A method for removing flesh from bone specimens
A bone and specimen technology, applied in the field of specimen preparation, can solve the problems of cumbersome production process, danger of strong acid and strong alkali, and limited application range, etc., and achieve the effect of simple flesh removal method, time saving and convenient use
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] Example 1 A method for removing flesh from bone specimens
[0044] A method for removing flesh from a bone specimen, comprising the following steps:
[0045] (1) Use a scalpel to remove 85% to 90% of the soft tissue of the dead animal, keep the bone part, and then divide it into limbs, skull, thorax, lumbar spine and hip bone parts through the bones, and pack them in mesh bags;
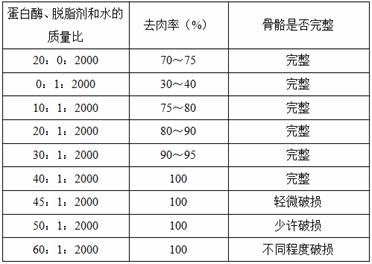
[0046] (2) Prepare the solution: Prepare the solution according to the mass ratio of Novozymes protease: fur degreasing agent: water = 40:1:2000; put the solution in a constant temperature water bath at 60°C for 4 hours until the solution temperature is constant; among them, The concentration of Novozymes protease is 2%, and the concentration of fur degreasing agent is 0.05%;
[0047] (3) Put the encapsulated bone in step (1) into the above solution so that the solution just submerges the bone. It should be noted that the skull is relatively thin and does not take too long, so the skull is pla...
Embodiment 2
[0049] Example 2 A method for removing flesh from bone specimens
[0050] A method for removing flesh from a bone specimen, comprising the following steps:
[0051] (1) Use a scalpel to remove 85% to 90% of the soft tissue of the dead animal, keep the bone part, and then divide it into limbs, skull, thorax, lumbar spine and hip bone parts through the bones, and pack them in mesh bags;
[0052] (2) Prepare the solution: Prepare the solution according to the mass ratio of alkaline protease: alkaline degreasing agent: water = 30:1:2050; put the solution in a constant temperature water bath at 55°C for 5 hours until the solution temperature is constant; among them, The concentration of alkaline protease is 1.5%, and the concentration of alkaline degreasing agent is 0.1%; Alkaline protease and alkaline degreasing agent are commercially available;
[0053] (3) Put the encapsulated bone in step (1) into the above solution so that the solution just submerges the bone. It should be no...
Embodiment 3
[0055] Example 3 A method for removing flesh from bone specimens
[0056] A method for removing flesh from a bone specimen, comprising the following steps:
[0057] (1) Use a scalpel to remove 85% to 90% of the soft tissue of the dead animal, keep the bone part, and then divide it into limbs, skull, thorax, lumbar spine and hip bone parts through the bones, and pack them in mesh bags;
[0058] (2) Prepare the solution: Prepare the solution according to the mass ratio of neutral protease: solvent degreasing agent: water = 45:2:2000; put the solution in a constant temperature water bath at 60°C for 5 hours until the solution temperature is constant; among them, The concentration of neutral protease is 2.5%, and the concentration of solvent degreasing agent is 0.08%; Neutral protease and solvent degreasing agent are commercially available;
[0059] (3) Put the encapsulated bone in step (1) into the above solution so that the solution just submerges the bone. It should be noted t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com