A method for modifying atomic force microscopy probes using magnetic nanoparticles
A technology of magnetic nanoparticles and atomic force microscopy, which is applied in scanning probe technology, scanning probe microscopy, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of affecting testing, demanding experimental conditions, and difficult observation, etc., so as to improve the adhesion rate and Adhesion strength, simplification of the modification process, and the effect of increasing the contact area
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0031] a) Synthesis of particles: micron-sized carbon spheres were prepared using the microemulsion method. Manganese-zinc-ferrite magnetic nanoparticles were prepared using a hydrothermal method.
[0032] b) Preparation of micron-sized carbon sphere-nanoparticle mixed dispersion: Take 2 mg of carbon sphere particles with a size of about 1 μm and add them to 10 mL of methanol, and ultrasonically disperse for 10 min with an ultrasonic cleaning oscillator to ensure that the carbon spheres are evenly dispersed in methanol. Then 1mg of magnetic nanoparticles was added to the above dispersion liquid, and ultrasonic cleaning oscillator was used to disperse again for 30 minutes to ensure that the magnetic nanoparticles and carbon spheres were in full contact and evenly adhered to obtain a uniform mixed dispersion liquid.
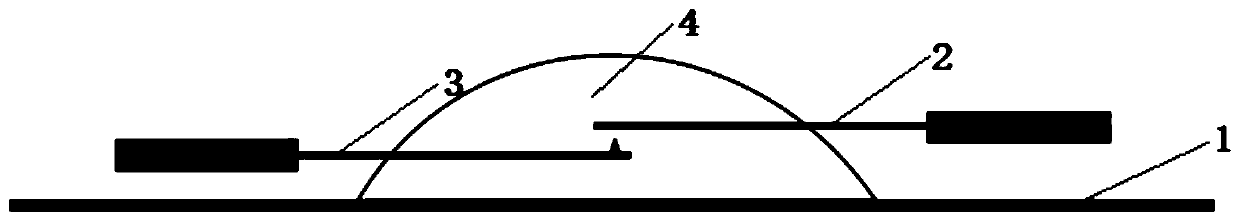
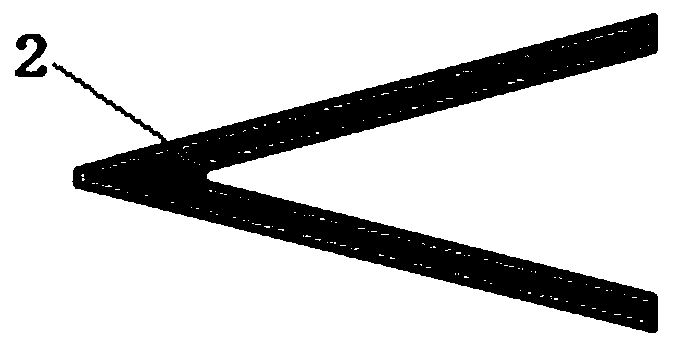
[0033] c) Modified probes: prepare V-shaped microcantilever and plate probe, and place them under an optical microscope. The vertical distance between V-shaped mic...
Embodiment 2
[0041]a) Synthesis of particles: Micron-sized carbon spheres were prepared using a solvothermal method. Cobalt ferrite magnetic nanoparticles were prepared using a co-precipitation method.
[0042] b) Preparation of micron-scale carbon sphere-nanoparticle mixed dispersion: 1 mg of carbon sphere particles with a size of about 5 μm was added to 10 mL of acetone, and ultrasonically dispersed for 10 min with an ultrasonic cleaning oscillator to ensure that the carbon spheres were evenly dispersed in acetone. Then 3 mg of magnetic nanoparticles were added to the above dispersion liquid, and the ultrasonic cleaning oscillator was used to ultrasonically disperse for 30 minutes to ensure that the magnetic nanoparticles and carbon spheres were in full contact and evenly attached, and a uniformly dispersed mixed dispersion liquid was obtained.
[0043] c) Modified probes: prepare a V-shaped microcantilever and a flat probe, and place them under an optical microscope. The vertical distan...
Embodiment 3
[0051] a) Synthesis of particles: Micron-sized carbon spheres were prepared using a hydrothermal method. Zinc-cobalt-chromium ferrite magnetic nanoparticles were prepared using a vapor deposition method.
[0052] b) Preparation of micron-scale carbon sphere-nanoparticle mixed dispersion: Take 5 mg of carbon sphere particles with a size of about 0.5 μm and add them to 10 mL of n-hexane, and ultrasonically disperse them with an ultrasonic cleaning oscillator for 10 minutes to ensure that the carbon spheres are evenly dispersed in n-hexane middle. Then 5 mg of magnetic nanoparticles were added to the above dispersion liquid, and the ultrasonic cleaning oscillator was used to ultrasonically disperse for 30 min to ensure that the magnetic nanoparticles were fully in contact with the carbon spheres and evenly adhered to obtain a uniformly dispersed mixed dispersion liquid.
[0053] c) Modified probes: prepare a V-shaped microcantilever and a plate probe, and place them under an opt...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com