Fluorescent probe for distinguishing GSH (Glutathione), Cys (Cysteine) and SO2 as well as preparation method and application of fluorescent probe
A technology of fluorescent probes and synthesis methods, applied in the field of organic small molecule fluorescent probes, can solve problems such as insufficient discrimination, and achieve the effect of broad application prospects
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] Example 1 Co-SO 2 Synthesis of fluorescent probe
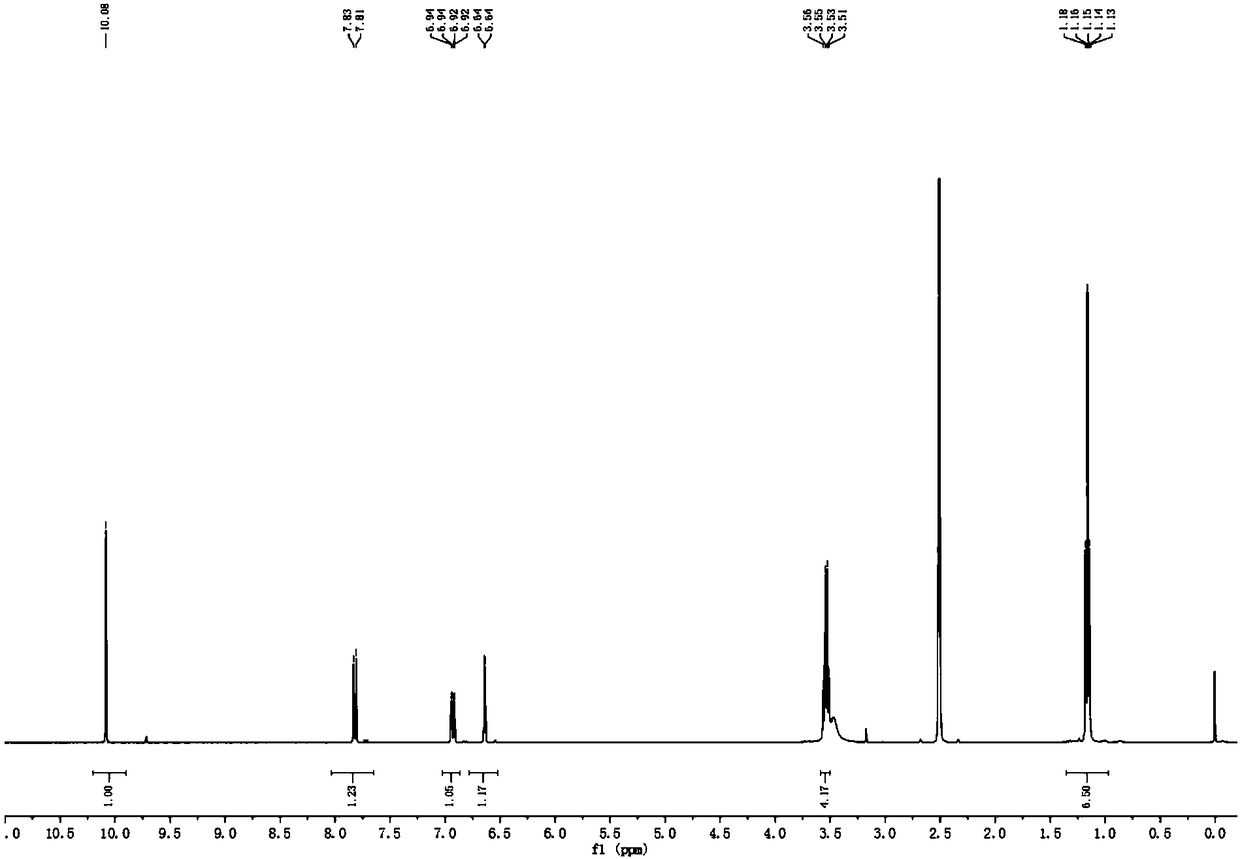
[0032] At 0℃, DMF (15 mL, 10.0 mmol) was added to a 100 mL single-necked flask, and POCl 3 (2 mL,) was added dropwise to the flask. After stirring for 30 min at 0℃, the compound 7-diethylamino-4-hydroxycoumarin was dissolved in DMF and added dropwise to the above solution. The temperature was gradually increased to 80°C and reacted for 4 hours. After the reaction, the reaction solution was cooled to room temperature, and then poured into ice water, adjusted to neutral pH to obtain a large amount of solids. The solids were filtered and purified by column chromatography (2 Chloroform: methanol=40:1, v / v), the yellow compound Co-SO2 is finally obtained; its 1 The H NMR spectrum is shown as figure 1 Shown.
Embodiment 2
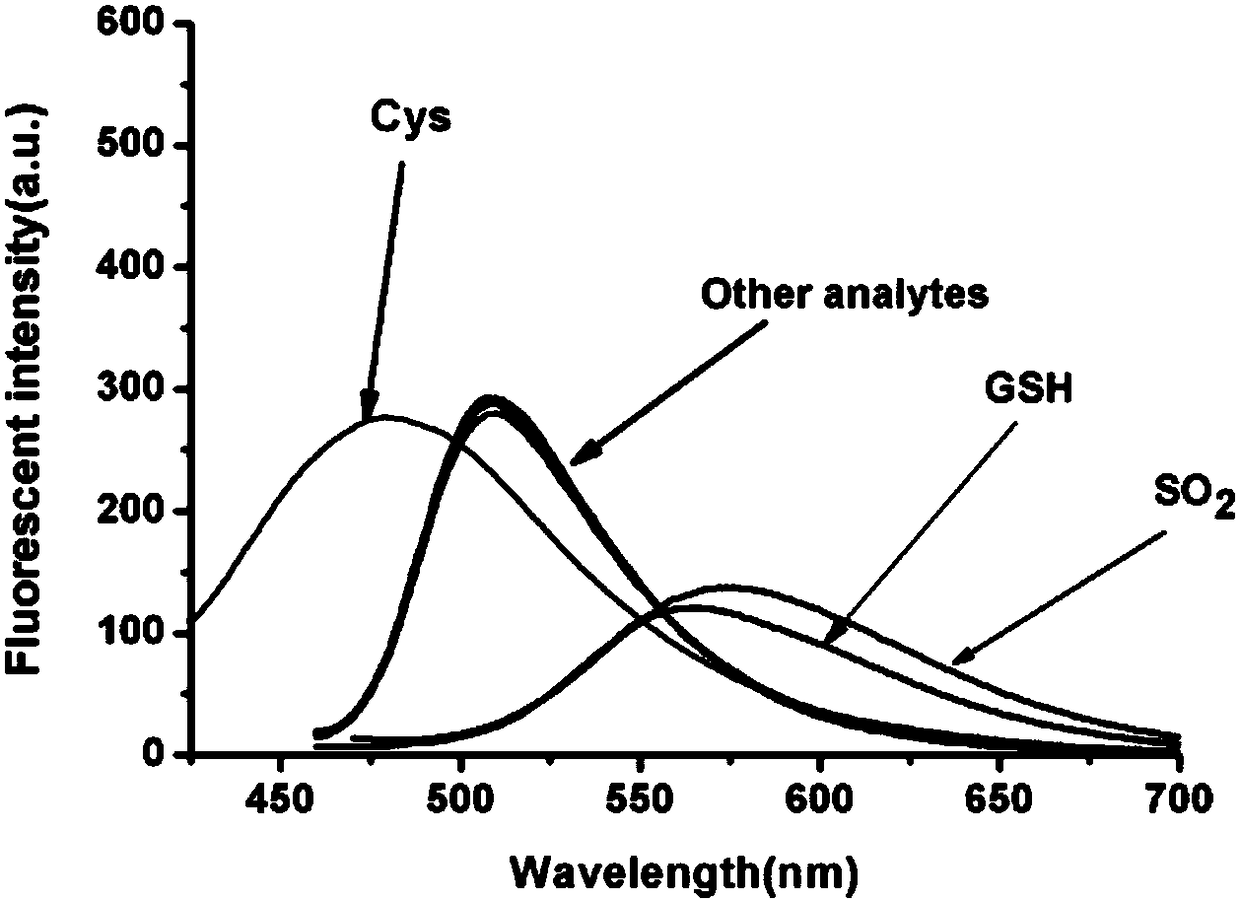
[0033] Example 2 Co-SO 2 Selectivity of fluorescent probes to different molecules or ions
[0034] The Co-SO in Example 1 2 The fluorescent probe was prepared into a mother liquor with a concentration of 1 mM.
[0035] Br - , ClO - , Cu 2+ , F - , Fe 2+ , H 2 O 2 , HClO, Hg 2+ , HPO 4 2- , Mg 2+ , N 3- ,Na + , Na 2 S, NaHS, NO 2- , NO 3- , OAC - , ONOO - , S 2 O 3 2- , SCN - , SO 4 2- , Zn 2+ , Singlet oxygen, SO 2 , GSH, Hcy, Cys are prepared with phosphate buffer (0.01 mM, pH=7.4) to prepare 5 mL mother liquor with a concentration of 40 mM.
[0036] Take 28 test tubes, add 25 μL probe mother solution, 225 μL DMSO, and the mother solution of each ion or molecule respectively, and use the same amount of water instead of interfering substances; dilute to 5 mL with phosphate buffer (0.01 mM, pH=7.4) , The final concentration of each ion or amino acid is 3 mM, and the final concentration of reactive oxygen and reactive nitrogen is 100 mM. After shaking the solution, perform fluorescen...
Embodiment 3
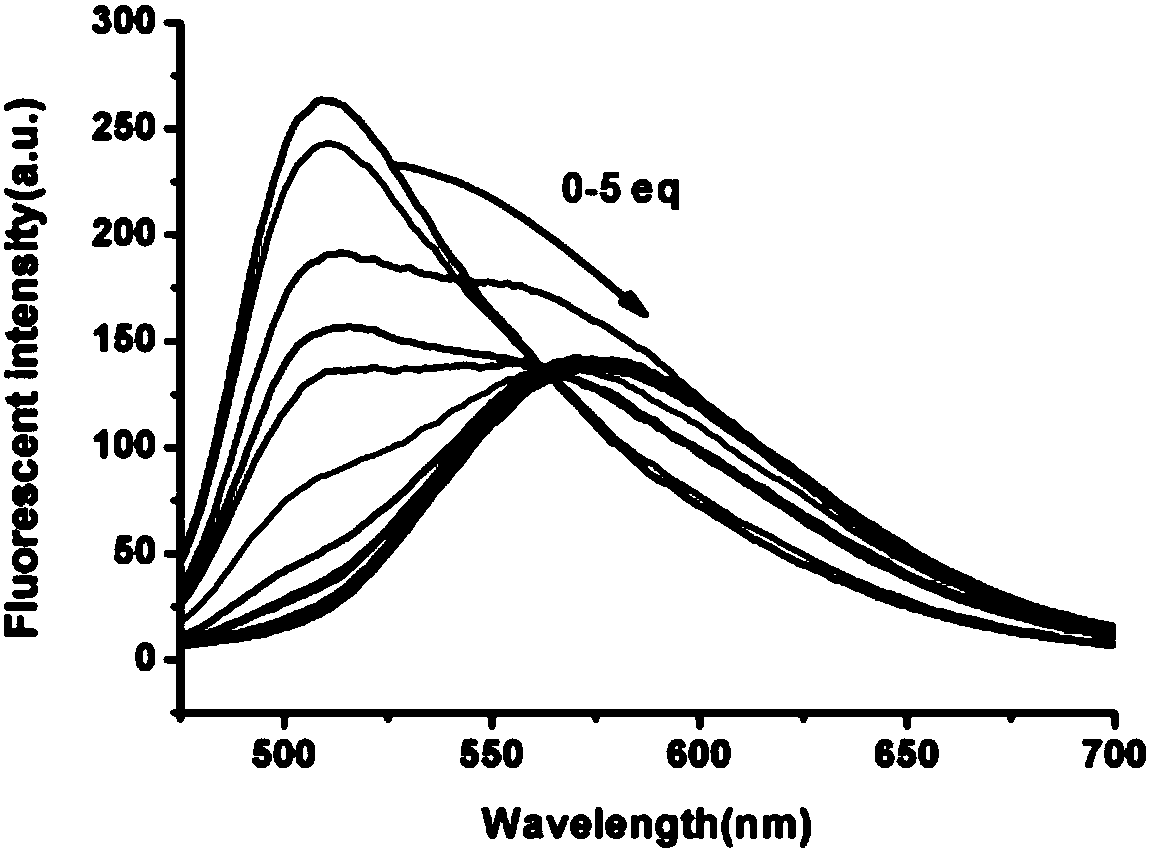
[0037] Example 3 Different concentrations of SO 2 Down Co-SO 2 Fluorescence intensity and wavelength change
[0038] Prepare 10 mL of 100 mM SO 2 The mother liquor was diluted with water to a total of 17 arithmetic concentrations of 0-40 μM, with water as the control. The Co-SO in Example 2 2 The mother liquor is diluted to 5 μM, and different concentrations of SO are added respectively 2 , After reacting for 5s, perform fluorescence detection (λex = 460 nm, λem = 575 nm), and detect the fluorescence intensity in each system. Use fluorescence intensity-SO 2 Concentration curve, such as image 3 Shown. It can be seen from the figure that with SO 2 As the concentration increases, not only the fluorescence intensity of the reaction system increases, but the emission wavelength also undergoes a red shift. When SO 2 When the concentration reached 25 μM, the fluorescence intensity of the reaction system reached saturation at 575 nm.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com