Bismuth niobate-based glass ceramic material with high energy storage density as well as preparation method and application thereof
A bismuth niobate-based glass, high energy storage density technology, applied in glass manufacturing equipment, glass molding, manufacturing tools and other directions, can solve the problems of low energy storage density, limited application, bulky pulse power system, etc. The effect of high energy density, wide crystallization temperature range, great research value and practical application significance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
preparation example Construction
[0030] The preparation method of the above-mentioned bismuth niobate-based glass-ceramic material with high energy storage density comprises the following steps:
[0031] (1) with Bi 2 o 3 , Nb 2 o 5 and SiO 2 As raw material, according to 25Bi 2 o 3 -25Nb 2 o 5 -50SiO 2 The molar chemical ratio ingredients, after rolling and mixing evenly, high-temperature melting, to obtain high-temperature glass melt;
[0032] (2) Pour the high-temperature glass melt prepared in step (1) into a preheated copper mold to form and maintain the preheating temperature to remove the residual stress in the glass, and prepare amorphous glass with uniform composition. After slicing get glass flakes;
[0033] (3) Performing controlled crystallization on the glass flakes prepared in step (2) to obtain the bismuth niobate-based glass-ceramic material with high energy storage density.
[0034] The preferred process condition for step (1) high-temperature melting is: heat preservation at 1500-...
Embodiment 1
[0039] A method for preparing a bismuth niobate-based glass-ceramic energy storage material with high energy storage density, comprising the following steps:
[0040] (1) Bi with a purity greater than 99wt% 2 o 3 , Nb 2 o 5 , SiO 2 For raw material batching, the mole percentage of each component is 25%, 25%, 50%, mixed by ball mill for 24h, dried at 120°C for 6 hours, then melted at 1550°C for 2h; Ethanol is used as the medium, and the ball-to-material ratio is 1.5:1).
[0041] (2) Pouring the high-temperature melt obtained in step (1) into a square copper mold, annealing for stress relief at 600° C. for 6 hours, and then cutting to obtain glass flakes with a thickness of 1.0 to 1.5 mm;
[0042] (3) Put an equal amount of the glass flakes prepared in step (2) into a square crucible, heat up to 700°C at a rate of 3°C / min, and keep warm for 6 hours to obtain glass ceramics.
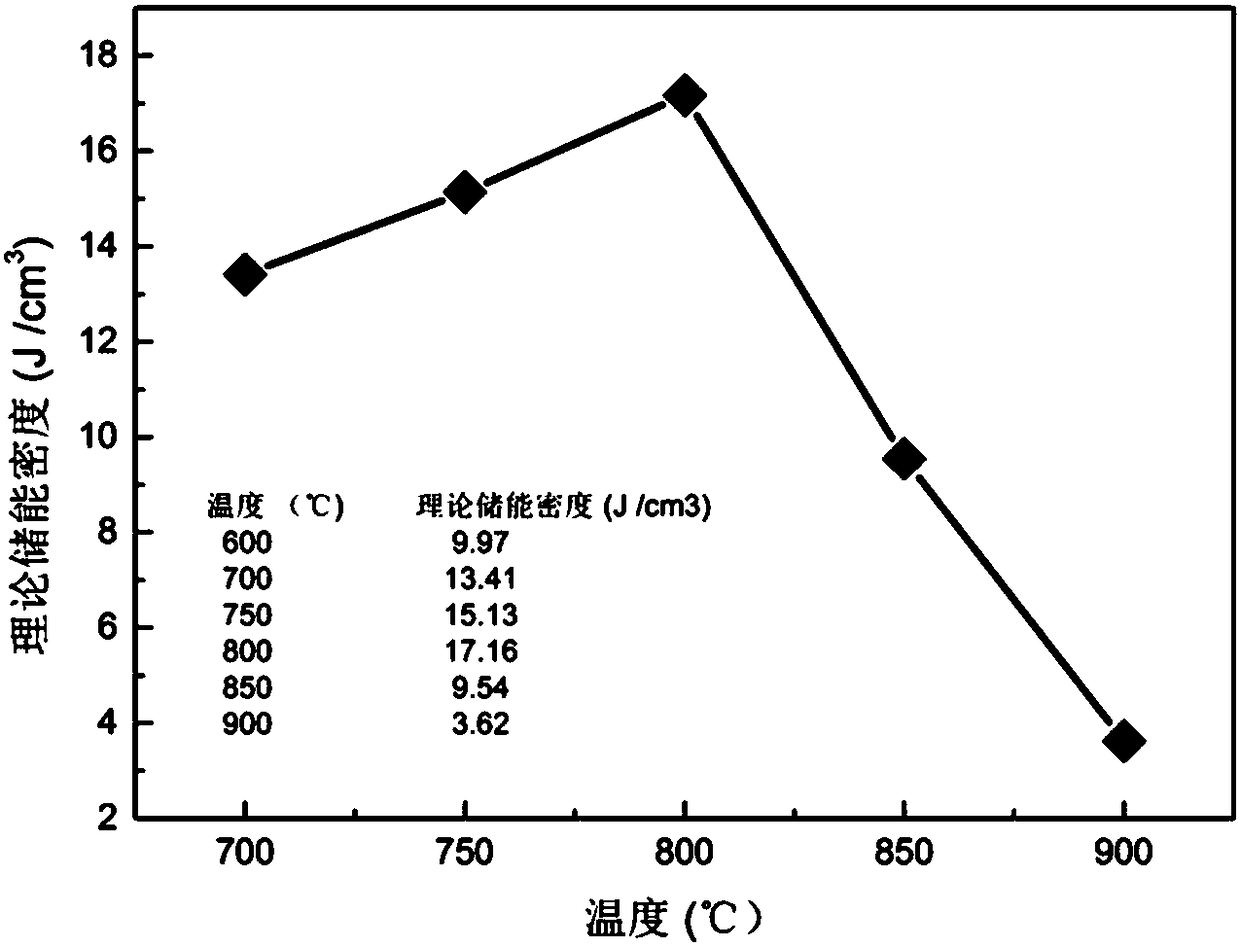
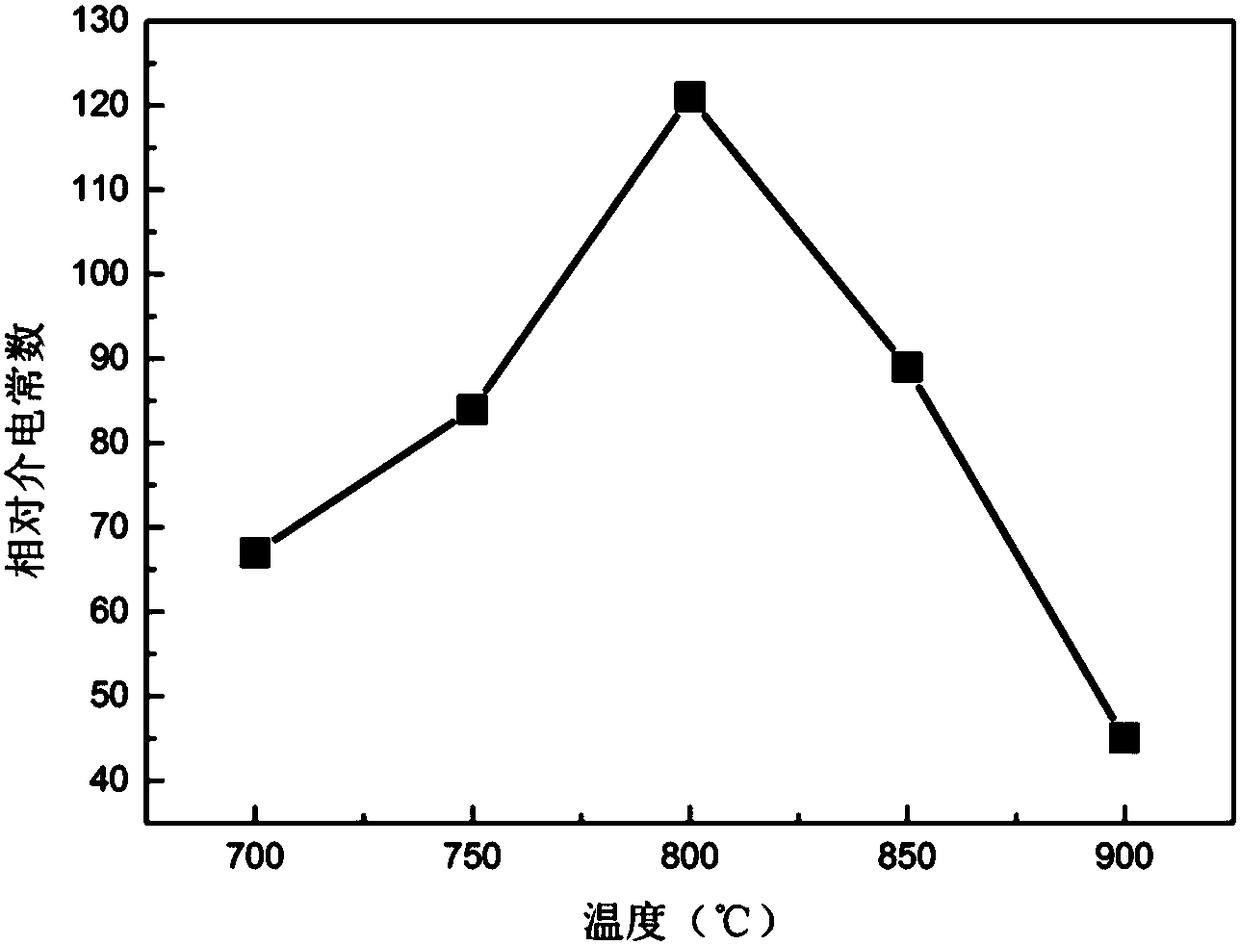
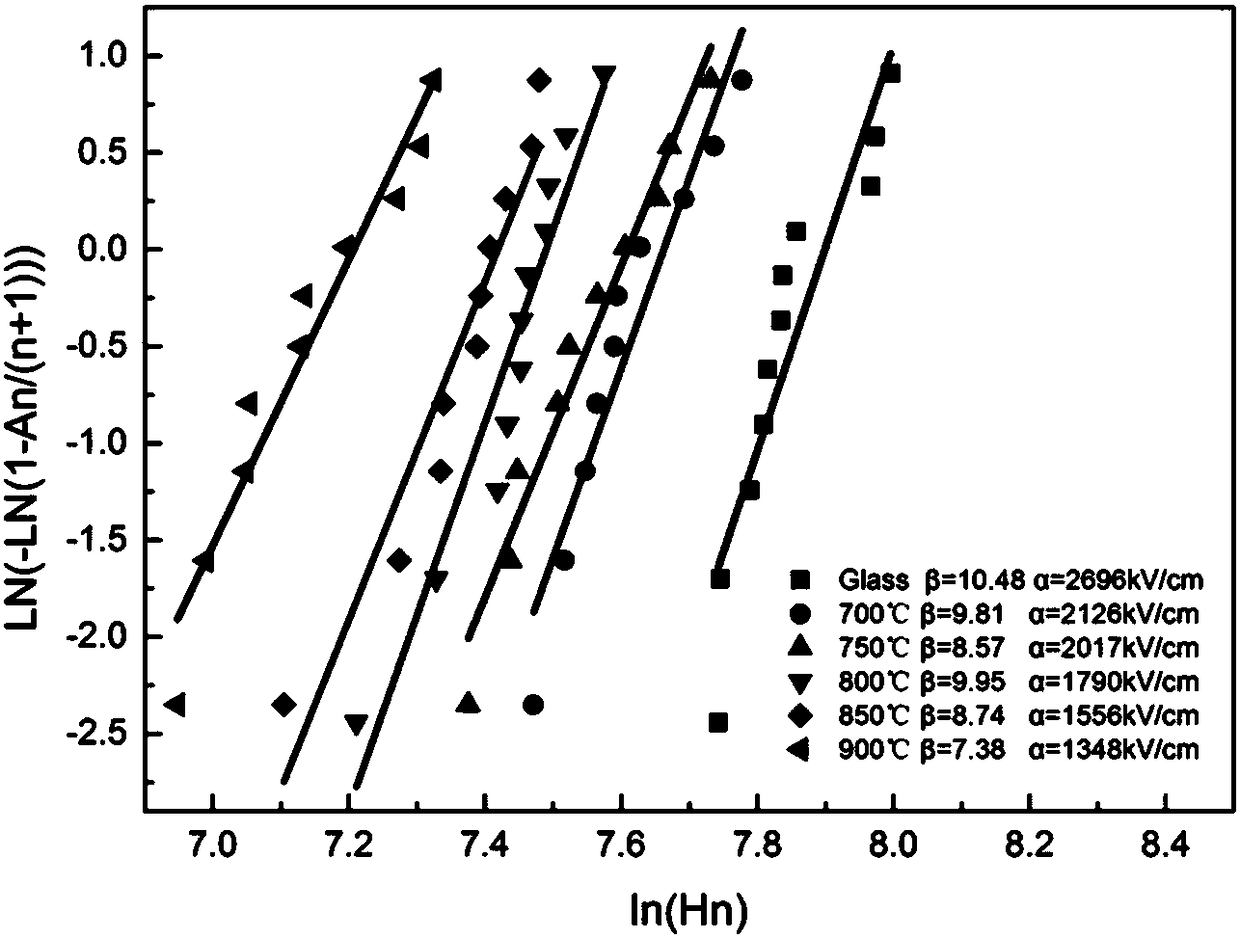
[0043] The energy storage density of the sample prepared in this embodiment is as follows: figure...
Embodiment 2
[0045] A method for preparing a bismuth niobate-based glass-ceramic energy storage material with high energy storage density, comprising the following steps
[0046] (1) Bi with a purity greater than 99wt% 2 o 3 , Nb 2 o 5 , SiO 2 For raw material batching, the mole percentage of each component is 25%, 25%, 50%, mixed by ball mill for 24h, dried at 120°C for 6 hours, then melted at 1550°C for 2h; Ethanol is used as the medium, and the ball-to-material ratio is 1.5:1).
[0047] (2) Pouring the high-temperature melt obtained in step (1) into a square copper mold, annealing for stress relief at 600° C. for 6 hours, and then cutting to obtain glass flakes with a thickness of 1.0 to 1.5 mm;
[0048] (3) Put an equal amount of the glass flakes prepared in step (2) into a square crucible, heat up to 750°C at a rate of 3°C / min, and keep warm for 6 hours to obtain glass ceramics.
[0049] The energy storage density of the sample prepared in this embodiment is as follows: figure ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| energy density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| breakdown field strength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| remanent polarization | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com