Pasteurella multocida gene knockout strain mediated by ngpiwi protein and its construction method and application
A Pasteurella and gene knockout technology, applied in the field of avian Pasteurella multocida gene knockout strains and their construction, can solve the problem of not being able to produce better cross-immune protection, lagging behind in attenuated vaccine research, and ineffective weakening mechanisms. Clear and other problems, to achieve the effect of good immune protection efficiency, significant reduction in virulence, and high screening efficiency
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
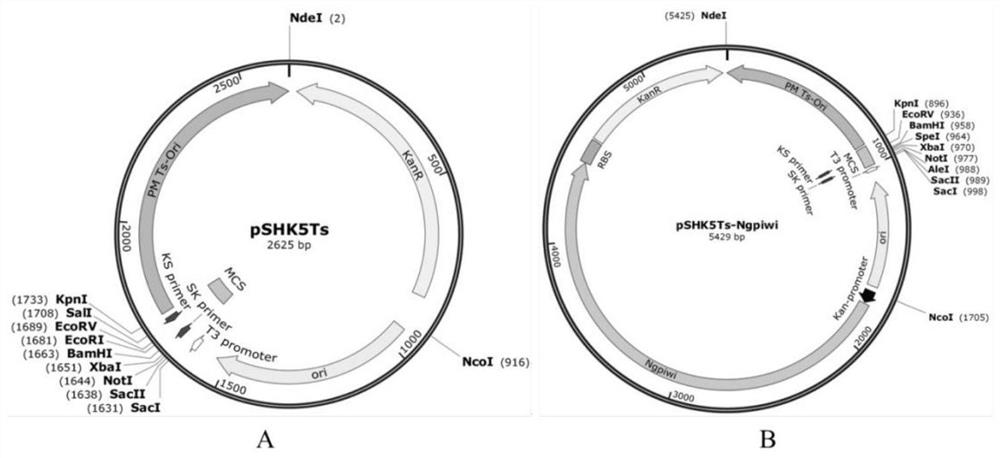
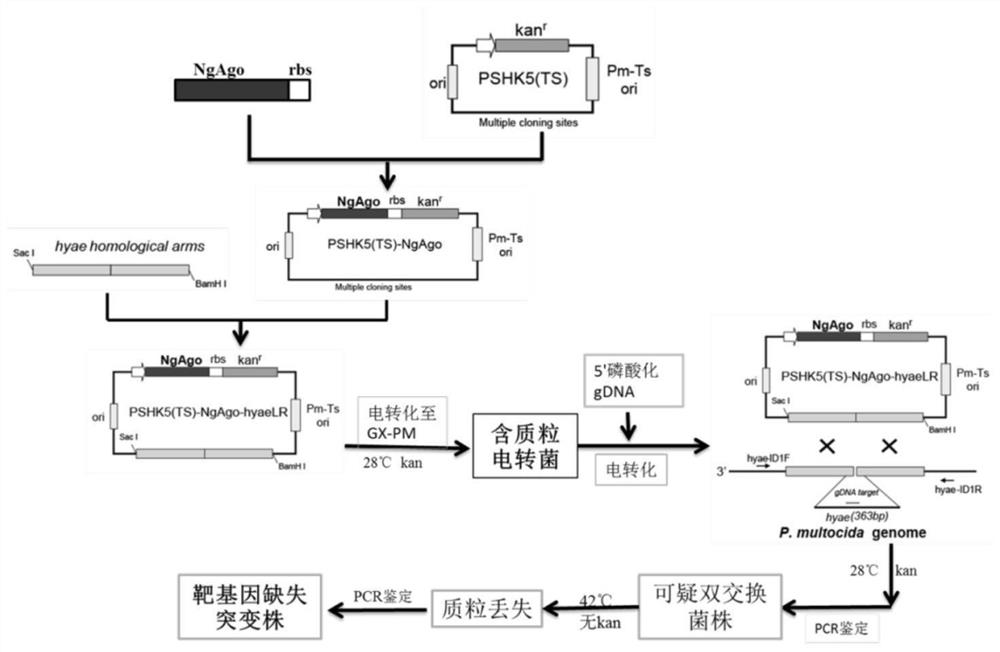
[0141] The specific method for constructing the temperature-sensitive suicide basic plasmid pSHK5Ts-NgPiwi for knocking out the target gene of Pasteurella multocida comprising the following steps:
[0142] 1) Using SEQ ID No.6 and SEQ ID No.7 as templates to design NgPiwi fragments and RBS fragment amplification fusion primers and identification primers for NgPiwi fragments; respectively:
[0143] NgPiwi forward and reverse amplification primers:
[0144] NgPiwi-L: ATGACAGTGATTGACCTCGATTCG,
[0145] NgPiwi-RH-R: GCAAGAAAAAATATCAATTAGAGGAATCCGACAT;
[0146] Forward and reverse amplification primers for RBS:
[0147] RBS-RH-L: TGTCGGATTCCTCTAATTGATATTTTTTTCTTGC,
[0148] RBS-R: TATGCACTCCTATTTATTTAACTAAGTTGAC;
[0149] Primers to identify NgPiwi fusions to the plasmid:
[0150] NgPiwi-JD-F: CAACCCGGTAAGACACGACTTATC,
[0151] NgPiwi-JD-R: ATCTGTAACATCATTGGCAACGC;
[0152] 2) Fusion primers were designed using the temperature-sensitive suicide plasmid pSHK5Ts and NgPiwi-RBS...
Embodiment 2
[0195] The acquisition of the P. multocida hyae gene ORF partial sequence deletion bacterial strain △hyae-GX-PM comprises the following steps:
[0196] 1) Using the ORF sequence of the capsular synthetic protein gene + 300bp sequences upstream and downstream (referred to as the ORF sequence of the hyae gene and the 300bp sequences upstream and downstream) as shown in SEQ ID No.8 as a template, design primers to knock out the partial sequence of the hyae gene ORF , respectively:
[0197] Left homology arm forward and reverse primers:
[0198] hyaE-KpnI-L-1: CATGGTACCGGTTATTATCATTGGAC,
[0199] hyaE-L-2: AACAGATGCAGTGAGATCTTGGTTTACTTCAATAATTTCC;
[0200] Right homology arm forward and reverse primers:
[0201] hyaE-R-3: TGAAGTAAACCAAGATCTCACTGCATCTGTTCAATC,
[0202] hyaE-SacI-R-4: AAAGAGCTCGAGTAAGCCACTTAAACGG;
[0203] Primers on both sides of the left and right homology arms of the ORF partial sequence of the hyae gene to be deleted on the genome:
[0204] hyaE-ID-F: CCTA...
Embodiment 3
[0257] The acquisition of the Pasteurella multocida lyi gene ORF sequence deletion strain Δlyi-GX-PM, the main steps are the same as in Example 2, and the differences include the following steps:
[0258] 1) Using the lyi ORF sequence and the upstream and downstream 1000bp sequences, as shown in SEQ ID No.9, as a template, design primers for knocking out the lyi gene ORF sequence, respectively:
[0259] Left homology arm forward and reverse primers:
[0260] lyi-SacI-L1:AAGAGCTCAGATGTTATTGAGTCTGCG,
[0261] lyi-RH-L2: TTTAGGAGTTTTTTATGTAAGTCAATACTGATC;
[0262] Right homology arm forward and reverse primers:
[0263] lyi-RH-R3: TGATCAGTATTGACTTACATAAAAACTCCTAAATTC,
[0264] lyi-BamHI-R4: TTGGATCCTGACTTTGTCTTTAACACTGC;
[0265] Primers on both sides of the left and right homology arms of the lyi gene ORF sequence to be deleted on the genome:
[0266] lyi-ID1F: TGGTGGCGTTGACTCTTCTGTCAC,
[0267] lyi-ID1R: AAATTACGAGCGATGGCCTCG;
[0268] Primers for internal identification...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com