Application of Ethiopian Brassica in the Breeding of Brassica napus Lines with Limited Inflorescences
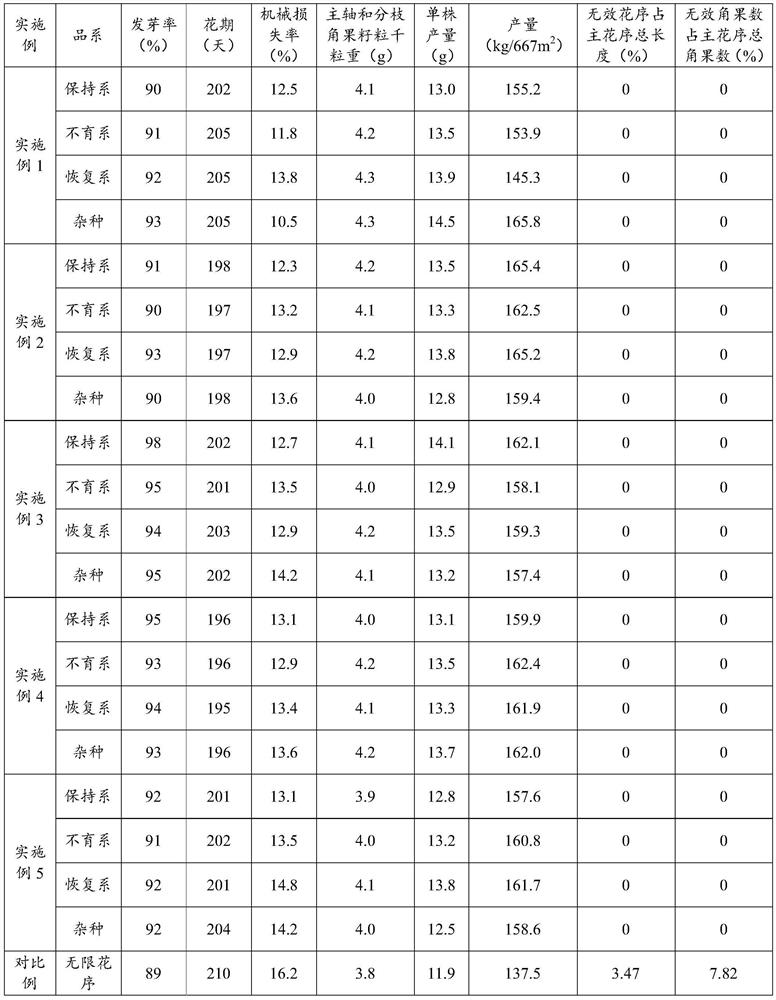
A technology of Brassica napus and inflorescence, which is applied in the fields of application, seed coating/seed dressing, plant genetic improvement, etc., can solve the problems of increasing the ineffective consumption of rapeseed biomass and unsuitable for mechanized operation of rapeseed varieties, and achieve thousand-grain weight and unit weight. The effect of increased plant yield, increased germination rate, and consistent maturity of siliques
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0044] All the breeding processes of the present embodiment are carried out under natural conditions;
[0045] This embodiment provides a kind of application of Ethiopian mustard in the selection and breeding of Brassica napus limited inflorescence maintainer line, and the selection method is specifically as follows:
[0046] In March 2010, in Nanchang, Jiangxi Province, 1 copy of E. chinensis was used as the female parent, and 1 copy of the Brassica napus line with unlimited inflorescences (Zhongshuang 11) was used as the male parent. Crossing was carried out, and the plants with limited inflorescence traits were screened to obtain 1 hybrid offspring F1;
[0047] In July 2010, in Xining, Qinghai, one copy of hybrid F1 was used as the female parent, and one copy of Zhongshuang11 was used as the male parent, and the first backcross was carried out, and 5 backcross offspring were obtained;
[0048] In March 2011, in Nanchang, Jiangxi, 5 copies of backcross offspring were used a...
Embodiment 2
[0072] In the breeding process of this embodiment, the daily light time of the plants is 15h, and when the light is insufficient, light is used to irradiate, and the light intensity is controlled to be the same as natural light;
[0073] This embodiment provides a kind of application of Ethiopian mustard in the selection and breeding of Brassica napus limited inflorescence maintainer line, and the selection method is specifically as follows:
[0074] In March 2010, in Nanchang, Jiangxi Province, 1 copy of E. chinensis was used as the female parent, and 1 copy of the Brassica napus line with unlimited inflorescences (Zhongshuang 11) was used as the male parent. Crossing was carried out, and the plants with limited inflorescence traits were screened to obtain 1 hybrid offspring F1;
[0075] In July 2010, in Xining, Qinghai, one copy of hybrid F1 was used as the female parent, and one copy of Zhongshuang11 was used as the male parent, and the first backcross was carried out, and ...
Embodiment 3
[0098] All the breeding processes of this embodiment are carried out under natural conditions;
[0099] This example provides an application of Ethiopian mustard in the selection and breeding of limited inflorescence maintainer lines of Brassica napus. Before planting, the seeds of Ethiopian mustard are soaked in an aqueous solution of potassium permanganate with a mass fraction of 0.5%, and then dried in the air after 6 hours. Dry, the breeding method is as follows:
[0100] In March 2010, in Nanchang, Jiangxi Province, 1 copy of E. chinensis was used as the female parent, and 1 copy of the Brassica napus line with unlimited inflorescences (Zhongshuang 11) was used as the male parent. Crossing was carried out, and the plants with limited inflorescence traits were screened to obtain 1 hybrid offspring F1;
[0101] In July 2010, in Xining, Qinghai, one copy of hybrid F1 was used as the female parent, and one copy of Zhongshuang11 was used as the male parent, and the first back...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com