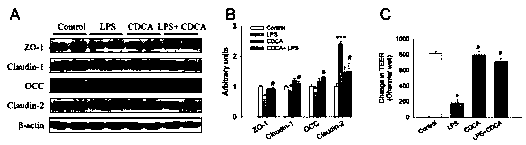Application of chenodeoxycholic acid in improving intestinal barrier function damage in animals
A technology of intestinal barrier function and chenodeoxycholic acid is applied in the application field of improving the intestinal barrier function damage of animals, and can solve the problems of damage to the growth performance of piglets, harm to human health, restricting the production level and efficiency of piglets, etc. Effects of improving intestinal barrier function damage, improving production performance, and improving intestinal barrier function damage in animals
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0038] Example 1 Chenodeoxycholic acid improves LPS-induced damage to the barrier function of porcine intestinal epithelial cells IPEC-J2
[0039]1. In order to study the improvement effect of chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) on the barrier function damage of porcine intestinal epithelial cells IPEC-J2 caused by LPS, the research object was pig intestinal epithelial cells IPEC-J2.
[0040] 2. Experimental method
[0041] (1) Cell culture method: Take out the cryopreservation tube from the liquid nitrogen tank, transfer it to warm water at 37°C and shake it quickly for thawing. After thawing, transfer the cells and cryopreservation solution to a 15 ml centrifuge tube, and centrifuge at 800 rpm for 5 min . After centrifugation, discard the frozen liquid, add complete medium (10 % FBS+DMEM medium, high glucose medium) to mix the cells by pipetting, and inoculate to 25 cm 2 in a culture bottle. Place the revived IPEC-J2 cells at 37°C, 5% CO 2 Cultivate in the incubator, and change...
Embodiment 2
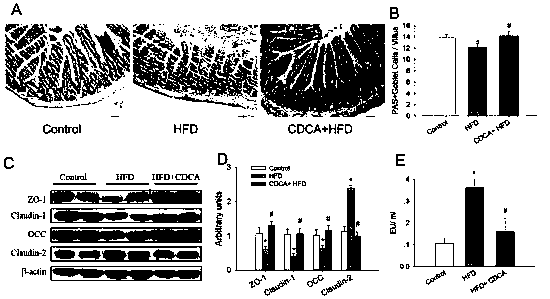
[0048] Example 2 Chenodeoxycholic acid can improve the damage of intestinal barrier function in high-fat fed mice
[0049] 1. In order to study the alleviating effect of chenodeoxycholic acid on intestinal barrier function damage in high-fat-fed mice, 4-week-old male C57BL / 6 mice were used as the research objects.
[0050] 2. Experimental method
[0051] (1) Animal breeding method: 1 animal / box, single-breeding; feeding temperature and humidity: 22-26°C, 40%-70%; 12 h: 12 h day and night intermittent lighting; the conditions of the breeding room are always kept stable to ensure the test reliability of the results. During the breeding period, the animals had free access to food and drinking water, and the feed and drinking water were provided by Guangdong Medical Experimental Animal Center.
[0052] (2) Animal grouping and treatment: 4-week-old mice were randomly divided into control group (Control), high-fat diet (HFD) group, HFD+chenodeoxycholic acid (HFD+CDCA) group, each ...
Embodiment 3
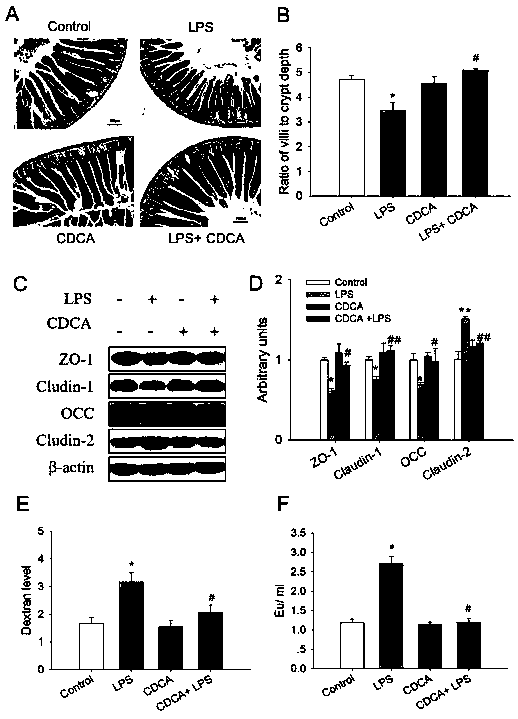
[0058] Example 3 Chenodeoxycholic acid can improve the damage of intestinal barrier function in mice caused by lipopolysaccharide (LPS)
[0059] 1. In order to study the improvement effect of chenodeoxycholic acid (CDCA) on LPS-induced intestinal barrier function damage in mice, 4-week-old female C57BL / 6 mice were used as the research object.
[0060] 2. Experimental method
[0061] (1) Animal feeding method: same as in Example 1.
[0062] (2) Animal grouping and treatment: 4-week-old mice were randomly divided into control group (Control), LPS group, LPS+chenodeoxycholic acid (LPS+CDCA) group, with 12 mice in each group. The mice in the control group were fed normal diet, the mice in the LPS group were only fed the normal diet and added 5 mg / ml LPS in the drinking water, and the mice in the LPS+CDCA group were fed the normal diet containing 0.5% CDCA and added 5 mg / ml LPS in the drinking water . The experiment was carried out for 6 weeks.
[0063] (3) Sampling and detecti...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com