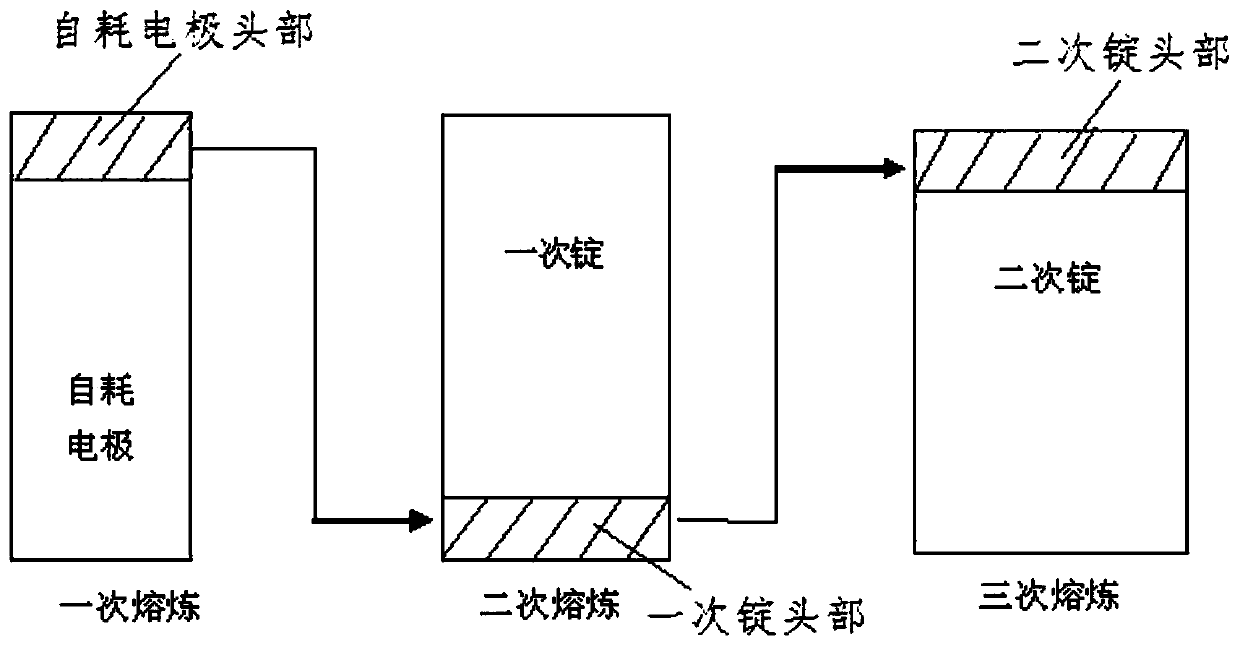
Method for avoiding iron element enrichment in head part of zirconium alloy ingot casting
A technology of zirconium alloy and iron element, which is applied in the field of zirconium alloy ingot preparation, can solve the problems of reducing the yield of the ingot, increasing the removal of the head of the ingot, difficulty in controlling the content of iron elements, etc., so as to improve the yield and improve the Fe segregation phenomenon and the effect of reducing iron enrichment phenomenon
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0027] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0028] Step 1, material preparation: select 2.2kg of zirconium particles, 980.7kg of nuclear-grade sponge zirconium, 13.5kg of Sn, 2.2839kg of Fe and 1.3kg of Cr according to the composition and content of each component in the target product Zr-4 zirconium alloy ingot Prepare materials;
[0029]Step 2, the preparation of master alloy: the Fe of 0.2139kg, the Sn of 1.35kg, the Cr of 0.13kg and the nuclear-grade zirconium grain of 0.2346kg carry out batching and obtain 1.928kg master alloy A through secondary smelting, the Fe of 2.07kg, 12.15kg of Sn, 1.17kg of Cr and 1.967kg of nuclear-grade zirconium grains were batched and 17.357kg of master alloy B was obtained through secondary melting; The temperature is 0.4Pa, and the pressure rise rate before smelting is 0.18Pa / min; the mass content of Fe in the master alloy A is 0.2139%, and the number of master alloy A is 48; the mass content of Fe in the master alloy B is is 0....
Embodiment 2
[0039] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0040] Step 1, material preparation: select 2.1942kg nuclear-grade zirconium particles, 980.715kg nuclear-grade zirconium sponge, 13.5kg of Sn, 2.2908kg of Fe and 1.3kg according to the composition and content of each component in the target product Zr-4 zirconium alloy ingot Cr for material preparation;
[0041] Step 2, the preparation of master alloy: the Fe of 0.2208kg, the Sn of 1.35kg, the Cr of 0.13kg and the nuclear-grade zirconium grain of 0.2272kg carry out batching and obtain 1.928kg master alloy A through secondary smelting, the Fe of 2.07kg, 12.15kg of Sn, 1.17kg of Cr and 1.967kg of nuclear-grade zirconium grains were batched and 17.357kg of master alloy B was obtained through secondary melting; The temperature is 0.42Pa, and the pressure rise rate before smelting is 0.2Pa / min; the mass content of Fe in the master alloy A is 0.2208%, and the number of master alloy A is 48; the mass content of Fe in the master...
Embodiment 3
[0045] This embodiment includes the following steps:
[0046] Step 1, material preparation: select 2.21kg nuclear-grade zirconium particles, 980.713kg nuclear-grade zirconium sponge, 13.5kg of Sn, 2.277kg of Fe and 1.3kg according to the composition and content of each component in the target product Zr-4 zirconium alloy ingot Cr for material preparation;
[0047] Step 2, the preparation of master alloy: the Fe of 0.207kg, the Sn of 1.35kg, the Cr of 0.13kg and the nuclear-grade zirconium grain of 0.241kg carry out batching and obtain 1.928kg master alloy A through secondary smelting, the Fe of 2.07kg, 12.15kg of Sn, 1.17kg of Cr and 1.967kg of nuclear-grade zirconium grains were batched and 17.357kg of master alloy B was obtained through secondary melting; The temperature is 0.44Pa, and the pressure rise rate before smelting is 0.2Pa / min; the mass content of Fe in the master alloy A is 0.207%, and the number of master alloy A is 48; the mass content of Fe in the master alloy...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com