Stress sensor based on Mach-Zehnder interference structure
A technology of stress sensor and interference structure, which is applied in the direction of measuring the change force of optical properties of materials when they are stressed, can solve the problems of variable frequency, difficult to filter out, unfavorable optical fiber sensors, etc., and achieve reliable work , The effect of small phase detection error
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
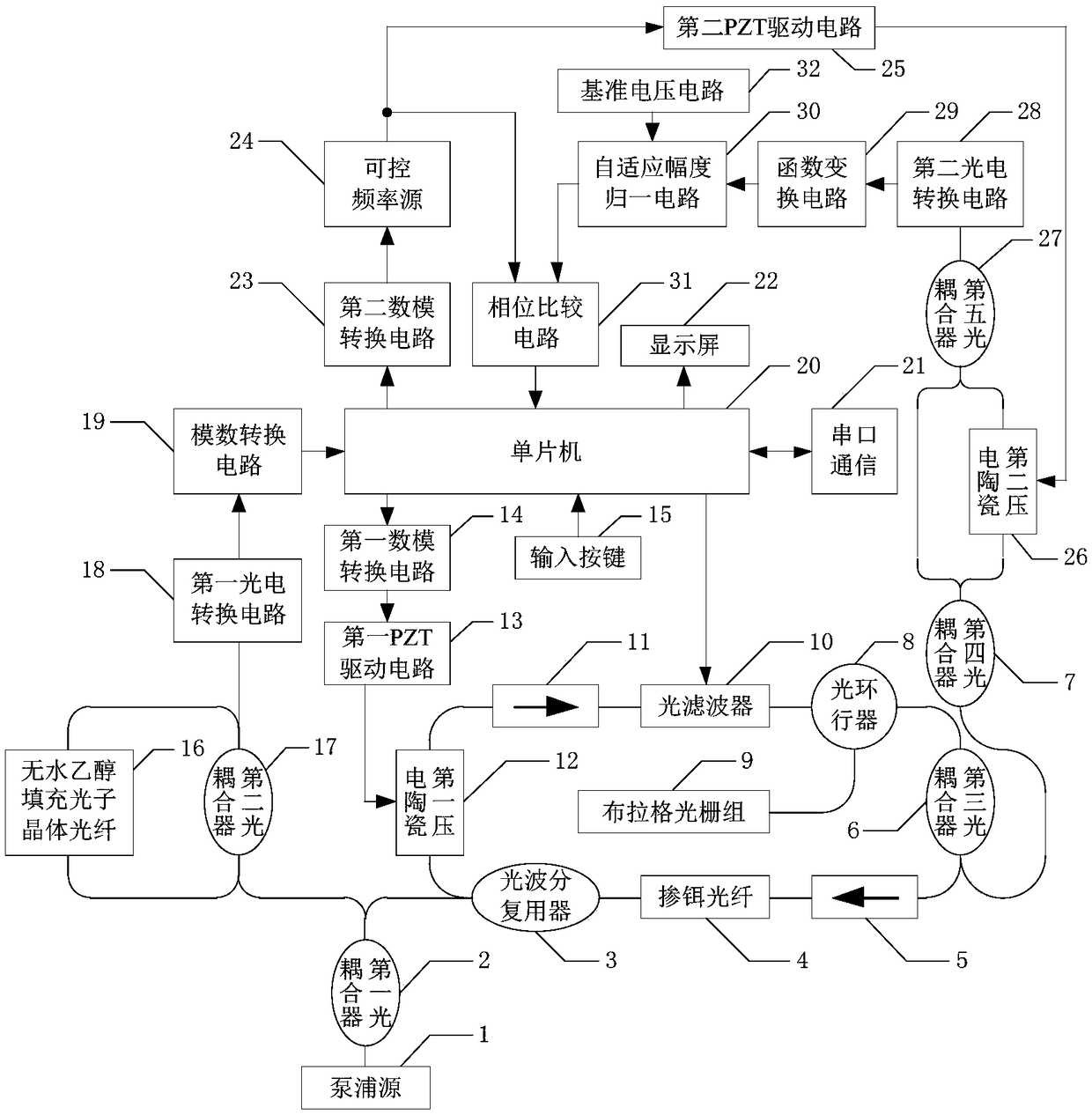
[0028] Embodiment 1 Overall structure of the present invention
[0029] Such as figure 1 As shown, the overall structure of the present invention has, the pumping source 1 (980nm laser, maximum output power is 1W) and the first optical coupler 2 (OZ-OPTICS company produces, model is FUSED-12-1064-7 / 125- 90 / 10-3U-3mm, splitting ratio is 90:10) input end is connected, 90% output end of the first optical coupler 2 is connected with the 980nm of optical wavelength division multiplexer 3 (980 / 1550nm wavelength division multiplexer) The 1550nm end of the optical wavelength division multiplexer 3 is connected to one end of the optical fiber wound on the first piezoelectric ceramic 12 (cylindrical piezoelectric ceramic, outer diameter 50mm, inner diameter 40mm, height 50mm), and wound on the first piezoelectric ceramic. The other end of the optical fiber on the electric ceramic 12 is connected with the input end of the first optical isolator 11 (1550nm polarization-independent optica...
Embodiment 2
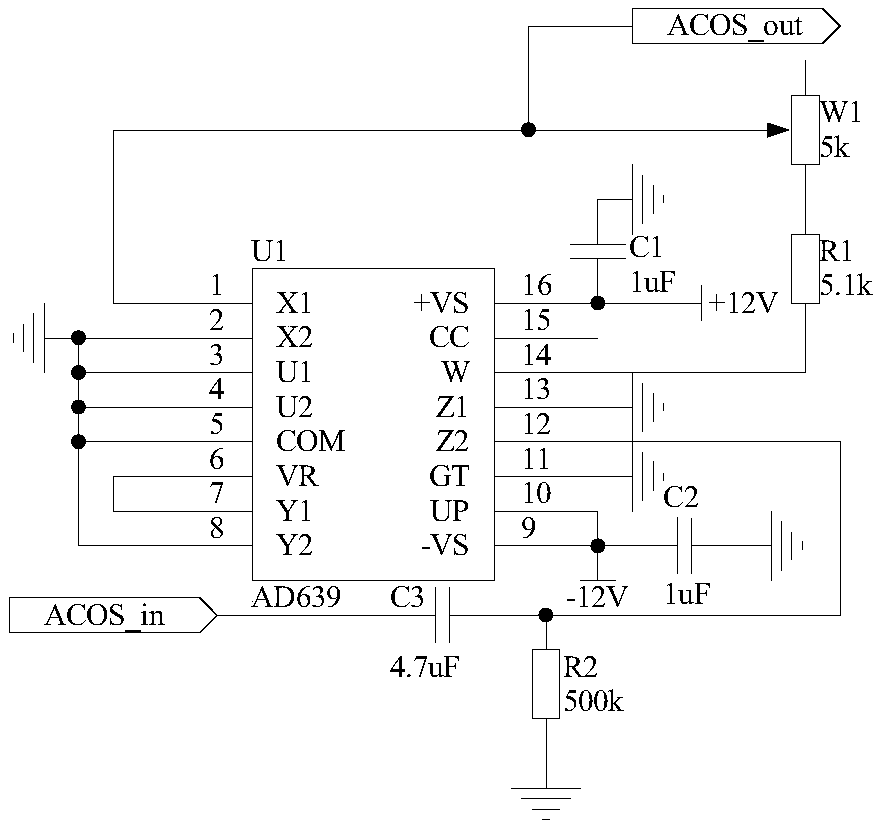
[0031] Embodiment 2 function transformation circuit
[0032] Such as figure 2As shown, the structure of the function conversion circuit 29 used in the present invention is that one end of the capacitor C3 is connected to the pin 12 of the trigonometric function converter U1 (AD639) and one end of the resistor R2, and the other end of the capacitor C3 is used as the function conversion circuit 29 The input end of the input port, denoted as port ACOS_in, is connected to the output end of the second photoelectric conversion circuit 28; the other end of the resistor R2 is grounded; the pins 2, 3, 4, 5, 8, 11, and 13 of the trigonometric function converter U1 are grounded , pins 9 and 10 are connected to one end of capacitor C2 and -12V power supply, and the other end of capacitor C2 is grounded; pin 6 of trigonometric function converter U1 is connected to pin 7, and pin 16 is connected to +12V power supply and capacitor C1 One end is connected, and the other end of the capacitor...
Embodiment 3
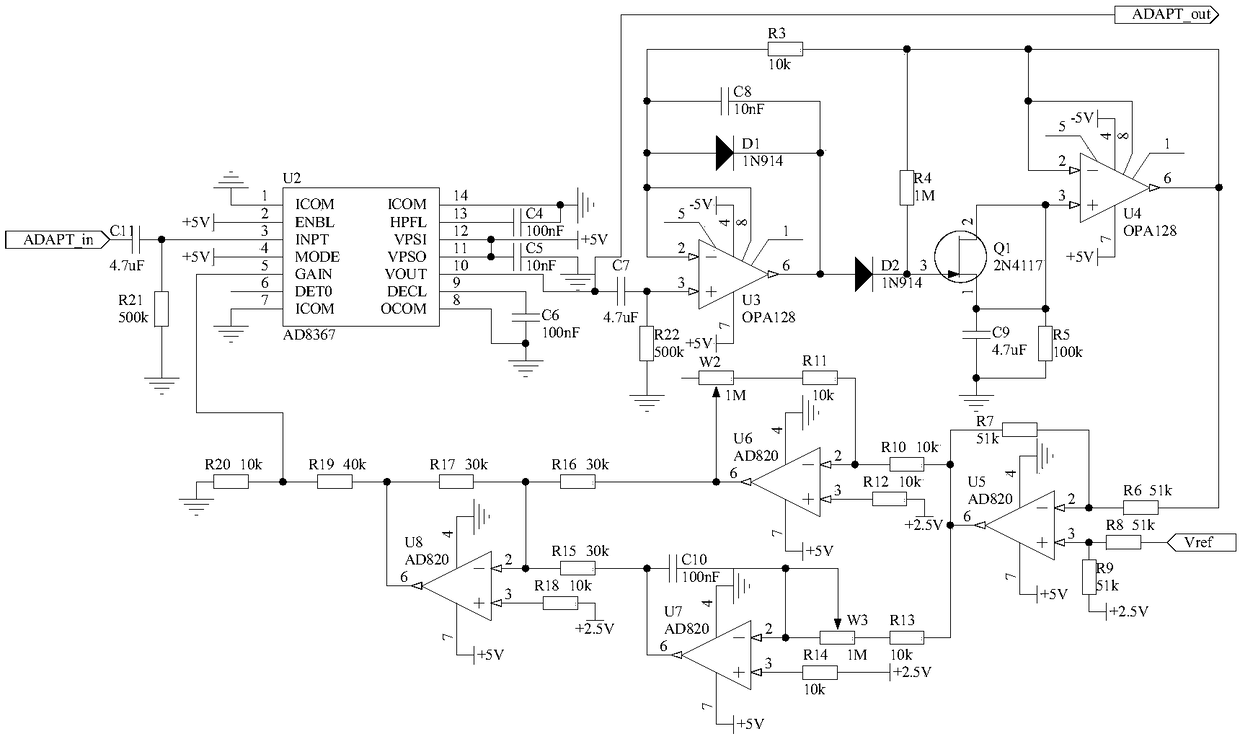
[0033] Embodiment 3 Adaptive Amplitude Normalization Circuit
[0034] Because the amplitude of the signal output by the function conversion circuit 29 is relatively small, and is affected by multiple parameters in the optical path and the circuit, the size is indefinite, so the present invention designs an adaptive amplitude normalization circuit 30, which is used to convert the signal output by the function conversion circuit 29 The amplitude is normalized to the optimal size to further improve the accuracy of demodulation. The specific structure is that one end of the capacitor C11 is connected to one end of the resistor R21 and the pin 3 of the chip U2, the other end of the resistor 21 is grounded, and the other end of the capacitor C11 is used as the input end of the adaptive amplitude normalization circuit 30, which is recorded as the port ADAPT_in , is connected with the port ACOS_out of the function conversion circuit 29; the pin 1, the pin 7, the pin 8 and the pin 14 o...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Bandwidth | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Center wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com