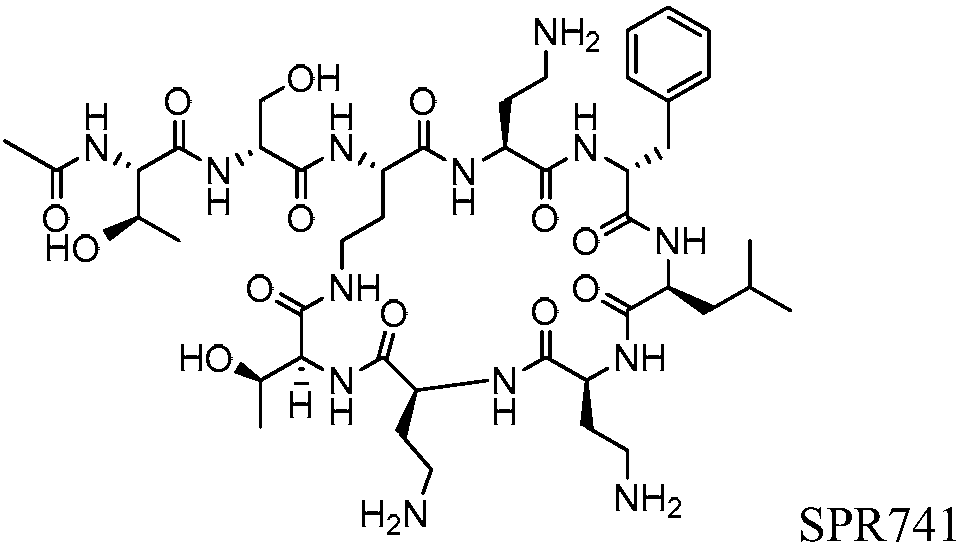
Potentiation of antibiotic activity by a novel cationic peptide, spr741
An antibiotic, effective dose technology, applied in the direction of organic active ingredients, resistance to vector-borne diseases, medical preparations containing active ingredients, etc.
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0018] The present disclosure includes a method of treating a bacterial infection in a subject comprising administering to the subject a therapeutically effective amount of SPR741 in combination with an antibiotic selected from the group consisting of retapalene, telithromycin, aztreonam, and combinations thereof.
[0019] In certain embodiments, the bacterial infection is an E. coli infection, a Klebsiella pneumoniae infection, or an Acinetobacter baumannii infection.
[0020] The present disclosure includes the following embodiments, in which:
[0021] (1) The antibiotic is retapalene.
[0022] (2) The antibiotic is telithromycin.
[0023] (3) The antibiotic is aztreonam.
[0024] (4) The subject is a mammal.
[0025] (5) The subject is a human patient.
[0026] (6) Retapalene is administered as a topical formulation containing SPR741 and less than 1 mg of retapalene per gram of formulation.
[0027] (7) Oral administration of telithromycin, 10 mg to 300 mg, or 10 mg to...
Embodiment 1
[0035] Example 1. Efficacy Evaluation of Combinations of SPR741 and Certain Antibiotics
[0036] SPR741 and azithromycin (AZ), aztreonam (AZT), clarithromycin (CLR), fusidic acid (FA), meropenem (MEM), mupirocin (MUP), rifampicin (RIF) and The efficacy of the combination of retapalene (RET) was assessed using a susceptibility testing method based on CLSI guideline M7-A10. Test against 25 Escherichia coli (Ec), 25 Klebsiella pneumoniae (Kp) and 17 Baumannii Acinetobacter (Ab) MDR and clinical isolates were performed. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) is defined as the lowest concentration of antibiotic required to inhibit visible bacterial growth. MIC values were determined for each antibiotic / SPR741 combination and the greatest reduction in MIC of the antibiotic in the combination was determined.
[0037] Combination with SPR741 resulted in potentiation of test antibiotics against isolates of Ab, Ec and Kp. For Ab, synergy follows the order FA>RIF>CLR>RET>MEM>AZ...
Embodiment 2
[0038] Example 2. Evaluation of the efficacy of SPR741 in combination with certain antibiotics in a checkerboard assay
[0039] Evaluate power in a checkerboard test. The minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) of SPR741, antibiotics and their combination was defined as the lowest concentration that inhibited the growth of Ec ATCC 25922, Ab NCTC 12156 and Kp ATCC 43816. Ec BW25113, ΔtolC and ΔacrA were used to evaluate the contribution of the multi-drug efflux pump AcrAB-TolC to the drug susceptibility of the combination. For each combination in which the MIC differs from the compounds in the isolate, the interaction is assessed by calculating the Fractional Inhibitory Concentration Index (FICI). Interactions were defined as: FICI >4, antagonism; 0.5 to 4, no interaction; <0.5, synergy. The minimum bactericidal concentration of each combination in the presence of 5% surfactant (Survanta) was also determined.
[0040] Of the 22 antibiotics tested, 7 antibiotics, azithromycin, c...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com