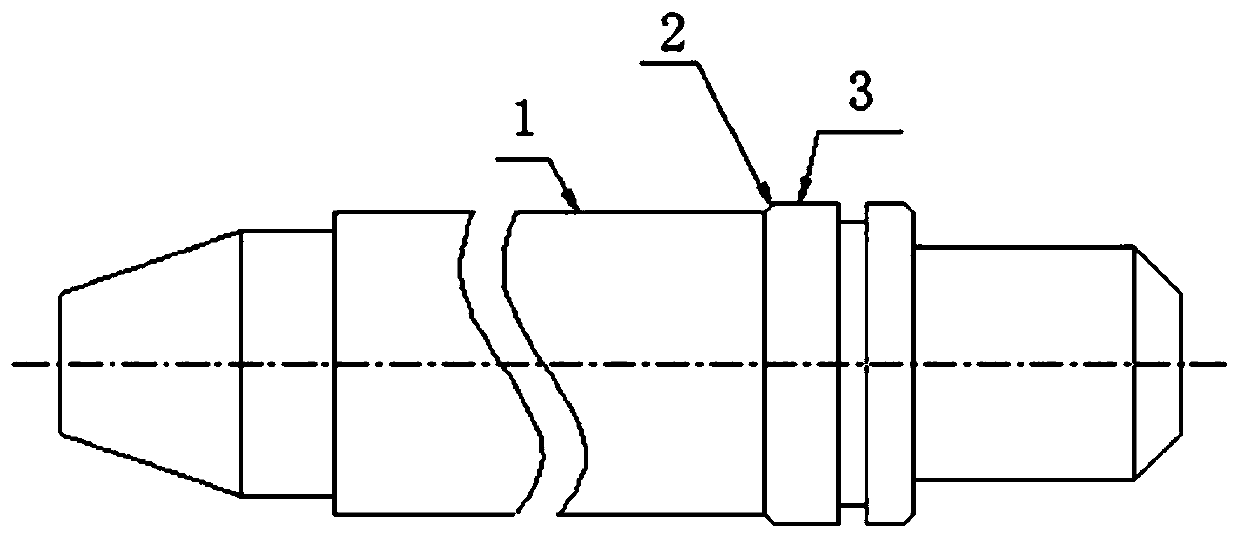
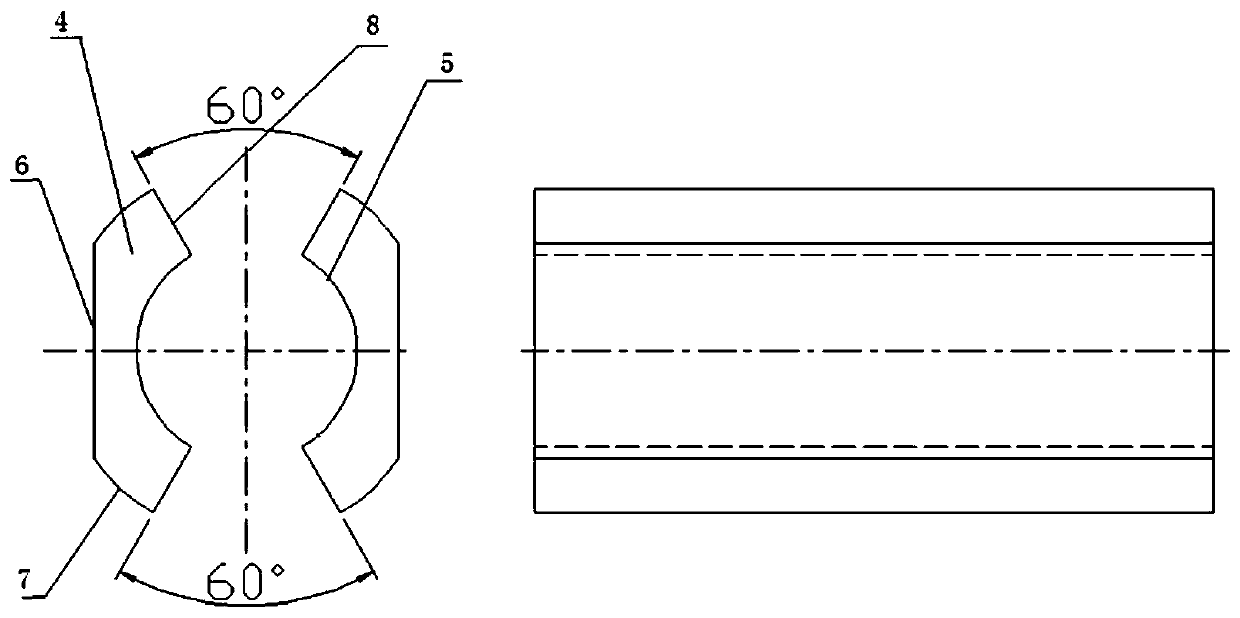
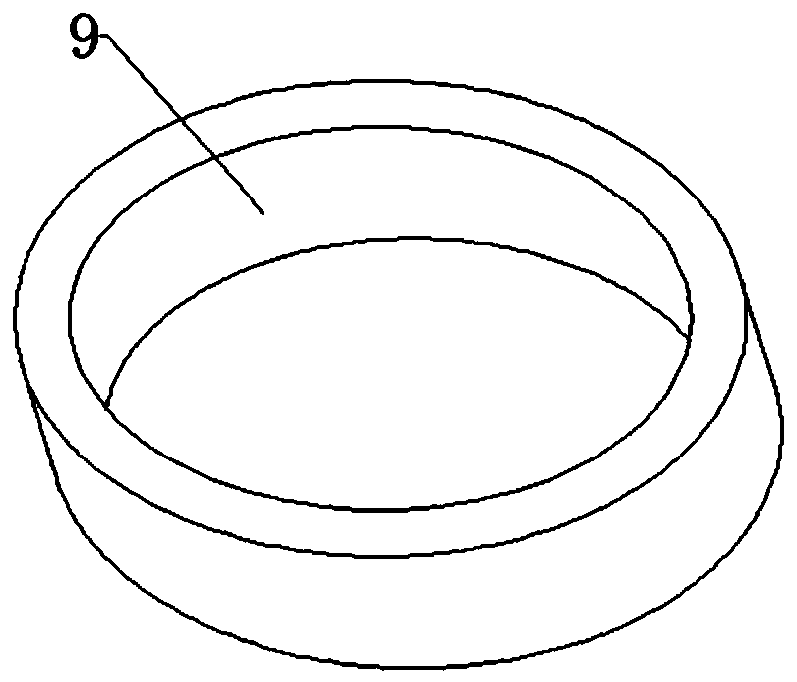
A fuel injector disassembly tool and its preparation material
A technology for dismantling tooling and fuel injection nozzles, applied in the field of metal materials, can solve problems such as impracticality and scratches on guide parts, and achieve the effects of ensuring integrity, increasing clamping area, and refining grains
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0040] A metal composite material for preparing fuel injector disassembly tooling, comprising outer layer copper alloy powder, middle layer hard iron alloy powder and inner layer copper alloy powder, which are formed by pressing and sintering under vacuum pressure; the outer layer and inner layer of copper The alloy powder is composed of 75% copper, 10% tungsten carbide, 1% cobalt and 4% nickel, 5% silicon dioxide, 3% iron tetroxide, and 2% graphene; the middle layer of hard iron alloy powder is made of 85 % iron, 2% manganese and 3% nickel, 3% titanium carbide, 2% carbon, 3% aluminum oxide, 2% chromium.
[0041] A method for preparing a tooling material for removing a fuel injector, comprising the following steps:
[0042] a. Preparation of raw materials:
[0043] Copper alloy powder of the outer layer and the inner layer: According to the copper alloy powder formula of the outer layer and the inner layer, the raw material and ethanol are put into the stirring ball mill acco...
Embodiment 2
[0051] A metal composite material for disassembling tooling for fuel injectors, comprising an outer layer of copper alloy powder, a middle layer of hard iron alloy powder, and an inner layer of copper alloy powder that are formed by pressing and sintering under vacuum pressure; the copper alloy of the outer layer and the inner layer The powder is composed of 79% copper, 8% tungsten carbide, 2% cobalt and 3% nickel, 4% silicon dioxide, 3% iron tetroxide, and 1% graphene; the middle layer of hard iron alloy powder is composed of 80% Iron, 6% manganese and 2% nickel, 3% titanium carbide, 4% carbon, 3% aluminum oxide, 2% chromium.
[0052] A method for preparing a tooling material for removing a fuel injector, comprising the following steps:
[0053] a. Preparation of raw materials:
[0054] Copper alloy powder of the outer layer and the inner layer: according to the copper alloy powder formula of the outer layer and the inner layer, the raw material and ethanol are put into the st...
Embodiment 3
[0062] A metal composite material for disassembling tooling for fuel injectors, comprising an outer layer of copper alloy powder, a middle layer of hard iron alloy powder, and an inner layer of copper alloy powder that are formed by pressing and sintering under vacuum pressure; the copper alloy of the outer layer and the inner layer The powder is composed of 80% copper, 10% tungsten carbide, 0.5% cobalt and 2.5% nickel, 2% silicon dioxide, 3% iron tetroxide, and 2% graphene; the middle layer of hard iron alloy powder is composed of 83% Iron, manganese and 3% nickel, 3% titanium carbide, 3% carbon, 3% aluminum oxide, 2% chromium.
[0063] A method for preparing a tooling material for removing a fuel injector, comprising the following steps:
[0064] a. Preparation of raw materials:
[0065] The copper alloy powder of the outer layer and the inner layer: According to the copper alloy powder formula of the outer layer and the inner layer, put the raw material and ethanol in the ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com