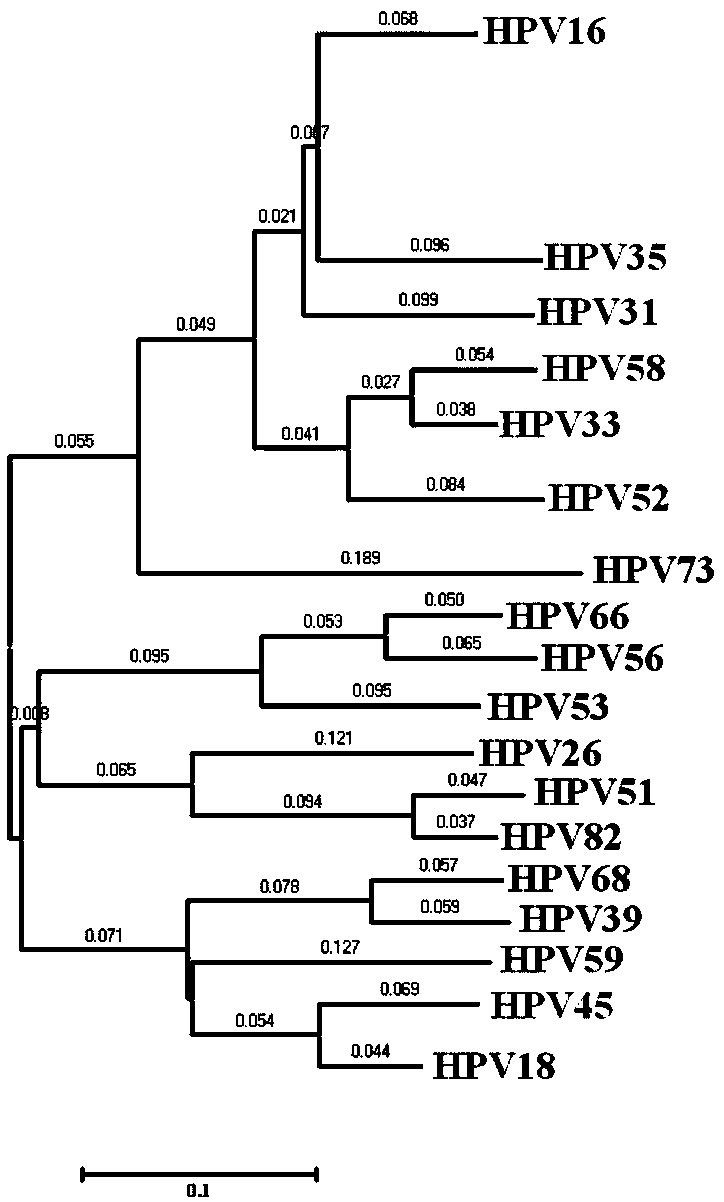
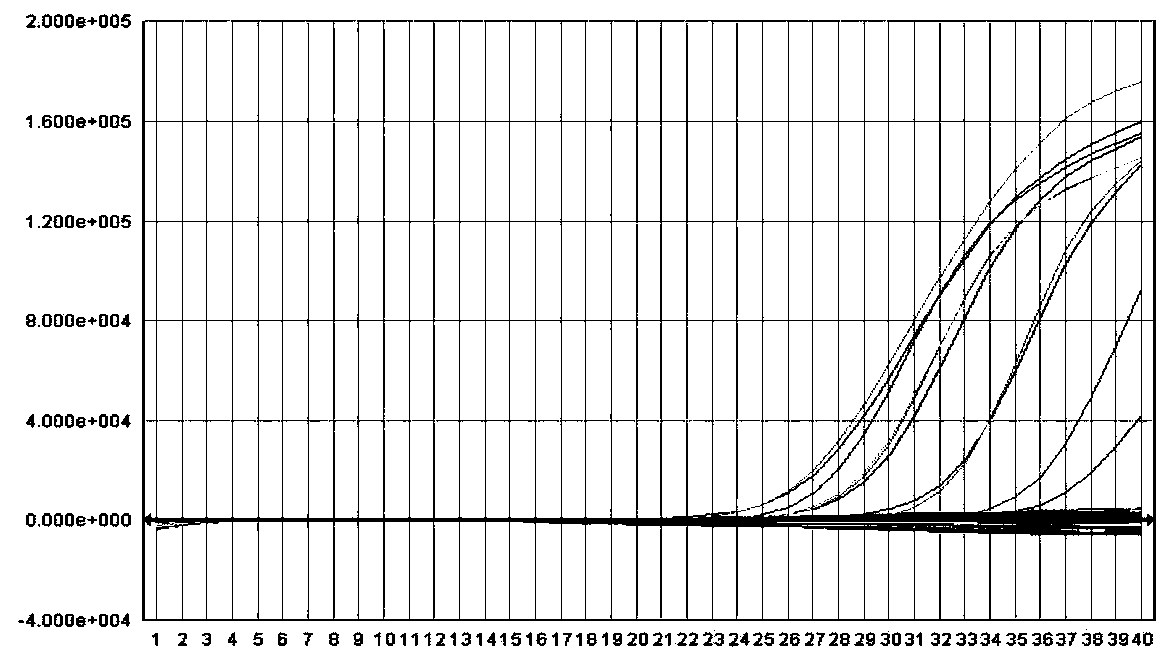
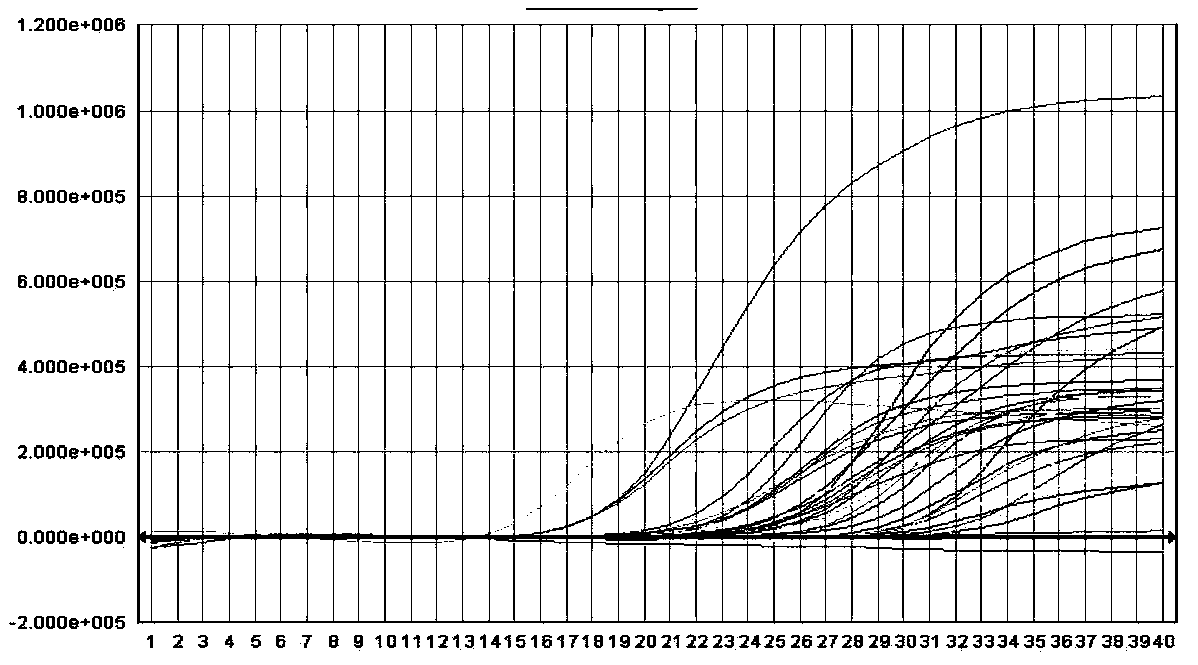
Design method of primers and probes for detecting pathogens
一种设计方法、病原体的技术,应用在生物科学和生物领域,能够解决增加样品和检测试剂用量、不能分型、增加检测成本等问题,达到降低背景荧光值、保证检测准确性、降低检测成本的效果
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0052] Embodiment 1: sample DNA extraction
[0053] For the sake of illustration, this embodiment takes a cervical cotton swab sample and the sample nucleic acid extraction reagent used to contain lysate, isopropanol and 1×TE buffer as examples:
[0054] (1) Take out the cervical cotton swab sample, vortex and mix well, pipette 1mL sample into a 1.5mL centrifuge tube, centrifuge at 12000rpm for 1min, carefully discard the supernatant, and keep the precipitate;
[0055] (2) Add 500 μl of lysate to the precipitate in (1), oscillate to mix, and bathe in water or dry bath at 100°C for 10 minutes, wherein the lysate contains 0.2M NaCl, 10mM NaOH, 0.1% SDS, 0.5% NP-40 and 0.5 1×TE buffer of % Tween-20;
[0056] (3) Add 500 μl of isopropanol, vortex and mix, place at room temperature for 2 minutes, centrifuge at 12000 rpm for 5 minutes, discard the supernatant, and place at room temperature for 2 minutes;
[0057] (4) Add 50 μl of 1×TE buffer solution, fully dissolve, let stand at ...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Embodiment 2: fluorescent PCR reaction steps
[0059] (1) Prepare high-risk HPV fluorescent PCR reaction solution: 4μl 10×PCR Buffer (100mM Tris-HCl, 500mMKCl); 0.08μl dATP (0.4mM), 0.08μl dTTP (0.4mM), 0.08μl dCTP (0.4mM), 0.08μl dGTP (0.4mM); 0.8μl BSA (10mg / mL); 6.4μl MgCl 2 (25mM); 0.05μl HPV16F (100μM), 0.08μl HPV16F (100μM), 0.08μl Probe1 (100μM); 0.05μl HPV18F (100μM), 0.08μl HPV18F (100μM), 0.08μl Probe2 (100μM); ), 0.08 μl HPV35F (100 μM), 0.08 μl HPV31 / 35R (100 μM), 0.08 μl HPV33F (100 μM), 0.08 μl HPV52F (100 μM), 0.08 μl HPV58F (100 μM), 0.08 μl HPV33 / 52 / 58R (100 μM), 0.06 μl Probe3 (100 μM); 0.08 μl HPV45F (100 μM), 0.06 μl HPV45R (100 μM), 0.08 μl HPV59F (100 μM), 0.06 μl HPV59R (100 μM), 0.06 μl Probe4 (100 μM); 0.08 μl HPV39 / 68M ( 0.08μl HPV39 / 68R (100μM), 0.06μl Probe5 (100μM); ), 0.06 μl Probe6 (100 μM); 0.08 μl HPV26F (100 μM), 0.06 μl HPV51 / 82F (100 μM), 0.08 μl HPV26 / 51 / 82R (100 μM), 0.06 μl Probe7 (100 μM); 0.08 μl HPV73F (100 μM), 0.08 HPV73R ...
Embodiment 3
[0068] Embodiment 3: clinical sample detection
[0069] According to the method in Example 1, the DNA in 140 cases of HPV cervical swab samples was extracted, and then the DNA in the 140 cases of HPV cervical swab samples was subjected to fluorescent PCR amplification according to the method in Example 2. Meanwhile, for comparison purposes, the Roche Combas 480 14 high-risk HPV (i.e., HPV16, 18, 31, 33, 35, 39, 45, 51, 52, 56, 58, 59, 68, and 66) detection kit was used The DNA in the 140 HPV cervical swab samples was detected, and the detection results are shown in Table 4.
[0070] Table 4 Test results
[0071] Number of clinical samples
Roche test results
Acon test results
16
HPV16
HPV16
5
HPV18
HPV18
8
++、HPV16
++、HPV16
3
++、HPV18
++、HPV18
93
++
++
9
--
--
6
--
++
[0072] The results in Table 4 show that among these 140 clinical samples, the present invention...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com