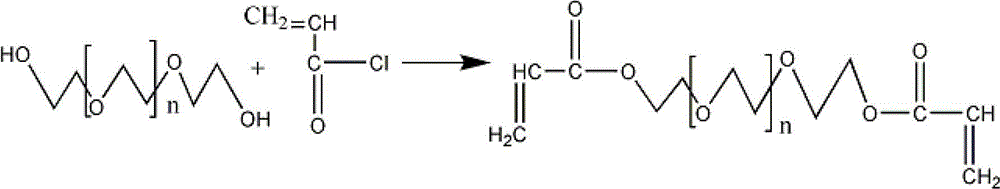
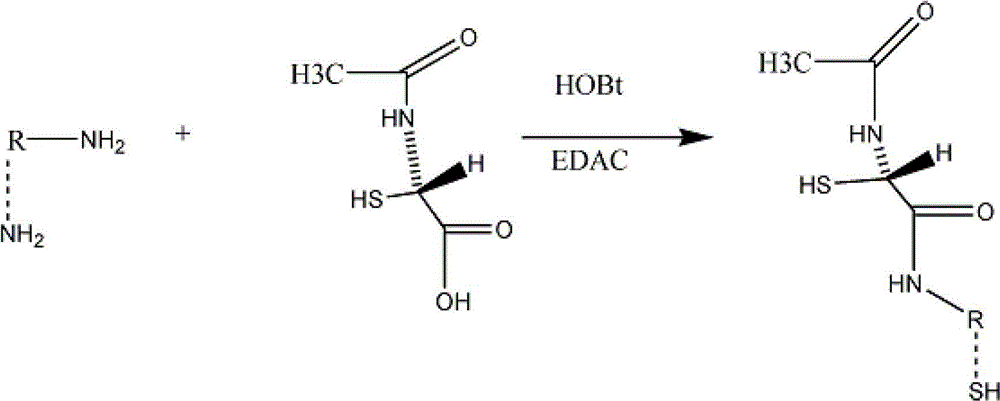
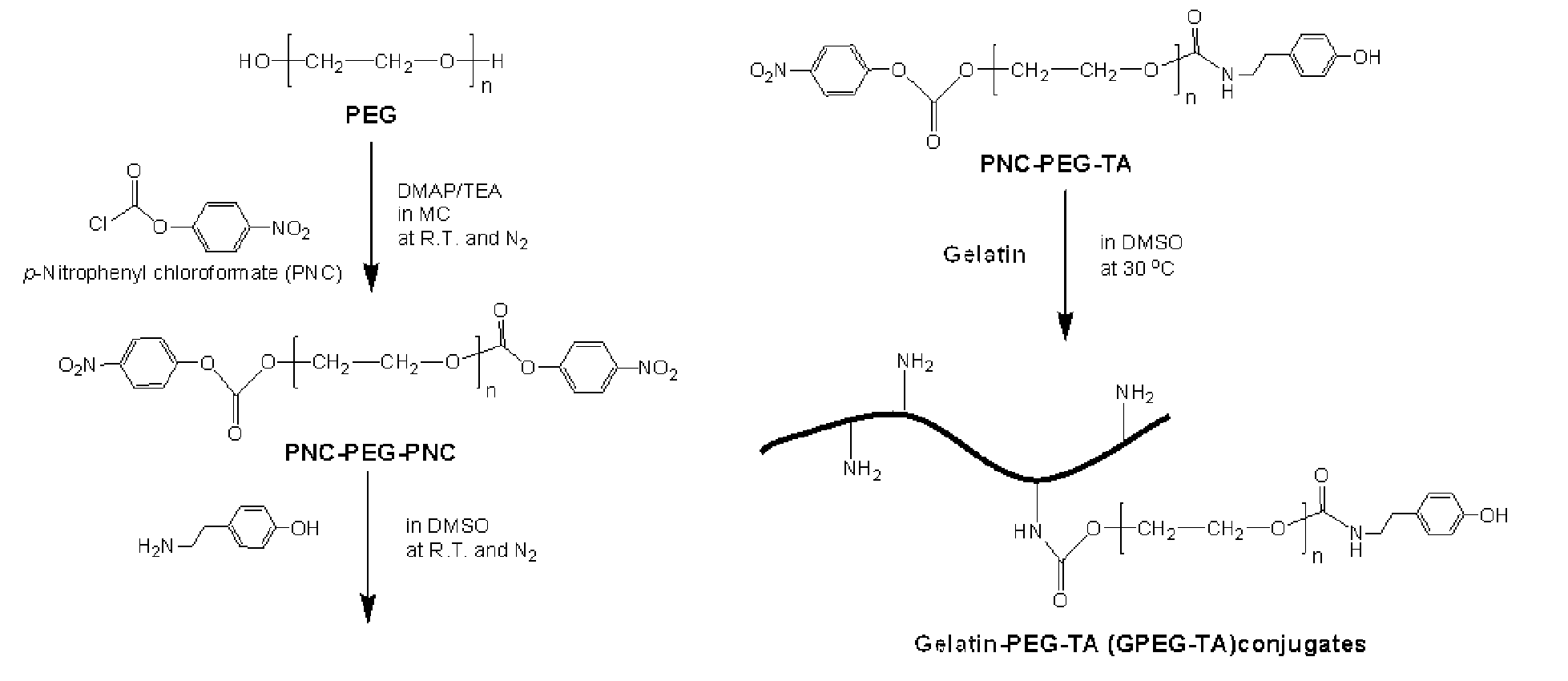
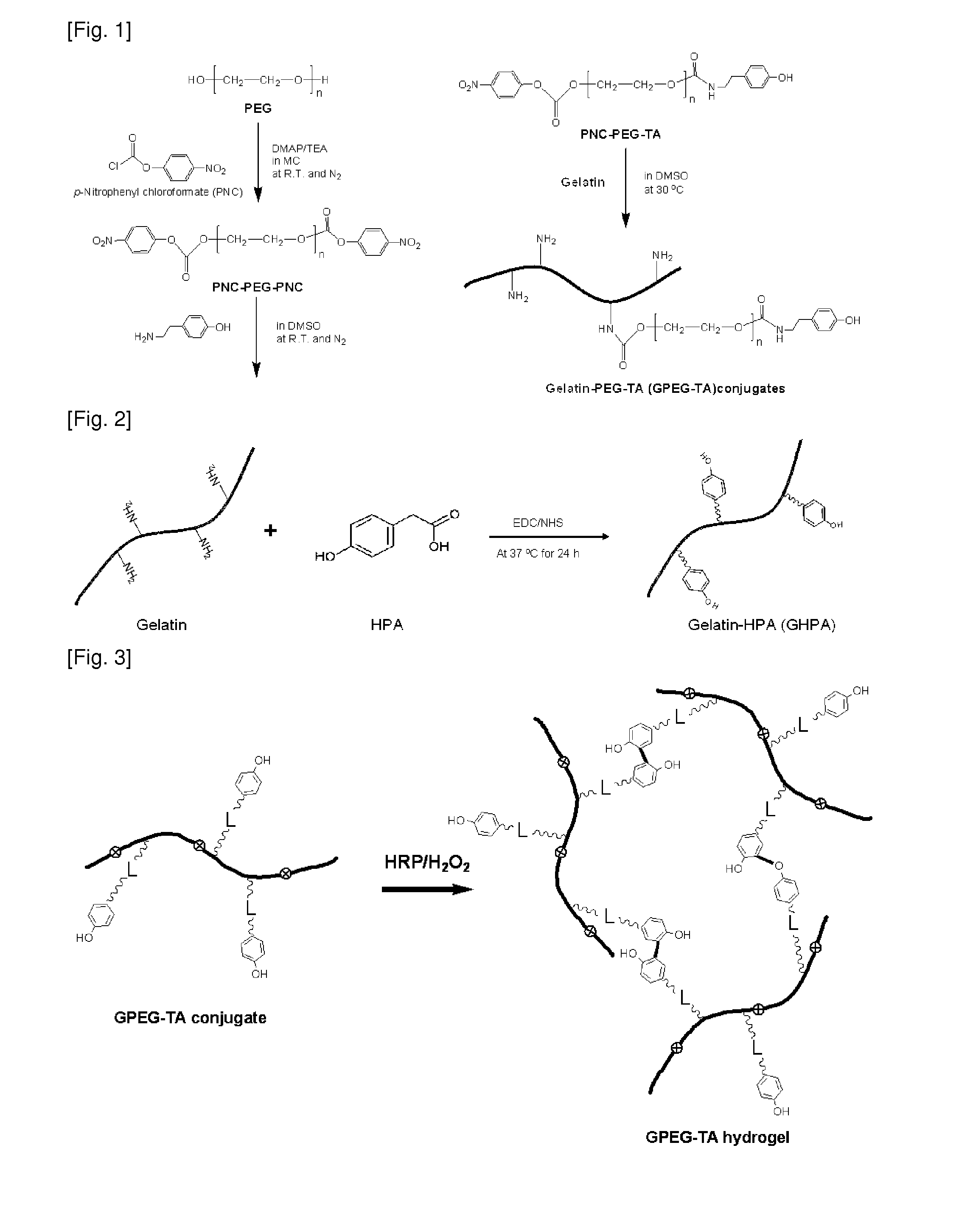
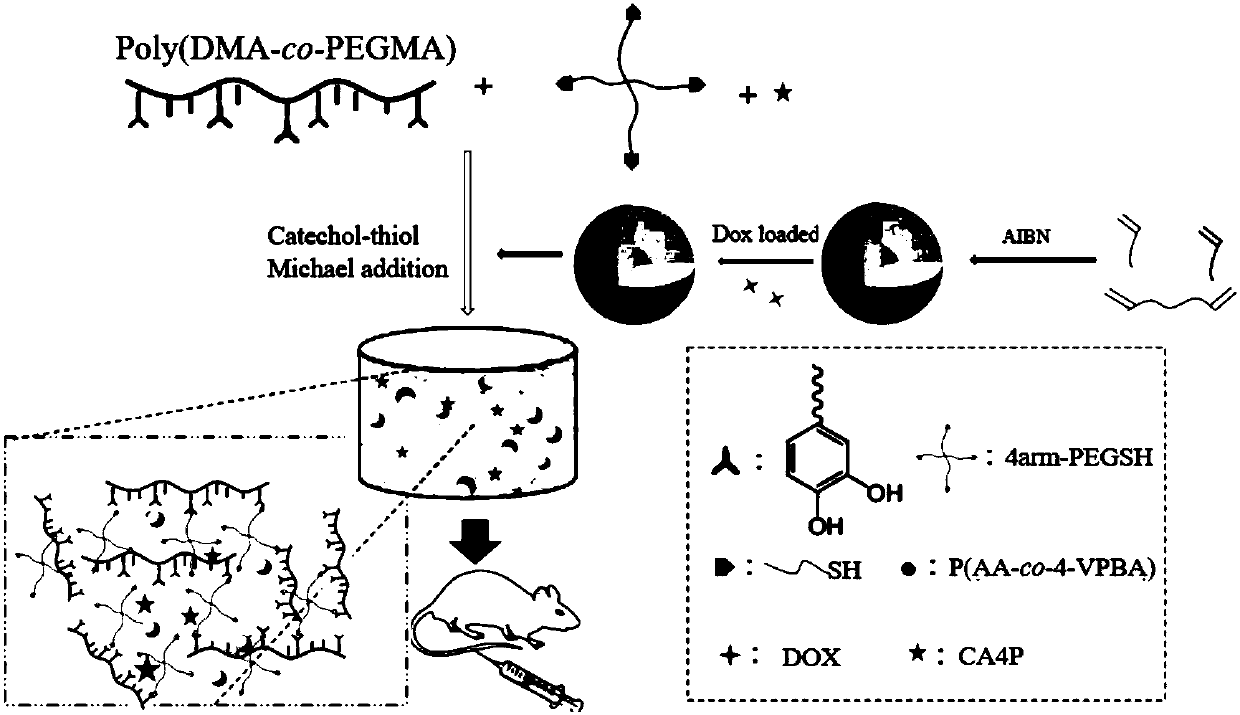
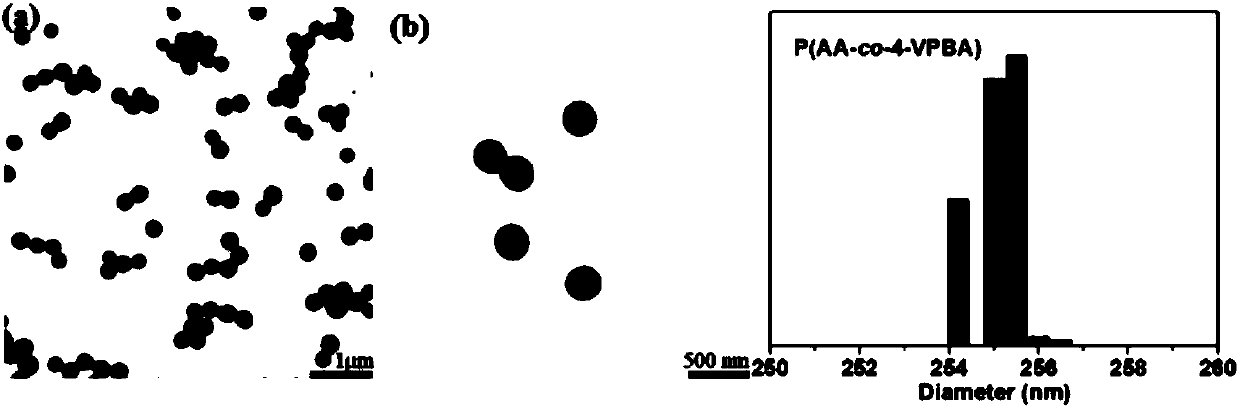
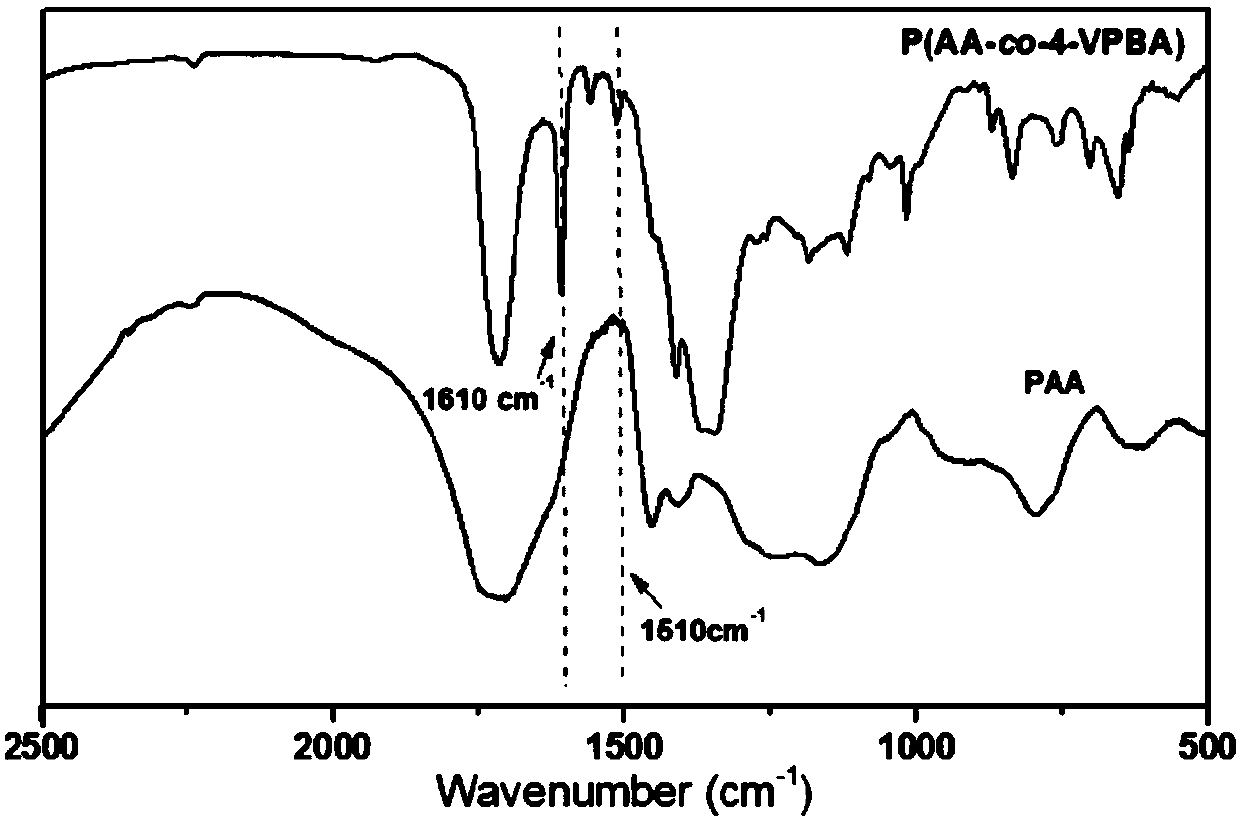
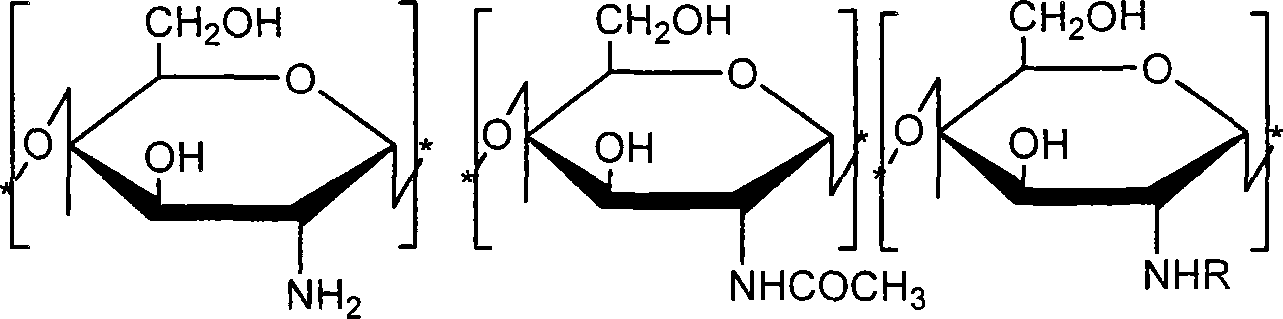
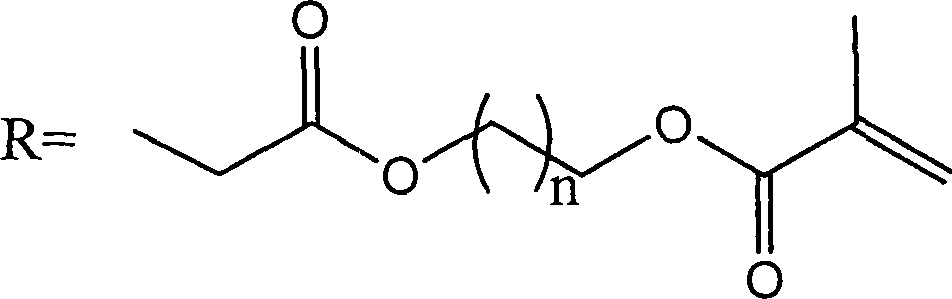
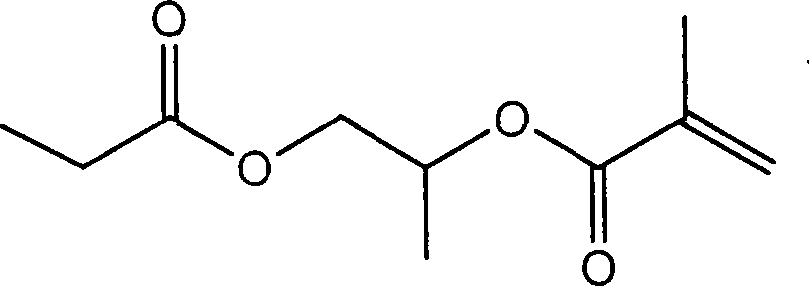
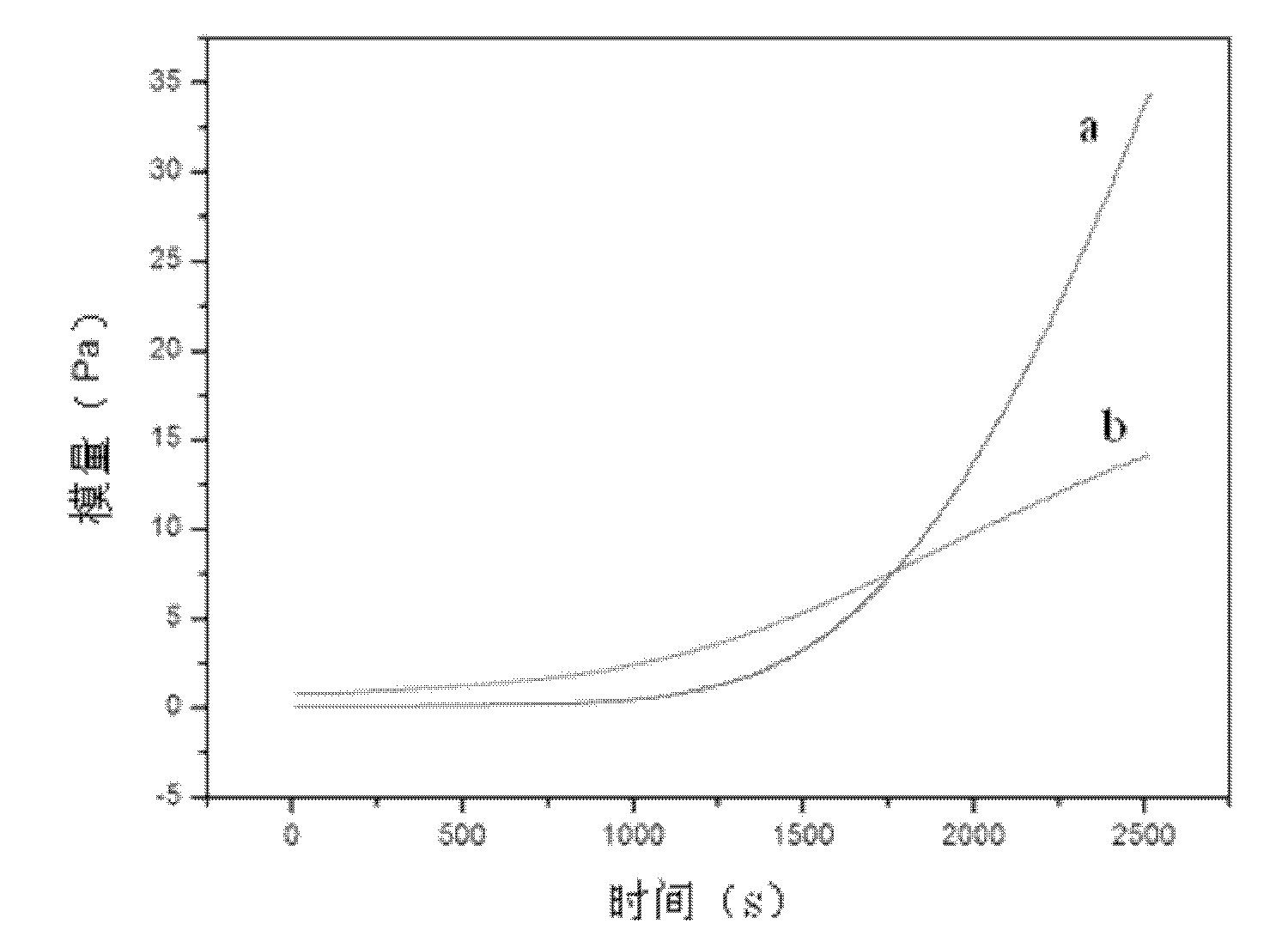
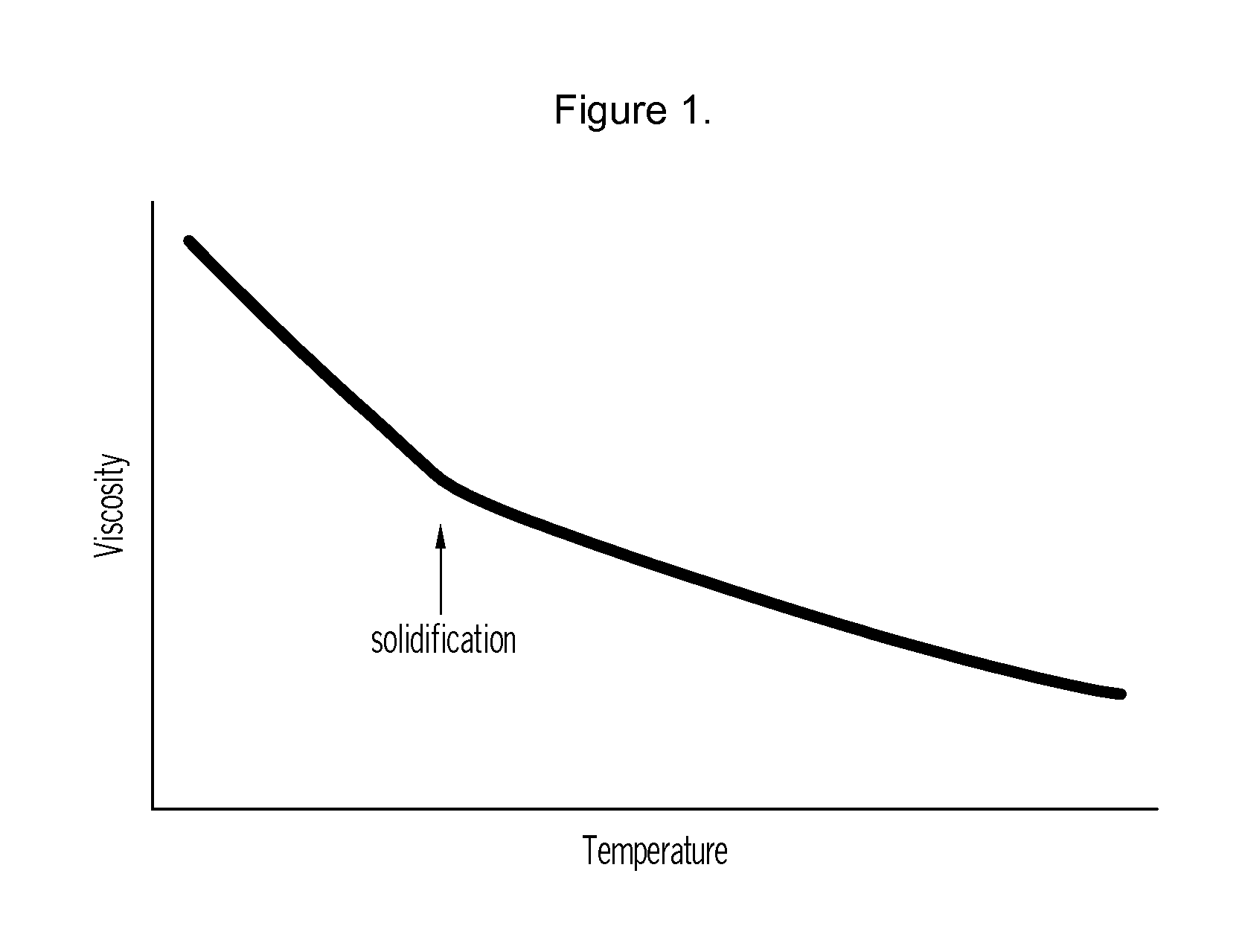
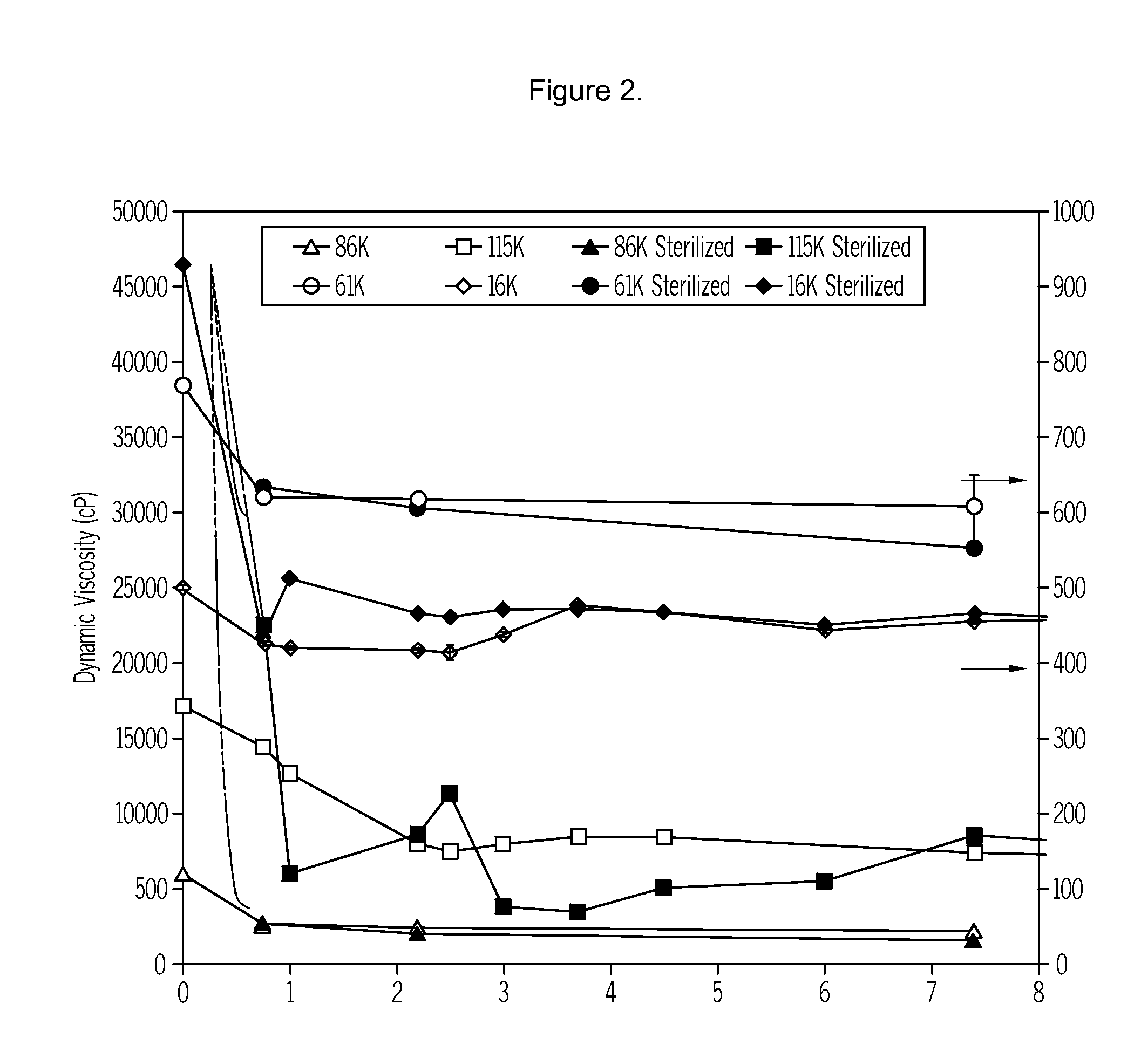
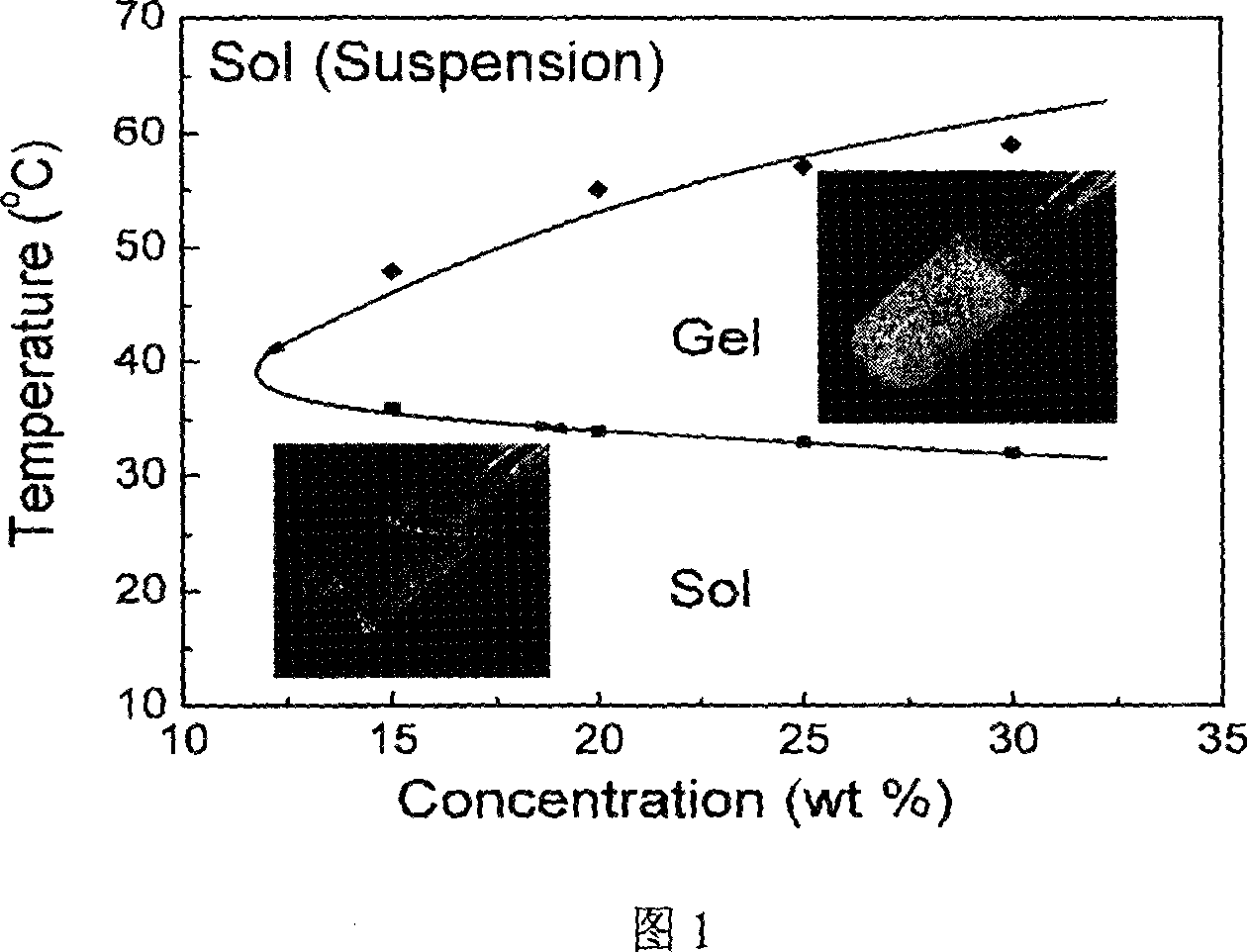
Patents
Literature
306 results about "Injectable hydrogels" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
Blends of temperature sensitive and anionic polymers for drug delivery
ActiveUS20060280797A1Faster rate of gellingDecrease gelling temperaturePowder deliveryOrganic active ingredientsRoom temperatureAnionic polymers
A physical blend of inverse thermal gelling and shear-thinning, thixotropic polymers that has a lower gelation temperature than the thermal gelling polymer alone is provided. The blend results in an injectable hydrogel that does not flow freely at room temperature, but is injectable due to its shear-thinning properties. The thermal-gelling properties of the polymer promote a more mechanically stable gel at body temperature than at room temperature. The polymer matrix gel has inherent therapeutic benefit and can also be used as a drug delivery vehicle for localized release of therapeutic agents.
Owner:SHOICHET MOLLY S +2
Preparation method of multiple cross-linked polysaccharide injectable hydrogel
InactiveCN104479150AGood biocompatibilityReduce usagePharmaceutical non-active ingredientsProsthesisPolymer scienceWater soluble chitosan
The invention discloses a preparation method of multiple cross-linked polysaccharide injectable hydrogel. Modified water-soluble chitosan with carboxyl or hydroxyl groups as a first component and a hydroformylation-modified polysaccharide polymer or polysaccharide polymer mixer as a second component produce electrostatic action with each other and undergo a Schiff-base reaction to produce the hydrogel with a multiple cross-linked net structure. The multiple cross-linked polysaccharide injectable hydrogel has gelling time of 5-200s and has good mechanical properties. Through change of a chitosan and polysaccharide modification rate, a mole ratio of two components and solid content of hydrogel, gelling time, mechanical strength, microscopic morphology and water content are adjusted and controlled. The gel network contains a large amount of amino, carboxyl and aldehyde groups as active groups, the active groups can be bonded to drugs and proteins by covalent bonds, the multiple cross-linked polysaccharide injectable hydrogel as a novel medical material with excellent biocompatibility has a good application prospect in the fields of regeneration medical science, tissue engineering and drug controlled release.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIV
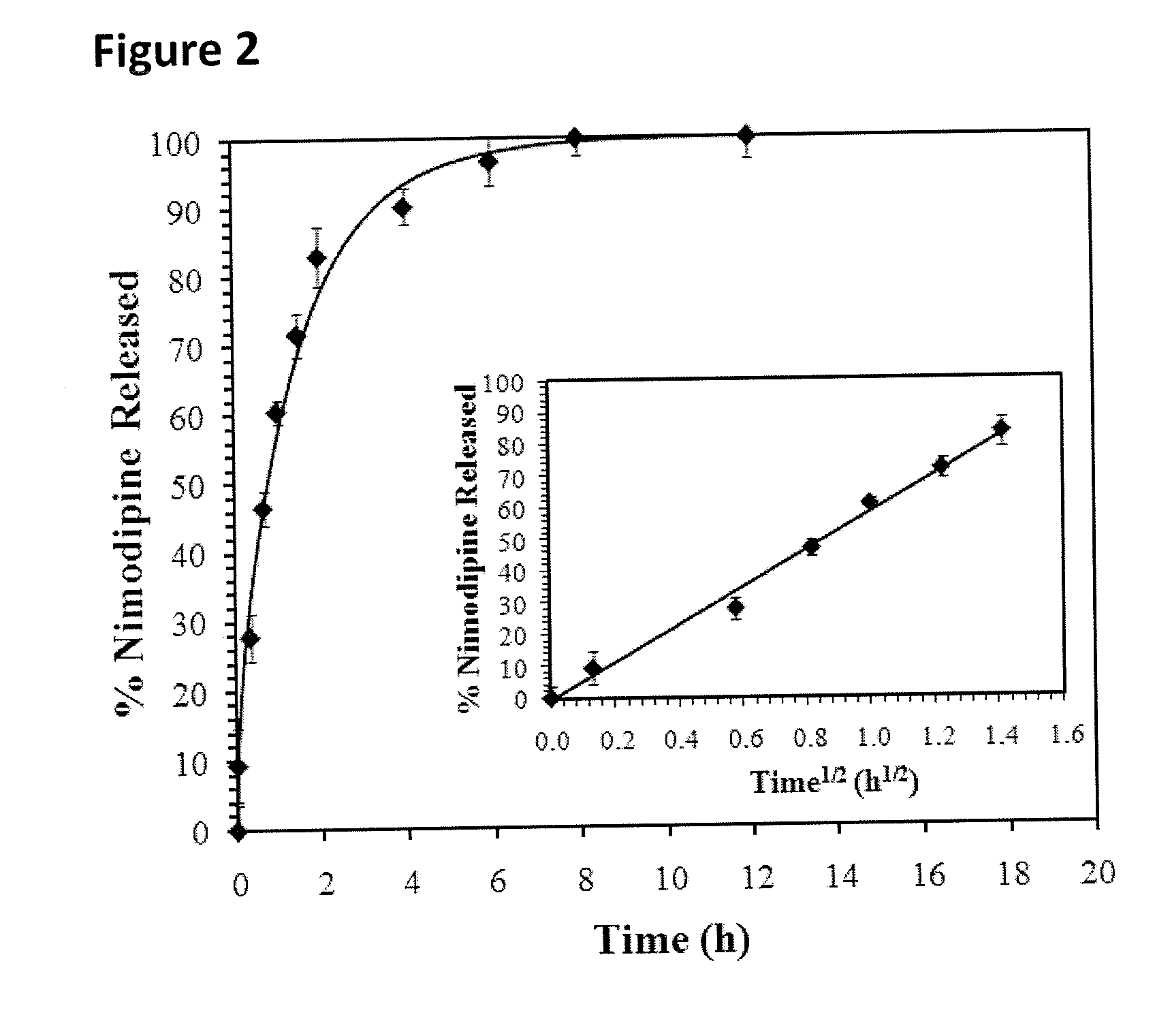
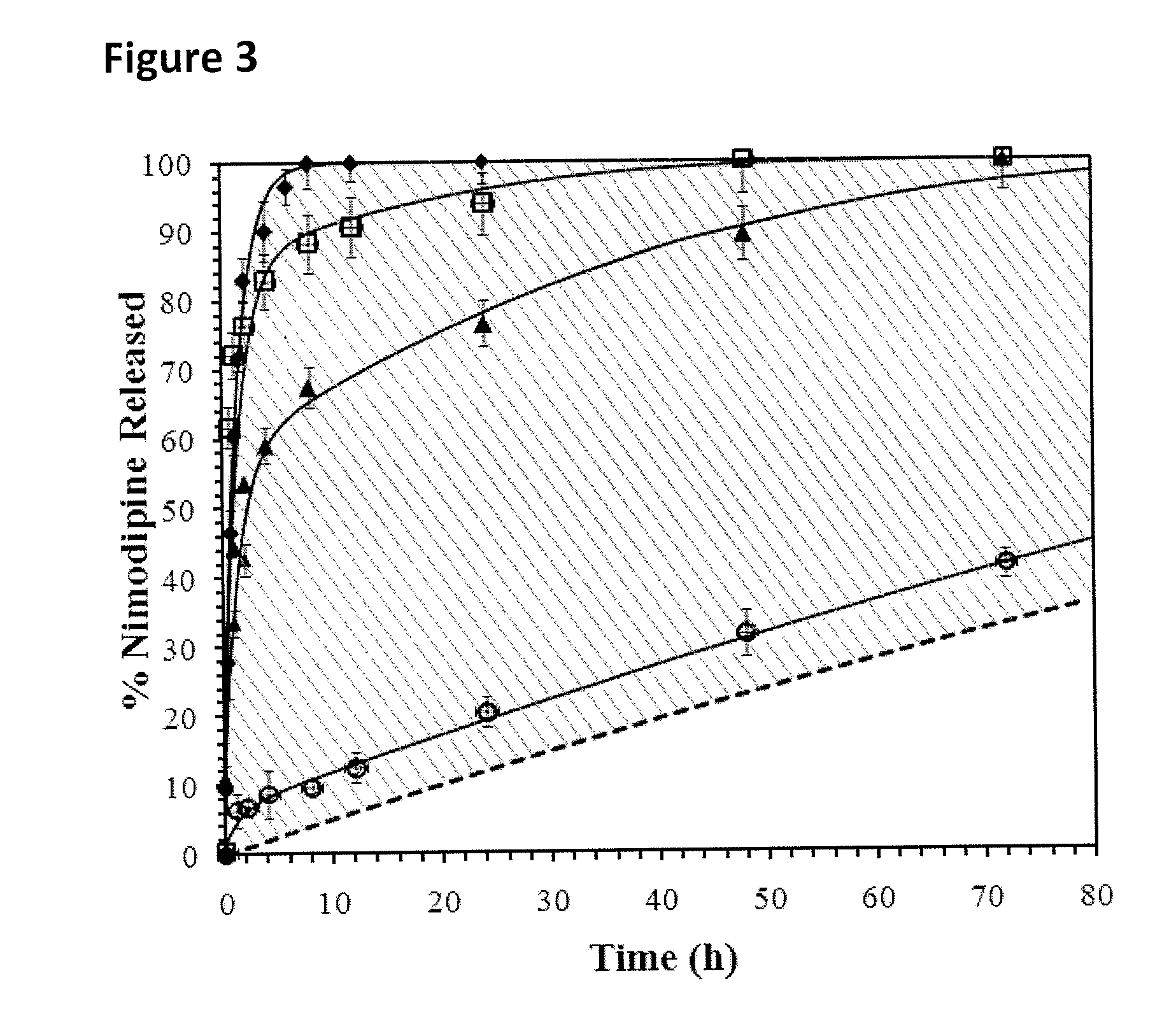
Tunable sustained release of a sparingly soluble hydrophobic therapeutic agent from a hydrogel matrix
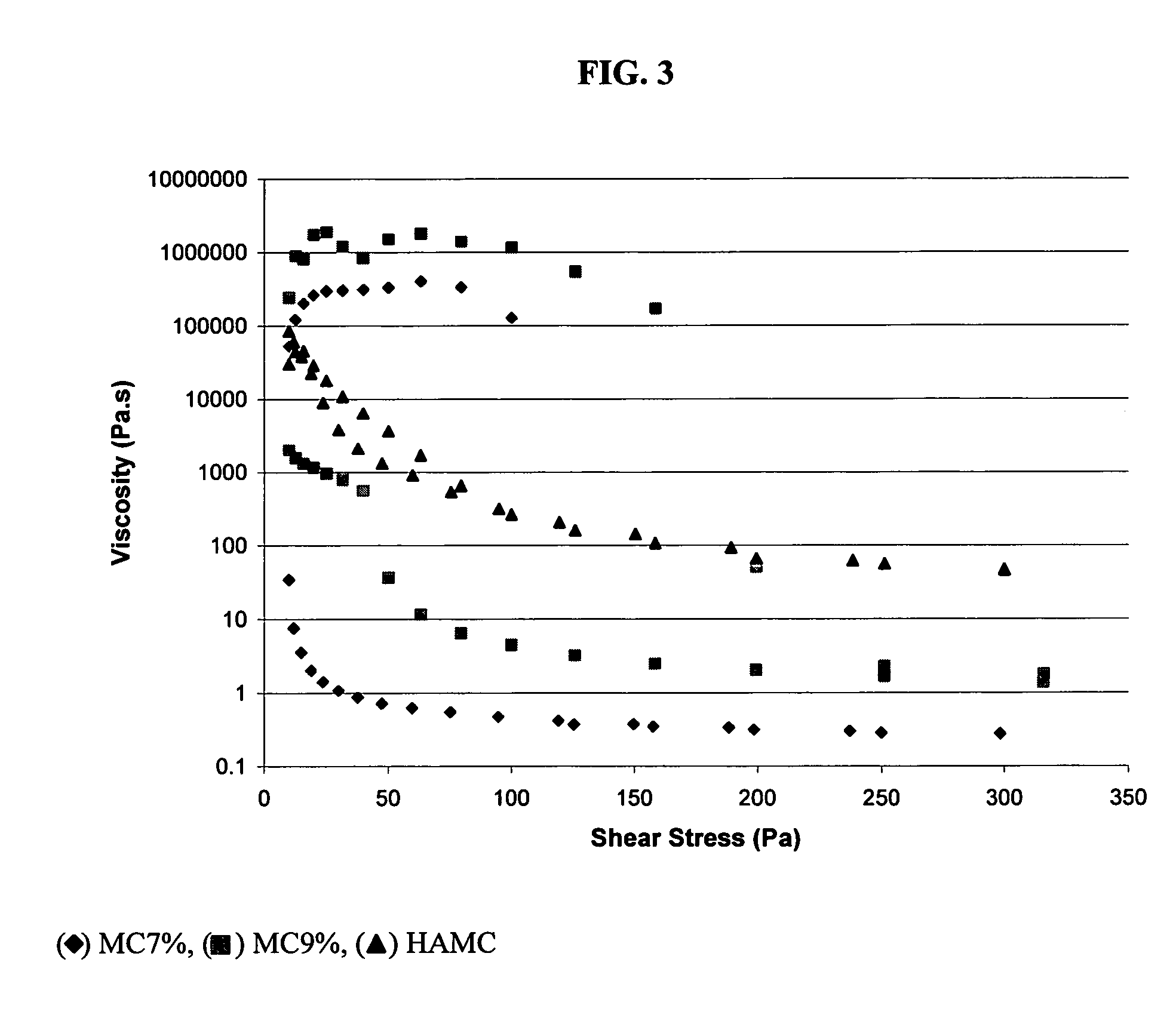
ActiveUS20100291191A1Improve solubilityGood effectAntibacterial agentsBiocideSolubilityMethyl cellulose
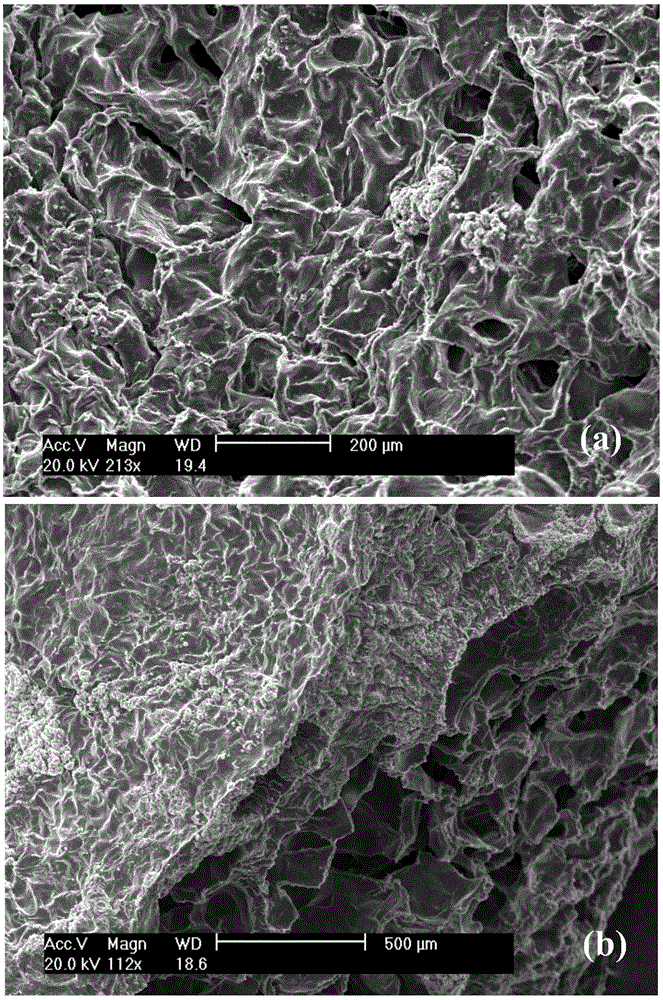
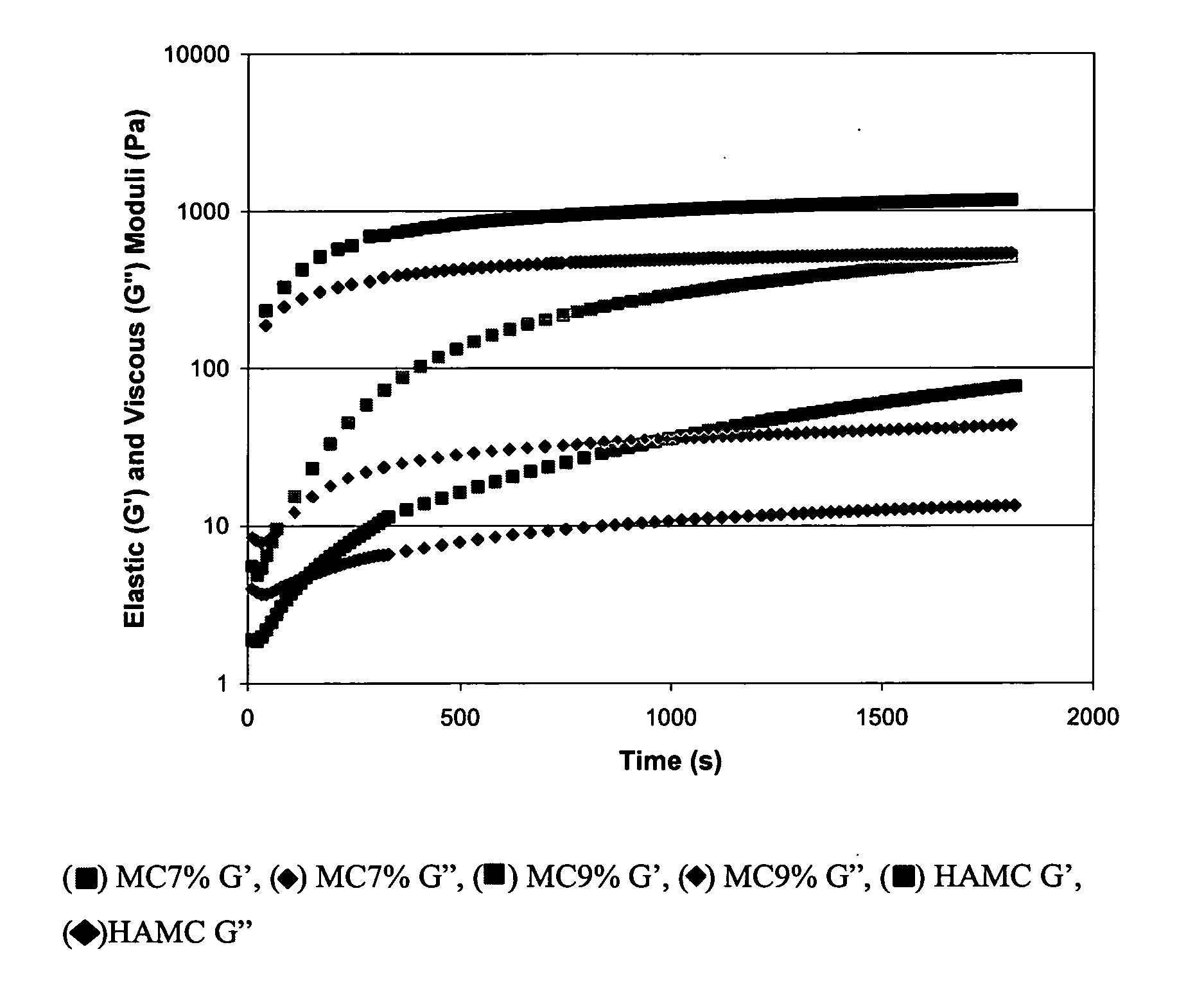
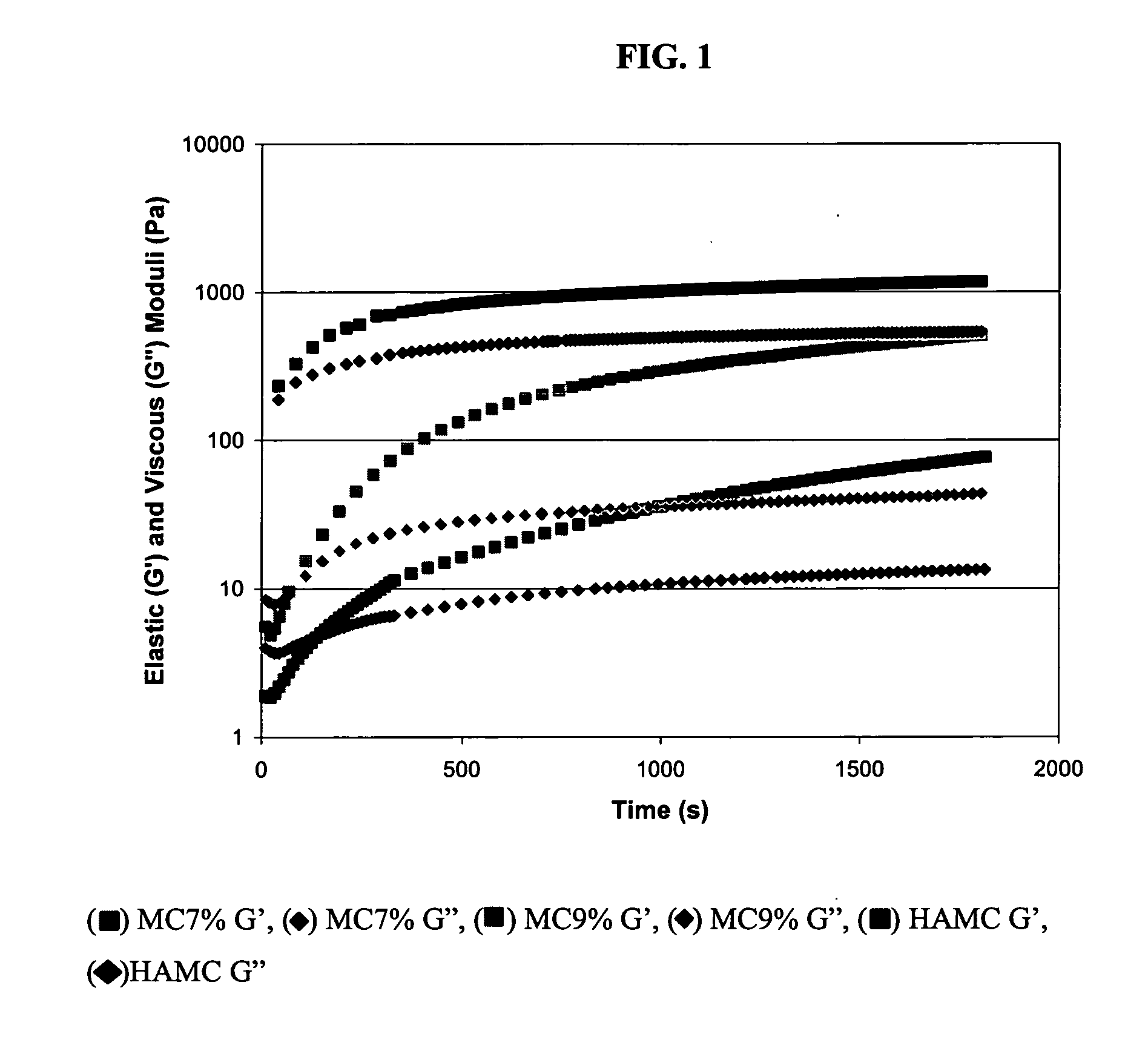
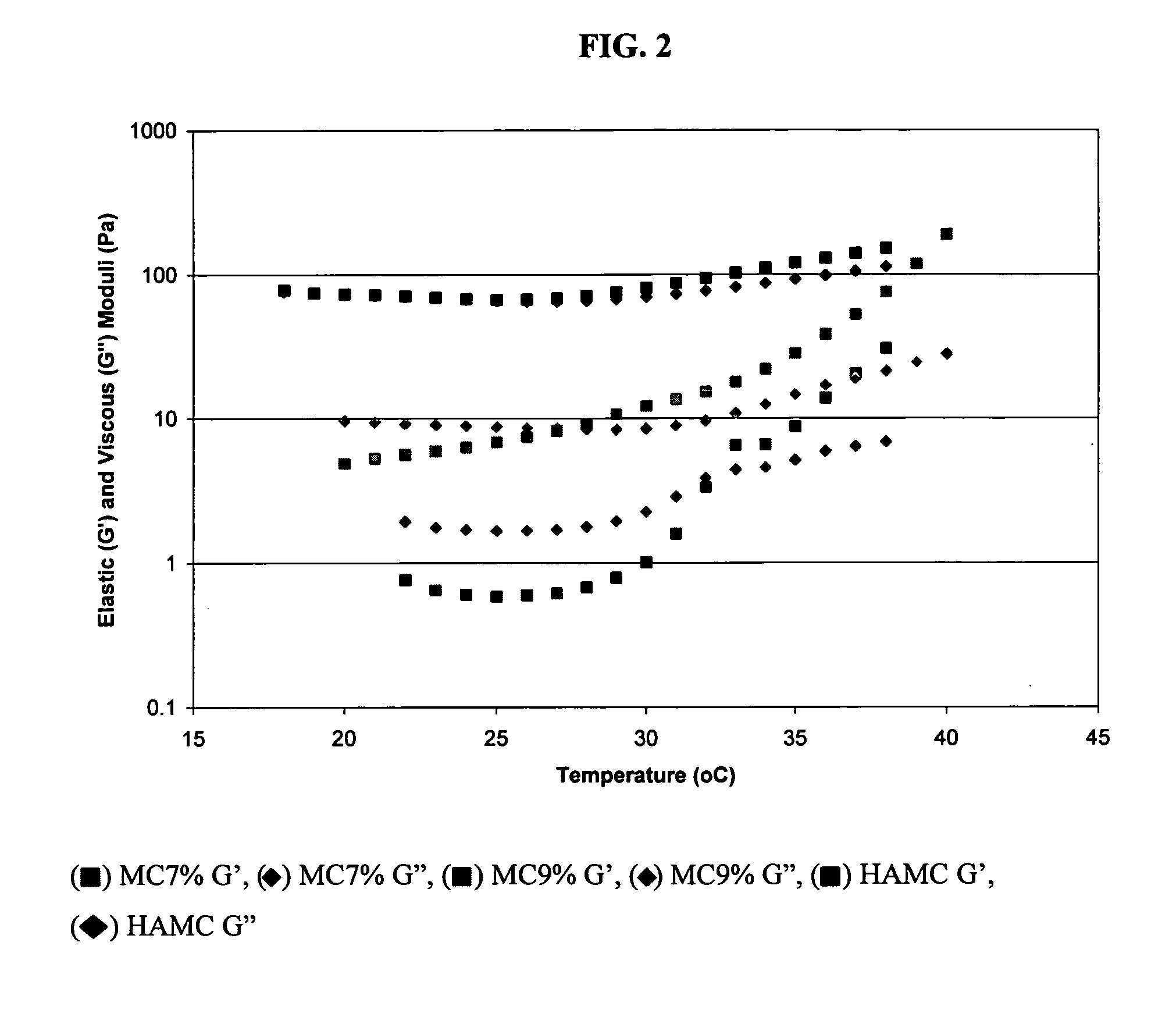
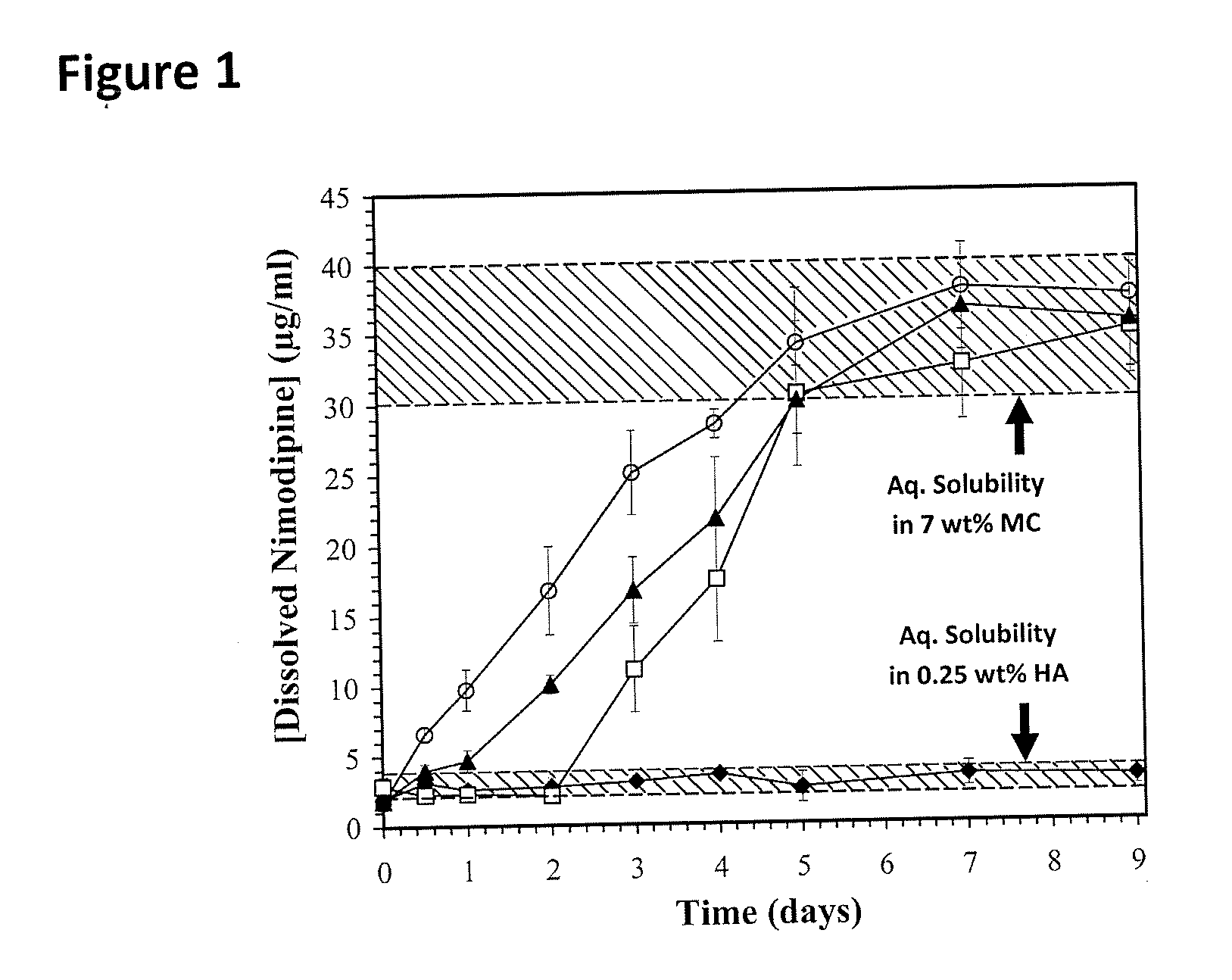
The incorporation of polymeric excipients into an injectable hydrogel matrix, for example, methyl cellulose in the case of a hydrogel matrix comprising hyaluronan and methylcellulose (HAMC) has been found to increase the solubility of sparingly soluble hydrophobic drugs and tune their rate of release. The hydrogel matrix may also include other sparingly soluble hydrophobic food or cosmetic agents.
Owner:THE GOVERNINIG COUNCIL OF THE UNIV OF TORANTO
Blends of temperature sensitive and anionic polymers for drug delivery
A physical blend of inverse thermal gelling and shear-thinning, thixotropic polymers that has a lower gelation temperature than the thermal gelling polymer alone is provided. The blend results in an injectable hydrogel that does not flow freely at room temperature, but is injectable due to its shear-thinning properties. The thermal-gelling properties of the polymer promote a more mechanically stable gel at body temperature than at room temperature. The polymer matrix gel has inherent therapeutic benefit and can also be used as a drug delivery vehicle for localized release of therapeutic agents.
Owner:SHOICHET MOLLY S +2
Anti-cross-linking agents and methods for inhibiting cross-linking of injectable hydrogel formulations
InactiveUS20070275030A1Easy injectionPowder deliveryTransportation and packagingCross-linkCross linker
The invention relates to cross-link-resistant injectable hydrogel formulations and methods of partially or practically wholly inhibiting injectable hydrogel formulations from cross-linking, for example, during irradiation, using anti-cross-linking agents, which facilitates injectability of the hydrogel formulation. The invention also relates to methods of making the cross-link-resistant, for example, irradiation cross-link resistant, injectable hydrogel formulations, and methods of administering the same in treating a subject in need.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Injectable dendrimer hydrogel nanoparticles
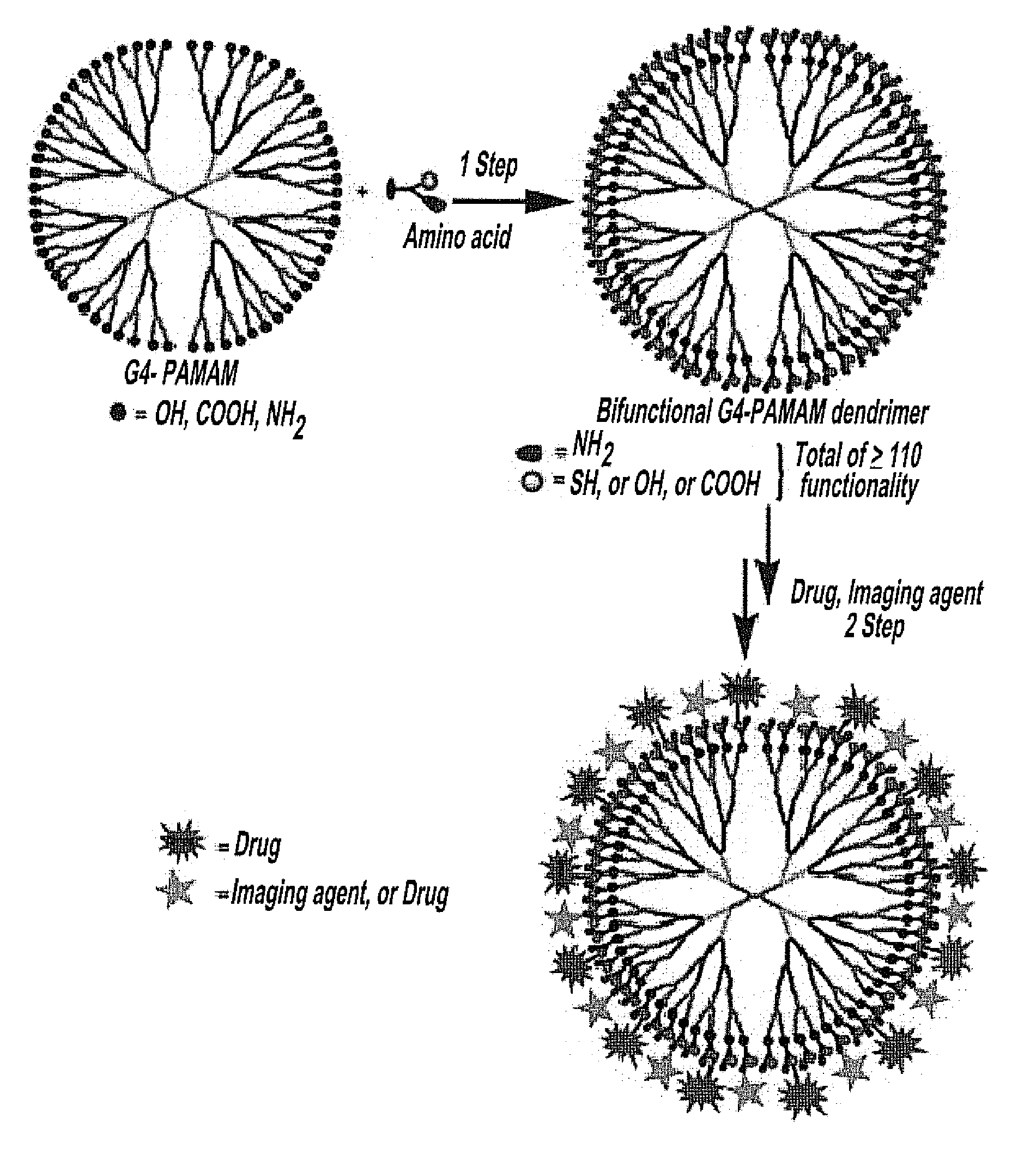
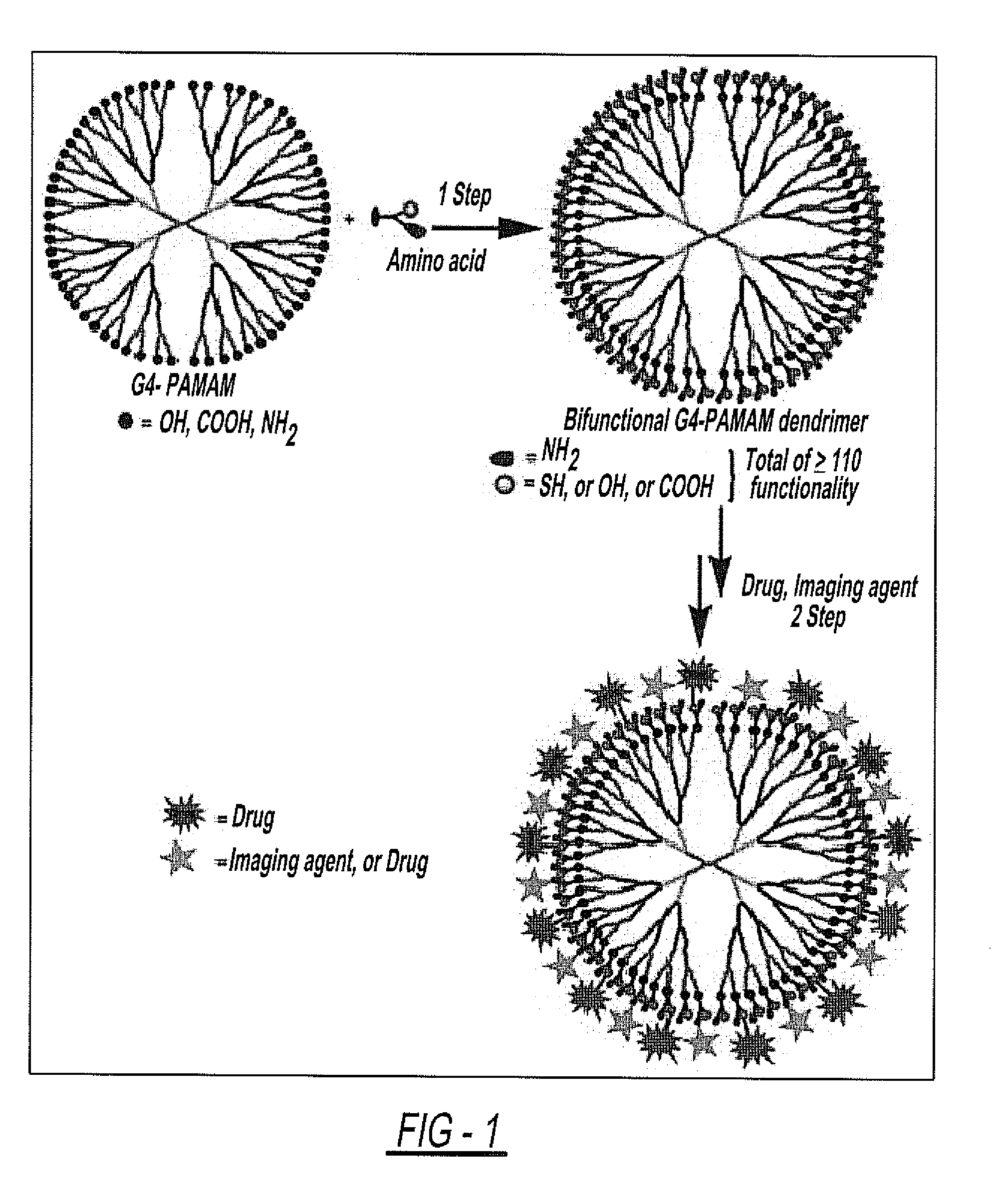
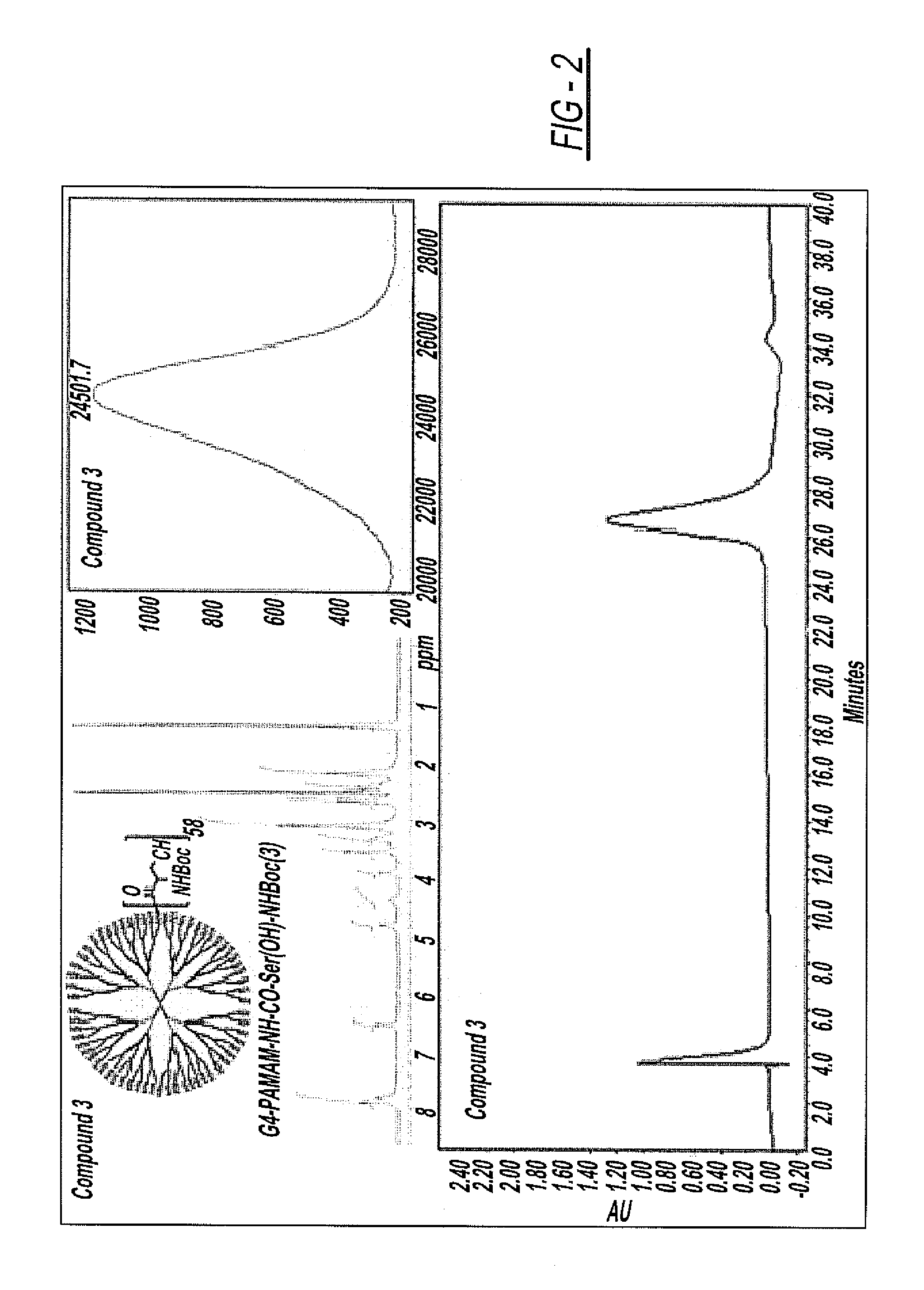
The invention discloses injectable hydrogels which are in the form of crosslinked nano beads or particle in the size range 5 nm to 10 μm, comprising PAMAM dendrimer with asymmetrical peripheral end groups such that one of the terminal groups is involved in formation of hydrogel and the other in involved in the conjugation of drugs or imaging agents and their methods of preparation. The said gel is formed by reaction of the PAMAM dendrimer with asymmetrical end groups with other polymer wherein the other polymer is selected from the group of linear, branched, hyperbranched or star shaped polymers with functionalized terminal groups. The PAMAM dendrimer with asymmetrical terminal groups consists of a Generation 2 and above PAMAM dendrimer with symmetrical end groups modified using the amino acids or their modified forms. The gel disclosed in the present invention is formed as small crosslinked particles in the size range 25 nm to 10 μm and is suitable for injectable delivery of hydrogel to any of the body orifices, tissues by intramuscular or subcutaneous route and ocular delivery for the purpose of therapeutic treatment and imaging.
Owner:WAYNE STATE UNIV +1
Chitosan double-network quick response-type injectable hydrogel and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN103937014AHigh mechanical strengthShort mechanical strengthFlow propertiesBiocompatibility TestingResponse type
The invention relates to chitosan double-network quick response-type injectable hydrogel and a preparation method thereof. The injectable hydrogel is prepared from chitosan or derivatives of the chitosan and sodium glycerophosphate serving as raw materials, and dialdehyde compounds or diepoxy compounds serving as crosslinking agents, wherein the mass ratio of the chitosan to the sodium glycerophosphate is 1:(0.5-10); the mass ratio of the crosslinking agents to the chitosan is (0.01-1):1. The method comprises the following steps: evenly mixing a hydrochloric acid aqueous solution of the chitosan with a sodium glycerophosphate solution in the environment at -1 to 5 DEG C, so as to obtain a solution of which the pH is 7-7.2, and evenly mixing the solution with a crosslinking solution at 35-37 DEG C. Transformation from a sol state to a gel state can be quickly finished under a specific condition, the process is irreversible, and the transition time is controllable. The chitosan double-network quick response-type injectable hydrogel has the advantages of simple reaction condition, short response time, good thermal stability of gel, high mechanical strength, good biocompatibility and the like. The chitosan double-network quick response-type injectable hydrogel is applied to the fields such as tissue filling and repairing, biological scaffolds, scar resistance and anti-adhesion, biogel, and quickly molding or three-dimensional printing materials and the like.
Owner:IMEIK TECH DEV CO LTD
Injectable hydrogel microspheres from aqueous two-phase system
InactiveUS7776240B2Big lossSustained releaseLiquid surface applicatorsPeptide/protein ingredientsSolubilityEmulsion
Injectable hydrogel microspheres are prepared by forming an emulsion where hydrogel precursors are in a disperse aqueous phase and polymerizing the hydrogel precursors. In a preferred case, the hydrogel precursors are poly(ethylene glycol) diacrylate and N-isopropylacrylamide and the continuous phase of the emulsion is an aqueous solution of dextran and a dextran solubility reducer. The microspheres will load protein, e.g., cytokines, from aqueous solution.
Owner:CORNELL RES FOUNDATION INC
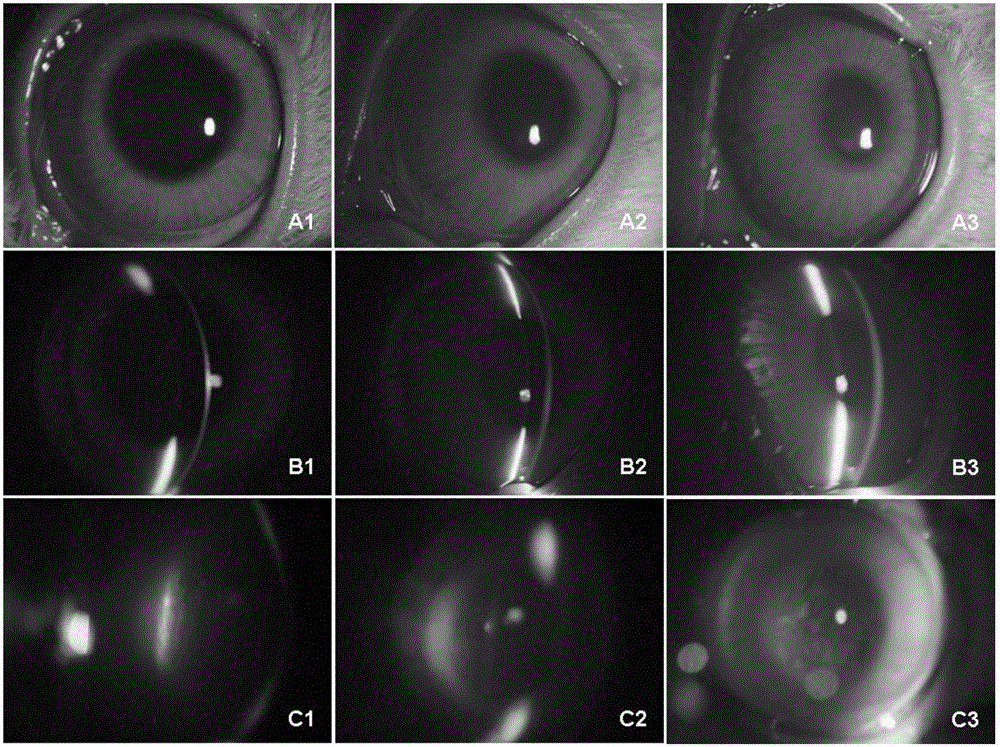
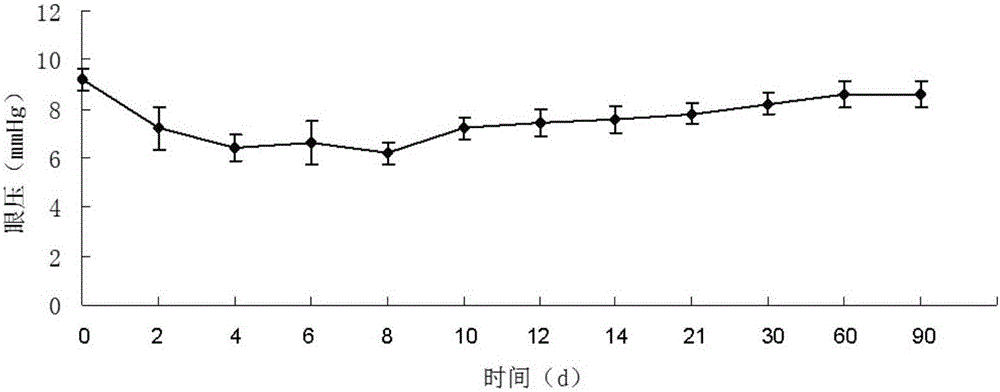
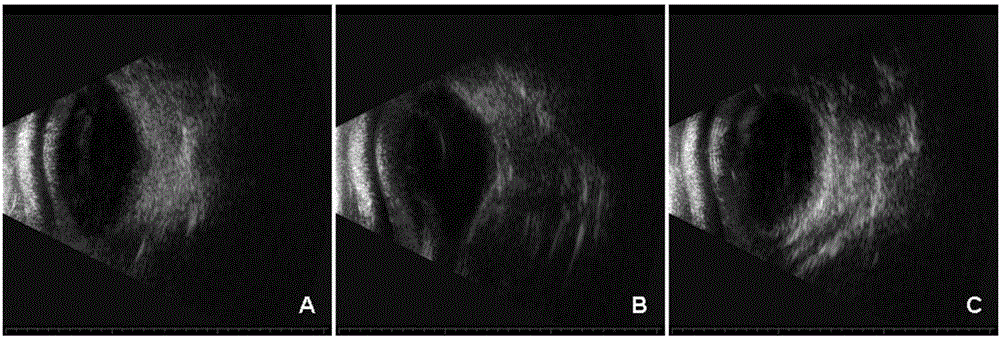
Application of injectable hydrogel in preparing intraocular filling materials
ActiveCN105833344AGood biocompatibilityEasy to fillPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsTissue regenerationOphthalmologySurgery
The invention discloses an application of injectable hydrogel in preparing intraocular filling materials. The application is characterized by being application of the injectable hydrogel as intraocular filling materials in vitreoretinal surgery as well as application of the injectable hydrogel as an intraocular drug carrier, wherein the injectable hydrogel is composed of two agents; the first agent is a glue solution containing oxidized polysaccharide; the second agent is a glue solution containing a chitin derivative and / or collagen; the two agents are separately contained in two injection tubes of a duplicate injector; the two glue solutions are simultaneously pushed and injected by the duplicate injector; in the pushing and injecting process, mixing and cross-linking are generated, namely, a dialdehyde group of the oxidized polysaccharide generates cross-linking reaction with amino of the chitin derivative and / or the collagen to form hydrogel with viscoelasticity. The constituents of the hydrogel are biomacromolecules different from chemical macromolecules, and a micromolecule cross-linking agent is not introduced, so that the biocompatibility is good, the hydrogel can be degraded and absorbed, toxic and side effects are avoided, and the safety is good.
Owner:QINGDAO HUISHENG HUIZHONG BIOLOGICAL TECH CO LTD
High strength injectable hydrogel and preparation method thereof
InactiveCN102718991AMacromolecular non-active ingredientsProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingPolyethylene glycol
The invention relates to a high strength injectable hydrogel and a preparation method thereof, and specifically relates to the hydrogel formed by using the double bond of polyethyleneglycol diacrylate (PEGDA) and the mercapto group of a sulfhydrylation natural polymer to undergo a Michael addition reaction and at the same time taking the nanoparticles of the triblock copolymer of polyethylene glycol and polycaprolactone (PEG-PCL-PEG) as a reinforcing agent. This kind of hydrogel has relatively high mechanical strength, is injectable hydrogel and degradable hydrogel with good biocompatibility, and has a high gelating speed. The hydrogel has the characteristics of cheap and easily available raw materials and simple preparation method, and therefore has a good application prospect in the biomedical field.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
In situ forming hydrogel and biomedical use thereof
ActiveUS20120100103A1Improve solubilityEasy to handleAntibacterial agentsPeptide/protein ingredientsDehydrogenationWater soluble
Disclosed are in situ-forming injectable hydrogel and medical uses thereof. In the in situ-forming injectable hydrogel two or more homogeneous or heterogeneous polymers are bonded to each other by a dehydrogenation reaction between phenol or aniline moieties on adjacent polymers, wherein a polymer backbone is grafted with a phenol or aniline moiety using a linker. In contrast to conventional hydrogel, the in situ-forming injectable hydrogel is superior in terms of in vivo stability and mechanical strength thanks to the introduction of a water-soluble polymer as a linker which leads to an improvement in the reactivity of phenol or aniline moieties. Having the advantage of superior bio stability and mechanical strength, the hydrogel finds a variety of applications in the biomedical field.
Owner:AJOU UNIV IND ACADEMIC COOP FOUND
Antibacterial adhesion injectable hydrogel dressing, preparation method and applications thereof
ActiveCN108912352AImprove antibacterial propertiesImprove the bactericidal effectPharmaceutical delivery mechanismBandagesSelf-healingCross-link
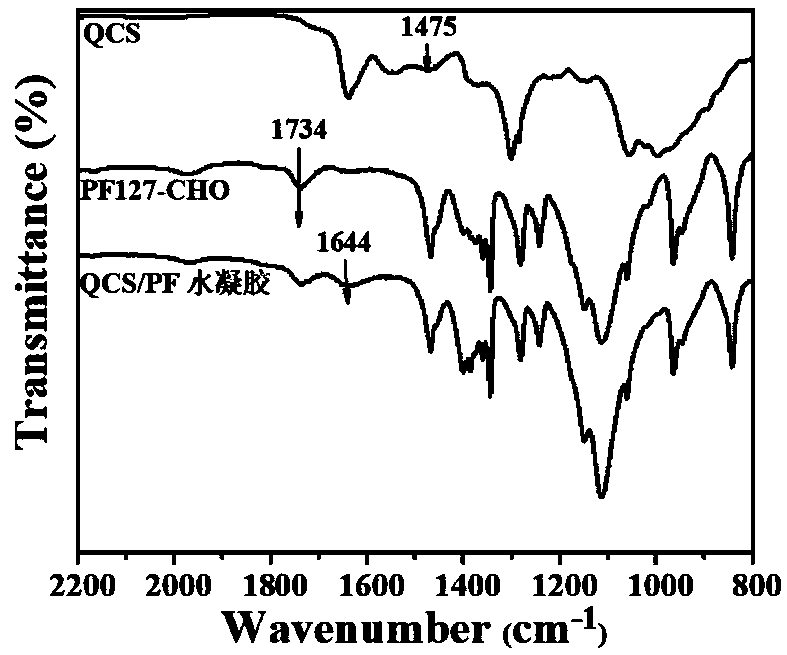
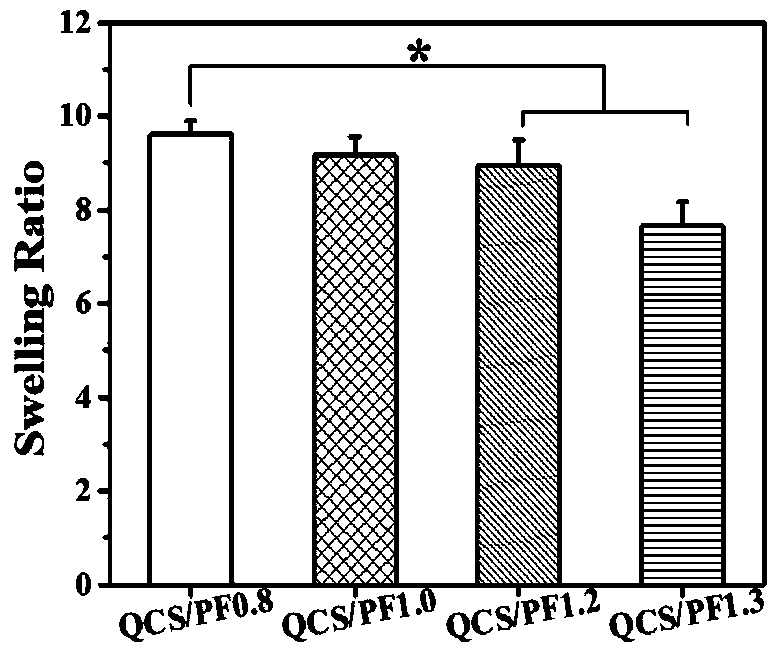
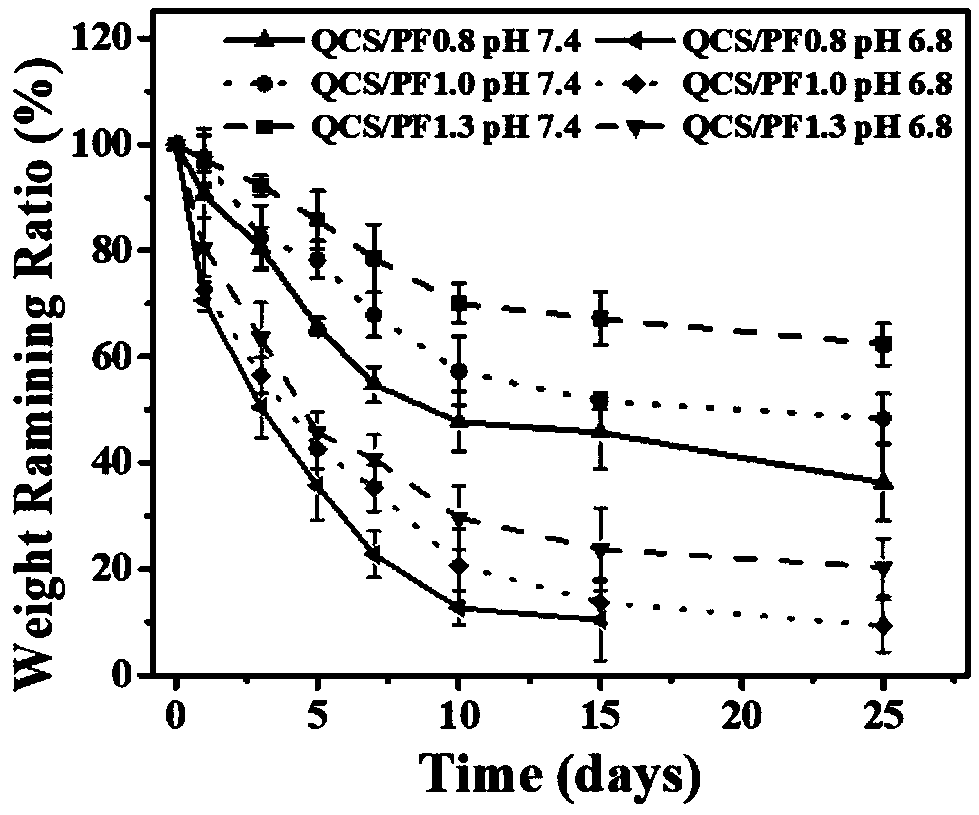
The invention discloses an antibacterial adhesion injectable hydrogel dressing, a preparation method and applications thereof, and belongs to the technical field of biodegradable biomedical materials.According to the method, 2,3-epoxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride (GTMAC) is grafted onto chitosan to obtain a quaternized chitosan polymer (QCS) as the main raw material of a hydrogel, p-carboxybenzaldehyde is grafted onto a triblock copolymer Pluronic< >F127 to obtain an aldehyde group-terminated Pluronic< >F127 polymer (PF127-CHO) as the cross-linking agent of the gel, and the aldehyde group-terminated Pluronic< >F127 polymer (PF127-CHO) and the quaternized chitosan polymer (QCS) are subjected to a cross-linking reaction under a physiological environment to obtain the antibacterial adhesion injectable hydrogel dressing (QCS / PF) with advantages of rapid self-healing, easy extending and easy compression. According to the present invention, the method has advantages of simple process, wide raw material source and low preparation cost; and the hydrogel dressing prepared by using the method has advantages of good adhesion, good pH responsiveness, good mechanical property, good self-healing property, good bleeding stopping property and good antibacterial property so as to be used in the field of skin injury treatment drugs.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Injectable high-strength and temperature-sensitive modified chitin-based hydrogel as well as preparation method and application thereof
ActiveCN108310460AImprove liquidityGood biocompatibilitySurgical adhesivesPharmaceutical delivery mechanismCross-linkSolubility
The invention discloses injectable high-strength and temperature-sensitive modified chitin-based hydrogel as well as a preparation method and application thereof. The gel is characterized in that a temperature-sensitive chitin derivative is dissolved into a water system at low temperature and a crosslinking agent or a photoinitiator is introduced to form an injectable hydrogel precursor solution with good flowability; after the injectable hydrogel precursor solution is injected into a body, the injectable high-strength hydrogel is formed through spontaneous chemical crosslinking or light illumination crosslinking under physiological conditions. The hydrogel disclosed by the invention has abundant precursor material sources and is easy to prepare; the photoinitiator or the crosslinking agent, which has relatively good solubility and very low toxicity in water, is used. The temperature-sensitive chitin derivative is utilized and can be physically cross-linked and molded under the physiological conditions and is further subjected to chemical crosslinking or photocrosslinking to prepare the injectable high-strength hydrogel and the injectable high-strength hydrogel does not need to besubjected to any post-treatment. Furthermore, the hydrogel has biodegradability and can be widely used for fields including biomedical materials, tissue engineering technologies and the like.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Preparation method of injectable double-cross-linked hydrogel for tissue engineering
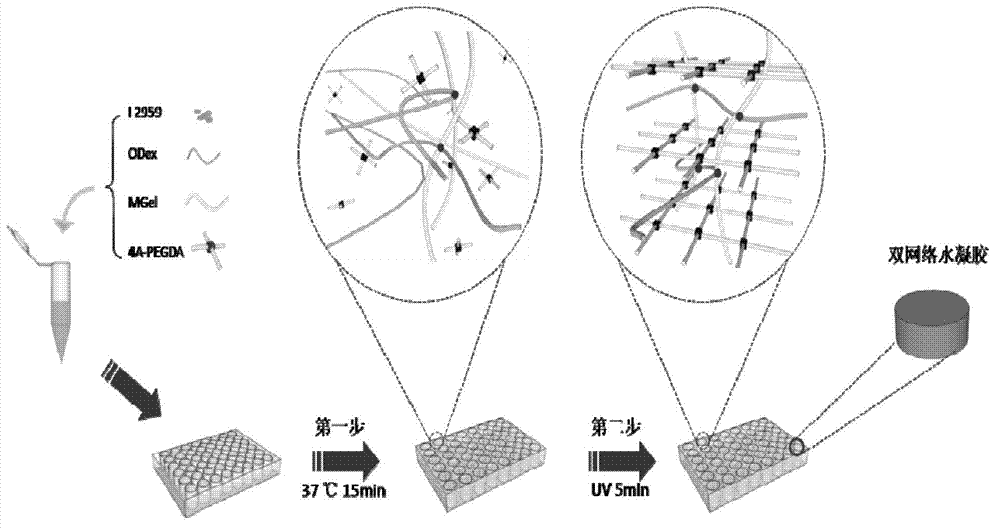
ActiveCN102784414AAvoid moving aroundStrong mechanical propertiesProsthesisCross-linkBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a preparation method of injectable double-cross-linked hydrogel for tissue engineering, which comprises the following steps that: an aqueous solution of aminated gelatin, an aqueous solution of aldehyde dextran, and an aqueous solution of terminated vinyl poly ethylene glycol are mixed according to a volume ratio of 4:4:3, then are cross-linked for 10-20 minutes at a temperature of 35 to 40 DED C, and finally are cross-linked for 3 to 8 minutes by ultraviolet irradiation. The preparation method provided by the invention has a simple operation process and mild implementation conditions; and the double-cross-linked hydrogel obtained by the invention is non-toxic and biodegradable, has good mechanical properties and biocompatibility, and can be used for injectable hydrogel scaffold in the tissue engineering.
Owner:烟台沃德麦克斯纳米科技有限公司
Method for preparing temperature-responsive adhesive injectable hydrogel
ActiveCN108929412AGel time controlImprove adhesion strengthSurgical adhesivesAerosol deliveryMethacrylateWound dressing
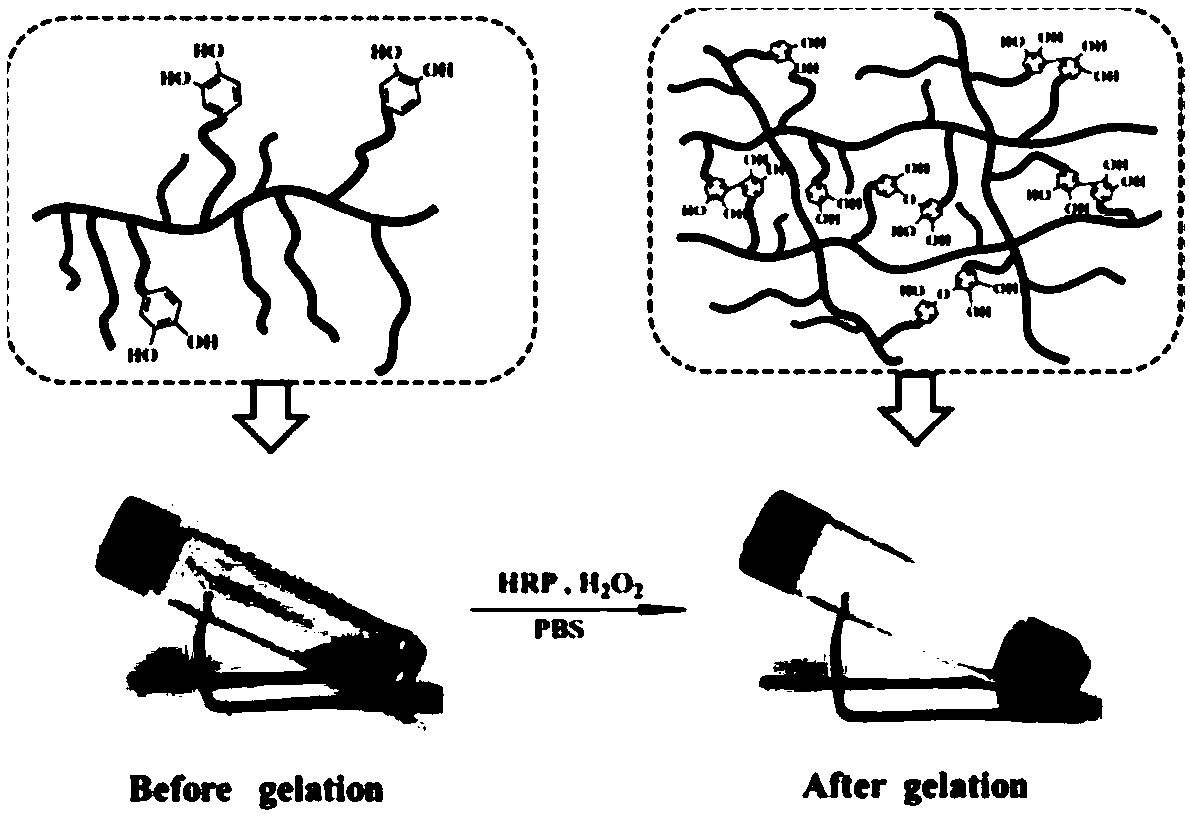
The invention provides a method for preparing a temperature-responsive adhesive injectable hydrogel. The method comprises the following steps: synthesizing a temperature-responsive polymer with different dopamine contents from dopamine methacrylamide used as an adhesive monomer and ethyl 2-(2-methoxyethoxy)methacrylate and oligo(ethylene glycol)methyl ether methacrylate as temperature-sensitive monomers, and carrying out enzyme catalytic crosslinking on the polymer and a dopamine group under the catalysis of horseradish peroxidase and hydrogen peroxide to prepare the temperature-responsive adhesive hydrogel. The hydrogel prepared in the invention has the characteristics of fastness in gel formation, realization of in-situ injection molding, realization of regulating the gelation time and the gel strength by regulating the concentrations of the polymer, horseradish peroxidase and hydrogen peroxide, and convenience in use; and the adhesion strength of the hydrogel is enhanced with the rising of the temperature, so the temperature-responsive characteristic makes the obtained hydrogel applied to fields of tissue adhesives, wound dressings, cell culture media and drug controlled releasecarriers.
Owner:NANCHANG UNIV
Nano particle-polymer injectable composite hydrogel double drug loading system and preparation method thereof
ActiveCN107550921AReasonable structural designLow costOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryCross-linkTreatment effect
The invention belongs to the field of synthesis of drug carrier base materials and provides a nano particle-polymer injectable composite hydrogel double drug loading system and a preparation method thereof. The double drug loading system is loaded with not only an anti-cancer drug I of which polymer nano particles are synthesized through a disulfide bond cross-linking agent by taking acrylic acidand 4-vinylphenylboric acid as monomers, but also an anti-cancer drug II of which injectable hydrogel is synthesized through Michael addition reaction between a macromolecular cross-linking agent witha sulfhydryl functional group and a polymer containing a catechol functional group aiming at the drug loading capacity, the action time, the treatment effect and other demands. The bi-stimulus response is pH stimulus response and reducing stimulus response of glutathione to the disulfide bond cross-linking agent in a tumor cell environment respectively, the interaction between the nano particlesand the drug I as well as the degradation process of the nano particle can be affected, and the long-term delivery of the drug I is realized. The nano particle-polymer injectable composite hydrogel double drug loading system provided by the invention realizes the effects of local long-time administration, step-by-step osmotic treatment and combined treatment of a variety of drugs.
Owner:NANJING UNIV OF POSTS & TELECOMM
Natural polysaccharide-based hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof in conjunctival repair
ActiveCN104958783AControl swelling rateControl degradation rateProsthesisOperabilitySodium glycerophosphate
The invention belongs to the field of tissue engineering and discloses chemically-crosslinked natural polysaccharide-based injectable hydrogel, a preparation method thereof and application thereof in tissue engineering materials, especially in conjunctival repair. The preparation method includes the following steps: adding an acrylated natural polysaccharide material water solution into a sulfhydrylated natural polysaccharide material water solution, mixing well, adding a beta-sodium glycerophosphate solution to adjust pH to be neutral, and incubating at temperature of 37 DEG C to obtain the chemically-crosslinked natural polysaccharide-based injectable hydrogel. The hydrogel is controllable in performance, can realize gelation under human physiological conditions, is needless of adding other chemical crosslinking agents, can be used as a tissue engineering material and is especially suitable for conjunctival repair, injectable, quick in reaction, capable of realizing gelation within 5-15min, in-situ in forming, high in surgical operability and automatic in bonding in the process of surgery, stitching for fixing is not needed, and wound surfaces in any shape and at any position can be protected effectively.
Owner:JINAN UNIVERSITY
Temperature response type injectable hydrogel and preparation method and usage thereof
The invention relates to a temperature response type injectable hydrogel and a preparation method and the usage of the injectable hydrogel; the hydrogel comprises component A, component B and water, wherein the component A is cholesterol-polyethylene glycol-cholesterol; and the component B is amination beta cyclodextrin graft hydroformylation glucan. The preparation process of the injectable hydrogel is simple and convenient, and the prepared injectable hydrogel has a certain strength and toughness as well as self-repairability; compared with the prior art, the invention improves the controllability of the performances of the hydrogel, and further improves the biocompatibility of the hydrogel; the hydrogel prepared by the invention has biodegradability and can be etabolized by human body; and the hydrogel has temperature responsiveness and injectability, and can be used for a drug carrier, embolism material and tissue engineering material.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV
Injection aquagel of sodium alginate cross-linking gelatin comprising biphase calcium phosphor granule, method for making same and use thereof
The invention relates to an ejected aquagel of sodium alginate crosslink dope, with dual-phase calcium-phosphorus particle, wherein it is prepard from aldehyde group sodium alginate, dope, and dual-phase calcium-phosphorus particles; the mass percentages of each material are: aldehyde group sodium alginate at 5-20%; dope at 10-30%; and dual-phase calcium-phosphorus particles at 50-70%. The invention also discloses a relative preparation and application, wherein said inventive product is characterized in that: (1), the materials are safe and innocuous; (2), it can provide best physical chemical environment for regenerating and rebuilding skelton, with better biological compatibility and adjustable physical property and biological degrade function; (3), the material can stuff the skeleton damage in any shape, to contact the around organism, with simple operation.
Owner:THE FIRST AFFILIATED HOSPITAL OF SUN YAT SEN UNIV
Thermosensitive injectable hydrogel for drug delivery
ActiveUS9364545B2Efficient Growth InhibitionGood curative effectOrganic active ingredientsAerosol deliveryPolyethylene oxideMedicine
The invention develops a developed a thermosensitive injectable hydrogel based on HA and a copolymer of polyethylene oxide (PEO) and polypropylene oxide (PPO), which has a gel formation temperature from 30° C. to 37° C. The thermosensitive injectable hydrogel of the invention provides a potential drug delivery system that can increase therapeutic efficacy of the drug.
Owner:TAIPEI MEDICAL UNIV
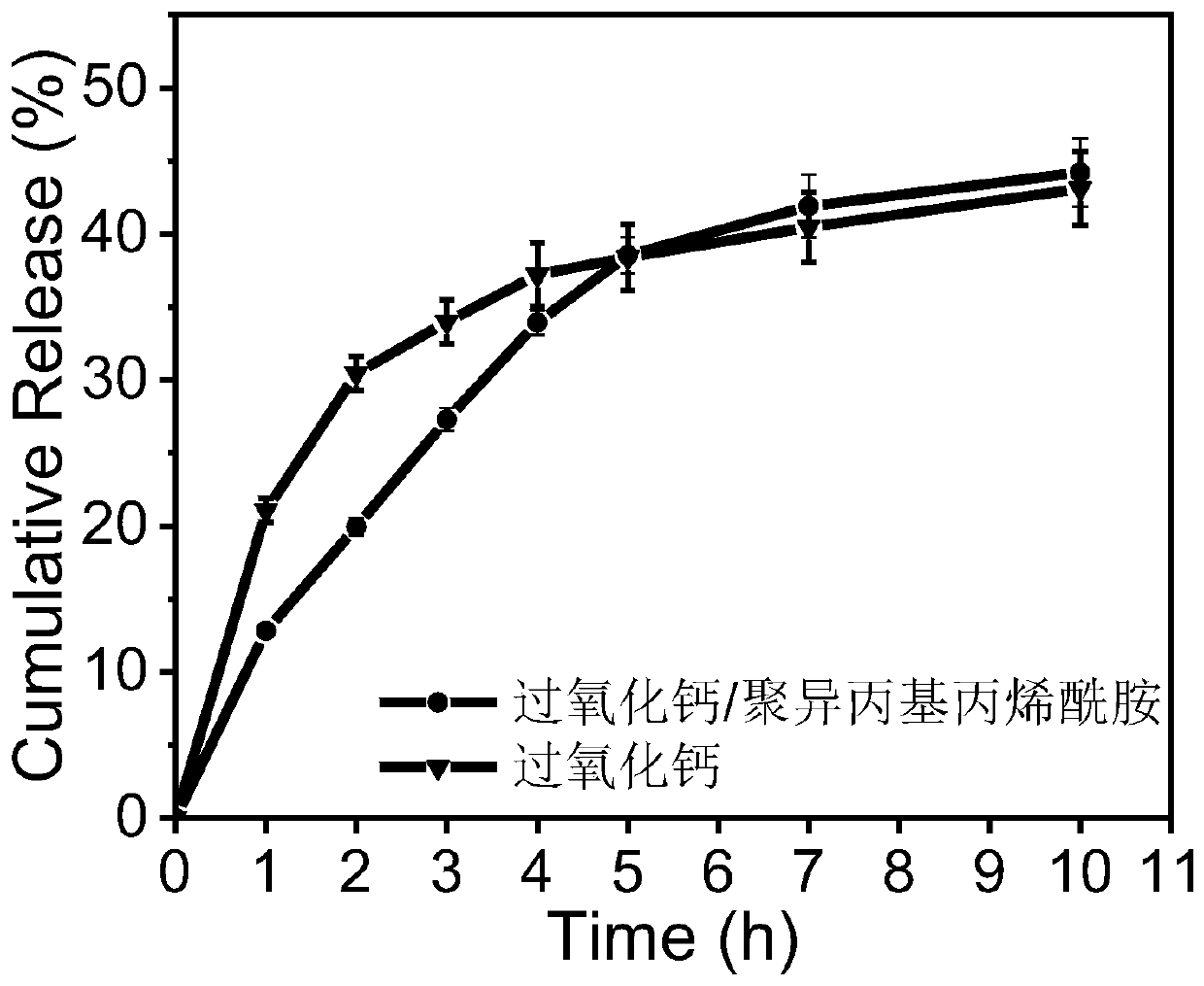
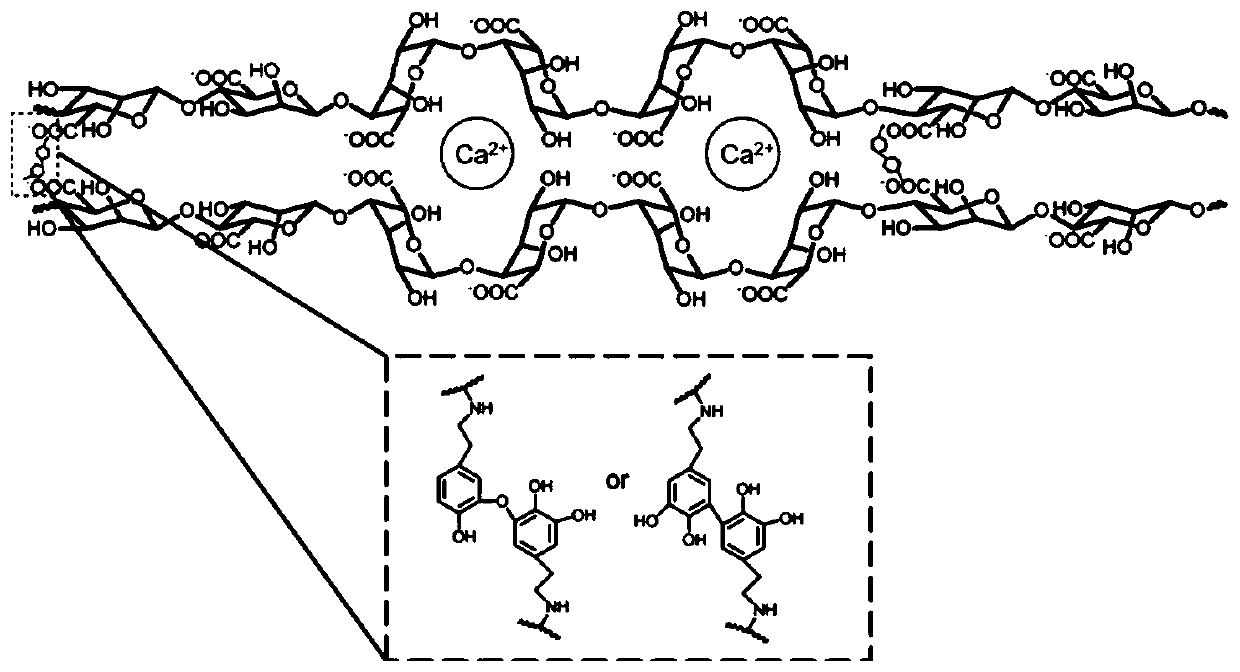
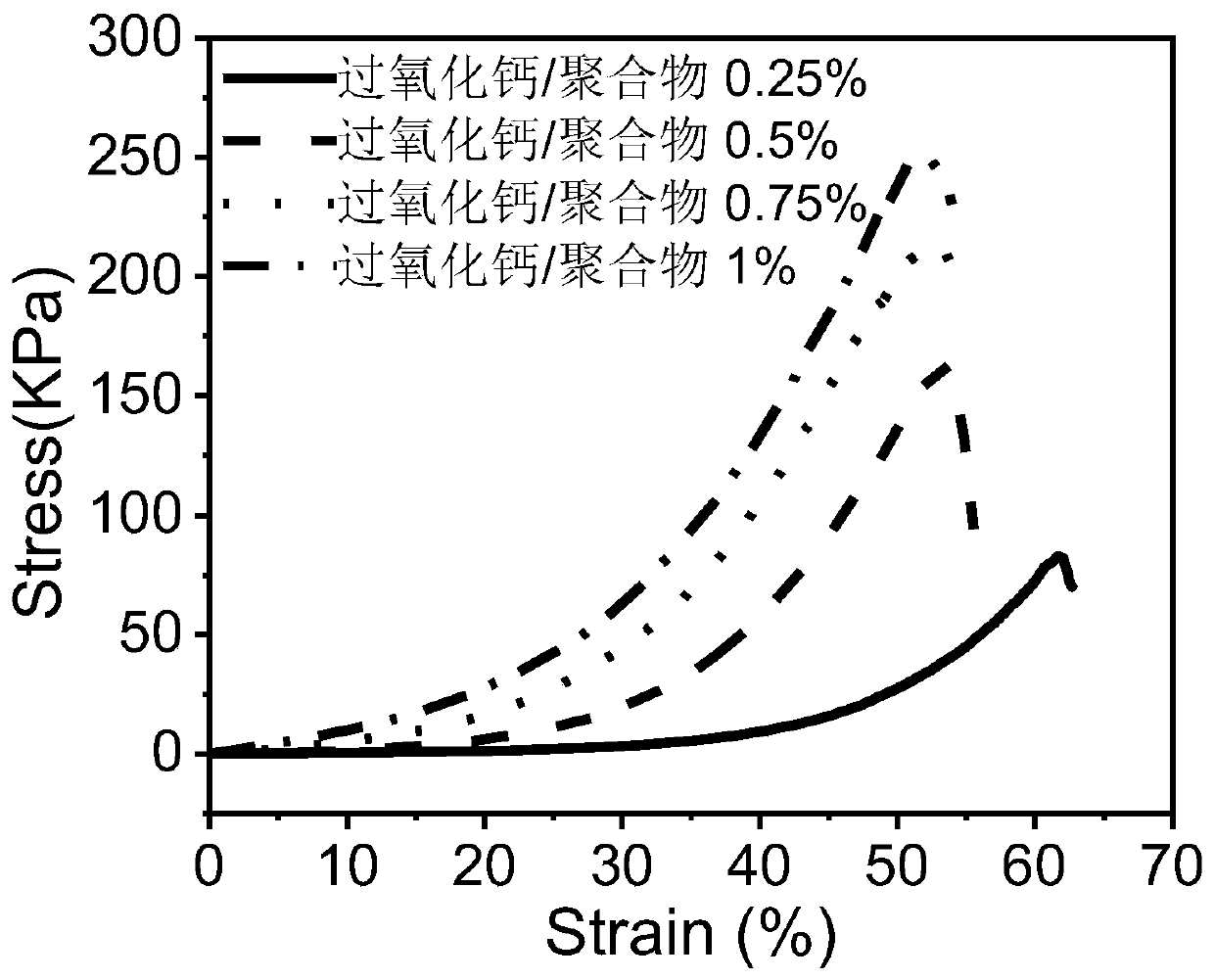
Double crosslinked hydrogel based on calcium peroxide/polymer oxygen generating particles and preparation method of hydrogel
The invention discloses a double crosslinked hydrogel based on calcium peroxide / polymer oxygen generating particles and a preparation method of the hydrogel. The hydrogel is characterized in that thecalcium peroxide / polymer composite particles are introduced into a sodium alginate dopamine solution, crosslinking points are formed by calcium ions and carboxyl groups of sodium alginate, crosslinking points are also formed by self-crosslinking of dopamine, a mass concentration of calcium chloride is 3 wt%, and a mass concentration of the polymer is 3-60 wt%; and the hydrogel is a double crosslinked injectable hydrogel. Sodium alginate is used as a skeleton of the polymer, is simply modified by dopamine, and then is mixed with the calcium peroxide / polymer oxygen generating particles to prepare the physicochemical double crosslinked injectable oxygen generating hydrogel in one step. A compressive strength of the double crosslinked hydrogel can be up to 247+ / -1.15 KPa; and the oxygen content inside the hydrogel is increased, and the inside of the hydrogel maintains a high oxygen environment for 4 days or more at 37 DEG C. In addition, the used materials of the prepared injectable oxygengenerating hydrogel are non-toxic or low-toxic.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV
Thermo-sensitive type injectable chitosan hydrogel product and applications thereof
InactiveCN103524795AGood biocompatibilityAerosol deliveryOintment deliveryDrug carrierPolysaccharide
The present invention relates to a thermosensitive injectable chitosan hydrogel. Genipin (a natural crosslinking agent) crosslinked natural cationic polysaccharide chitosan is used to prepare the product, which is a solution when the temperature is below 25°C and becomes a thermosensitive injectable hydrogel in an hour when the temperature is warmed up to 28-42 °C. The prepared hydrogel can be used as a drug carrier or a tissue engineering scaffold.
Owner:DALIAN INST OF CHEM PHYSICS CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
Water-soluble chitosan derivatives as well as preparation method and uses thereof
InactiveCN101225123ASimple operation processMild reaction conditionsProsthesisSolubilityBiocompatibility Testing
The invention relates to a water soluble chitosan derivative and the preparation method and application of the water soluble chitosan derivative. The water soluble chitosan derivative adopts the chitosan as raw material to synthesize substitutional derivatives on the chitosan -NH2 with the following structural formula (I). The preparation method is making the chitosan react with an ester with a methacrylic oxyl on one end and a propylene oxyl on the other end in the medium of water, acetic acid and ethanol, obtaining the chitosan derivative with both polymerized unsaturated carbon-carbon double bond and water solubility at the same time. The the preparation method for the water soluble chitosan derivative has the advantages of mild conditions, simple operation, natural and non toxic prepared chitosan derivatives, biodegradation and biocompatibility, and ability to be used as injectable hydrogel support and cartilage repair materials for tissue engineering scaffold material after further polymerization.
Owner:BEIJING UNIV OF CHEM TECH
Injectable gel material of sodium alga acid-protein adhesive used for treating myocardial infarction and preparation method of injectable gel material
ActiveCN102178984AStrong mechanical propertiesStrong chemical stabilityProsthesisFreeze-dryingAdhesive
The invention discloses a preparation method of an injectable gel material of sodium alga acid-protein adhesive used for treating myocardial infarction, relating to injectable hydrogelin and a preparation method of the hydrogelin. The material and the method solve the technical problems of the existing injectable hydrogelin using calcium ion for crosslinking such as poor compatibility with organisms and undesirable mechanical property. The injectable gel material of sodium alga acid-protein adhesive used for treating myocardial infarction is made from the component sodium alga acid and the component protein adhesive that are mixed. The preparation method includes: adding sodium alga acid in water to oscillate with light avoidance on a table concentrator, thus generating partially oxidized sodium alga acid solution; adding glycol to the solution and placed on the table concentrator to oscillate, then adding sodium chloride to oscillate, dissolve and precipitate, dissolving the precipitate in water to attain collosol, and dialyzing and freeze-drying to obtain partially oxidized sodium alga acid; formulating the sodium alga acid solution to obtain sodium alga acid component; formulating gelatin or collagen to obtain protein adhesive component; and mixing the sodium alga acid component with the protein adhesive component for use. The injectable gel material can be used for treating myocardial infarction.
Owner:HARBIN INST OF TECH
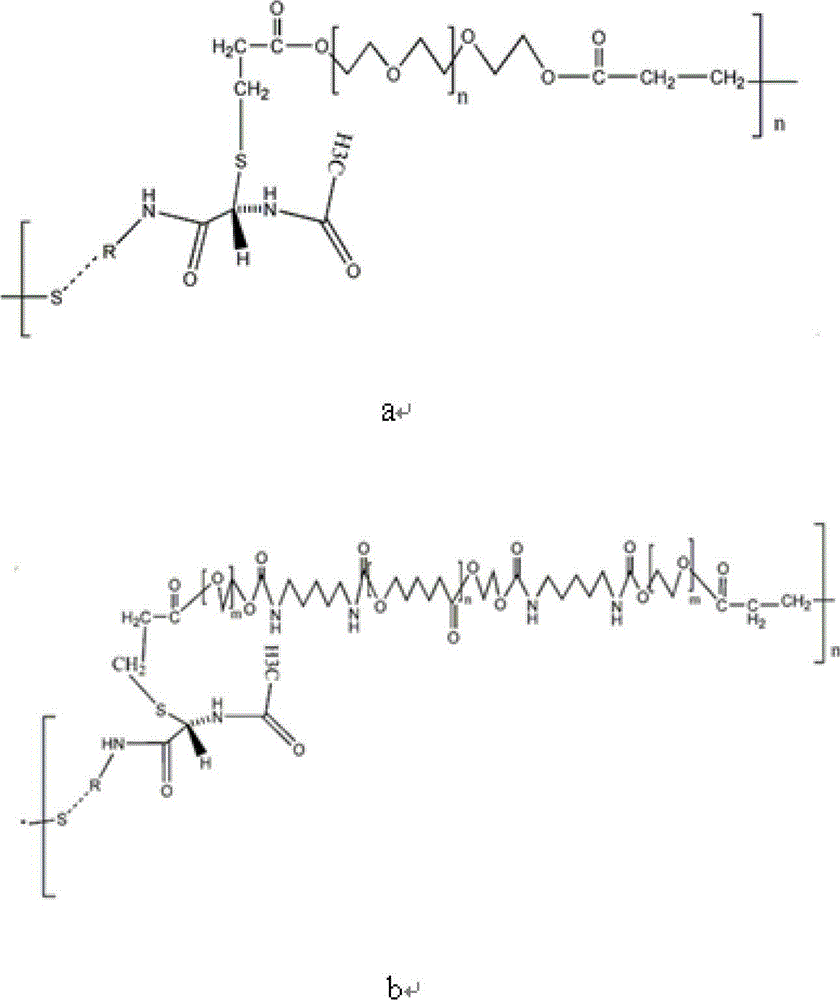
Injectable self-healing hydrogel with adjustable mechanical properties as well as preparation method and application of injectable self-healing hydrogel
ActiveCN111518289AGood biocompatibilityRemain biodegradablePharmaceutical delivery mechanismBandagesImidePolymer science
The invention relates to an injectable self-healing hydrogel with adjustable mechanical properties as well as a preparation method and application of the injectable self-healing hydrogel. The hydrogeldisclosed by the invention is prepared from the following raw materials: oxidized hyaluronic acid and succinyl chitosan, and further is prepared from one or more of calcium ions, polyethylene glycolderivatives, 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride and N-hydroxysuccinimide. According to the invention, hyaluronic acid and succinyl chitosan are oxidized; introducing one or more of calcium ions, a polyethylene glycol derivative, 1-(3-dimethylaminopropyl)-3-ethylcarbodiimide hydrochloride (EDC) and N-hydroxysuccinimide (NHS) is adopted; the self-healing and injectable hydrogel is prepared by adjusting the components and the component content of the hydrogel, so that the hydrogel has the characteristic of adjustable mechanical properties, and the biocompatibility, hemostasis, wound healing promotion, angiogenesis promotion and other properties of the hydrogel are improved.
Owner:SHANDONG UNIV
Biodegradability hydrogel controlled-release preparation and its preparation method and application
InactiveCN101283966ASimple manufacturing methodControl release speedPharmaceutical delivery mechanismLactidePLA-PEG-PLA
The invention relates to a biodegradable hydrogel controlled release preparation and a preparation and an application thereof, belonging to the technology field of medicines. The preparation method comprises the steps of: synthesizing poly(lactic acid)-polyethylene glycol-poly(lactic acid) (PLA-PEG-PLA) triblock copolymer by inducing L-lactide and D-lactide to respectively conduct ring-expansion polymerization by using zinc powder, zinc lactate or stannous octoate as catalyst and polyethylene glycol (PEG) 2,000-20,000; respectively dissolving poly-L-lactic acid-polyethylene glycol-poly-L-lactic acid and poly-D-lactic acid-polyethylene glycol-poly-D-lactic acid in water to obtain solutions with concentration of 0.05-0.5g / mL, swelling, mixing, and allowing gelatinization under constant temperature to obtain PLA-PEG-PLA triblock copolymer hydrogel for injection by complexing reaction. The hydrogel has good biological compatibility and biodegradability, can be used for embedding water-soluble drugs, and is an ideal drug controlled release carrier.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Anti-cross-linking agents and methods for inhibiting cross-linking of injectable hydrogel formulations
InactiveUS20090054545A1Easy injectionTransportation and packagingMixing methodsCross-linkIrradiation
The invention relates to cross-link-resistant injectable hydrogel formulations and methods of partially or practically wholly inhibiting injectable hydrogel formulations from cross-linking, for example, during irradiation, using anti-cross-linking agents, which facilitates injectability of the hydrogel formulation. The invention also relates to methods of making the cross-link-resistant, for example, irradiation cross-link resistant, injectable hydrogel formulations, and methods of administering the same in treating a subject in need.
Owner:THE GENERAL HOSPITAL CORP
Injectable hydrogel preparation of pegylated medicament
InactiveCN1965802AEasy to usePharmaceutical delivery mechanismPharmaceutical non-active ingredientsPolyesterMedicine
The invention relates to a method for preparing injection aquagel agent which packs PEG drug, wherein said PEG drug is obtained by combining PEG decorator onto original drug molecule via covalence reaction; the carrier packing the drug is the mixture of degradable polymer and water; said degradable polymer is block copolymer or derivant whose hydrophilic section is PEG and hydrophobic section is degradable polyester. The inventive aquagel agent is fluid under body temperature; and it is gel at body temperature. It can be injected to release PEG drug for several days or several months.
Owner:FUDAN UNIV
Growth factor porous micro-sphere compound system coated by injectable hydrogel
InactiveCN105288594AHigh drug loadingImprove stabilityNervous disorderPeptide/protein ingredientsCompound systemHyaluronic acid
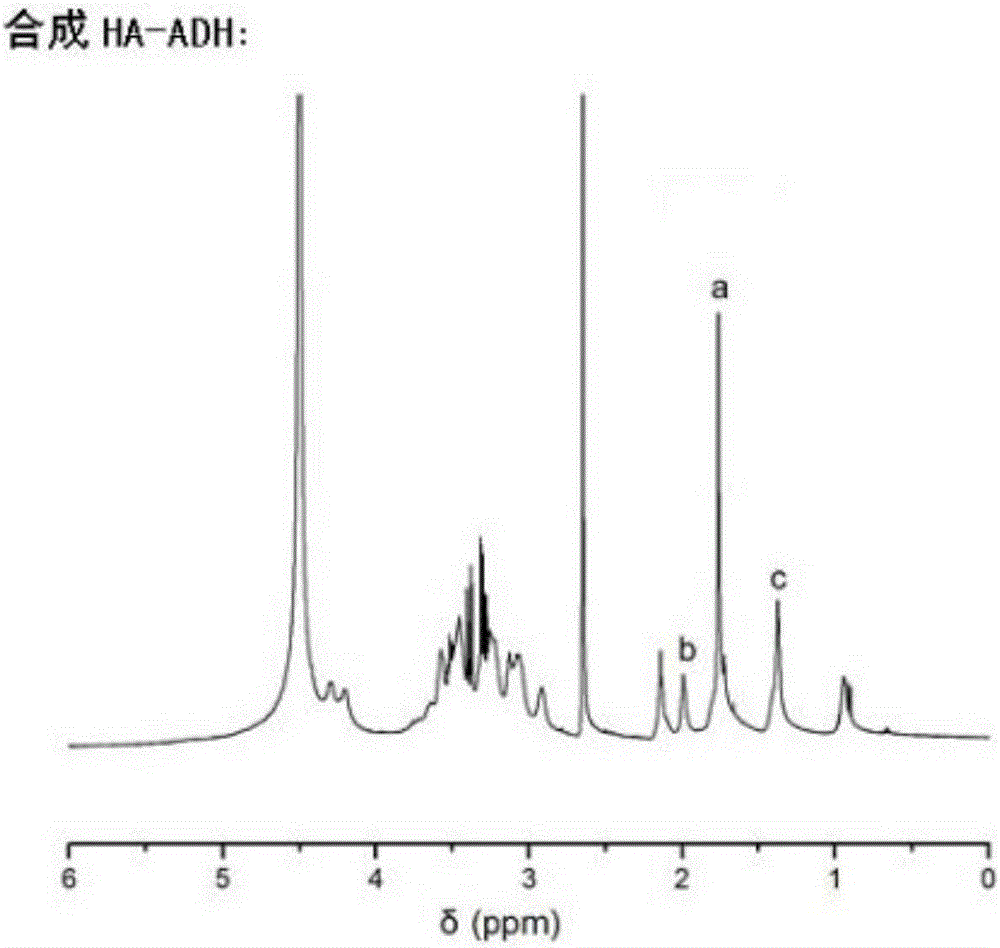
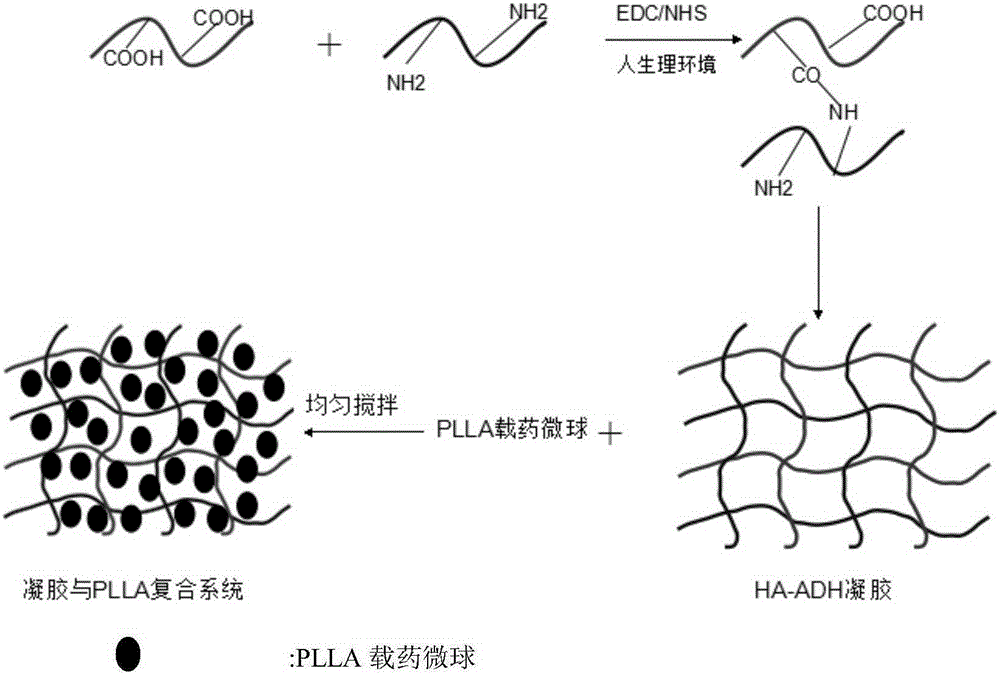
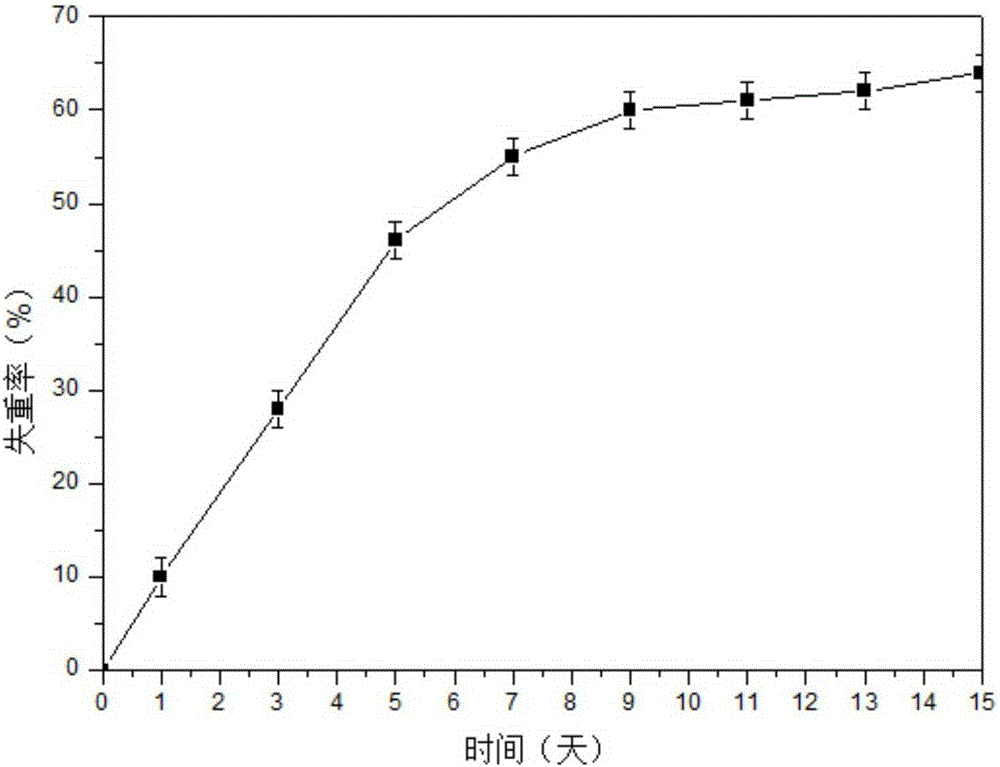
The invention relates to the preparation of a growth factor porous micro-sphere compound system coated by an injectable hydrogel. The preparation is characterized by comprising a first component, namely HA-ADH sol obtained by cross-linking of hyaluronic acid (HA) and adipic dihydrazide (ADH), and polylactic acid (PLLA) porous micro-spheres which are carried with growth factors and loaded in the first component. The compound system is capable of degrading and slowly releasing the growth factors under physiological conditions, so that the slow releasing of the growth factors in a body is realized, and the problems that the growth factors are released too fast and an action period is too short are solved, thereby reaching the effect of neural restoration.
Owner:WUHAN UNIV OF TECH
Dynamic imine bond polysaccharide polymer-based injectable hydrogel and preparation method and application thereof
InactiveCN109718395AEasy to compressGood biocompatibilitySurgical adhesivesProsthesisBiocompatibility TestingCartilage repair
The present invention relates to a dynamic imine bond polysaccharide polymer-based injectable hydrogel and a preparation method and an application thereof. The dynamic imine bond polysaccharide polymer-based injectable hydrogel comprises the following raw material components in weight percentages: 5-18% of a component A: oxidized sodium alginate, 0.1-20% of a component B: a mixture of one or two of water-soluble chitosan and 3,3'-dithiobis(propanohydrazide), and the balanced solvent. The materials are prepared into an even solution according to the ratio. Compared with the prior art, "Schiff base", amide bonds and other dynamic imine bonds are used to realize cross-linking and can form a gel under mild conditions of human body temperature and acid and alkali, and no biotoxic initiators areneeded. The hydrogel is fast in gel-forming speed and injectable after forming. The hydrogel is mild in the preparation conditions, and excellent in compression properties, biocompatibility and injectability, and has broad application prospects in the field of cartilage repair.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com