Preparation for in-situ compounding simple-substance nano silvery bacteria cellulose membrane
A technology of bacterial cellulose film and bacterial cellulose is applied in the field of preparation of novel silver-containing antibacterial nano-bacterial cellulose film, which can solve the problem that restricts the development and application of antibacterial biomedical materials, and the bacterial cellulose film has no antibacterial activity and cannot prevent Wound infection and other problems, to achieve the effect of low cost, excellent antibacterial properties, and a wide range of uses
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] The commercially available bacterial cellulose membrane prepared from Acetobacter xylinum was cut into 2×2 cm bacterial cellulose membrane samples.
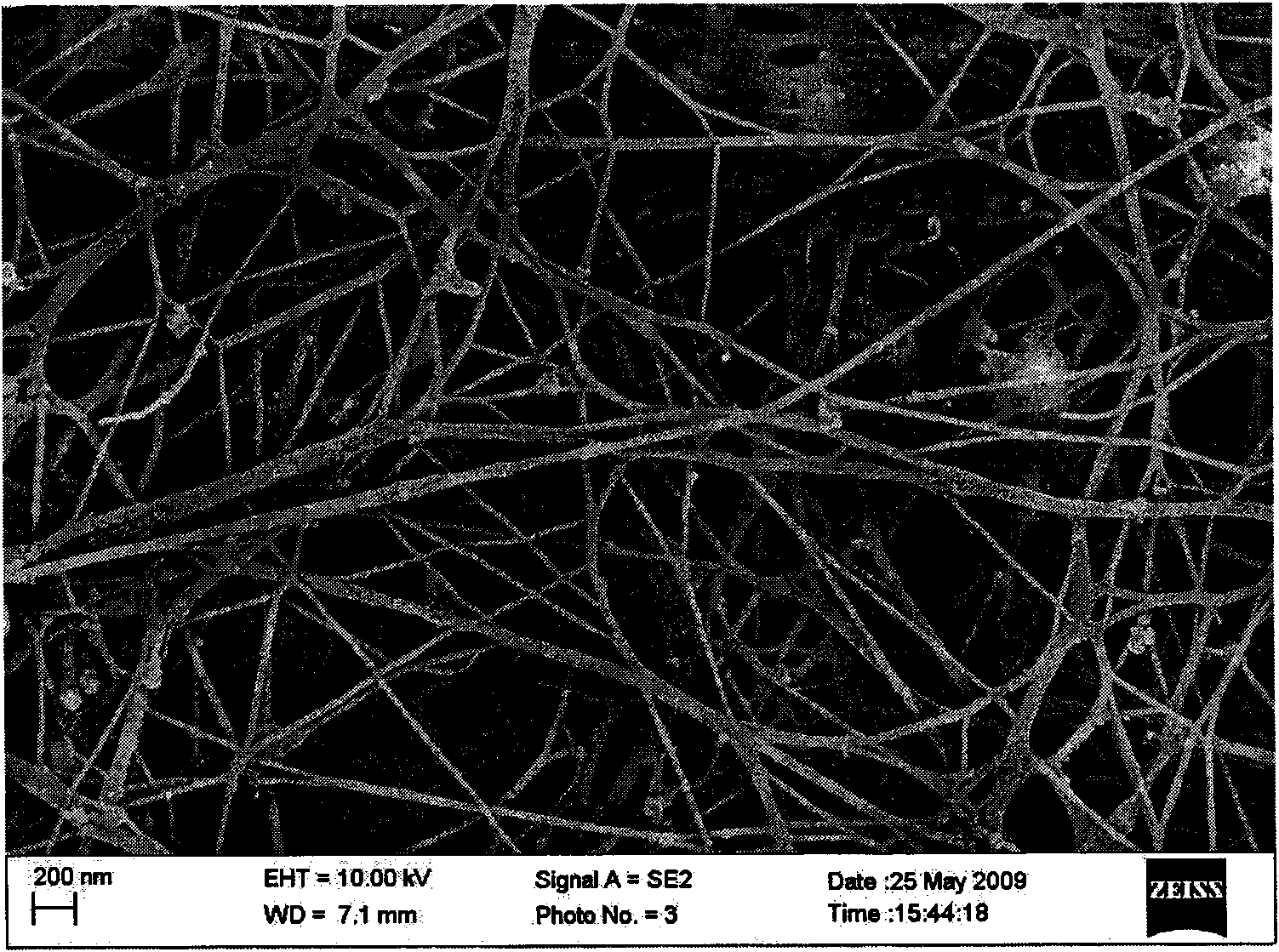
[0044] Step 1. Take the bacterial cellulose membrane and rinse it with clean water several times to remove the medium and impurities on the membrane surface. Then immerse the membrane in a 0.1 mol / L NaOH solution and boil it at 100°C for 20 minutes to remove the bacteria and residual culture medium in the liquid membrane. At this time, the membrane is milky white and translucent. Then rinse with distilled water several times to control the pH value to about 7.2 to obtain a purified bacterial cellulose membrane. The bacterial cellulose membrane produced has a three-dimensional porous network structure (see attached figure 2 );
[0045] Step 2. Drop sodium hydroxide dilute solution into the silver salt solution with a concentration of 0.0001mol / L, which produces white silver hydroxide precipitate and then decomposes into brown s...
Embodiment 2
[0053] The commercially available bacterial cellulose membrane prepared by Sarcina spp. was cut into 2×2 cm bacterial cellulose membrane samples.
[0054] Step 1. Take the bacterial cellulose membrane and rinse it with clean water several times to remove the medium and impurities on the membrane surface. Then immerse the membrane in a 0.05mol / L NaOH solution and boil it at 100°C for 30 minutes to remove the bacteria and residual culture medium in the liquid membrane. At this time, the membrane is milky white and translucent. Then rinse with distilled water several times to control the pH to about 7.2 to obtain a purified bacterial cellulose membrane;
[0055] Step 2. Add a few drops of dilute sodium hydroxide solution to the silver salt solution with a concentration of 0.001 mol / L to produce a white silver hydroxide precipitate and then decompose into brown silver oxide and water; then add concentrated ammonia water dropwise to the solution, Until the brown precipitate just dissol...
Embodiment 3
[0063] The commercially available bacterial cellulose membrane made from soil rhizobia was cut into 2×2 cm bacterial cellulose membrane samples.
[0064] Step 1. Take the bacterial cellulose membrane and rinse it with clean water several times to remove the medium and impurities on the membrane surface. Then immerse the membrane in 0.2mol / L NaOH solution and boil it at 80°C for 15 minutes to remove the bacteria and residual medium in the liquid membrane. At this time, the membrane is milky white and translucent. Then rinse with distilled water several times to control the pH to about 7.2 to obtain a purified bacterial cellulose membrane;
[0065] Step 2: Add a few drops of dilute sodium hydroxide solution to the silver salt solution with a concentration of 0.01 mol / L to produce a white silver hydroxide precipitate and then decompose into brown silver oxide and water; then drop concentrated ammonia water into the solution, Until the brown precipitate just dissolved, the silver ammo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| particle diameter | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com