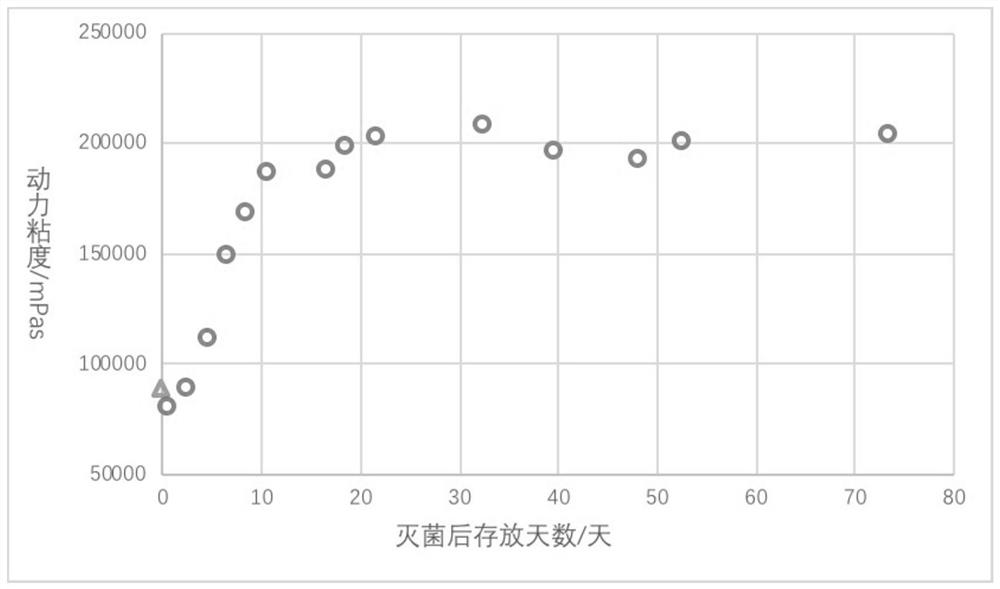
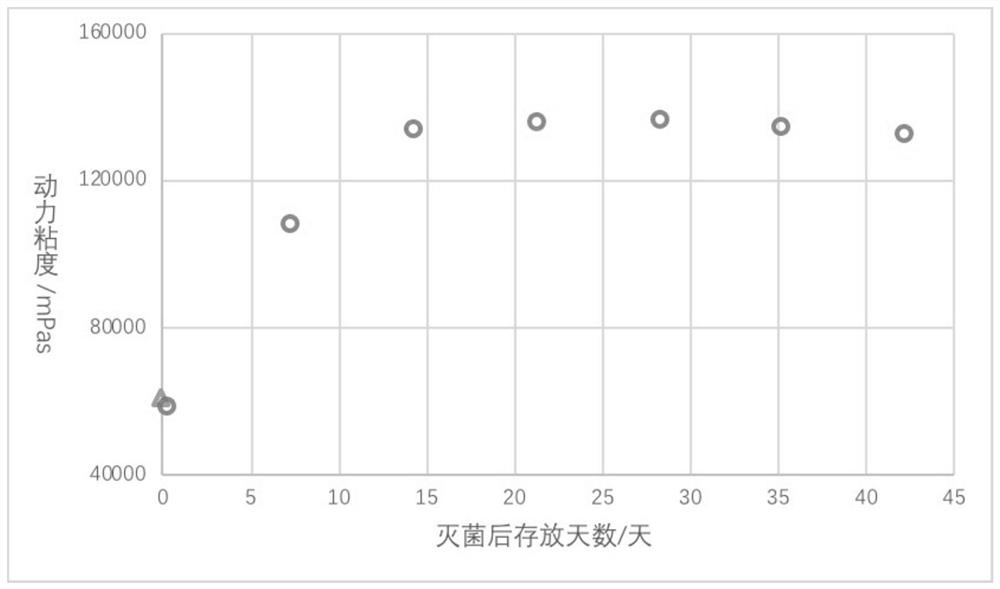
Preparation of a class of injectable hydrogels with cohesion-enhancing properties
A technology for injecting water and properties, which is applied in the field of medical biomaterials and can solve problems such as gel cohesion enhancement
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0043] This example describes the preparation of hyaluronic acid-chitosan cohesion-enhanced injectable hydrogels.
[0044]Weigh 0.8 g of chitosan oligosaccharide and dissolve it in 100 g of 1.8% NaCl solution, then add 2 g of sodium hyaluronate and stir at low temperature (2-8° C.) for 12 hours to mix well. Then 1M HCl solution was added dropwise to adjust the pH of the system to 4.5-6, and 0.48g EDC and 0.29g NHS were added in sequence. After stirring for 1 hour at 2 to 8°C, the reaction was allowed to stand for 7 hours. Then 300g of 0.1M NaOH solution was added for alkalization, and the mixture was stirred at 2-8°C for 18 hours, and then sedimented with 1200mL of ethanol. The obtained powder was thoroughly washed with 800 mL of ethanol, and the washing step was repeated 3 times. Then drain the ethanol in the powder, reconstitute the powder with 100 g PBS, and stir well. The reconstituted homogeneous system was placed in a dialysis bag (MWCO=16000) and placed in 1000 g PBS...
Embodiment 2
[0046] This example describes the preparation of sodium alginate-chitosan cohesion-enhanced injectable hydrogels.
[0047] Weigh 2.8g of chitosan oligosaccharide and dissolve it in 100g of 0.1M PBS solution, then add 3g of sodium alginate and stir at room temperature for 24 hours to fully dissolve and mix. Then, 1M HCl solution was added dropwise to adjust the pH of the system to 4.5-6, 0.73 g EDC and 0.44 g NHS were added in sequence, and the mixture was fully stirred and reacted at 2-8° C. for 24 hours. Next, 275 g of a 0.08 M KOH solution was added for alkalization, and after stirring at room temperature for 12 hours, sedimentation was carried out with 1500 mL of ethanol. The obtained powder was thoroughly washed with 500 mL of ethanol, and the washing step was repeated 3 times. It was then vacuum dried in a vacuum oven overnight. The obtained powder was reconstituted with 200 g of 0.9% NaCl solution, fully stirred and then dialyzed in a dialysis bag (MWCO=16000). The out...
Embodiment 3
[0049] This example describes the preparation of carboxymethylchitin-polyarginine cohesion-enhanced injectable hydrogels.
[0050] 3.3g of polyarginine was weighed and dissolved in 100g of 0.1M PBS solution, and then 3g of carboxymethyl chitin was added and stirred at room temperature for 6 hours to fully dissolve and mix. Then, 0.88 g of DMTMM was added, and the mixture was fully stirred and reacted at -20° C. for 120 hours. Then, 200 g of 0.08M NaOH solution was added for alkalization, and the mixture was stirred at room temperature for 4 hours, and then transferred to 2-8° C. for 12 hours. Settling was then performed with 1800 mL of ethanol. The obtained powder was thoroughly washed with 600 mL of ethanol, and the washing step was repeated 3 times. After the powder was drained, it was reconstituted with 150g PBS solution, fully stirred and then dialyzed in a dialysis bag (MWCO=16000), and the outer dialysate solution was 1200g PBS solution. Dialysis was performed at 2-8°...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com