Energy-saving heat insulation material prepared from waste tea leaf residues and preparation method of material
A technology for thermal insulation materials and tea residues, applied in the field of thermal insulation materials, can solve the problems of insufficient flame retardant performance, lack of moisture resistance, poor mechanical strength, etc. good effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
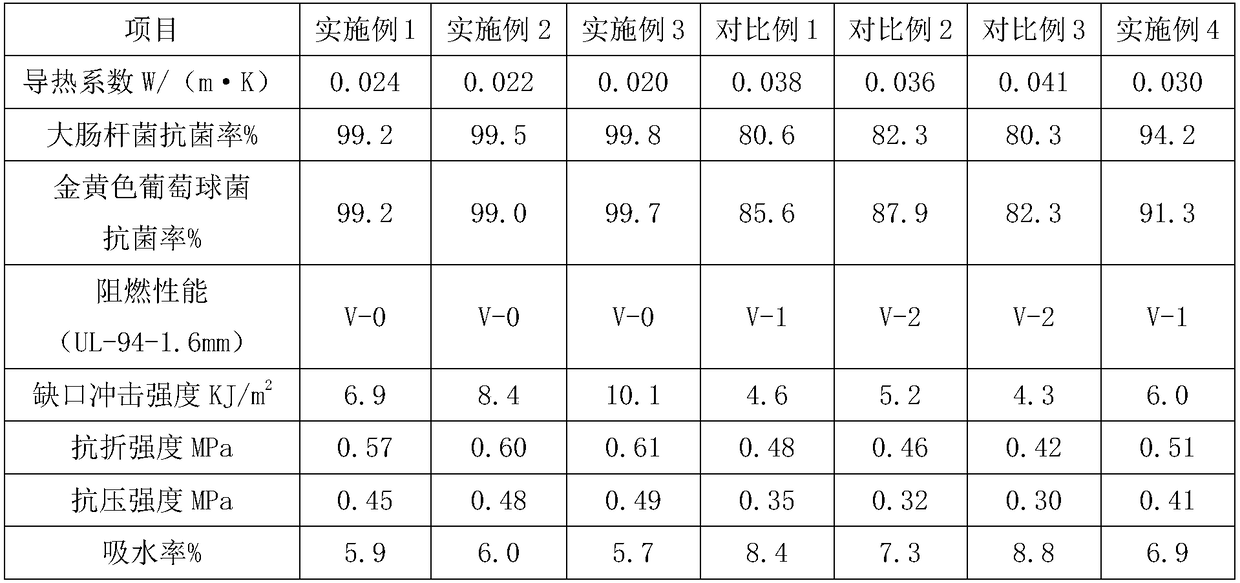
Embodiment 1
[0022] An energy-saving heat preservation material prepared by using waste tea leaves, the energy-saving heat preservation material comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 15 parts of cement, 30 parts of waste tea leaves, 12 parts of itaconic acid, and 7 parts of sodium polystyrene sulfonate , 8 parts of sodium ethylenediamine tetramethylene phosphonate, 14 parts of polysilicate aluminum ferric chloride, and 85 parts of water.
[0023] A method for preparing an energy-saving thermal insulation material prepared from waste tea residues, comprising the following steps: (1) mixing cement with 30 parts of water, stirring evenly, adding sodium ethylenediamine tetramethylene phosphonate, raising the temperature to 118°C, After stirring for 10 minutes, keep warm for 10 minutes; (2) mix itaconic acid with the remaining water evenly to obtain an aqueous solution of itaconic acid, then soak the discarded tea leaves in the aqueous solution of itaconic acid for 1 hour; fi...
Embodiment 2
[0025] An energy-saving heat-preservation material prepared by using waste tea leaves, the energy-saving heat preservation material comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 23 parts of cement, 42 parts of waste tea leaves, 17 parts of itaconic acid, and 10 parts of sodium polystyrene sulfonate , 12 parts of sodium ethylenediamine tetramethylene phosphonate, 18 parts of polysilicate aluminum ferric chloride, and 150 parts of water.
[0026] A method for preparing an energy-saving thermal insulation material prepared by using waste tea leaves, comprising the following steps: (1) mixing cement with 50 parts of water, stirring evenly, adding sodium ethylenediamine tetramethylene phosphonate, raising the temperature to 135°C, After stirring for 20 minutes, keep warm for 20 minutes; (2) mix itaconic acid with the remaining water evenly to obtain an aqueous solution of itaconic acid, then soak the discarded tea leaves in the aqueous solution of itaconic acid for 2 hou...
Embodiment 3
[0028] An energy-saving heat-preservation material prepared by using waste tea leaves. The energy-saving heat preservation material comprises the following raw materials in parts by weight: 19 parts of cement, 36 parts of waste tea leaves, 15 parts of itaconic acid, and 9 parts of sodium polystyrene sulfonate , 10 parts of sodium ethylenediamine tetramethylene phosphonate, 16 parts of polysilicate aluminum ferric chloride, and 118 parts of water.
[0029] A method for preparing an energy-saving thermal insulation material prepared by using waste tea leaves, comprising the following steps: (1) mixing cement with 40 parts of water, stirring evenly, adding sodium ethylenediamine tetramethylene phosphonate, raising the temperature to 125°C, After stirring for 15 minutes, keep warm for 16 minutes. (2) mix itaconic acid with the water of surplus, obtain the aqueous solution of itaconic acid, then soak the discarded tea leaves in the aqueous solution of itaconic acid for 1.4h; filter...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com