Deletion of the gene and its application, the strain of the gene deletion and its application in improving the production of microbial secondary metabolites
A gene and strain technology, applied in microorganism-based methods, microorganisms, biochemical equipment and methods, etc., can solve the problems of low yield of deoxyvioletine, less research on properties and biological activities, and difficult separation.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1 Method for continuous evolution of haploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae phenotype
[0044] The invention provides a research method for accelerating the phenotypic evolution of strains by utilizing synthetic Saccharomyces cerevisiae circular chromosomes, using PDV, a downstream metabolite of aromatic amino acids as a marker, to generate a large number of phenotypic variant yeast strains by inducing circular chromosome rearrangement.
[0045] 1. Design primers PCR-amplify the open reading frames (ORFs) of vioA, vioB and vioE from the BioBrick element library, and recover DNA fragments from agarose gel.
[0046] 2. Designing primers The promoter and terminator were amplified from Saccharomyces cerevisiae BY4741 genomic DNA, wherein there was a 40 base pair (bp) overlapping region between the promoter, the open reading frame and the terminator. DNA fragments were recovered from agarose gel.
[0047] 3. Digest the pRS416 plasmid with EcoRI restriction enzyme and perf...
Embodiment 2
[0068] Example 2 The yield of Saccharomyces cerevisiae purple bacteriocin precursor metabolizing strains increased continuously
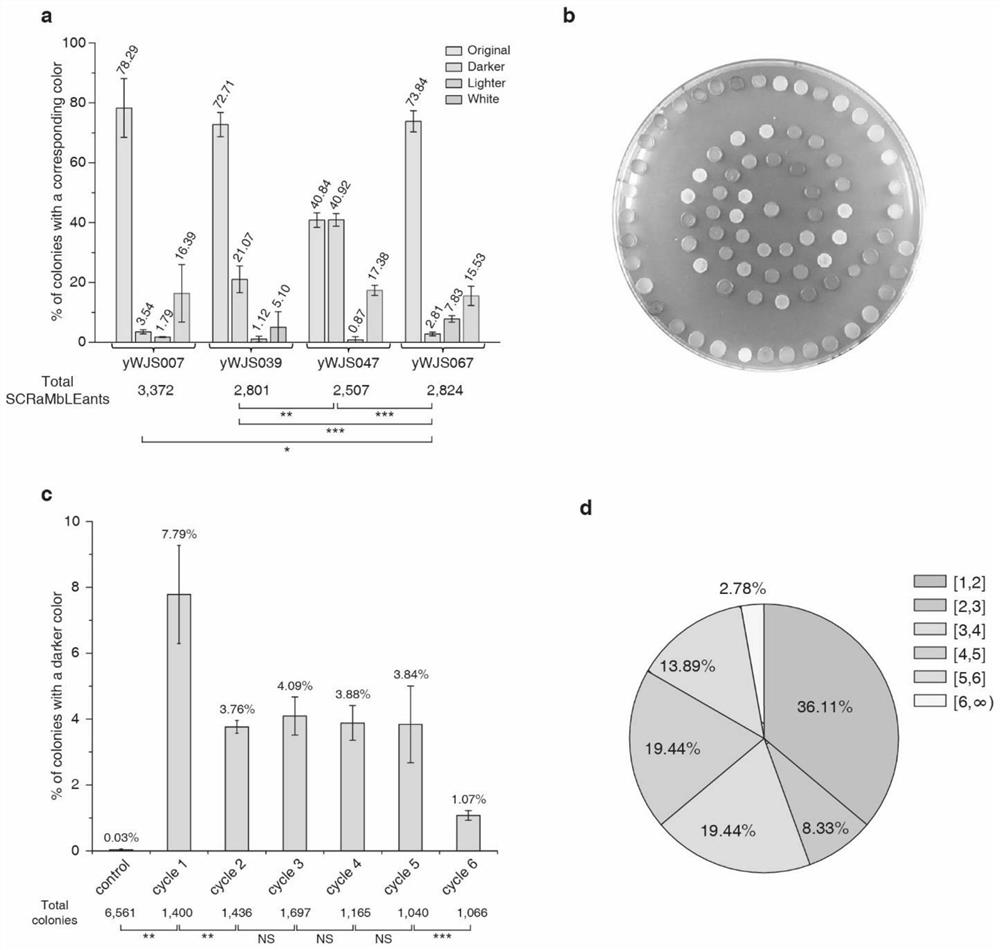
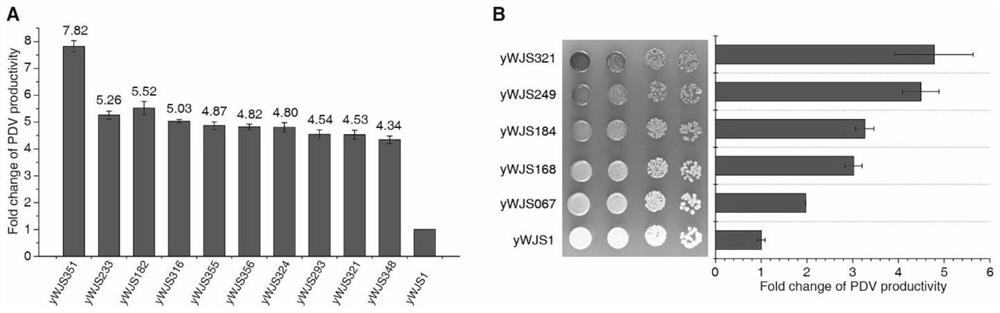
[0069] Circular synthetic yeast chromosomal rearrangements can achieve continuous improvement in the phenotype of yeast strains. We performed 5 rounds of rearrangement experiments on the strain (yWJS067), expecting to obtain a strain with improved PDV production. For the final selected strains, the percentages of dark colonies were 7.79%, 3.76%, 4.09%, 3.88%, 3.84% and 1.07%, respectively. For each round of rearrangement experiments, the strain with the darkest visible color and similar growth fitness compared to the parental strain was selected for quantification of PDV productivity by HPLC. After six rounds of rearrangement experiments, we obtained a strain with approximately seven-fold increased PDV production, and this strain had a favorable growth phenotype.
[0070] Table 4 figure 2 araw data
[0071]
[0072] table 5 figure 2 braw d...
Embodiment 3
[0075] Example 3 Continuous variation of chromosome number of Saccharomyces cerevisiae
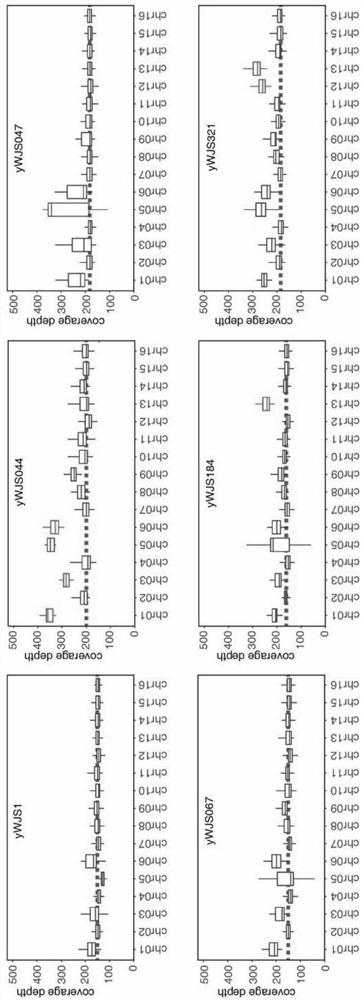
[0076] In order to shed light on the genetic variation generated in ring_synV, the applicant performed whole genome sequencing (WGS) analysis on some strains induced to rearrangement (SCRaMbLEants), yWJS044, yWJS047, yWJS067, yWJS184 and yWJS321. Among the rearranged strains analyzed, yWJS044, yWJS047 and yWJS067 were obtained from the starting strain yWJS1 after the first round of SCRaMbLE, yWJS184 was obtained from yWJS067 after the third round of SCRaMbLE, and yWJS321 was obtained from yWJS184 , The rearranged strain obtained after the fifth round of SCRaMbLE.
[0077] image 3The boxplot based on WGS results in Zhongwei shows the coverage depth of different chromosomes, representing the copy number of different chromosomes, and shows that the haploid Saccharomyces cerevisiae synthetic circular chromosome V SCRaMbLE can lead to chromosomal aneuploidy. Strain yWJS044 (aneuploid chromos...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com