Osteochondral tissue engineering scaffold material and preparation method thereof
A tissue engineering scaffold and osteochondral technology, applied in the field of medical materials, can solve the problems of no bionic layered structure and poor biomechanical strength
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0058] The preparation method of the above-mentioned osteochondral tissue engineering scaffold material of one embodiment, comprises the following steps:
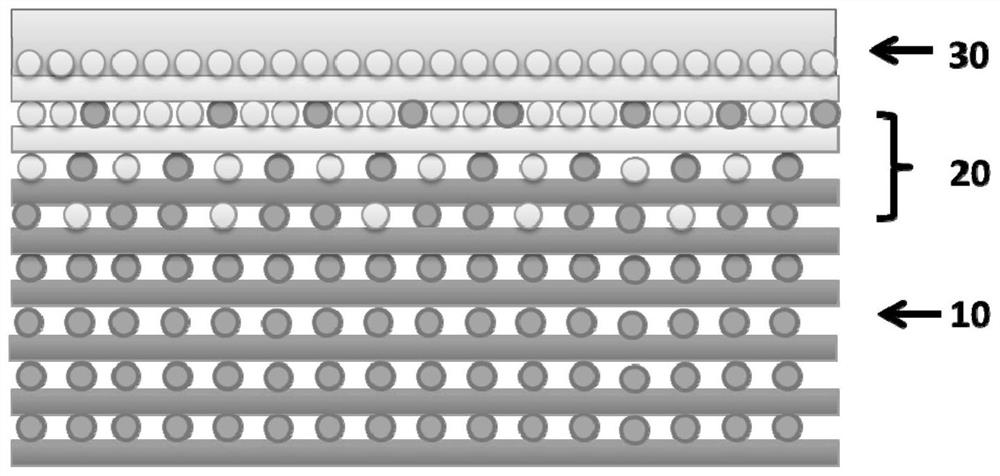
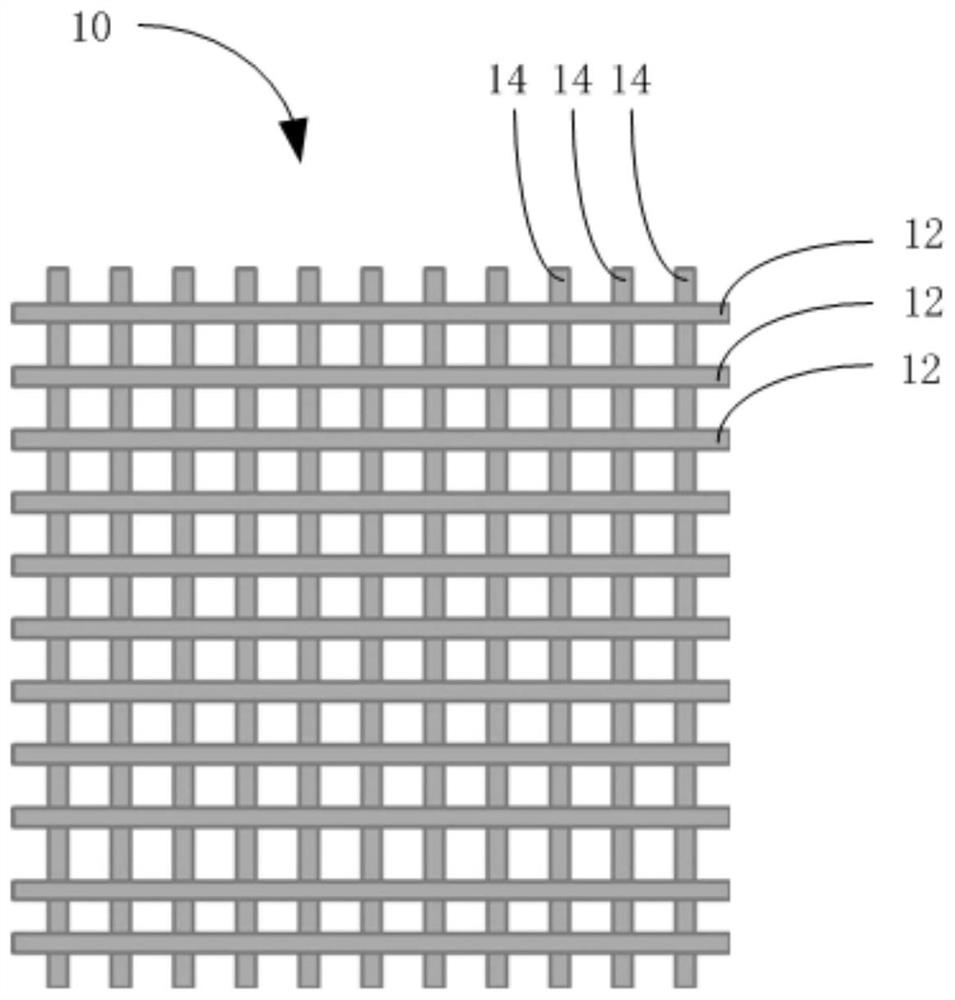
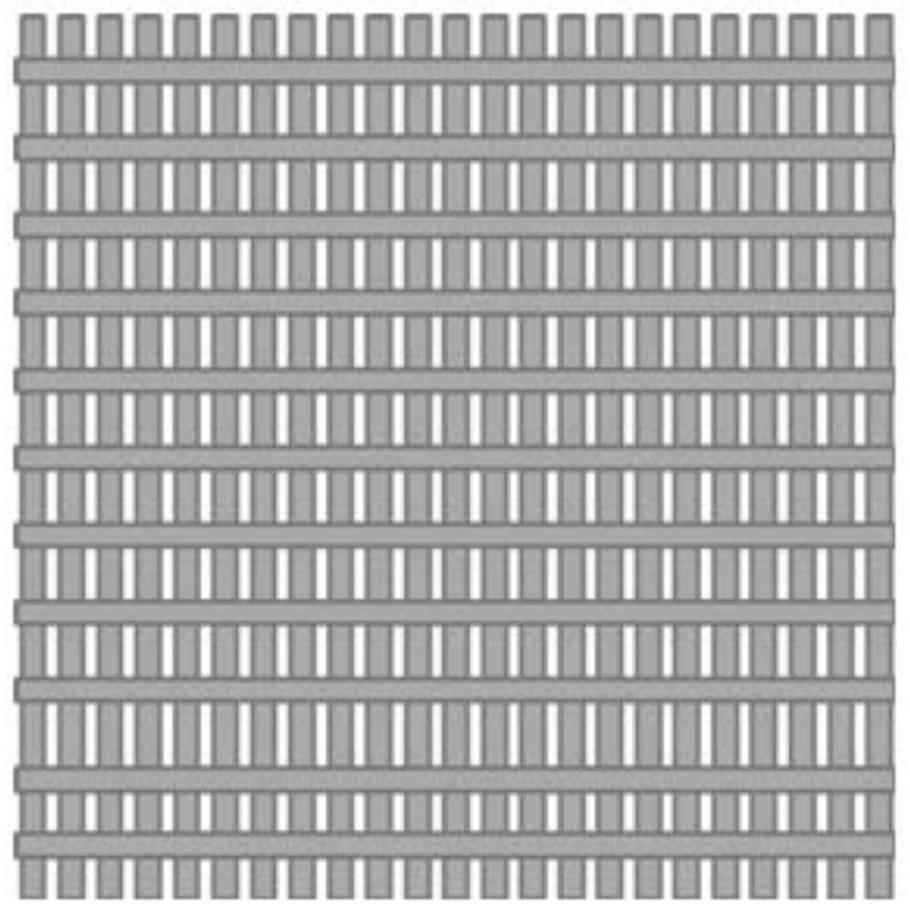
[0059] S10. Using 3D printing technology, input the preset three-dimensional model of the above-mentioned osteochondral tissue engineering scaffold material including subchondral bone layer 10, calcified cartilage layer 20, and cartilage layer 30 that are sequentially stacked and changed gradually, and set the temperature of the printing platform to 10°C ~37°C, the pressure is 0.2Mpa~0.8Mpa.
[0060] S20, adding the polyaryletherketone-based material and the artificial polymer material into the first barrel and the second barrel respectively, selecting a suitable needle, and raising the temperature of the first barrel to the melting point of the polyaryletherketone-based material As mentioned above, the temperature of the second cylinder is raised above the melting point of the artificial polymer material.
[0061] S30 , t...
Embodiment 1
[0078] 1. Input the designed osteochondral tissue engineering scaffold material model into the computer. The osteochondral tissue engineering scaffold material model has a three-layer structure: cartilage layer, calcified cartilage layer and subchondral bone layer.
[0079] 2. Set the printing parameters and operating procedures of the osteochondral tissue engineering scaffold material, and print the osteochondral tissue engineering scaffold material.
[0080] 3. During the printing process, the platform temperature is set to 25°C, and the pressure is set to 0.5MPa.
[0081] 4. Add L-polylactic acid with a molecular weight of 100,000 to the first barrel, select the first needle of 0.15mm, and raise the temperature of the first barrel and the first needle to 190°C. Add polyether ether ketone to the second barrel, select a second needle of 0.15 mm, and increase the temperature of the second barrel and the second needle to 400°C.
[0082] 5. Run the program of the second barrel ...
Embodiment 2
[0086] 1. Input the designed osteochondral tissue engineering scaffold material model into the computer. The osteochondral tissue engineering scaffold material model has a three-layer structure: cartilage layer, calcified cartilage layer and subchondral bone layer.
[0087] 2. Set the printing parameters and operating procedures of the osteochondral tissue engineering scaffold material, and print the osteochondral tissue engineering scaffold material.
[0088] 3. During the printing process, the platform temperature is set to 37°C and the pressure is set to 0.6MPa.
[0089] 4. Add polylactic acid-glycolic acid copolymer with a molecular weight of 100,000 to the first cylinder, select the first needle of 0.20mm, and raise the temperature of the first cylinder and the first needle to 160°C. Add polyether ketone ketone to the second barrel, select a second needle of 0.20 mm, and raise the temperature of the second barrel and the second needle to 390°C.
[0090] 5. Run the progra...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com