Method for measuring preservative through hollow fiber film microextraction combining online derivatization-gas chromatography
A technology of gas chromatography and fiber membrane, which is applied in the field of preservative determination, can solve the problems of large consumption of organic solvents, cumbersome extraction steps, and long time consumption, and achieve less consumption of organic solvents, fewer extraction steps, and avoid cross-contamination Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] The selection of embodiment 1 derivatization reagent
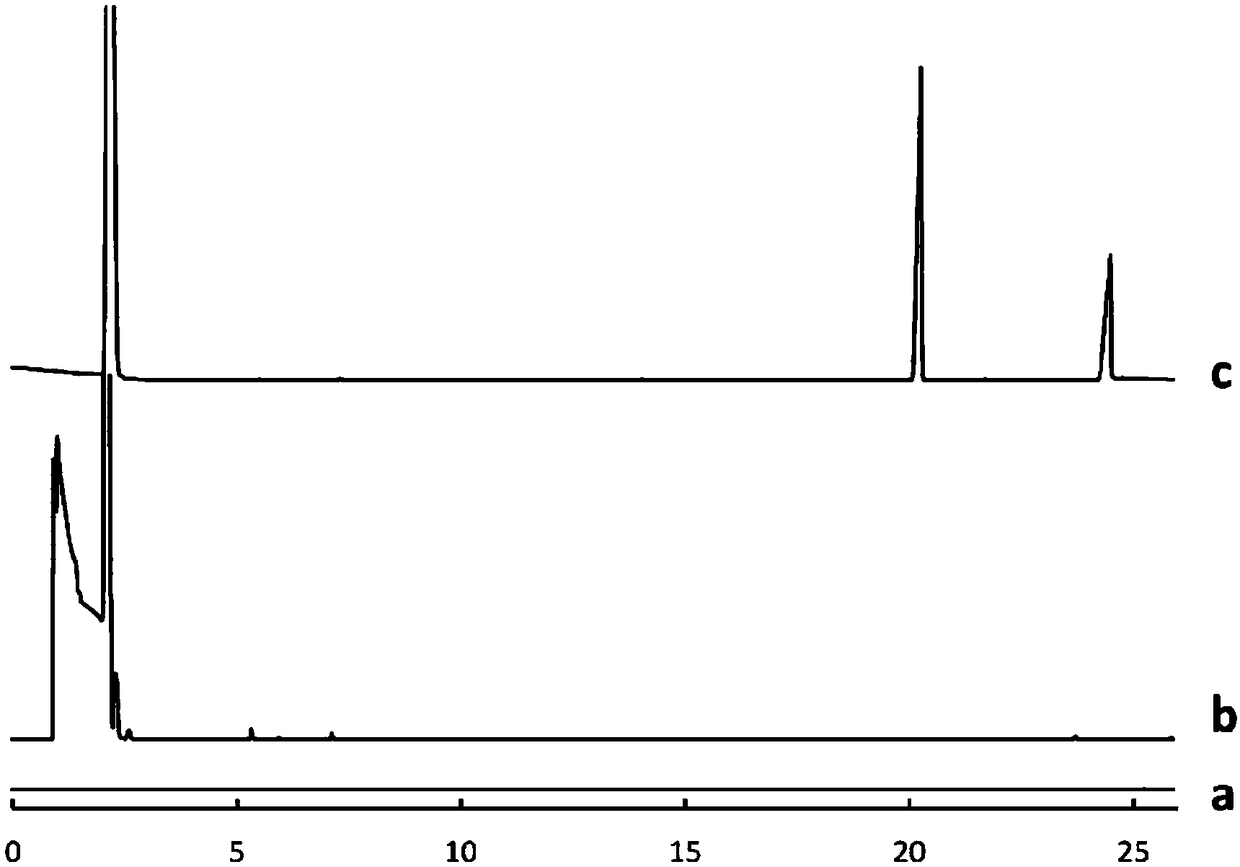
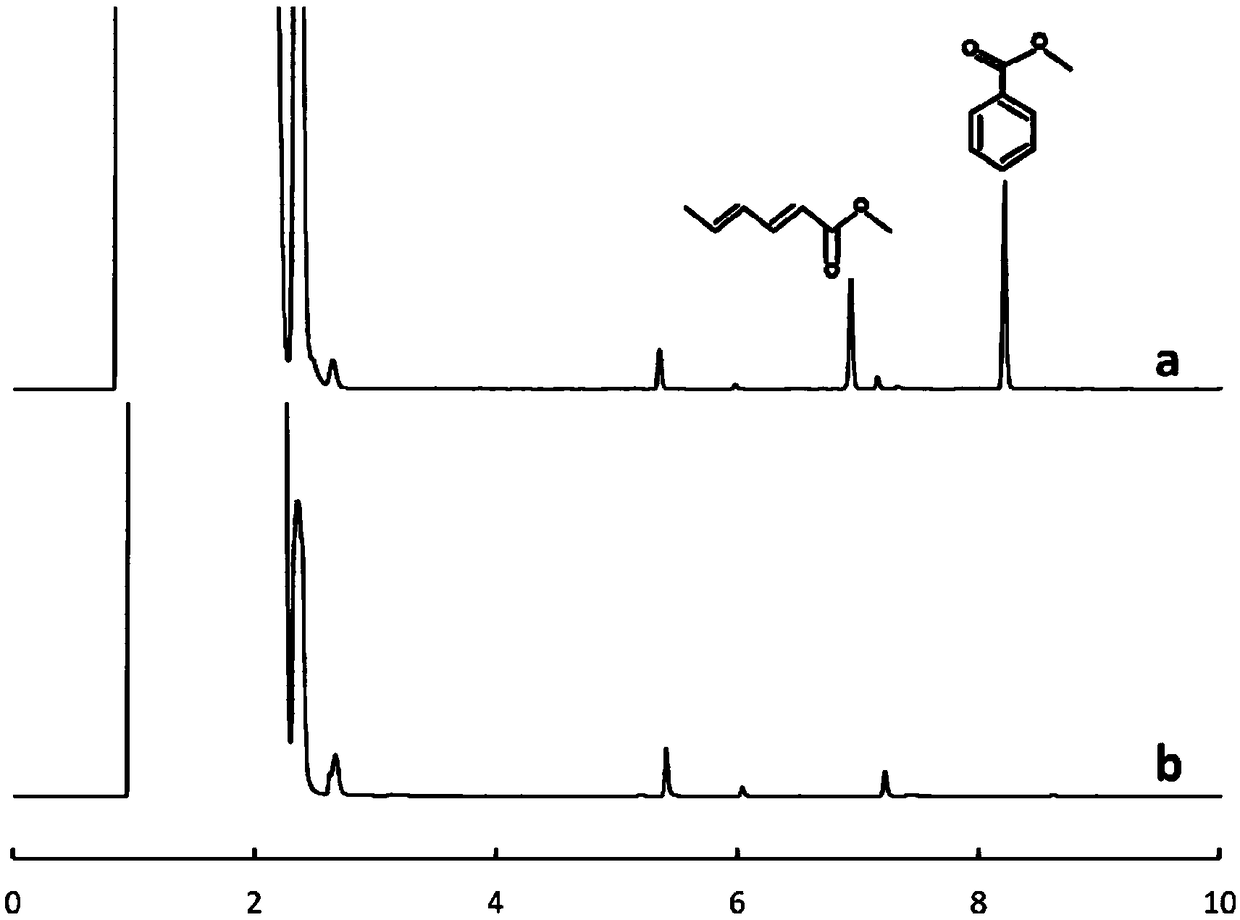
[0028] The role of the derivatization reagent during the experiment is to derivatize the acidic substance into an ester substance that is easy for gas phase analysis under the high temperature inlet. Choosing the appropriate derivatization reagent is beneficial to improve the detection sensitivity. Depend on figure 1 It can be seen that the polysulfone membrane will not decompose at 300°C, but after adding TMAH (tetramethylammonium hydroxide), two peaks were observed around 20min and 25min, which may be due to the decomposition of the membrane. Adding TMSH (trimethylammonium hydroxide) Sulfur) and no obvious peak was observed. Therefore, TMSH was chosen as the derivatization reagent.
Embodiment 2
[0029] The selection of embodiment 2 acid concentration
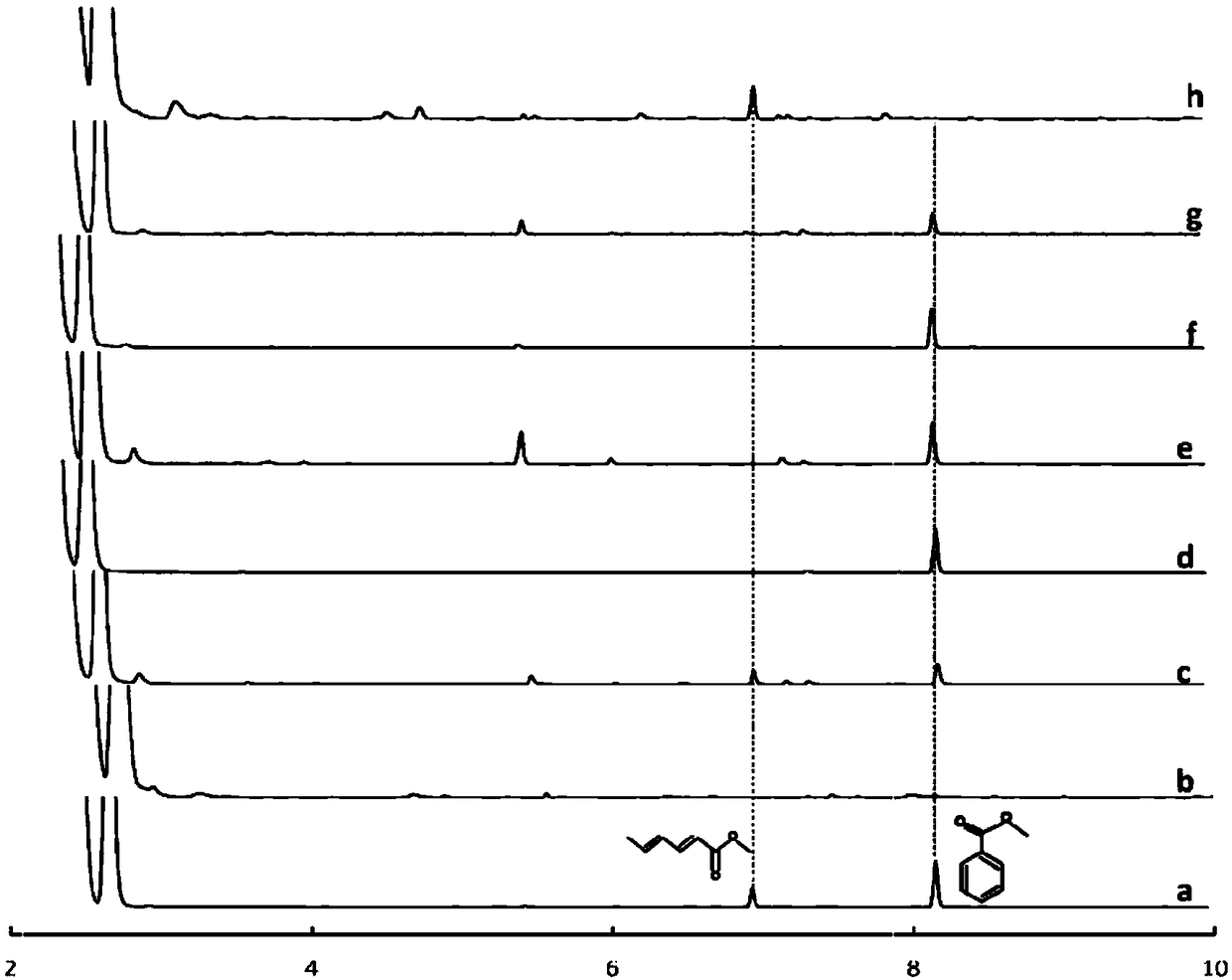
[0030] During the experiment, by adjusting the acidity of the water-soluble sample, the target object is deionized, thereby reducing its solubility in the sample aqueous solution. The influence of the concentration of HCl (0.01, 0.1, 0.5, 1 and 1.5mol / L) in the sample solution on the extraction efficiency was investigated. Other experimental conditions were: the stirring speed was 300rpm, the temperature was 50℃, and the extraction time was 30min. The results showed that when the concentration of hydrochloric acid increased from 0 to 0.5mol / L, the extraction efficiencies of both sorbic acid and benzoic acid increased significantly. efficiency. However, when the acid concentration was further increased, the extraction efficiency did not increase, so the concentration of hydrochloric acid was selected as 0.5mol / L.
Embodiment 3
[0031] The selection of embodiment 3 stirring speed
[0032] Accelerating the stirring speed can improve the mass transfer process, accelerate the speed of the target substance entering the membrane, and improve the extraction efficiency, but too fast stirring will destroy the structure of the membrane and reduce the extraction efficiency. The extraction efficiency was investigated when the stirring speed was 100, 200, 300, 400, and 500rpm. Other experimental conditions were: the concentration of hydrochloric acid was 0.5mol / L, the temperature was 50°C, and the extraction time was 30min. The results showed that the extraction efficiency was the highest at 200rpm, so the stirring rate was selected at 200rpm.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| pore size | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com