Method for degrading antibiotics
An antibiotic and magnetic technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, natural water treatment, special compound water treatment, etc., can solve the problems of secondary pollution of water body, high cost, hydrogen peroxide or persulfate cannot be recycled and reused, and achieve The effect of reducing the preparation cost, low cost and shortening the preparation cycle
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0025] This example studies magnetic MIL-101(Fe) / TiO 2 For the degradation effect of tetracycline, the specific steps are as follows:
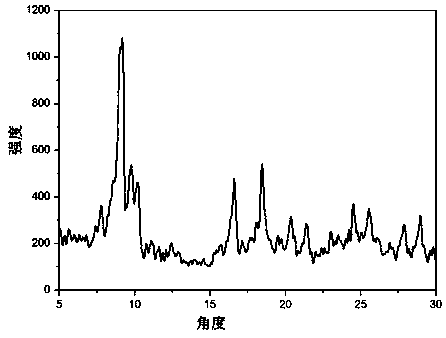
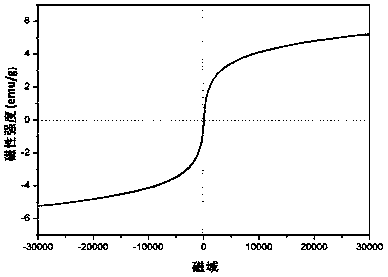
[0026] (1) Magnetic MIL-101(Fe) / TiO 2 Preparation: Dissolve ferric chloride hexahydrate, terephthalic acid, and titanium dioxide in a molar ratio of 1:1:1 in 80 mL of DMF, and after stirring for 1 hour, transfer the solution to a 100 mL Teflon-lined In the reaction kettle, place the reaction kettle in a blast drying oven, take out the reaction kettle after reacting at 120°C for 8 hours, cool the reaction kettle to room temperature naturally, take out the product after the reaction kettle is cooled, and filter it with a sand core funnel, and use DMF and ethanol were rinsed repeatedly three times, dried at 60°C for 3 hours, and then placed in a muffle furnace for constant temperature oxidation at 350°C for 5 minutes. Then, the obtained material was adsorbed by a strong magnet through weighing paper, and the impurities that did not impart magnet...
Embodiment 2
[0035] This embodiment studies magnetic MIL-101(Fe) / TiO 2 For the degradation effect under different antibiotic concentrations, the specific steps are as follows:
[0036] (1) Magnetic MIL-101(Fe) / TiO 2 Preparation: Dissolve ferric chloride hexahydrate, terephthalic acid and titanium dioxide in a molar ratio of 1:1:1 in 80mL of DMF, and after stirring for 1 hour, transfer the solution to a 100mL polytetrafluoroethylene-lined reaction Place the reaction kettle in a blast drying oven, take out the reaction kettle after reacting at 120°C for 8 hours, cool the reaction kettle to room temperature naturally, take out the product after the reaction kettle is cooled, filter it with a sand core funnel, and filter it with DMF Rinse with ethanol three times, dry at 60°C for 3 hours, put it in a muffle furnace for constant temperature oxidation at 350°C for 1 minute, then use a strong magnet to absorb the obtained material through weighing paper, blow out the impurities that do not impar...
Embodiment 3
[0045]This implementation case study magnetic MIL-101(Fe) / TiO 2 The effect of the dosage (0.1, 0.4, 0.7, 1.0g / L) on the degradation of tetracycline, the specific steps are as follows:
[0046] (1) Magnetic MIL-101(Fe) / TiO 2 Preparation: Dissolve ferric chloride hexahydrate, terephthalic acid and titanium dioxide in a molar ratio of 1:1:1 in 80mL of DMF, and after stirring for 1 hour, transfer the solution to a 100mL polytetrafluoroethylene-lined reaction The reactor was placed in a forced air drying oven, and after reacting at 120°C for 8 hours, the reactor was taken out, and the reactor was naturally cooled to room temperature. After the reaction kettle was cooled, the product was taken out with a sand core funnel for suction filtration, washed three times with DMF and ethanol, dried at 60°C for 3 hours, then placed in a muffle furnace for constant temperature oxidation at 250°C for 5 minutes, and then the obtained material was washed with strong The magnet is adsorbed thro...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com