Flanking sequence of disease-resistant transgenic soybean event B5B9013-4 exogenous insertion element and application thereof
A technology of genetically modified soybeans and exogenous insertion, applied in the field of plant biology, can solve problems such as undiscovered disease-resistant genetically modified soybeans, and achieve effective supervision and management
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1. Analysis of the insertion site of the exogenous fragment of the transgenic soybean event B5B9013-4
[0039] 1. Genomic DNA extraction of transgenic soybean B5B9013-4
[0040] (1) Genomic DNA extraction: Take 1-2 g of young soybean leaves, grind them into powder with liquid nitrogen, and put them into a 50 mL centrifuge tube. Add 5mL extract solution A (100mmol / L Tris-HCl, pH8.0, 0.35mol / L sorbitol, 5mmol / L EDTA, pH8.0, 1% 2-mercaptoethanol), 3.5mL extract solution B (50mmol / L L Tris-HCl, pH8.0, 4.0mol / LNaCl, 1.8% CTAB, 25mmol / L EDTA, pH8.0), 0.3mL 30% sodium lauroyl sarcosinate and 2% PVP-360, incubated at 55°C 60-90 minutes, shaking gently several times during the period. Take out the centrifuge tube, add an equal volume of chloroform:isoamyl alcohol (24:1), shake it upside down for 15 minutes, and then centrifuge at room temperature for 10 minutes (13000rpm). Aspirate the supernatant, add 2 / 3 volume of pre-cooled isopropanol mixed with 1 / 10 volume of sup...
Embodiment 2
[0045] Example 2. Analysis of the left and right border flanking sequences of the transgenic soybean event B5B9013-4 exogenous insert
[0046]According to the exogenous insertion sequence of the transgenic soybean event B5B9013-4 and the upstream and downstream sequences of the insertion site in the soybean reference genome, PCR detection primers were designed. B5B9013-4 insertion site upstream sequence amplification primers are B5B9013LB-F1 (5'-CCCTCACTCCATTTGTCCTCT-3') and B5B9013LB-R1 (5'-TCCCACATACTTCCTCCCTCT-3'); B5B9013-4 insertion site downstream sequence amplification primers are B5B9013RB-F1 (5'-TACTTCCTCCCTCTTCAGCACC-3') and B5B9013RB-R1 (5'-GGTAGCGATGTGGACCTTAGCCTT-3').
[0047] Using the B5B9013-4 genomic DNA as a template, PCR amplification was performed using the above primers. The PCR reaction system (25uL) is: 10×PCR buffer 2.5uL, 10mmol / L dNTPs 0.5uL, 5U / uL Taq enzyme 0.5uL, sample DNA 1.0uL, 10umol / L forward primer 0.5uL, 10umol / L reverse Primer 0.5uL, ddH ...
Embodiment 3
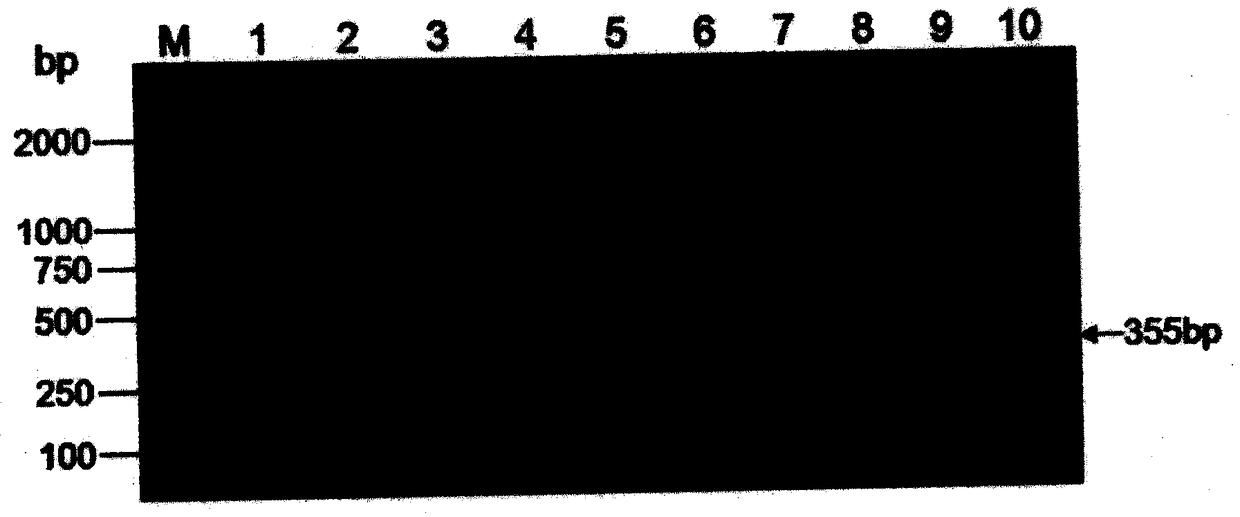
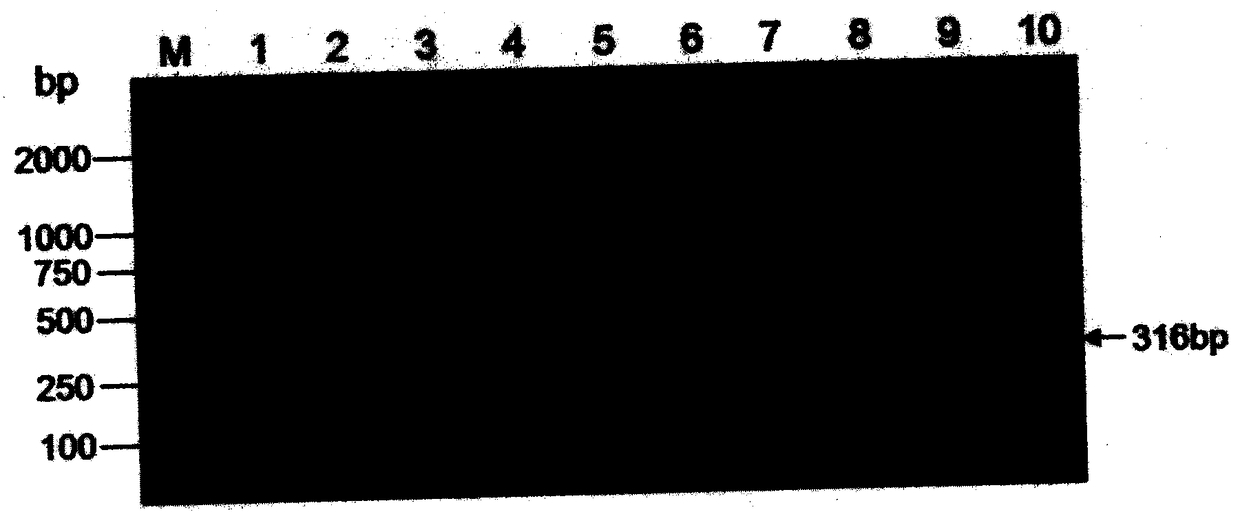
[0049] Example 3. Specific PCR detection of transgenic soybean event B5B9013-4
[0050] According to the left border flanking sequence (as shown in SEQ-2) and the right border flanking sequence (as shown in SEQ-3) of the exogenous insert fragment of the transgenic soybean event B5B9013-4, specific detection primers were designed respectively. In the left border flanking sequence-specific detection primer combination, one of the primers is a forward primer designed based on the sequence of SEQ-2 No. 1-1071, as shown in SEQ-4; the other primer is based on SEQ-2 No. 1072- The reverse primer designed for the 1401 site sequence is shown in SEQ-5. In the right border flanking sequence-specific detection primer combination, one of the primers is a forward primer designed based on the sequence of the 1-323 positions of SEQ-3, as shown in SEQ-6; the other primer is based on the 324- The reverse primer designed for the sequence at position 845 is shown in SEQ-7.
[0051] The DNA sampl...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com