Recycling and purification method of silicon cutting waste material
A purification method and silicon cutting technology, applied in chemical instruments and methods, silicon compounds, inorganic chemistry, etc., can solve the problems of low silicon purity, low production capacity, large equipment corrosion, etc., to achieve high comprehensive recovery rate and reduce power generation. The effect of large cost and production capacity
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] Embodiment 1: the silicon cutting waste of this embodiment is the silicon cutting waste of a certain silicon factory in Yunnan;
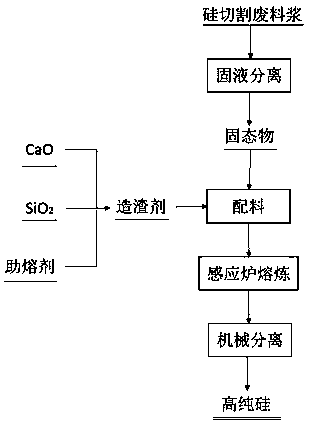
[0028] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for recycling and purifying silicon cutting waste, the specific steps are:
[0029] (1) Solid-liquid separation of the silicon waste slurry generated during the silicon ingot cutting process and drying to obtain solid silicon waste; the Si content in the solid silicon waste is 88.01%, and the main chemical components of impurities are shown in Table 1;
[0030] Table 1 The main chemical components of impurities in solid silicon waste
[0031]
[0032] (2) 16.2g CaO, 10.7g SiO 2 , 8.1g flux (flux is CaF 2 ) mixed evenly to obtain a slagging agent; where CaO, SiO 2 , flux (flux is CaF 2 ) are analytically pure, SiO 2 It is granular and the particle size is 10~20 mesh, CaO, SiO 2 , flux (flux is CaF 2 ) with a mass ratio of 2:1.33:1;
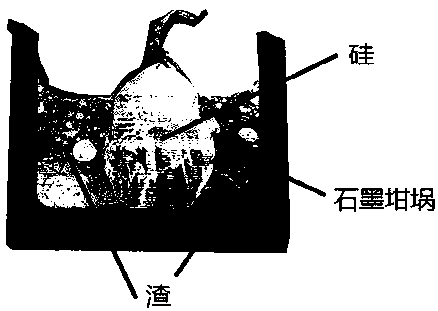
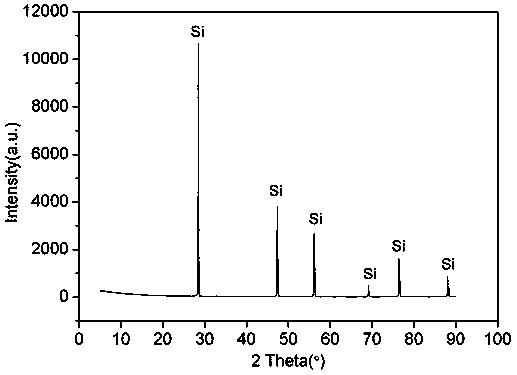
[0033] (3) Mix the slagging agent in step (2) with 35g o...
Embodiment 2
[0036] Embodiment 2: the silicon cutting waste of this embodiment is the silicon cutting waste of a certain silicon factory in Yunnan;
[0037] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for recycling and purifying silicon cutting waste, the specific steps are:
[0038] (1) Solid-liquid separation of the silicon waste slurry generated during the silicon ingot cutting process and drying to obtain solid silicon waste; the Si content in the solid silicon waste is 88.01%, and the main chemical components of impurities are shown in Table 2;
[0039] Table 2 The main chemical components of impurities in solid silicon waste
[0040]
[0041](2) 16.2g CaO, 10.7g SiO 2 , 8.1g flux (flux is Na 2 CO 3 ) mixed evenly to obtain a slagging agent; where CaO, SiO 2 , flux (flux is Na 2 CO 3 ) are analytically pure, SiO 2 It is granular and the particle size is 10~20 mesh, CaO, SiO 2 , flux (flux is Na 2 CO 3 ) with a mass ratio of 2:1.33:1;
[0042] (3) Mix the slagging agent in step ...
Embodiment 3
[0044] Embodiment 3: the silicon cutting waste of this embodiment is the silicon cutting waste of a certain silicon factory in Yunnan;
[0045] Such as figure 1 As shown, a method for recycling and purifying silicon cutting waste, the specific steps are:
[0046] (1) Solid-liquid separation of the silicon waste slurry generated during the silicon ingot cutting process and drying to obtain solid silicon waste; the Si content in the solid silicon waste is 88.01%, and the main chemical components of impurities are shown in Table 3;
[0047] Table 3 The main chemical composition of impurities in solid silicon waste
[0048]
[0049] (2) 16.2g CaO, 10.7g SiO 2 , 8.1g flux (flux is Al 2 o 3 ) mixed evenly to obtain a slagging agent; where CaO, SiO 2 , flux (flux is Al 2 o 3 ) are analytically pure, SiO 2 It is granular and the particle size is 10~20 mesh, CaO, SiO 2 , flux (flux is Al 2 o 3 ) with a mass ratio of 2:1.33:1;
[0050] (3) Mix the slagging agent in step (...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com