Microbial composite soil conditioning fertilizer
A soil conditioning and microbial technology, applied in the field of microbial composite soil conditioning fertilizer, can solve the problems of not being able to be used as a fertilizer source, the cycle of decomposition and transformation is long, and the resistance to the promotion of straw returning technology is large, and the decomposition speed is accelerated and the decomposition speed is optimized. , the effect of facilitating absorption
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
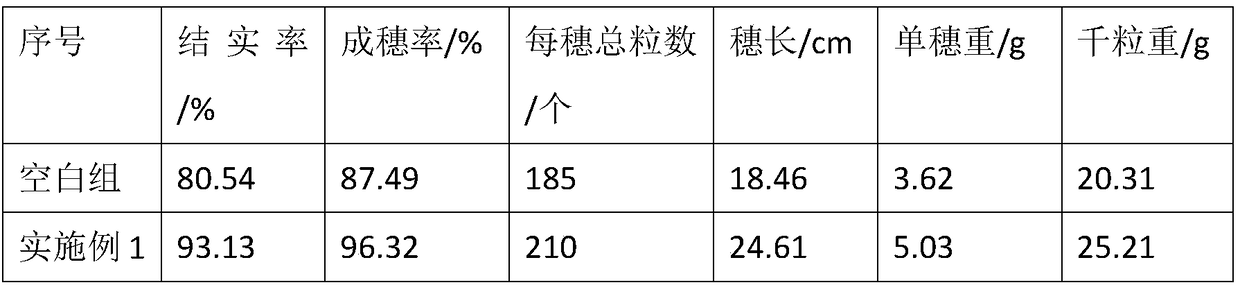
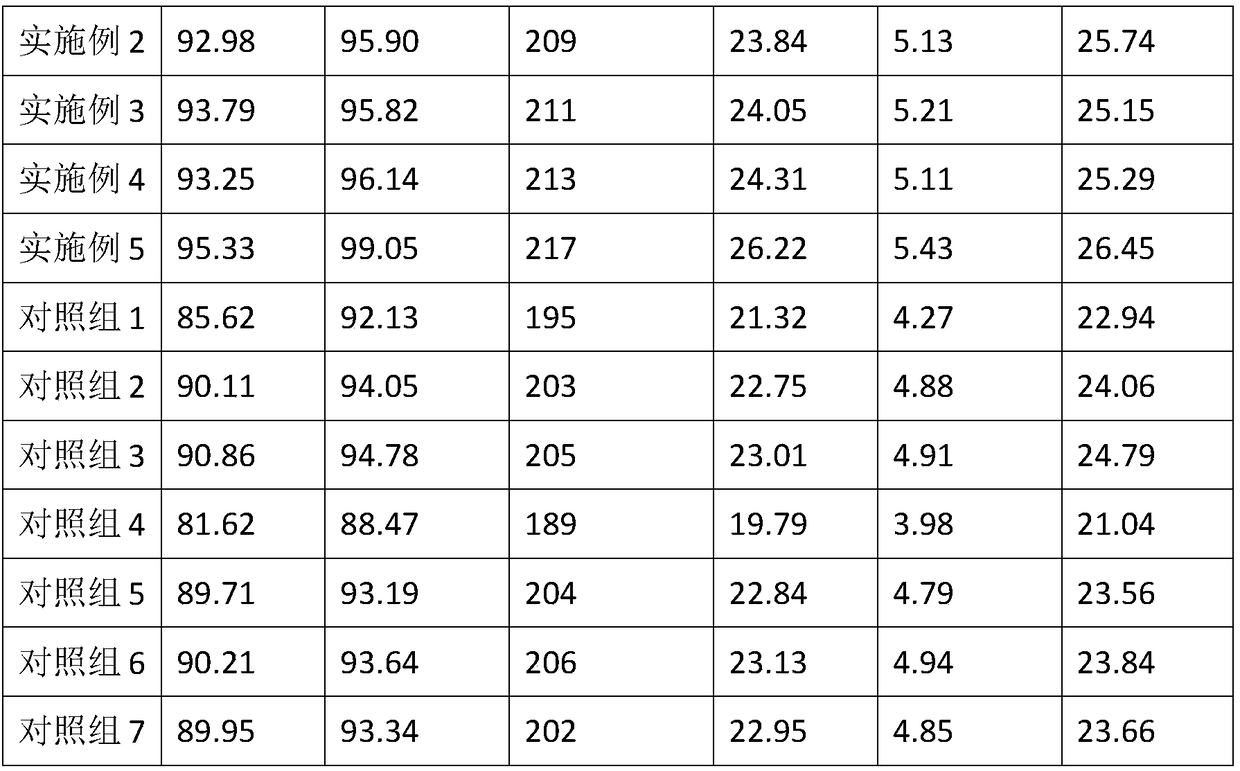
Examples
Embodiment 1
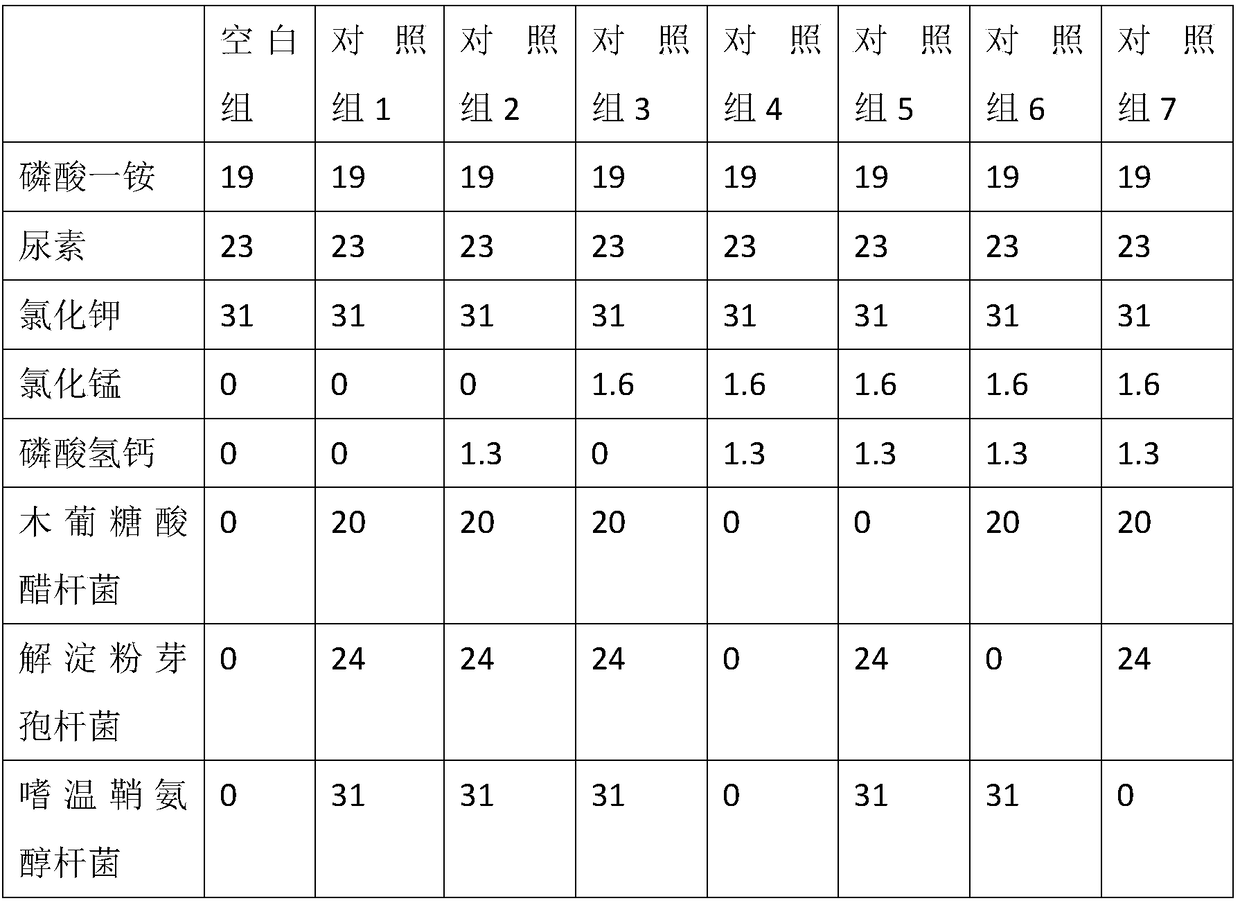
[0015] A microbial composite soil conditioning fertilizer, comprising the following parts by weight of raw materials: 10 parts of monoammonium phosphate, 30 parts of urea, 25 parts of potassium chloride, 3 parts of manganese chloride, 0.5 parts of calcium hydrogen phosphate, and Acetobacter xyluconate 25 parts, 20 parts of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and 35 parts of Sphingosine mesophila.
Embodiment 2
[0017] A microbial composite soil conditioning fertilizer, which comprises the following parts by weight of raw materials: 25 parts of monoammonium phosphate, 15 parts of urea, 35 parts of potassium chloride, 0.5 parts of manganese chloride, 2 parts of calcium hydrogen phosphate, Acetobacter xyluconate 15 parts, 30 parts of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and 25 parts of Sphingomyces mesophila.
Embodiment 3
[0019] A microbial composite soil conditioning fertilizer, which comprises the following parts by weight of raw materials: 15 parts of monoammonium phosphate, 26 parts of urea, 28 parts of potassium chloride, 2 parts of manganese chloride, 1 part of calcium hydrogen phosphate, Acetobacter xyluconate 23 parts, 22 parts of Bacillus amyloliquefaciens and 33 parts of Sphingomyces mesophila.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com