Magnetic nondestructive testing method for testing ferritic transformation quantity of austenitic stainless steel after being subjected to ion irradiation
A technology of austenitic stainless steel and ion irradiation, which is applied in the direction of material magnetic variable and test sample preparation, can solve the problems of low irradiation fluence rate, shallow irradiation damage depth, and inability to carry out, and achieve data duplication Good performance, high test accuracy, strong practical effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] In this embodiment, the ferrite transformation amount of 316 austenitic stainless steel after ion irradiation is measured.
[0039] Specific steps are as follows:
[0040] (1) Process the initial state of austenitic stainless steel into a diameter of 3 mm and a thickness of L 0 It is a 25μm wafer; v ≤5×10-5 Solid solution treatment is carried out in the environment of Pa, heat treatment temperature T=1060°C, heat treatment time t=1.5h;
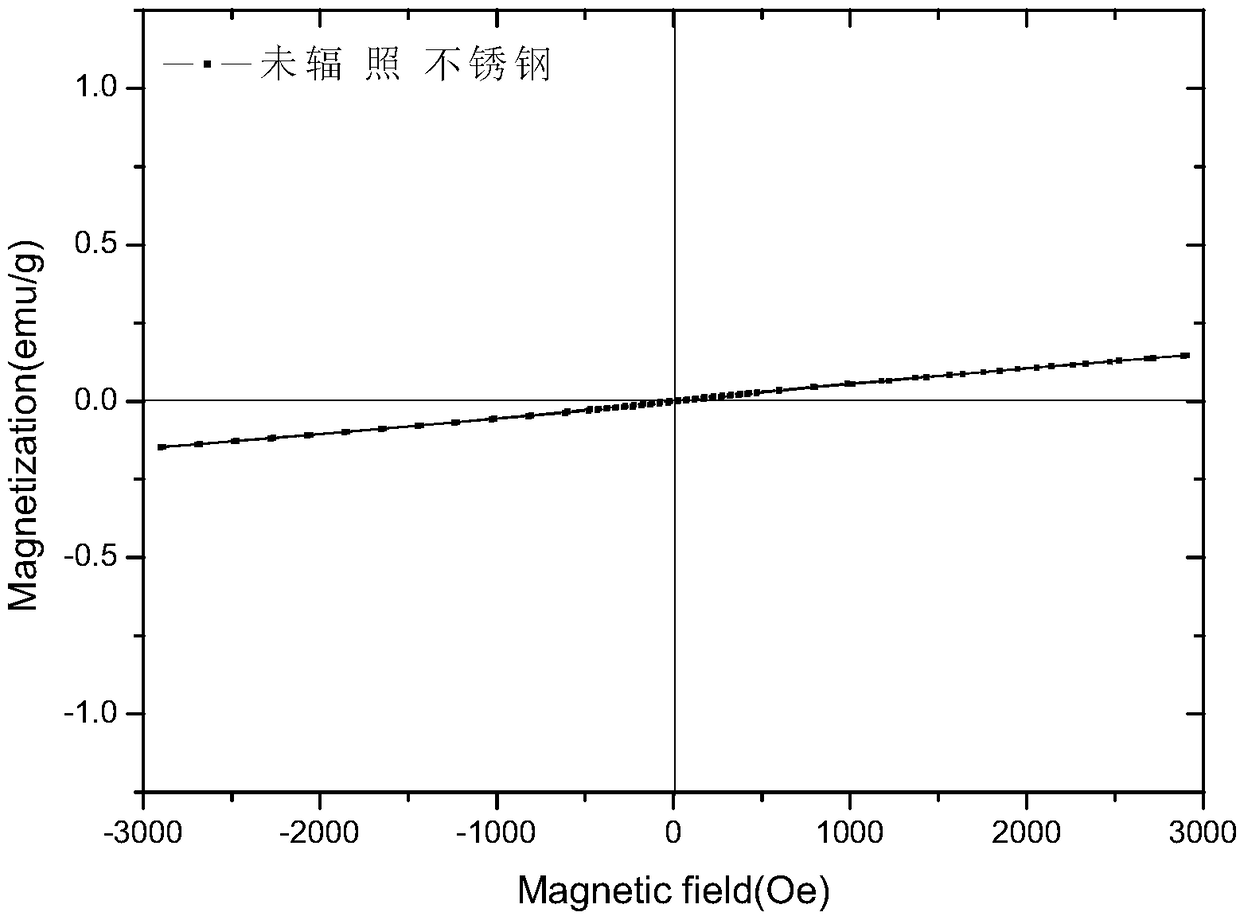
[0041] (2) Carry out magnetic measurement on the wafer processed in step (1) to obtain the first M-H curve, see attached figure 1 shown;
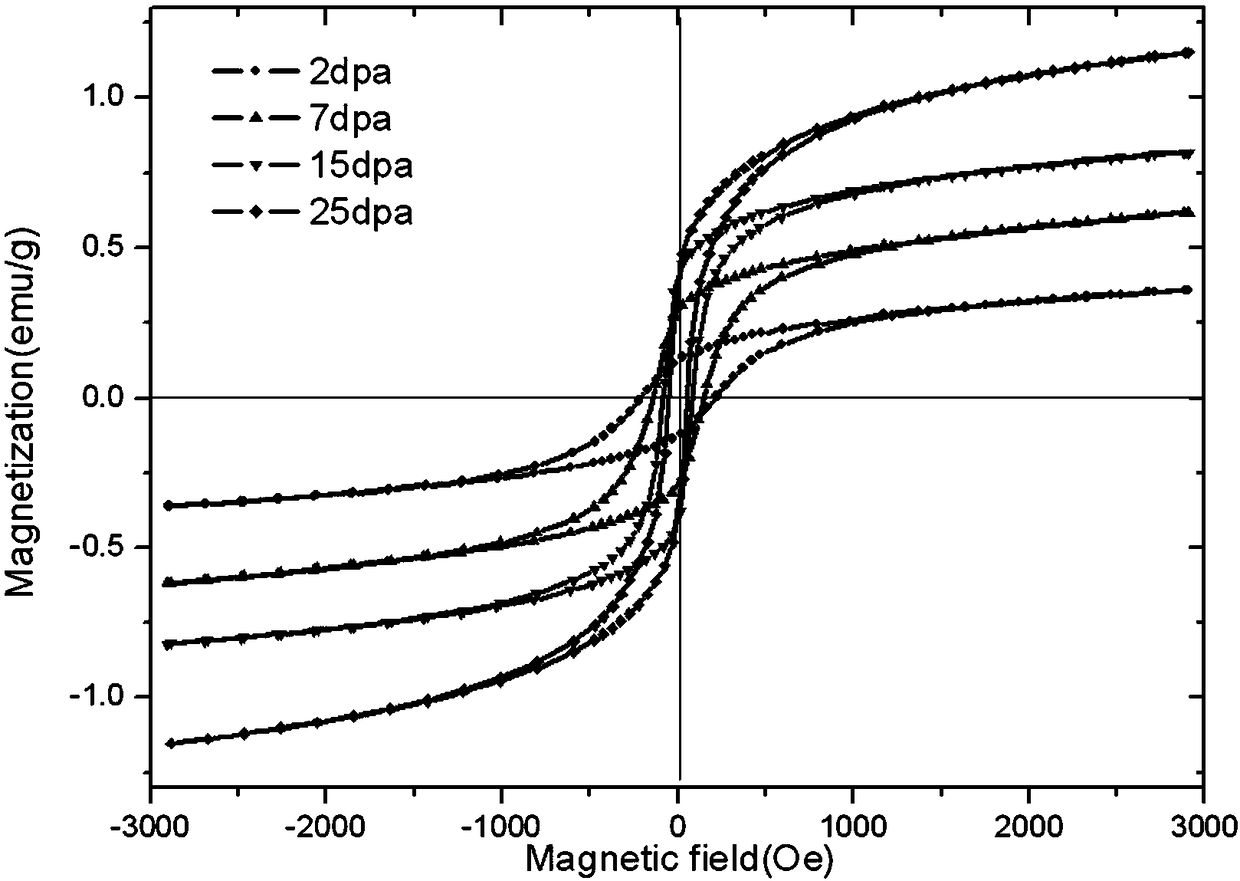
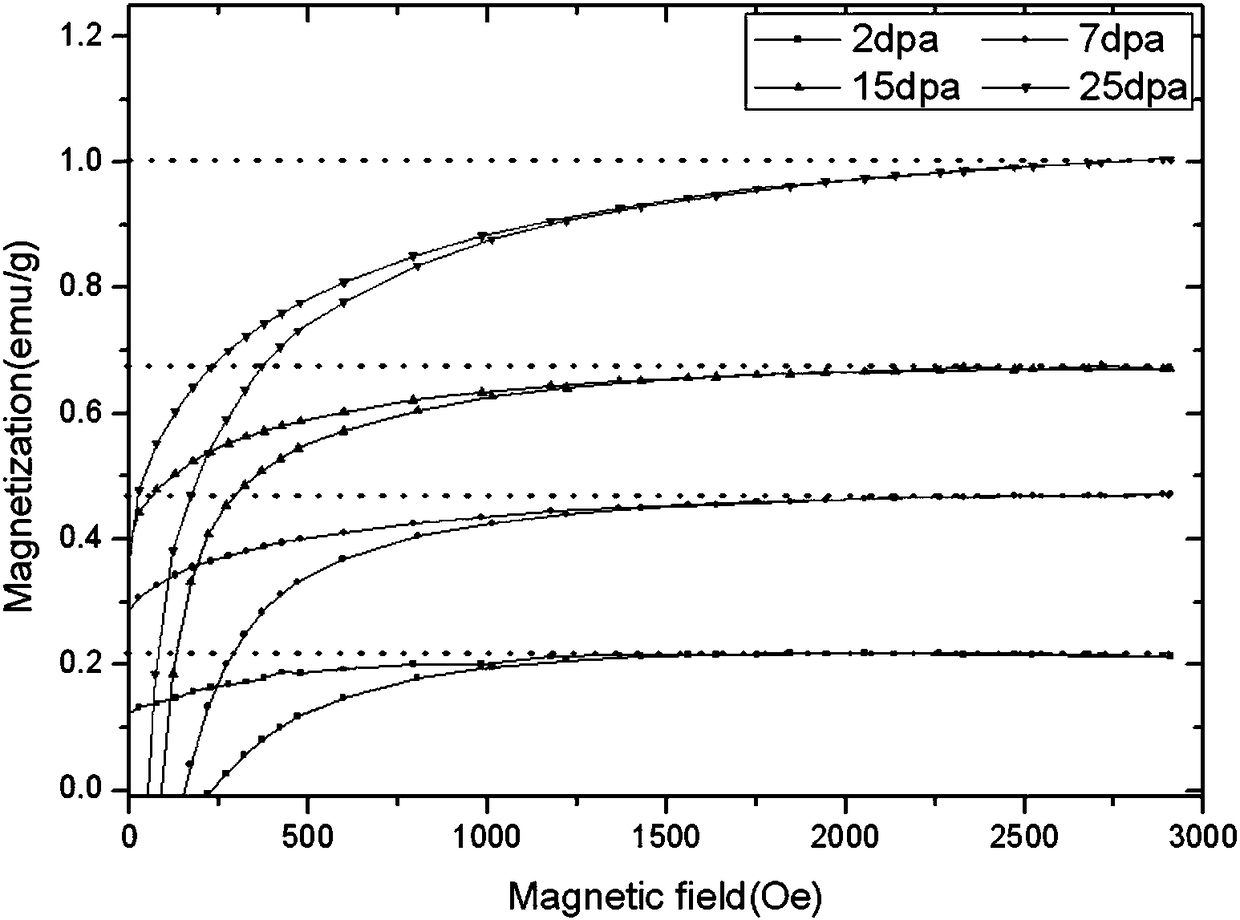
[0042] (3) carry out ion irradiation test with the disc processed in step (1), the irradiation ion is Xe, energy is 6MeV, and Fe, Cr, Ni atomic percentage are respectively 72%, 17%, 11% in the stainless steel, Dislocation threshold energy E d = 40eV, using the Monte Carlo simulation calculation method to obtain the ion irradiation damage curve of austenitic stainless steel with ion implantation ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com