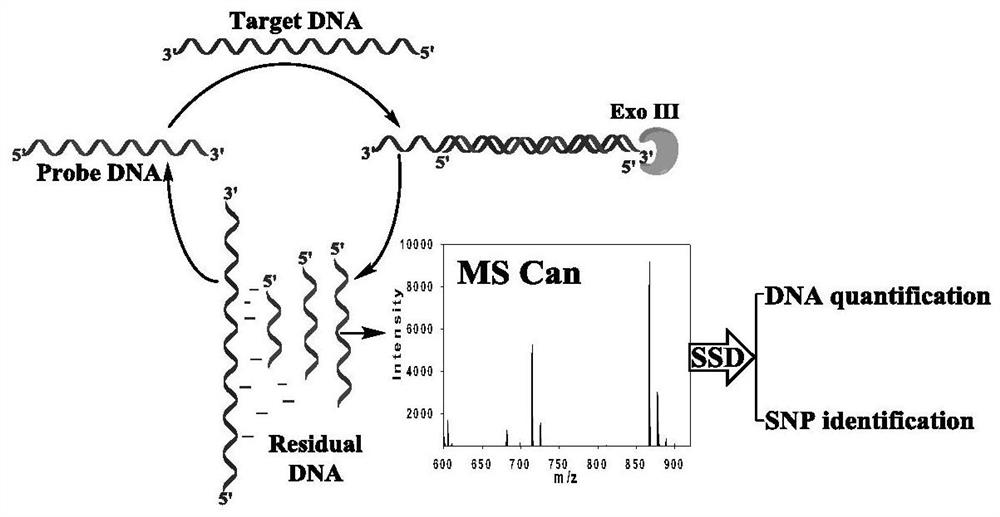
A method for quantitative analysis of label-free DNA mass spectrometry based on exonuclease III-assisted target cyclic amplification
A technology of exonuclease and target circulation, applied in the field of biological detection
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
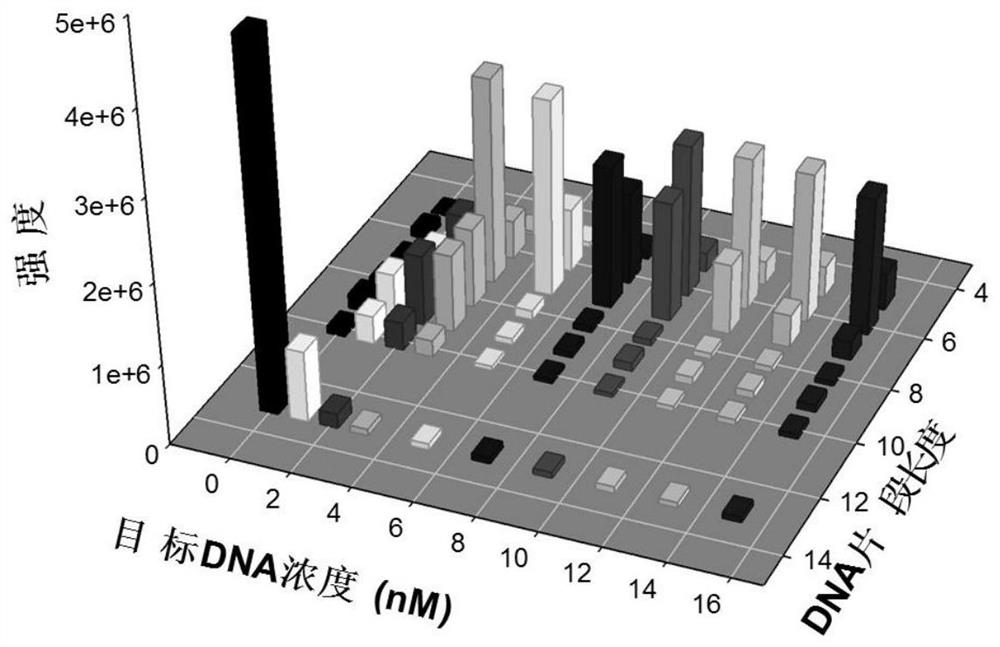
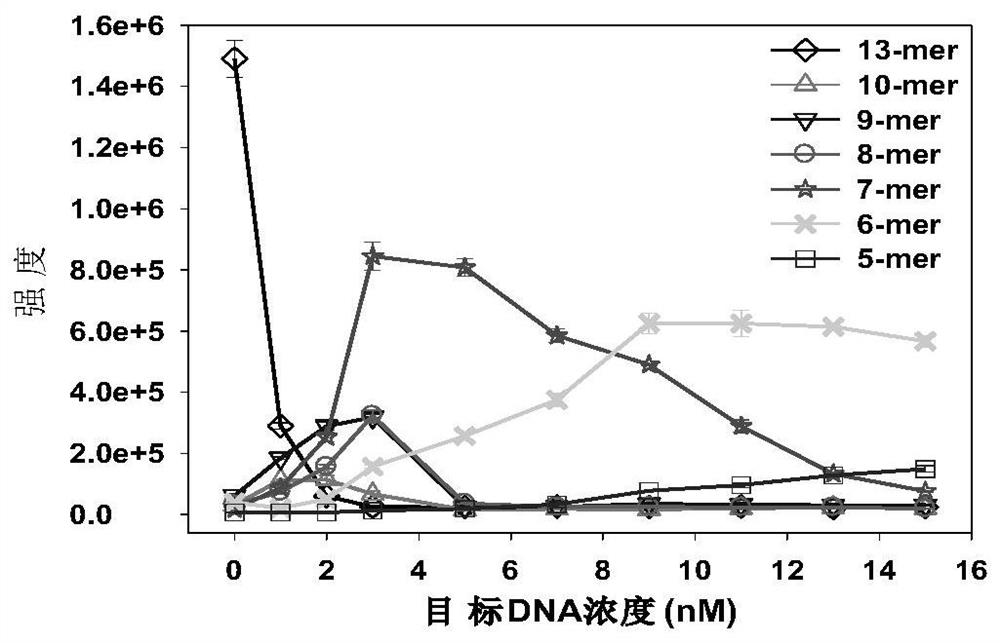
[0045] Example 1: Quantitative analysis of target DNA in simulated biological samples
[0046] This embodiment combines the Exo III-assisted target cyclic amplification strategy, mass spectrometry detection and spectral deformation quantitative analysis theory (SSD) to achieve accurate quantitative analysis of target DNA in simulated biological samples.
[0047] Reagents: HPLC grade acetonitrile was purchased from Sweden Opson Company; HPLC grade ammonia water was purchased from Aladdin Reagent Co., Ltd.; Exonuclease III (Exo III) and 10×NEB buffer 1 were purchased from New England Biolabs Company, USA; serum was purchased from Changsha Healthy volunteers in the blood bank center; HPLC-purified target DNA was synthesized by Bao Bioengineering (Dalian) Co., Ltd.; dialysis membrane (1KD, standard grade regenerated cellulose membrane) and other HPLC-purified oligonucleotide strands were purchased from Shenggong Bioengineering (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. The DNA sequence used is as foll...
Embodiment 2
[0071] Example 2: Identification of Base Mismatched DNA Samples
[0072] To test the specificity of the DNA quantitative analysis strategy proposed in the present invention, we designed a base mismatch DNA sequence with the same length as the target DNA (see the reagent section), including a single base mismatch DNA sequence: its mismatched base The positions of the 5th (DNA@5), 9th (DNA@9) and 12th (DNA@12) bases located at the 5′ end of the target DNA sequence, respectively, and the DNA with three base mismatches (DNA@9.10 .11): The mismatched bases are located at the 9th, 10th and 11th bases of the 5' end of the target DNA sequence.
[0073] A sample of base mismatch DNA was prepared in the same manner as in Example 1 for preparing the standard sample. Two samples were prepared at final concentrations of 5 and 15 nM for each base mismatched DNA. Compared with DNA detection methods based on absorption or emission spectroscopy (such as UV-Vis, fluorescence, Raman, etc. spec...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com