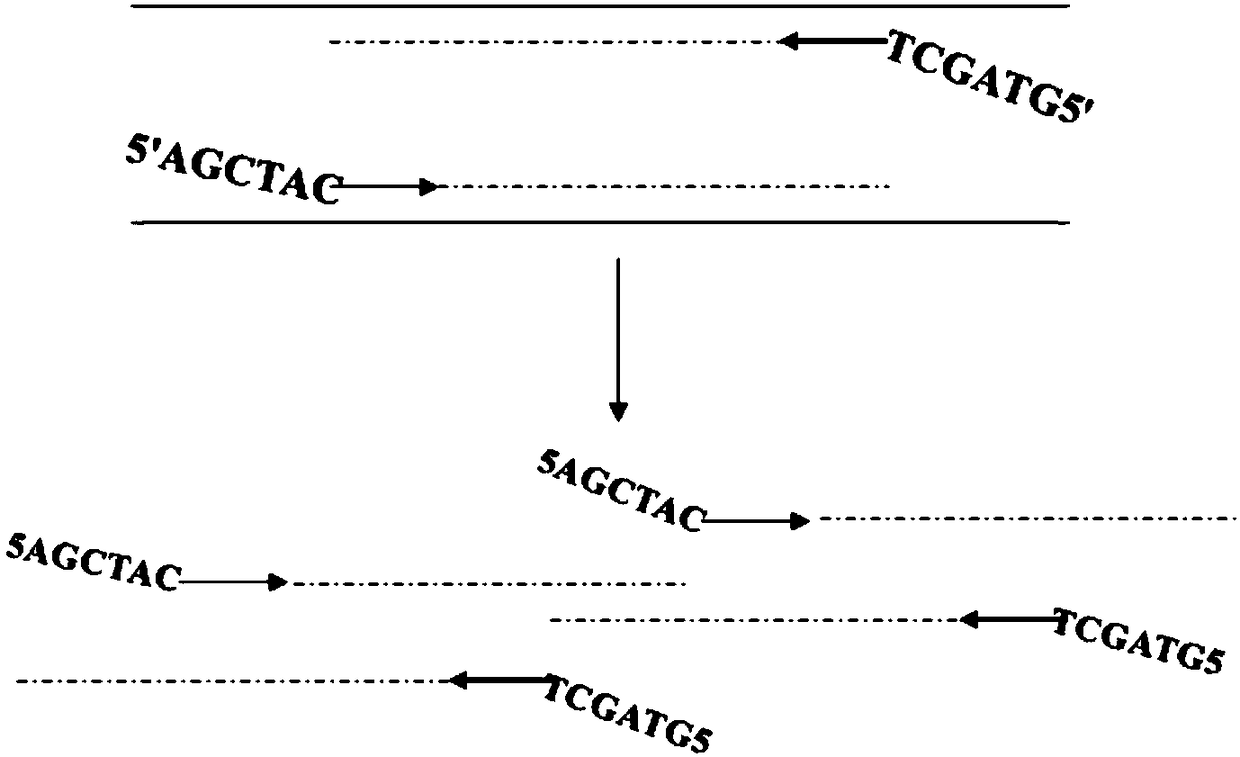
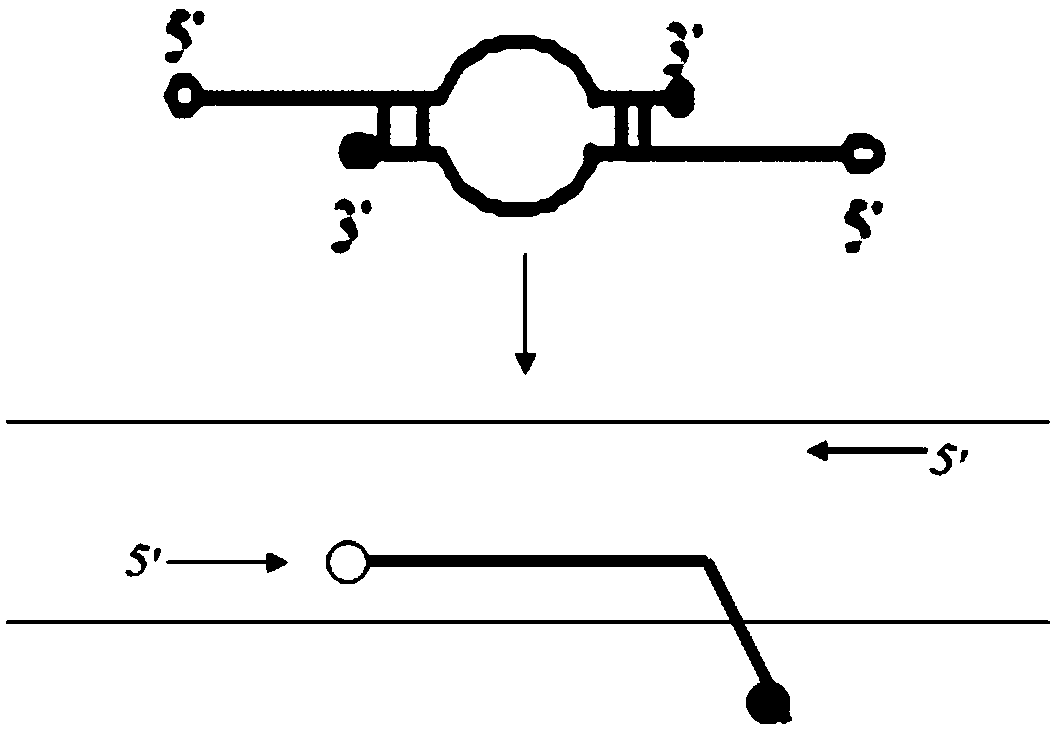
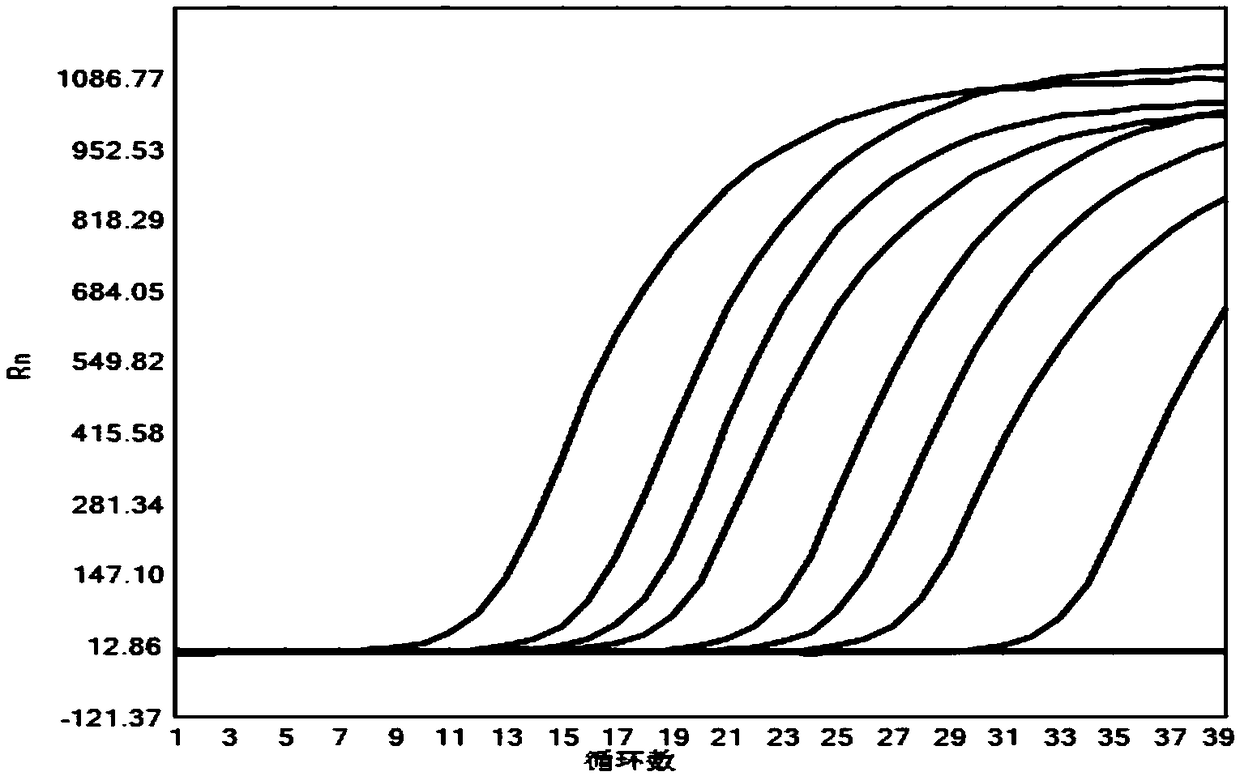
Oriented-polymerization fluorescent probe PCR
A fluorescent probe and directional polymerization technology, applied in the field of fluorescent probe PCR technology, can solve problems such as complexity, insufficient sensitivity of single-molecule detection, and increased pretreatment steps
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0102] The following examples further illustrate the content of this patent, but should not be interpreted as the limitation of this patent. Without departing from the spirit and essence of the present invention, any modifications or replacements made to the methods, conditions, steps and applications of this patent belong to the scope of this patent. Example 1: Fluorescent probe PCR of human hepatitis B virus-directed polymerization:
[0103] Hepatitis B virus (hepatitis B for short) is a worldwide Class III infectious disease infected by hepatitis B virus (Hepatitis B virus, HBV). According to the World Health Organization (WHO), about 2 billion people in the world carry hepatitis B virus. The infection rate of hepatitis B among Chinese people is very high (nearly 10%). Liver cancer, which is mainly caused by hepatitis virus, has ranked first in tumors, which has greatly endangered people's health. At present, the detection methods of hepatitis B mainly include 5 items / 7 it...
example 2
[0150] Example 2: Mycobacterium tuberculosis-directed polymerization fluorescent probe PCR:
[0151] Tuberculosis is a chronic wasting infectious disease caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis. Many organs can be invaded, but mainly the lungs, known as pulmonary tuberculosis. Respiratory transmission between people is the main mode of infection of the disease, and the source of infection is tuberculosis patients who have contact with bacteria. With factors such as AIDS, drug abuse, application of immunosuppressants, and population movement, the incidence of tuberculosis is increasing. According to the WHO report, 1 out of every 3 people in the world has been infected with Mycobacterium tuberculosis, 8 million new cases occur every year, and 3 million people die from the disease, which ranks the first cause of death in my country. At present, the main detection methods are sputum tuberculosis microscopic examination / tuberculosis culture, tuberculin OT / PPD test, ELISA, and X-ray...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com