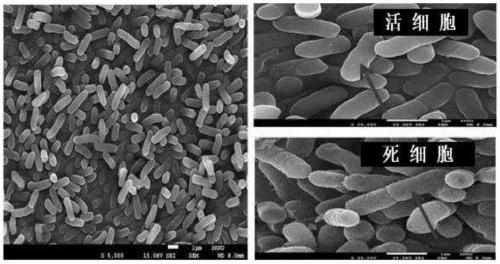
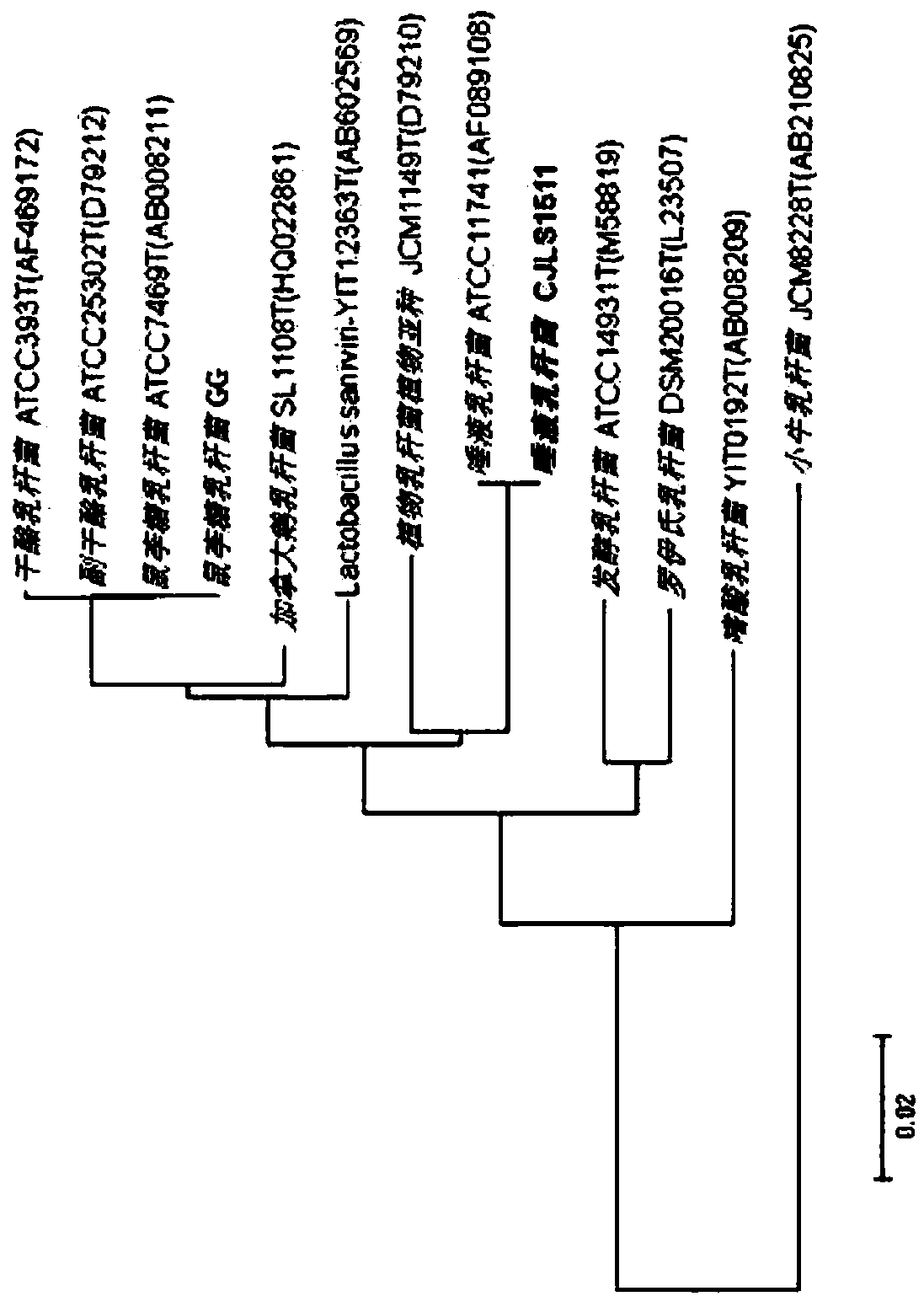
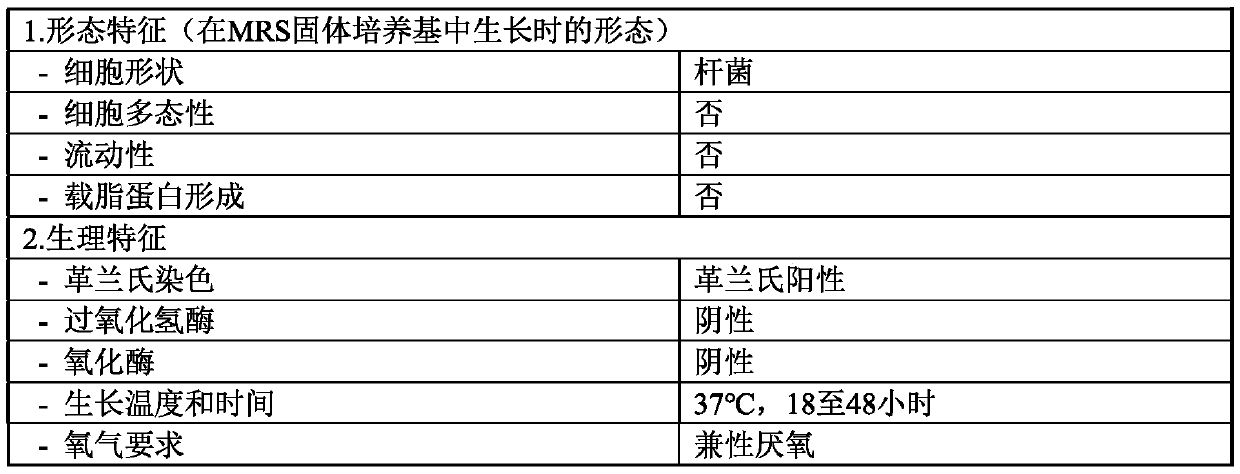
Lactobacillus salivarius cjls1511, animal feed additive composition comprising same bacterium or dead cells thereof, and method for producing same dead cells
A CJLS1511, Lactobacillus salivarius technology, applied in animal feed, animal feed, microbial-based methods, etc., to achieve the effects of improving immune status, excellent neutral lipid degradation, and enhancing animal growth performance
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment approach
[0047] According to another exemplary embodiment of the present invention, there is provided a method for preparing inactivated bacterial cells of Lactobacillus salivarius CJLS1511 (KCCM11829P), including:
[0048] Cultivate Lactobacillus salivarius CJLS1511 (KCCM11829P) to prepare a culture solution,
[0049] Heat the culture medium at a temperature of 70 to 160°C,
[0050] Cool the heated broth to a temperature of 10 to 60°C, and
[0051] The inactivated bacterial cells of Lactobacillus salivarius CJLS1511 (KCCM11829P) were separated from the cooled culture broth.
[0052] Specifically, in the step of culturing Lactobacillus salivarius CJLS1511 (KCCM11829P) to prepare a culture solution, an agar medium, specifically, MRS medium may be used. The culturing may be performed at 25°C to 40°C for 5 to 48 hours, more specifically at 30 to 40°C for 12 to 36 hours, and more specifically at 35 to 40°C for 20 to 30 hours, thereby preparing a culture solution.
[0053] Then, the culture solution ...
Embodiment 1-6
[0066] Using Lactobacillus salivarius KCCM 40210 known in the art as a reference strain, the safety, acid resistance, bile resistance, antimicrobial activity, digestive enzyme activity and triglycerides of the Lactobacillus salivarius CJLS1511 (KCCM11829P) strain of the present invention were evaluated as follows Degradation activity.
experiment example 1
[0067] Experimental example 1: Safety evaluation of Lactobacillus salivarius CJLS1511 (KCCM11829P)
[0068] In order to evaluate the safety of Lactobacillus salivarius CJLS1511 (KCCM11829P) strain, hemolysis test, gelatin liquefaction test, confirmation of the occurrence of harmful metabolites (ammonia) and phenylalanine were carried out according to the safety evaluation test method proposed by the Korean Biotechnology Industry Organization Standard Deamination test. The results are shown in Table 3 below.
[0069] [table 3]
[0070]
[0071] As confirmed in Table 3, it can be found that Lactobacillus salivarius CJLS1511 (KCCM11829P) was negative in the confirmation of gelatin liquefaction test, phenylalanine deamination test and ammonia test, and it was safe in the hemolysis test.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com