemical process catalysts, etc. , to achieve the effect of reducing production cost and high degradation rate
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0039] Preparation of Indium Phosphide Doped Modified TiO 2 The photocatalytic material comprises the following steps:
[0040] 1) Dissolve 34.0g of tetrabutyl titanate in 500ml of ethanol and stir evenly to obtain an ethanol solution of tetrabutyl titanate;
[0041] 2) 1.1g of 8-hydroxyquinoline was dissolved in 30ml of ethanol to obtain an ethanol solution of 8-hydroxyquinoline, and 10ml of indium phosphide toluene dispersion (containing indium phosphide 0.29g), and stirred evenly to obtain the first mixed liquid;
[0042] 3) Raise the temperature of the first mixed solution to 60-70°C, adjust the stirring speed to 1000rpm, then add the ethanol solution of tetrabutyl titanate dropwise, and keep stirring for 1-2 hours after the dropwise addition to obtain the second mixed solution;
[0043] 4) Add acetic acid dropwise to the second mixed solution, adjust the pH to 2-3 to obtain a gel-like suspension, stir for 4-6 hours, cool down to 30-40°C and leave to age for 24-48 hours ...
Embodiment 1-A
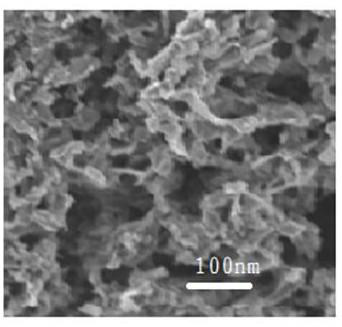
[0048] Using the single factor variable method to compare and illustrate the influence of 8-hydroxyquinoline as an organic additive on the catalytic performance of the prepared catalytic material, compared with Example 1, the difference is that 8-hydroxyquinoline is not added, and the rest are completely consistent with Example 1 , the prepared product is abbreviated as InP / TiO 2 .
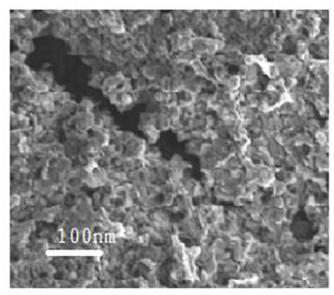
[0049] The scanning electron microscope picture of the photocatalytic material prepared by embodiment 1-A is as follows figure 2 As shown, it can be seen from the figure that the morphology of the photocatalytic material prepared by the present invention is porous particles, and the pore diameter is obviously larger than that of the sample prepared in Example 1; the specific surface area and pore size distribution tester (JW-K type) The specific surface area of the sample was measured, and its specific surface area was only 117.1m 2 / g (BET method).
Embodiment 1-B
[0051] The influence of indium phosphide as an additive on the catalytic performance of the prepared catalytic material is compared and illustrated by the single factor variable method. Compared with Example 1, the difference is that no indium phosphide is added, and the rest are completely consistent with Example 1. The prepared product Abbreviated as 8-HQ / TiO 2 .
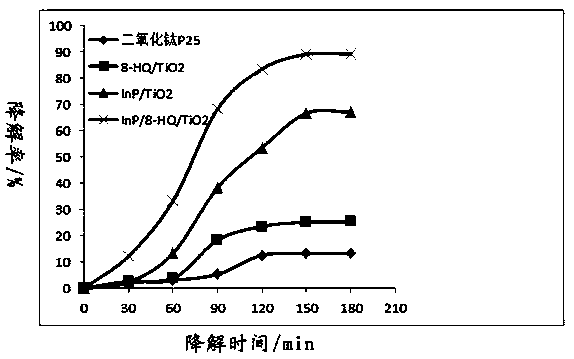
[0052] Take sulfadiazine wastewater (wastewater is brown, CODcr=8940mg / L, pH=7.2-7.5; the concentration of sulfadiazine is 42-48mg / L) and filter it with activated carbon to remove solids and colloids, adjust the pH of the filtrate to 6 with hydrochloric acid, and carry out Catalytic oxidation degradation test:
[0053] Get titanium dioxide P25, embodiment 1 product (InP / 8-HQ / TiO 2 ) and its Example 1-A (InP / TiO 2 ) and Example 1-B (8-HQ / TiO 2 20 mg each of the products, respectively placed in 1L of filtrate with pH=6, were subjected to photocatalytic oxidative degradation at 40°C under natural light and ultrav...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| specific surface area | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com