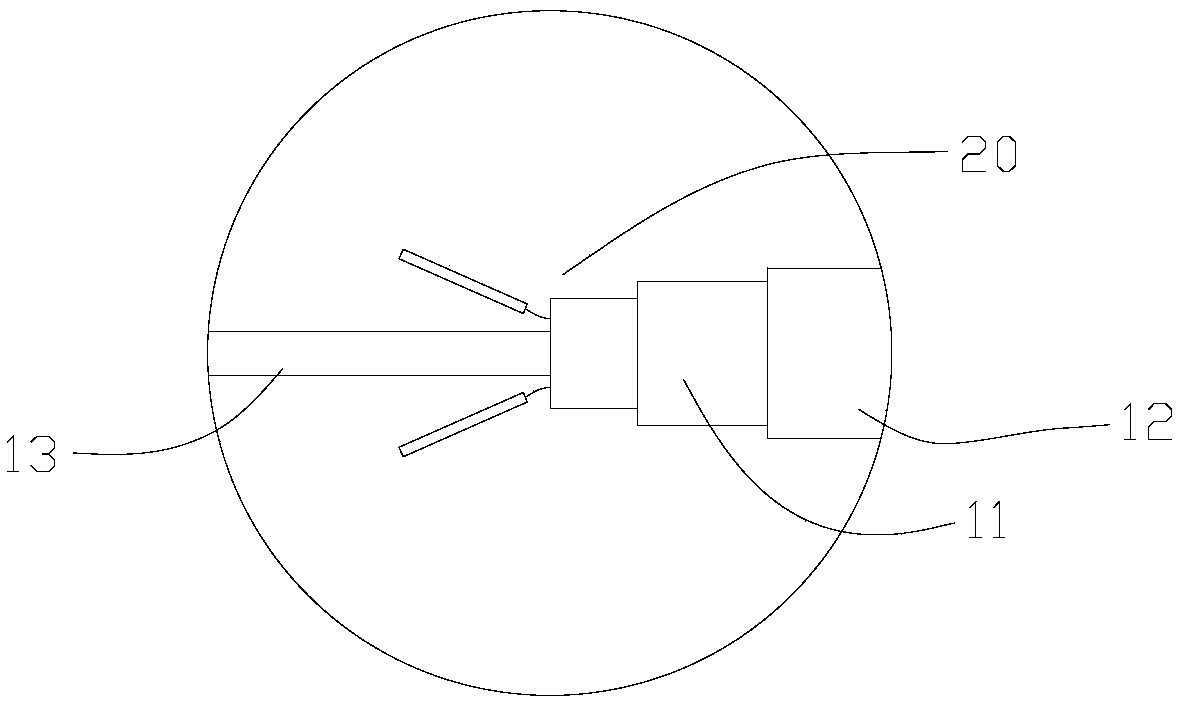Implant delivery system
A delivery system and implant technology, applied in the field of implant delivery systems, can solve the problems of luminal stent position deviation, inability to adjust the release position, easy separation, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
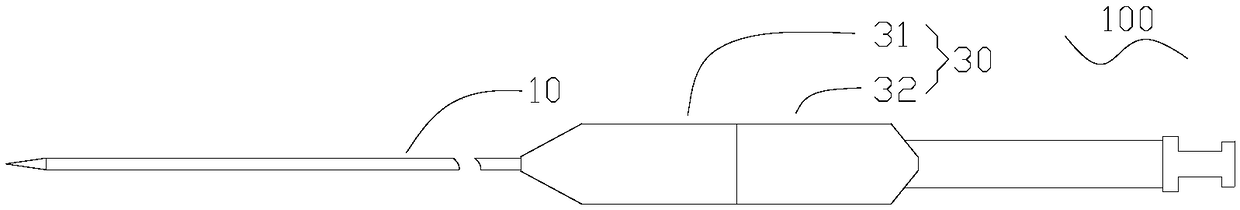
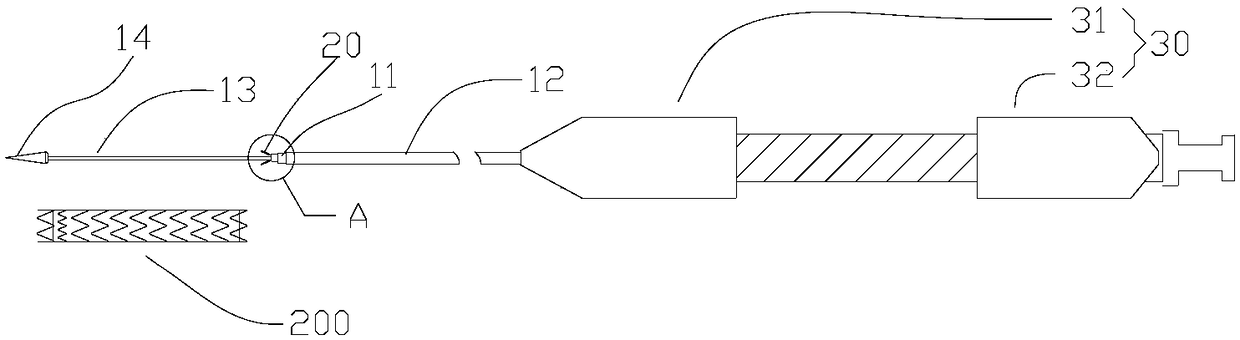
[0049] See also Figure 1a to Figure 1c , the delivery system 100 provided in Embodiment 1 is used to deliver the implant to the lesion in the lumen of the human body. The delivery system 100 includes a tube body 10 , an anchor unit 20 , and a handle 30 . In this embodiment, the implant is a lumen stent 200 .
[0050] The handle 30 includes a first shell 31 and a second shell 32 which are symmetrically arranged. The first housing 31 and the second housing 32 can move relative to each other in the axial direction, and the first housing 31 is closer to the distal end than the second housing 32 .
[0051] The tube body 10 includes a hollow inner sheath tube 11 axially penetrating through the handle 30, a hollow inner sheath core tube 13 penetrating through the inner sheath tube 11 and protruding from the inner sheath tube 11 at the distal end, and movably sleeved on the inner sheath tube 11 An outer sheath tube 12 with a cavity on the outside and between the inner sheath core t...
Embodiment 2
[0097] The structure of the endoluminal stent delivery system provided in this embodiment is basically the same as that of the endoluminal stent delivery system 100 provided in the first embodiment. The difference is that, in this embodiment, the structure of the tightening piece, the number and structure of the anchoring pieces are different from those of the first embodiment.
[0098] Specifically, see Figure 6a , in this embodiment, the anchoring unit 40 includes a sleeve-shaped tightening member 41 with a certain wall thickness, and at least one anchoring member 42 connected to the tightening member 41 .
[0099] Please also see Figure 6b , The tightening member 41 has at least one pair of guide holes 411 . The guide hole 411 includes a first hole 411a located on the distal end surface of the tightening member 41, and a second hole 411b located on the outer wall of the tightening member 41, and the first hole 41a and the second hole 41b are connected, A pair of guide ...
Embodiment 3
[0111] The structure of the endoluminal stent delivery system provided in this embodiment is basically the same as that of the endoluminal stent delivery system 100 provided in the first embodiment. The difference is that in this embodiment, the structure of the inner sheath core tube and the tightening parts, the number and structure of the anchor parts are the same as those of the inner sheath core tube and the tightening parts, the number and structure of the anchor parts in the first embodiment. The structures are all different.
[0112] Specifically, see Figure 9a , in this embodiment, the anchoring unit 50 includes a sleeve-shaped tightening member 51 and five anchoring members 52 connected to the tightening member 51 . The anchoring part 52 includes a deformation part 521 connected to the tightening part 51 and a spherical locking part 522 connected to the deformation part 521 .
[0113] The anchoring unit 50 is laser-engraved from a nickel-titanium tube whose wall t...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Length | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com