Lactobacillus engineering bacterium with improved acid stress resistance and application of lactobacillus engineering bacteria
A technology of lactic acid bacteria and engineering bacteria, applied in the fields of genetic engineering and microbial engineering, can solve problems such as weakening, accumulation of by-products, osmotic stress, etc., and achieve the effects of improving resistance and improving acid stress resistance.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0057] Embodiment 1: Construction of recombinant bacterial strain
[0058] Specific steps are as follows:
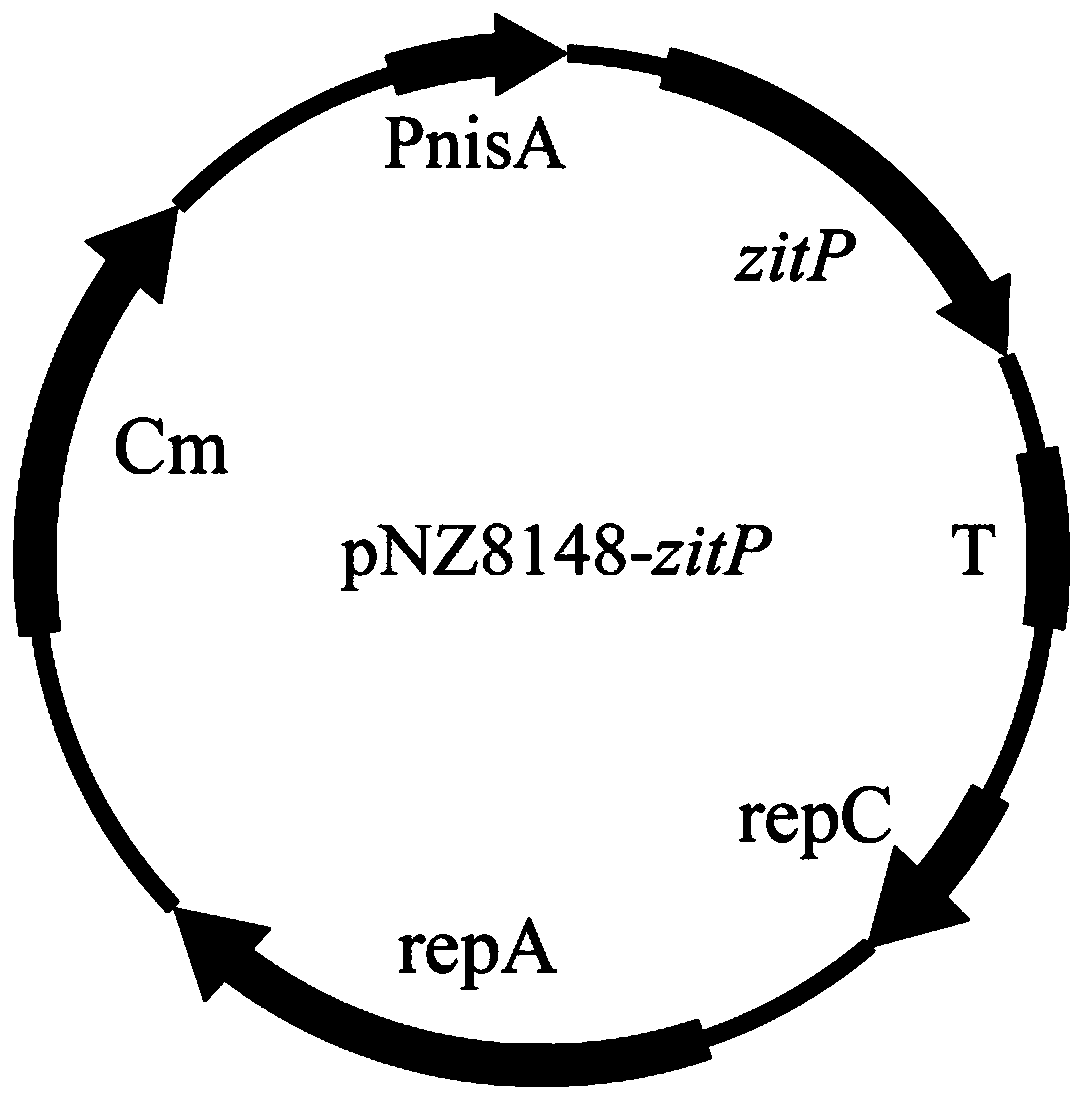
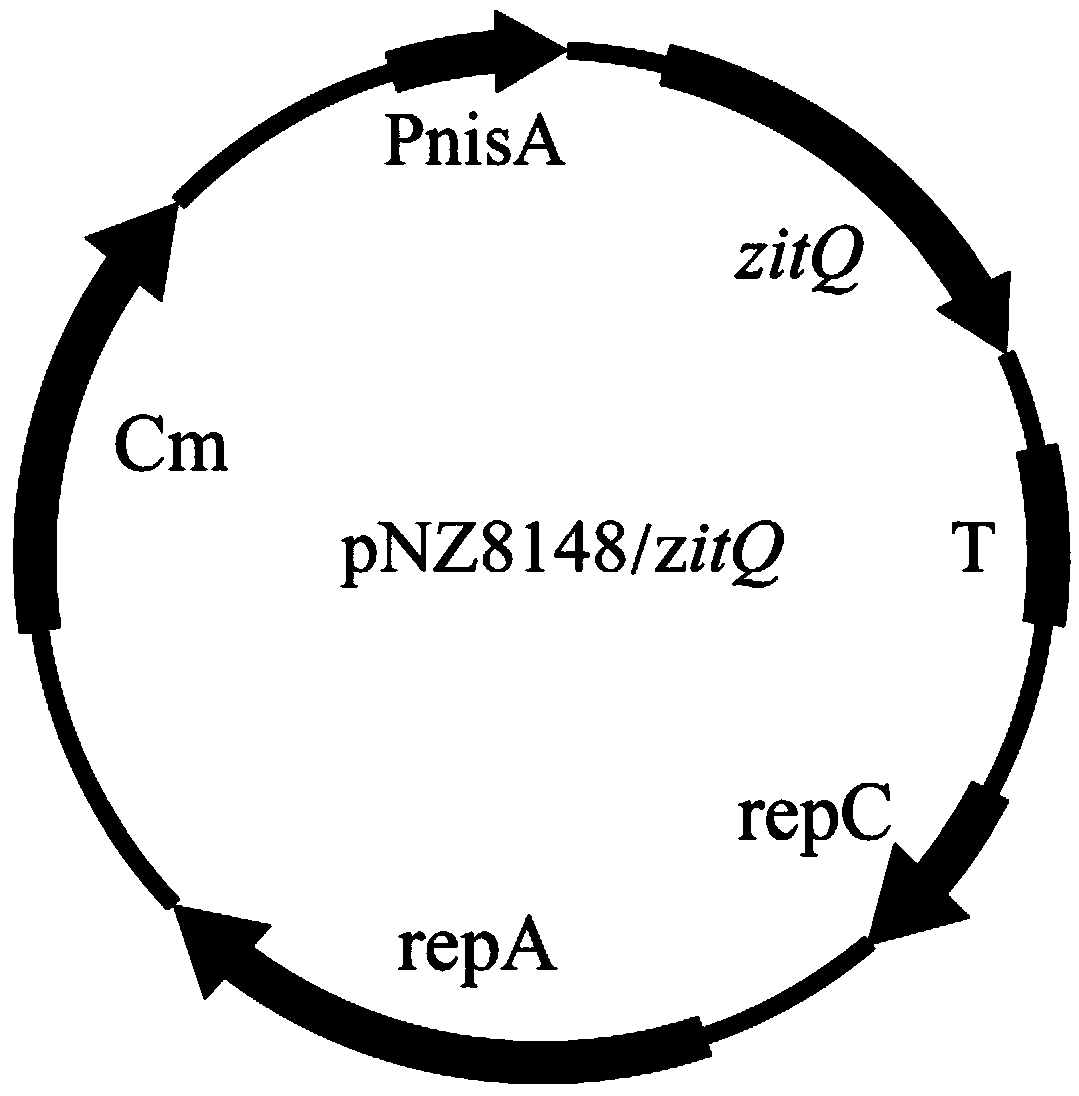
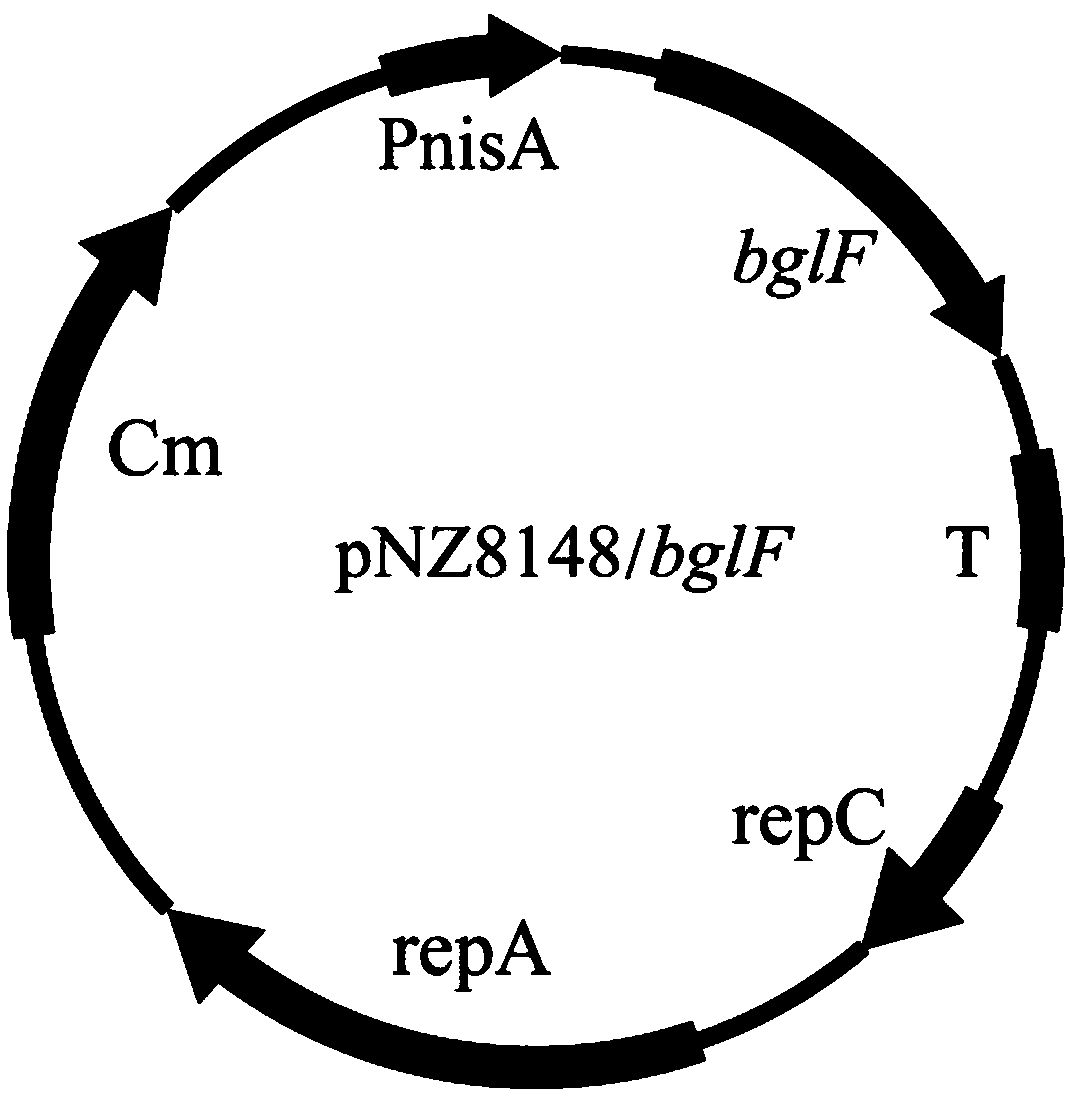
[0059] (1) Obtain the zitP gene sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.1, the zitQ gene sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.3, the bglF gene sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.4, and the bglF gene sequence shown in SEQ ID NO.4 from the NCBI database. For the ganP gene sequence shown in ID NO.5, the primers shown in Table 1 were designed according to the gene sequence;
[0060] (2) Using the genome of L.lactis NZ9000 as a template, the primers in Table 1 were amplified by PCR to obtain SEQ ID NO.1, SEQ ID NO.3, SEQ ID NO.4, and SEQ ID NO.5. gene fragments;
[0061] (3) The PCR product and the carrier pNZ8148 were double-digested with the restriction endonucleases in Table 1, and the digested products were purified and ligated;
[0062] (4) Transform the ligation product into Escherichia coli MC1061 (commercialized strain) competent, screen positive clones on a chloramphenicol plate, verify by c...
Embodiment 2
[0066] Embodiment 2: the growth performance test of recombinant bacterial strain
[0067] Specific steps are as follows:
[0068] (1) The bacterial strain L lactis NZ9000 (pNZ8148) (control) and the bacterial strain L lactis NZ9000 (pNZ8148 / zitP) obtained in Example 1, L lactis NZ9000 (pNZ8148 / zitQ), L lactis NZ9000 (pNZ8148 / bglF), L lactis NZ9000 (pNZ8148 / ganP) were respectively inoculated in GM17 liquid medium supplemented with 10 μg / mL chloramphenicol for activation, and placed in a 30°C incubator for static culture overnight;
[0069] (2) Transfer the above-obtained seed solution to fresh chloramphenicol (10 μg / mL) GM17 liquid medium with an inoculum size of 2%, and culture it statically at 30° C.;
[0070] (3) During the culturing process, samples were taken at regular intervals to measure the OD value at a wavelength of 600nm;
[0071] (4) Cultivate to OD 600 Add 10ng / mL nisin at 0.4 to induce the expression of the transporter, take time as the abscissa, OD 600 The ...
Embodiment 3
[0074] Example 3: Tolerance test of recombinant strains under lactic acid stress conditions
[0075] Specific steps are as follows:
[0076] The bacterial strain L lactis NZ9000 (pNZ8148) (control) and the bacterial strains L lactis NZ9000 (pNZ8148 / zitP) and lactis NZ9000 (pNZ8148 / zitQ) obtained in Example 1 were respectively induced and cultured for 6 h, and the cells were collected by centrifugation, and washed with 0.85% normal saline for two times. Resuspend in an equal volume of fresh GM17 (containing chloramphenicol 10 μg / mL) at pH 4.0 (adjusted by lactic acid) for the second time, and stress for different times; wash the stressed bacterial suspension twice and resuspend in an equal volume of In normal saline, take 10 μ L of the resuspension, dilute different gradients, and plant on the GM17 chloramphenicol plate to determine the number of viable bacteria and the survival rate (the results are as follows: Figure 7 and Figure 8 shown).
[0077] Such as Figure 7 and...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com